Campaign history of the Roman military
 |
| Part of a series on the |
| Military of ancient Rome |
|---|
|
|
From its origin as a city-state on the peninsula of Italy in the 8th century BC, to its rise as an empire covering much of Southern Europe, Western Europe, Near East and North Africa to its fall in the 5th century AD, the political history of Ancient Rome was closely entwined with its military history. The core of the campaign history of the Roman military is an aggregate of different accounts of the Roman military's land battles, from its initial defense against and subsequent conquest of the city's hilltop neighbors on the Italian peninsula, to the ultimate struggle of the Western Roman Empire for its existence against invading Huns, Vandals and Germanic tribes. These accounts were written by various authors throughout and after the history of the Empire. Following the First Punic War, naval battles were less significant than land battles to the military history of Rome due to its encompassment of lands of the periphery and its unchallenged dominance of the Mediterranean Sea.
The Roman army battled first against its tribal neighbours and Etruscan towns within Italy, and later came to dominate the Mediterranean and at its height the provinces of Britannia and Asia Minor. As with most ancient civilizations, Rome's military served the triple purpose of securing its borders, exploiting peripheral areas through measures such as imposing tribute on conquered peoples, and maintaining internal order.[1] From the outset, Rome's military typified this pattern, and the majority of Rome's campaigns were characterised by one of two types. The first is the territorial expansionist campaign, normally begun as a counter-offensive,[2] in which each victory brought subjugation of large areas of territory and allowed Rome to grow from a small town to a population of 55 million in the early empire when expansion was halted.[3] The second is the civil war, which plagued Rome from its foundation to its eventual demise.
Despite their formidable reputation and host of victories, Roman armies were not invincible.[4] Romans "produced their share of incompetents"[5] who led Roman armies into catastrophic defeats. Nevertheless, it was generally the fate of even the greatest of Rome's enemies, such as Pyrrhus and Hannibal, to win the battle but lose the war. The history of Rome's campaigning is, if nothing else, a history of obstinate persistence overcoming appalling losses.[6][7]
Kingdom (753–509 BC)
[edit]
Knowledge of Roman history stands apart from other civilizations in the ancient world. Its chronicles, military and otherwise, document the city's very foundation to its eventual demise. Although some histories have been lost, such as Trajan's account of the Dacian Wars, and others, such as Rome's earliest histories, are at least semi-apocryphal, the extant histories of Rome's military history are extensive.
Rome's earliest history, from the time of its founding as a small tribal village,[8] to the downfall of its kings, is the least well preserved. Although the early Romans were literate to some degree,[9] this void may be due to the lack of will to record their history at that time, or such histories as they did record were lost.[10]
Although the Roman historian Livy (59 BC – 17 AD)[11] lists a series of seven kings of early Rome in his work Ab urbe condita, from its establishment through its earliest years, the first four kings (Romulus,[12] Numa,[13][14] Tullus Hostilius[14][15] and Ancus Marcius)[14][16] may be apocryphal. A number of points of view have been proposed. Grant and others argue that prior to the establishment of the Etruscan kingdom of Rome under the traditional fifth king, Tarquinius Priscus,[17] Rome would have been led by a religious leader of some sort.[18] Very little is known of Rome's military history from this era, and what history has come down to us is more legendary than factual. Traditionally, Romulus fortified the Palatine Hill after founding the city, and shortly thereafter Rome was "equal to any of the surrounding cities in her prowess in war".[19]
| "Events before the city was founded or planned, which have been handed down more as pleasing poetic fictions than as reliable records of historical events, I intend neither to affirm nor to refute. To antiquity we grant the indulgence of making the origins of cities more impressive by comingling the human with the divine, and if any people should be permitted to sanctify its inception and reckon the gods as its founders, surely the glory of the Roman people in war is such that, when it boasts Mars in particular as its parent... the nations of the world would as easily acquiesce in this claim as they do in our rule." |
| Livy, on Rome's early history[20] |
The first of the campaigns fought by the Romans in this legendary account are the wars with various Latin cities and the Sabines. According to Livy, the Latin village of Caenina responded to the event of the abduction of the Sabine women by invading Roman territory, but were routed and their village captured. The Latins of Antemnae and those of Crustumerium were defeated next in a similar fashion. The remaining main body of the Sabines attacked Rome and briefly captured the citadel, but were then convinced to conclude a treaty with the Romans under which the Sabines became Roman citizens.[21]
There was a further war in the 8th century BC against Fidenae and Veii. In the 7th century BC there was a war with Alba Longa, a second war with Fidenae and Veii and a second Sabine War. Ancus Marcius led Rome to victory against the Latins and, according to the Fasti Triumphales, over the Veientes and Sabines also.
