August 2008 lunar eclipse
| Partial eclipse | |||||||||||||
 Partiality as viewed from Cape Town, South Africa. | |||||||||||||
| Date | August 16, 2008 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gamma | 0.5646 | ||||||||||||
| Magnitude | 0.8095 | ||||||||||||
| Saros cycle | 138 (28 of 82) | ||||||||||||
| Partiality | 188 minutes, 8 seconds | ||||||||||||
| Penumbral | 330 minutes, 31 seconds | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
A partial lunar eclipse occurred at the Moon’s ascending node of orbit on Saturday, August 16, 2008,[1] with an umbral magnitude of 0.8095. A lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon moves into the Earth's shadow, causing the Moon to be darkened. A partial lunar eclipse occurs when one part of the Moon is in the Earth's umbra, while the other part is in the Earth's penumbra. Unlike a solar eclipse, which can only be viewed from a relatively small area of the world, a lunar eclipse may be viewed from anywhere on the night side of Earth. Occurring about 6.2 days before apogee (on August 10, 2008, at 16:20 UTC), the Moon's apparent diameter was smaller.[2]
Visibility
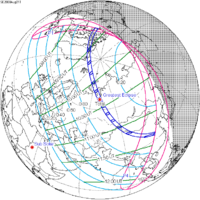
[edit]The eclipse was completely visible over Africa, Europe, Antarctica, and west, central, and south Asia, seen rising over South America and setting over east Asia and Australia.[3]
The planet Neptune was 2 days past opposition, visible in binoculars as an 8th magnitude "star" just two degrees west and slightly south of the Moon.

|
 Hourly motion shown right to left |
 The Moon's hourly motion across the Earth's shadow in the constellation of Capricornus. |
 Visibility map | ||
Images
[edit]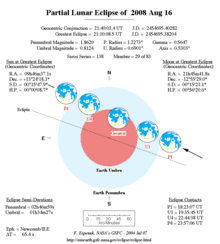
Gallery
[edit]
Progression from Oslo, Norway
-
Brighton, Queensland, 20:03 UTC
-
Ruzsky District, Russia, 20:21 UTC
-
Palinuro, Italy, 20:31 UTC
-
Tel Aviv, Israel, 20:43 UTC
-
Groningen, Netherlands, 20:50 UTC
-
Madrid, Spain, 20:53 UTC
-
Jaguariúna, Brazil, 21:00 UTC
-
Zürich, Switzerland, 21:06 UTC
-
Toulouse, France, 21:07 UTC
-
Solna, Sweden, 21:09 UTC
-
Boralesgamuwa, Sri Lanka, 21:12 UTC
-
Johor Bahru, Malaysia, 21:15 UTC
-
Langenbernsdorf, Germany, 21:23 UTC
-
Bucharest, Romania, 21:27 UTC
-
Rozbórz Długi, Poland, 21:45 UTC
-
Nasr City, Egypt, 22:12 UTC
Eclipse details
[edit]Shown below is a table displaying details about this particular solar eclipse. It describes various parameters pertaining to this eclipse.[4]
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Penumbral Magnitude | 1.83849 |
| Umbral Magnitude | 0.80946 |
| Gamma | 0.56463 |
| Sun Right Ascension | 09h46m37.2s |
| Sun Declination | +13°24'18.2" |
| Sun Semi-Diameter | 15'47.9" |
| Sun Equatorial Horizontal Parallax | 08.7" |
| Moon Right Ascension | 21h45m41.8s |
| Moon Declination | -12°55'29.2" |
| Moon Semi-Diameter | 15'21.1" |
| Moon Equatorial Horizontal Parallax | 0°56'20.6" |
| ΔT | 65.7 s |
Eclipse season
[edit]This eclipse is part of an eclipse season, a period, roughly every six months, when eclipses occur. Only two (or occasionally three) eclipse seasons occur each year, and each season lasts about 35 days and repeats just short of six months (173 days) later; thus two full eclipse seasons always occur each year. Either two or three eclipses happen each eclipse season. In the sequence below, each eclipse is separated by a fortnight.
| August 1 Descending node (new moon) |
August 16 Ascending node (full moon) |
|---|---|
 |

