Portal:Asia

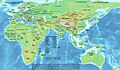
 Asia (/ˈeɪʒə/ ⓘ AY-zhə, UK also /ˈeɪʃə/ AY-shə) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometres, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which has long been home to the majority of the human population, was the site of many of the first civilisations. Its 4.7 billion people constitute roughly 60% of the world's population. Asia shares the landmass of Eurasia with Europe, and of Afro-Eurasia with both Europe and Africa. In general terms, it is bounded on the east by the Pacific Ocean, on the south by the Indian Ocean, and on the north by the Arctic Ocean. The border of Asia with Europe is a historical and cultural construct, as there is no clear physical and geographical separation between them. A commonly accepted division places Asia to the east of the Suez Canal separating it from Africa; and to the east of the Turkish straits, the Ural Mountains and Ural River, and to the south of the Caucasus Mountains and the Caspian and Black seas, separating it from Europe. Since the concept of Asia derives from the term for the eastern region from a European perspective, Asia is the remaining vast area of Eurasia minus Europe. Therefore, Asia is a region where various independent cultures coexist rather than sharing a single culture, and the boundary between Europe is somewhat arbitrary and has moved since its first conception in classical antiquity. The division of Eurasia into two continents reflects East–West cultural differences, some of which vary on a spectrum. (Full article...) Featured articleThe Sind sparrow (Passer pyrrhonotus) is a passerine bird of the sparrow family, Passeridae, found around the Indus valley region in South Asia. Its name refers to the province of Sindh, and it is also known as the jungle, Sind jungle, or rufous-backed sparrow. Very similar to the related house sparrow, it is smaller and has distinguishing plumage features. As in the house sparrow, the male has brighter plumage than female and young birds, including black markings and a grey crown. Distinctively, the male has a chestnut stripe running down its head behind the eye, and the female has a darker head than other sparrow species. Its main vocalisations are soft chirping calls that are extended into longer songs with other sounds interspersed by breeding males. Historically, this species was thought to be very closely related to the house sparrow, but its closest evolutionary affinities may lie elsewhere. The species was discovered around 1840, but went undetected for several decades afterwards. Within its Indus valley breeding range in Pakistan and western India, the Sind sparrow is patchily distributed in riverine and wetland habitats with thorny scrub and tall grass. During the non-breeding season, some birds enter drier habitats as they disperse short distances from their breeding habitat, or migrate into western Pakistan and the extreme east of Iran. Since this species is fairly common and expanding its range, it is assessed as least concern on the IUCN Red List. The Sind sparrow is social while feeding and gathers in small groups both while breeding and during winter dispersal. It feeds mostly on seeds and less often on insects, foraging close to the ground. Nests are made in the branches of thorny trees, and are untidy globular masses constructed from grass or other plant matter and lined with softer material. Both sexes are involved in building the nest and caring for the young, and usually raise two clutches of three to five young each breeding season. (Full article...) Selected Country Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Turkey to the northwest and Iraq to the west, Azerbaijan, Armenia, the Caspian Sea, and Turkmenistan to the north, Afghanistan to the east, Pakistan to the southeast, the Gulf of Oman and the Persian Gulf to the south. With a multi-ethnic population of about 86 million in an area of 1,648,195 km2 (636,372 sq mi), Iran ranks 17th globally in both geographic size and population. It is the sixth-largest country entirely in Asia and one of the world's most mountainous countries. Officially an Islamic republic, Iran has a Muslim-majority population. The country is divided into five regions with 31 provinces. Tehran is the nation's capital, largest city and financial centre. A cradle of civilisation, Iran has been inhabited since the Lower Palaeolithic. The large part of Iran was first unified as a political entity by the Medes under Cyaxares in the seventh century BC, and reached its territorial height in the sixth century BC, when Cyrus the Great founded the Achaemenid Empire, one of the largest in ancient history. Alexander the Great conquered the empire in the fourth century BC. An Iranian rebellion established the Parthian Empire in the third century BC and liberated the country, which was succeeded by the Sasanian Empire in the third century AD. Ancient Iran saw some of the earliest developments of writing, agriculture, urbanisation, religion and central government. Muslims conquered the region in the seventh century AD, leading to Iran's Islamisation. The blossoming literature, philosophy, mathematics, medicine, astronomy and art became major elements for Iranian civilisation during the Islamic Golden Age. A series of Iranian Muslim dynasties ended Arab rule, revived the Persian language and ruled the country until the Seljuk and Mongol conquests of the 11th to 14th centuries. (Full article...) Featured biography Al-Mukhtar ibn Abi Ubayd al-Thaqafi (Arabic: الْمُخْتَار ٱبْن أَبِي عُبَيْد الثَّقَفِيّ, romanized: al-Mukhtār ibn Abī ʿUbayd al-Thaqafī; c. 622 – 3 April 687) was a pro-Alid revolutionary based in Kufa, who led a rebellion against the Umayyad Caliphate in 685 and ruled over most of Iraq for eighteen months during the Second Fitna. Born in Ta'if, Mukhtar moved to Iraq at a young age and grew up in Kufa.in his young ages,Mukhtar Participated in Battles On Ali ibn Abu Talib side in Battle of Siffin.Following the death of Husayn ibn Ali, a grandson of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, at the hands of the Umayyad army in the Battle of Karbala in 680, he allied with the rival caliph Abd Allah ibn al-Zubayr in Mecca, but the alliance was short-lived. Mukhtar returned to Kufa where he declared Muhammad ibn al-Hanafiyya, a son of caliph Ali (r. 656–661) and brother of Husayn, the mahdi and the imam, and called for the establishment of an Alid caliphate and retaliation for Husayn's killing. He took over Kufa in October 685, after expelling its Zubayrid governor, and later ordered the execution of those involved in the killing of Husayn. Hostile relations with Ibn al-Zubayr ultimately led to Mukhtar's death by the forces of the Zubayrid governor of Basra, Mus'ab ibn al-Zubayr, following a four-month siege. (Full article...) General imagesThe following are images from various Asia-related articles on Wikipedia. Featured pictureThe Darvaza gas crater, also called the "Door to Hell" or the "Gates of Hell" by locals, a crater of natural gas that has been burning since 1971, is located in the Karakum Desert in Turkmenistan. The crater is a major tourist attraction, with hundreds of visitors arriving each year.
Did you know...
Updated: 6:33, 14 February 2024 In the news
Related portalsMajor Religions in Asia Middle East Central Asia and Caucasus Indian Subcontinent Southeast Asia East Asia Selected panorama
Nanga Parbat is the ninth highest mountain on Earth, the second highest mountain in Pakistan and among the eight-thousanders with a summit elevation of 8,126 meters (26,660 ft). TopicsCategoriesAssociated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
More portalsShortcuts to this page: Asia portal • P:ASIA |