Tarquinius Priscus (Ruled 616–579 BC)
[edit]Lucius Tarquinius Priscus' first war was waged against the Latins. Tarquinius took the Latin town of Apiolae by storm and took great booty from there back to Rome.[22] According to the Fasti Triumphales, the war occurred prior to 588 BC.
His military ability was tested by an attack from the Sabines. Tarquinius doubled the numbers of equites to help the war effort,[23] and defeat the Sabines. In the peace negotiations that followed, Tarquinius received the town of Collatia and appointed his nephew, Arruns Tarquinius, also known as Egerius, as commander of the garrison which he stationed in that city. Tarquinius returned to Rome and celebrated a triumph for his victories that, according to the Fasti Triumphales, occurred on 13 September 585 BC.
Subsequently, the Latin cities of Corniculum, old Ficulea, Cameria, Crustumerium, Ameriola, Medullia and Nomentum were subdued and became Roman.[24]
Servius Tullius (Ruled 578–535 BC)
[edit]Early in his reign, Servius Tullius warred against Veii and the Etruscans. He is said to have shown valour in the campaign, and to have routed a great army of the enemy. The war helped him to cement his position at Rome.[25] According to the Fasti Triumphales, Servius celebrated three triumphs over the Etruscans, including on 25 November 571 BC and 25 May 567 BC (the date of the third triumph is not legible on the Fasti).
Tarquinius Superbus (Ruled 535–509 BC)
[edit]Early in his reign Tarquinius Superbus, Rome's seventh and final king, called a meeting of the Latin leaders at which he persuaded them to renew their treaty with Rome and become her allies rather than her enemies, and it was agreed that the troops of the Latins would attend at a grove sacred to the goddess Ferentina on an appointed day to form a united military force with the troops of Rome. This was done, and Tarquin formed combined units of Roman and Latin troops.[26]
Tarquin next began a war against the Volsci. He took the wealthy town of Suessa Pometia, with the spoils of which he commenced the erection of the Temple of Jupiter Optimus Maximus which his father had vowed. He also celebrated a triumph for his victory.[27]
He was next engaged in a war with Gabii, one of the Latin cities, which had rejected the Latin treaty with Rome. Unable to take the city by force of arms, Tarquin had his son, Sextus Tarquinius, infiltrate the city, gain the trust of its people and command of its army. In time he killed or exiled the city's leaders, and handed control of the city over to his father.[28]
Tarquin also agreed to a peace with the Aequi, and renewed the treaty of peace between Rome and the Etruscans.[29] According to the Fasti Triumphales, Tarquin also won a victory over the Sabines.
Tarquinius later went to war with the Rutuli. According to Livy, the Rutuli were, at that time, a very wealthy nation. Tarquinius was desirous of obtaining the booty which would come with victory over the Rutuli.[30] Tarquin unsuccessfully sought to take the Rutulian capital, Ardea, by storm, and subsequently began an extensive siege of the city. The war was interrupted by the revolution which overthrew the Roman monarchy. The Roman army, camped outside Ardea, welcomed Lucius Junius Brutus as their new leader, and expelled the king's sons. It is unclear what was the outcome of the siege, or indeed the war.[31]
Republic
[edit]Early (509–275 BC)
[edit]Early Italian campaigns (509–396 BC)
[edit]
The first non-apocryphal Roman wars were wars of both expansion and defence, aimed at protecting Rome itself from neighbouring cities and nations and establishing its territory in the region.[32] Florus writes that at this time "their neighbours, on every side, were continually harassing them, as they had no land of their own ... and as they were situated, as it were, at the junction of the roads to Latium and Etruria, and, at whatever gate they went out, were sure to meet a foe."[33]
In the semi-legendary period of the early republic, sources record Rome was twice attacked by Etruscan armies. About 509 BC war with Veii and Tarquinii was said to have been instigated by the recently overthrown king Tarquinius Superbus.[34][35] Again in 508 BC Tarquin persuaded the king of Clusium, Lars Porsenna, to wage war on Rome, resulting in a siege of Rome and afterwards a peace treaty.[33][34][36]