|
| Total solar eclipse Solar Saros 126 |
Partial lunar eclipse Lunar Saros 138 |
Related eclipses
[edit]Eclipses in 2008
[edit]- An annular solar eclipse on February 7.
- A total lunar eclipse on February 21.
- A total solar eclipse on August 1.
- A partial lunar eclipse on August 16.
Metonic
[edit]- Preceded by: Lunar eclipse of October 28, 2004
- Followed by: Lunar eclipse of June 4, 2012
Tzolkinex
[edit]- Preceded by: Lunar eclipse of July 5, 2001
- Followed by: Lunar eclipse of September 28, 2015
Half-Saros
[edit]- Preceded by: Solar eclipse of August 11, 1999
- Followed by: Solar eclipse of August 21, 2017
Tritos
[edit]- Preceded by: Lunar eclipse of September 16, 1997
- Followed by: Lunar eclipse of July 16, 2019
Lunar Saros 138
[edit]- Preceded by: Lunar eclipse of August 6, 1990
- Followed by: Lunar eclipse of August 28, 2026
Inex
[edit]- Preceded by: Lunar eclipse of September 6, 1979
- Followed by: Lunar eclipse of July 27, 2037
Triad
[edit]- Preceded by: Lunar eclipse of October 16, 1921
- Followed by: Lunar eclipse of June 17, 2095
Lunar eclipses of 2006–2009
[edit]This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of lunar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[5]
The lunar eclipses on July 7, 2009 (penumbral) and December 31, 2009 (partial) occur in the next lunar year eclipse set.
| Lunar eclipse series sets from 2006 to 2009 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Descending node | Ascending node | |||||||
| Saros | Date Viewing |
Type Chart |
Gamma | Saros | Date Viewing |
Type Chart |
Gamma | |
113
|
2006 Mar 14
|
Penumbral
|
1.0211 | 118
|
2006 Sep 7
|
Partial
|
−0.9262 | |
123
|
2007 Mar 03
|
Total
|
0.3175 | 128
|
2007 Aug 28
|
Total
|
−0.2146 | |
133
|
2008 Feb 21
|
Total
|
−0.3992 | 138
|
2008 Aug 16
|
Partial
|
0.5646 | |
143
|
2009 Feb 09
|
Penumbral
|
−1.0640 | 148
|
2009 Aug 06
|
Penumbral
|
1.3572 | |
Saros 138
[edit]This eclipse is a part of Saros series 138, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, and containing 82 events. The series started with a penumbral lunar eclipse on October 15, 1521. It contains partial eclipses from June 24, 1918 through August 28, 2026; total eclipses from September 7, 2044 through June 8, 2495; and a second set of partial eclipses from June 19, 2513 through August 13, 2603. The series ends at member 82 as a penumbral eclipse on March 30, 2982.
The longest duration of totality will be produced by member 48 at 105 minutes, 24 seconds on March 24, 2369. All eclipses in this series occur at the Moon’s ascending node of orbit.[6]
| Greatest | First | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The greatest eclipse of the series will occur on 2369 Mar 24, lasting 105 minutes, 24 seconds.[7] | Penumbral | Partial | Total | Central |
| 1521 Oct 15 |
1918 Jun 24
|
2044 Sep 07
|
2116 Oct 21 | |
| Last | ||||
| Central | Total | Partial | Penumbral | |
| 2441 May 06 |
2495 Jun 08 |
2603 Aug 13 |
2982 Mar 30 | |
Eclipses are tabulated in three columns; every third eclipse in the same column is one exeligmos apart, so they all cast shadows over approximately the same parts of the Earth.
| Series members 17–38 occur between 1801 and 2200: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17 | 18 | 19 | |||
| 1810 Apr 19 | 1828 Apr 29 | 1846 May 11 | |||
| 20 | 21 | 22 | |||
| 1864 May 21 | 1882 Jun 01 | 1900 Jun 13 | |||
| 23 | 24 | 25 | |||
| 1918 Jun 24 | 1936 Jul 04 | 1954 Jul 16 | |||

