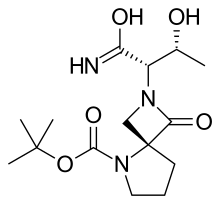
Zelquistinel
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | NMDA receptor modulator |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ~100% |
| Elimination half-life | 1.2–2 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C15H25N3O5 |
| Molar mass | 327.381 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Zelquistinel (GATE-251, formerly AGN-241751) is an orally active small-molecule NMDA receptor modulator which is under development for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD) by Gate Neurosciences, and previously by Allergan.[1][2][3]
Zelquistinel acts through a unique binding site on the NMDA receptor, independent of the glycine site, to modulate receptor activity and enhance NMDAR-mediated synaptic plasticity.[4][5] Its mechanism of action is similar to that of rapastinel. However, unlike rapastinel, zelquistinel is orally bioavailable, exhibits increased potency, and has improved drug properties.[2][3][5] The mean half-life of Zelquistinel is reported to be from 1.21 to 2.06 hours, reaching peak plasma concentrations 30 minutes after administration.[6] In preclinical studies, single doses of zelquistinel demonstrated both rapid-acting (24-hours) and sustained (1-week) antidepressant-like effects and enhancement of long-term synaptic plasticity.[6]
On July 23, 2018, the U.S. FDA granted Fast Track designation to the development of zelquistinel as an investigational new treatment for major depressive disorder.[7]
In 2019, Allergan completed an exploratory phase IIa clinical trial of once-weekly oral zelquistinel in major depressive disorder.[1][3][8] As of 2024, zelquistinel is undergoing a phase IIb clinical trial for depression sponsored by Gate Neurosciences.[2]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b "NMDA receptor modulators - AdisInsight". adisinsight.springer.com.
- ^ a b c "Home - Gate Neurosciences". Retrieved 2022-05-12.
- ^ a b c Aptinyx Inc. "Allergan Exercises Option to Acquire Compound from Aptinyx Discovery Platform Under Ongoing Research Collaboration". www.prnewswire.com (Press release).
- ^ Donello JE, Banerjee P, Li YX, Guo YX, Yoshitake T, Zhang XL, et al. (March 2019). "Positive N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptor Modulation by Rapastinel Promotes Rapid and Sustained Antidepressant-Like Effects". The International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology. 22 (3): 247–259. doi:10.1093/ijnp/pyy101. PMC 6403082. PMID 30544218.
- ^ a b Pothula S, Liu RJ, Wu M, Sliby AN, Picciotto MR, Banerjee P, Duman RS (March 2021). "Positive modulation of NMDA receptors by AGN-241751 exerts rapid antidepressant-like effects via excitatory neurons". Neuropsychopharmacology. 46 (4): 799–808. doi:10.1038/s41386-020-00882-7. PMC 8027594. PMID 33059355.
- ^ a b Burgdorf JS (26 July 2022). "Zelquistinel Is an Orally Bioavailable Novel NMDA Receptor Allosteric Modulator That Exhibits Rapid and Sustained Antidepressant-Like Effects". International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology.
- ^ plc A. "Allergan Receives FDA Fast Track Designation for AGN-241751 for the Treatment of Major Depressive Disorder (MDD)". www.prnewswire.com (Press release). Retrieved 2022-05-16.
- ^ Clinical trial number NCT03586427 for "A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Fixed-Dose Study of AGN-241751 in Adult Participants With Major Depressive Disorder" at ClinicalTrials.gov