Initially, Rome's immediate neighbours were either Latin towns and villages[37] on a tribal system similar to that of Rome, or else tribal Sabines from the Apennine hills beyond.[38] One by one, Rome defeated both the persistent Sabines and the local cities that were either under Etruscan control or else Latin towns that had cast off their Etruscan rulers, as had Rome.[38] Rome defeated the Lavinii and Tusculi in the Battle of Lake Regillus in 496 BC,[37][39][40] were defeated by the Veientes in the Battle of the Cremera in 477 BC,[41][42] defeated the Sabines in an unnamed battle in 449 BC,[39] the Aequi in the Battle of Mount Algidus in 458 BC, the Aequi and Volsci in 446 BC,[43][44] in the Battle of Corbio,[45] in 446 BC the Aurunci in the Battle of Aricia,[46] the Capture of Fidenae in 435 BC[42][47] and the Siege of Veii in 396 BC,[42][45][47][48] and the Capture of Antium in 377 BC.[49] After defeating the Veientes, the Romans had effectively completed the conquest of their immediate Etruscan neighbours,[50] as well as secured their position against the immediate threat posed by the tribespeople of the Apennine hills. In the meantime, it also affected the agriculture as well as diet regime of the empire. Since the enlargement the population in Apennine peninsula had increased and led to certain changes in agriculture, such as switch to goat breeding from cattle, indicating higher levels of protein supply in the diet which played a crucial role in stature of the locals.[51]
However, Rome still controlled only a very limited area and the affairs of Rome were minor even to those in Italy[45] and Rome's affairs were only just coming to the attention of the Greeks, the dominant cultural force at the time.[52] At this point the bulk of Italy remained in the hands of Latin, Sabine, Samnite and other peoples in the central part of Italy, Greek colonies to the south, and the Celtic people, including the Gauls, to the north.
Celtic invasion of Italia (390–387 BC)
[edit]By 390 BC, several Gallic tribes had begun invading Italy from the north as their culture expanded throughout Europe. Most of this was unknown to the Romans at this time, who still had purely local security concerns, but the Romans were alerted when a particularly warlike tribe,[52][53] the Senones,[53] invaded the Etruscan province of Siena from the north and attacked the town of Clusium,[54] not far from Rome's sphere of influence. The Clusians, overwhelmed by the size of the enemy in numbers and ferocity, called on Rome for help. Perhaps unintentionally[52] the Romans found themselves not just in conflict with the Senones, but their primary target.[54] The Romans met them in pitched battle at the Battle of the Allia[52][53] around 390–387 BC. The Gauls, under their chieftain Brennus, defeated the Roman army of around 15,000 troops[52] and proceeded to pursue the fleeing Romans back to Rome itself and partially sacked the town[55][56] before being either driven off[53][57][58] or bought off.[52][54] They were probably defeated by the exiled dictator Marcus Furius Camillus who gathered the scattered Roman forces that consisted partly of fugitives and partly those who had survived the battle of Alia, and marched to Rome. According to tradition, he took the Gauls by surprise, when Brennus, having tricked the weights in which the gold rescue that had been set for the city was measured, uttered the expression Vae Victis! (Woe to the losers!); Camillus claimed that, since he was a dictator, no agreement was valid without his acquiescence, so no ransom was due and he answered Breno with another famous phrase: ‘Non auro sed ferro liberanda est patria’ (It is with iron, not with gold, how the homeland is released). After defeating the Gauls in the subsequent battle, he entered the city in triumph, greeted by his fellow citizens as alter Romulus (the other Romulus), pater patriae (father of the homeland) and conditor alter urbis (second founder of the city).[59]
Now that the Romans and Gauls had blooded one another, intermittent Roman-Gallic wars were to continue between the two in Italy for more than two centuries, including the Battle of Lake Vadimo,[53] the Battle of Faesulae in 225 BC, the Battle of Telamon in 224 BC, the Battle of Clastidium in 222 BC, the Battle of Cremona in 200 BC, the Battle of Mutina in 194 BC, the Battle of Arausio in 105 BC, the Battle of Aquae Sextiae in 102 BC, and the Battle of Vercellae in 101 BC. The Celtic problem would not be resolved for Rome until the final subjugation of all Gaul following the Battle of Alesia in 52 BC.