|

|

|

|

|

|
| 26 | 27 | 28 | |||
| 1972 Jul 26 | 1990 Aug 06 | 2008 Aug 16 | |||

|

|

|

|

|

|
| 29 | 30 | 31 | |||
| 2026 Aug 28 | 2044 Sep 07 | 2062 Sep 18 | |||

|

|

|

|
||
| 32 | 33 | 34 | |||
| 2080 Sep 29 | 2098 Oct 10 | 2116 Oct 21 | |||

|

|
||||
| 35 | 36 | 37 | |||
| 2134 Nov 02 | 2152 Nov 12 | 2170 Nov 23 | |||
| 38 | |||||
| 2188 Dec 04 | |||||
Metonic series
[edit]The Metonic cycle repeats nearly exactly every 19 years and represents a Saros cycle plus one lunar year. Because it occurs on the same calendar date, the Earth's shadow will in nearly the same location relative to the background stars.
| Descending node | Ascending node | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saros | Date | Type | Saros | Date | Type | |
| 103 | 1951 Feb 21.88 | Penumbral | 108 | 1951 Aug 17.13 | Penumbral | |
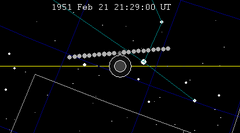
|
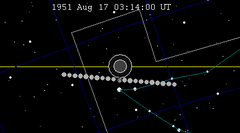
| |||||
| 113 | 1970 Feb 21.35 | Partial | 118 | 1970 Aug 17.14 | Partial | |
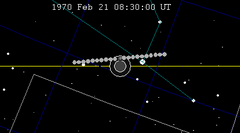
|
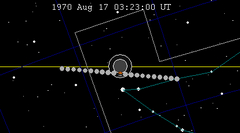
| |||||
| 123 | 1989 Feb 20.64 | Total | 128 | 1989 Aug 17.13 | Total | |
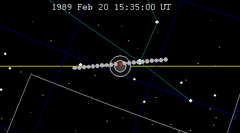
|
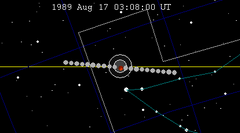
| |||||
| 133 | 2008 Feb 21.14 | Total | 138 | 2008 Aug 16.88 | Partial | |

|
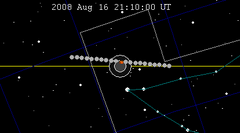
| |||||
| 143 | 2027 Feb 20.96 | Penumbral | 148 | 2027 Aug 17.30 | Penumbral | |
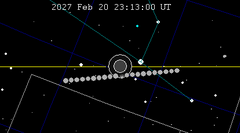
|
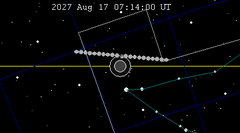
| |||||
Half-Saros cycle
[edit]A lunar eclipse will be preceded and followed by solar eclipses by 9 years and 5.5 days (a half saros).[8] This lunar eclipse is related to two total solar eclipses of Solar Saros 145.
| August 11, 1999 | August 21, 2017 |
|---|---|
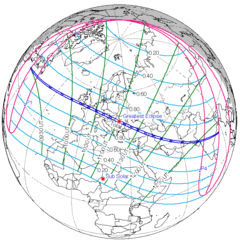
|
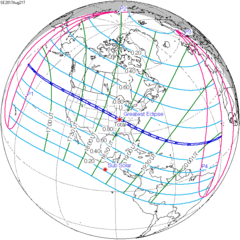
|
See also
[edit]- List of lunar eclipses and List of 21st-century lunar eclipses
- Solar eclipse of August 1, 2008
- File:2008-08-16 Lunar Eclipse Sketch.gif Chart
Notes
[edit]- ^ "August 16–17, 2008 Partial Lunar Eclipse". timeanddate. Retrieved 14 November 2024.
- ^ "Moon Distances for London, United Kingdom, England". timeanddate. Retrieved 14 November 2024.
- ^ "Partial Lunar Eclipse of 2008 Aug 16" (PDF). NASA. Retrieved 14 November 2024.
- ^ "Partial Lunar Eclipse of 2008 Aug 16". EclipseWise.com. Retrieved 14 November 2024.
- ^ van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
- ^ "NASA - Catalog of Lunar Eclipses of Saros 138". eclipse.gsfc.nasa.gov.
- ^ Listing of Eclipses of series 138
- ^ Mathematical Astronomy Morsels, Jean Meeus, p.110, Chapter 18, The half-saros
External links
[edit]- NASA: Partial Lunar Eclipse: August 16, 2008
- NASA
- 2008 Aug 16 chart: Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
- Hermit eclipse (Ian Cameron Smith) Partial Lunar Eclipse: August 16, 2008
- Sky&Telescope, Eclipses of 2008
- Animation of lunar eclipse 16 August 2008
- APOD August 20, 2008, [1]
- Composite photos showing Earth's shadow
- Spaceweather.com lunar eclipse gallery



