Expansion into Italia (343–282 BC)
[edit]
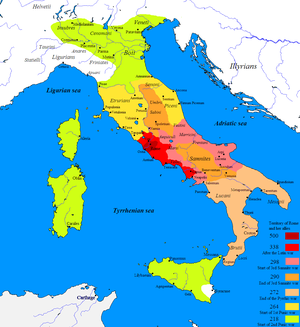
After swiftly recovering from the sack of Rome,[60] the Romans immediately resumed their expansion within Italy. Despite their successes, their mastery of the whole of Italy was by no means assured. The Samnites were a people just as martial[61] and as rich[62] as the Romans and had the objective of their own to secure more lands in the fertile[62] Italian plains on which Rome itself lay.[63] The First Samnite War of between 343 BC and 341 BC that followed widespread Samnite incursions into Rome's territory[64] was a relatively short affair: the Romans beat the Samnites in both the Battle of Mount Gaurus in 342 BC and the Battle of Suessula in 341 BC but were forced to withdraw from the war before they could pursue the conflict further due to the revolt of several of their Latin allies in the Latin War.[65][66]
Rome was therefore forced to contend by around 340 BC against both Samnite incursions into their territory and, simultaneously, in a bitter war against their former allies. Rome bested the Latins in the Battle of Vesuvius and again in the Battle of Trifanum,[66] after which the Latin cities were obliged to submit to Roman rule.[67][68] Perhaps due to Rome's lenient treatment of their defeated foe,[65] the Latins submitted largely amicably to Roman rule for the next 200 years.
The Second Samnite War, from 327 BC to 304 BC, was a much longer and more serious affair for both the Romans and Samnites,[69] running for over twenty years and incorporating twenty-four battles[62] that led to massive casualties on both sides. The fortunes of the two sides fluctuated throughout its course: the Samnites seized Neapolis in the Capture of Neapolis in 327 BC,[69] which the Romans then re-captured before losing at the Battle of the Caudine Forks[62][69][70] and the Battle of Lautulae. The Romans then proved victorious at the Battle of Bovianum and the tide turned strongly against the Samnites from 314 BC onwards, leading them to sue for peace with progressively less generous terms. By 304 BC the Romans had effectively annexed the greater degree of the Samnite territory, founding several colonies. This pattern of meeting aggression in force and so inadvertently gaining territory in strategic counter-attacks was to become a common feature of Roman military history.
Seven years after their defeat, with Roman dominance of the area looking assured, the Samnites rose again and defeated the Romans at the Battle of Camerinum in 298 BC, to open the Third Samnite War. With this success in hand they managed to bring together a coalition of several previous enemies of Rome, all of whom were probably keen to prevent any one faction dominating the entire region. The army that faced the Romans at the Battle of Sentinum[70] in 295 BC included Samnites, Gauls, Etruscans and Umbrians.[71] When the Roman army won a convincing victory over these combined forces it must have become clear that little could prevent Roman dominance of Italy and in the Battle of Populonia (282 BC) Rome destroyed the last vestiges of Etruscan power in the region.
Pyrrhic War (280–275 BC)
[edit]
By the beginning of the 3rd century Rome had established itself as a major power on the Italian Peninsula, but had not yet come into conflict with the dominant military powers in the Mediterranean at the time: Carthage and the Greek kingdoms. Rome had all but completely defeated the Samnites, mastered its fellow Latin towns, and greatly reduced Etruscan power in the region. However, the south of Italy was controlled by the Greek colonies of Magna Grecia[72] who had been allied to the Samnites, and continued Roman expansion brought the two into inevitable conflict.[73][74]
In the naval Battle of Thurii,[74] Tarentum appealed for military aid to Pyrrhus, ruler of Epirus.[74][75] Motivated by his diplomatic obligations to Tarentum, and a personal desire for military accomplishment,[76] Pyrrhus landed a Greek army of some 25,000 men[74] and a contingent of war elephants[74][77] on Italian soil in 280 BC,[78] where his forces were joined by some Greek colonists and a portion of the Samnites who revolted against Roman control, taking up arms against Rome for the fourth time in seventy years.
The Roman army had not yet seen elephants in battle,[77] and their inexperience turned the tide in Pyrrhus' favour at the Battle of Heraclea in 280 BC,[74][77][79] and again at the Battle of Ausculum in 279 BC.[77][79][80] Despite these victories, Pyrrhus found his position in Italy untenable. Rome steadfastly refused to negotiate with Pyrrhus as long as his army remained in Italy.[81] Furthermore, Rome entered into a treaty of support with Carthage, and Pyrrhus found that despite his expectations, none of the other Italic peoples would defect to the Greek and Samnite cause.[82] Facing unacceptably heavy losses with each encounter with the Roman army, and failing to find further allies in Italy, Pyrrhus withdrew from the peninsula and campaigned in Sicily against Carthage,[83] abandoning his allies to deal with the Romans.[73]
When his Sicilian campaign was also ultimately a failure, and at the request of his Italian allies, Pyrrhus returned to Italy to face Rome once more. In 275 BC, Pyrrhus again met the Roman army at the Battle of Beneventum.[80] This time the Romans had devised methods to deal with the war elephants, including the use of javelins,[80] fire[83] and, one source claims, simply hitting the elephants heavily on the head.[77] While Beneventum was indecisive,[83] Pyrrhus realised that his army had been exhausted and reduced by years of foreign campaigns, and seeing little hope for further gains, he withdrew completely from Italy.
The conflicts with Pyrrhus would have a great effect on Rome. It had shown that it was capable of pitting its armies successfully against the dominant military powers of the Mediterranean, and further showed that the Greek kingdoms were incapable of defending their colonies in Italy and abroad. Rome quickly moved into southern Italia, subjugating and dividing Magna Grecia.[84] Effectively dominating the Italian peninsula,[85] and with a proven international military reputation,[86] Rome now began to look to expand from the Italian mainland. Since the Alps formed a natural barrier to the north, and Rome was none too keen to meet the fierce Gauls in battle once more, the city's gaze turned to Sicily and the islands of the Mediterranean, a policy that would bring it into direct conflict with its former ally Carthage.[86][87]
Middle (274–148 BC)
[edit]Rome first began to make war outside the Italian peninsula during the Punic wars against Carthage, a former Phoenician colony[88] that had established on the north coast of Africa and developed into a powerful state. These wars, starting in 264 BC[89] were probably the largest conflicts of the ancient world yet[90] and saw Rome become the most powerful state of the Western Mediterranean, with territory in Sicily, North Africa, Iberia, and with the end of the Macedonian wars (which ran concurrently with the Punic wars) Greece as well. After the defeat of the Seleucid Emperor Antiochus III the Great in the Roman-Syrian War (Treaty of Apamea, 188 BC) in the eastern sea, Rome emerged as the dominant Mediterranean power and the most powerful city in the classical world.
Punic Wars (264–146 BC)
[edit]
The First Punic War began in 264 BC when settlements on Sicily began to appeal to the two powers between which they lay – Rome and Carthage – in order to solve internal conflicts.[89] The willingness of both Rome and Carthage to become embroiled on the soil of a third party may indicate a willingness to test each other's power without wishing to enter a full war of annihilation; certainly there was considerable disagreement within Rome about whether to prosecute the war at all.[91] The war saw land battles in Sicily early on, such as the Battle of Agrigentum, but the theatre shifted to naval battles around Sicily and Africa. For the Romans, naval warfare was a relatively unexplored concept.[92] Before the First Punic War in 264 BC there was no Roman navy to speak of, as all previous Roman wars had been fought on land in Italy. The new war in Sicily against Carthage, a great naval power,[93] forced Rome to quickly build a fleet and train sailors.[94]
Rome took to naval warfare "like a brick to water"[87] and the first few naval battles of the First Punic War such as the Battle of the Lipari Islands were catastrophic disasters for Rome, as might fairly be expected from a city that had no real prior experience of naval warfare. However, after training more sailors and inventing a grappling engine known as a Corvus,[95] a Roman naval force under C. Duillius was able to roundly defeat a Carthaginian fleet at the Battle of Mylae. In just four years, a state without any real naval experience had managed to better a major regional maritime power in battle. Further naval victories followed at the Battle of Tyndaris and the Battle of Cape Ecnomus.[96]
After having won control of the seas, a Roman force landed on the African coast under Marcus Regulus, who was at first victorious, winning the Battle of Adys[97] and forcing Carthage to sue for peace.[98] However, the terms of peace that Rome proposed were so heavy that negotiations failed,[98] and in response, the Carthaginians hired Xanthippus of Carthage, a mercenary from the martial Greek city-state of Sparta, to reorganise and lead their army.[99] Xanthippus managed to cut off the Roman army from its base by re-establishing Carthaginian naval supremacy and then defeated and captured Regulus[100] at the Battle of Tunis.[101]
Despite being defeated on African soil, the Romans with their newfound naval abilities, roundly beat the Carthaginians in naval battle again – largely through the tactical innovations of the Roman fleet[89] – at the Battle of the Aegates Islands. Carthage was left without a fleet or sufficient coin to raise a new one. For a maritime power, the loss of their access to the Mediterranean stung financially and psychologically, and the Carthaginians again sued for peace,[102] during which negotiations, Rome battled the Ligures tribe in the Ligurian War[103] and the Insubres in the Gallic War.[104]
Continuing distrust led to the renewal of hostilities in the Second Punic War when Hannibal, a member of the Barcid family of Carthaginian nobility, attacked Saguntum,[105][106] a city with diplomatic ties to Rome.[107] Hannibal then raised an army in Iberia and famously crossed the Italian Alps with elephants to invade Italy.[108][109] In the first battle on Italian soil at Ticinus in 218 BC Hannibal defeated the Romans under Scipio the Elder in a small cavalry fight.[110][111] Hannibal's success continued with victories in the Battle of the Trebia,[110][112] the Battle of Lake Trasimene, where he ambushed an unsuspecting Roman army,[113][114] and the Battle of Cannae,[115][116] in what is considered one of the great masterpieces of tactical art, and for a while "Hannibal seemed invincible",[108] able to beat Roman armies at will.[117]
In the three battles of Nola, Roman general Marcus Claudius Marcellus managed to hold off Hannibal but then Hannibal smashed a succession of Roman consular armies at the First Battle of Capua, the Battle of the Silarus, the Second Battle of Herdonia, the Battle of Numistro and the Battle of Asculum. By this time Hannibal's brother Hasdrubal Barca sought to cross the Alps into Italy and join his brother with a second army. Despite being defeated in Iberia in the Battle of Baecula, Hasdrubal managed to break through into Italy only to be defeated decisively by Gaius Claudius Nero and Marcus Livius Salinator on the Metaurus River.[108]
| "Apart from the romance of Scipio's personality and his political importance as the founder of Rome's world-dominion, his military work has a greater value to modern students of war than that of any other great captain of the past.. His genius revealed to him that peace and war are the two wheels on which the world runs." |
| BH Liddell Hart on Scipio Africanus Major[118] |
Unable to defeat Hannibal himself on Italian soil, and with Hannibal savaging the Italian countryside but unwilling or unable to destroy Rome itself, the Romans boldly sent an army to Africa with the intention of threatening the Carthaginian capital.[119] In 203 BC at the Battle of Bagbrades the invading Roman army under Scipio Africanus Major defeated the Carthaginian army of Hasdrubal Gisco and Syphax and Hannibal was recalled to Africa.[108] At the famous Battle of Zama Scipio decisively defeated[120] – perhaps even "annihilated"[108] – Hannibal's army in North Africa, ending the Second Punic War.
Carthage never managed to recover after the Second Punic War[121] and the Third Punic War that followed was in reality a simple punitive mission to raze the city of Carthage to the ground.[122] Carthage was almost defenceless and when besieged offered immediate surrender, conceding to a string of outrageous Roman demands.[123] The Romans refused the surrender, demanding as their further terms of surrender the complete destruction of the city[124] and, seeing little to lose,[124] the Carthaginians prepared to fight.[123] In the Battle of Carthage the city was stormed after a short siege and completely destroyed,[125] its culture "almost totally extinguished".[126]
Conquest of the Iberian Peninsula (219–18 BC)
[edit]Rome's conflict with the Carthaginians in the Punic Wars led them into expansion in the Iberian Peninsula of modern-day Spain and Portugal.[127] The Punic empire of the Carthaginian Barcid family consisted of territories in Iberia, many of which Rome gained control of during the Punic Wars. Italy remained the main theatre of war for much of the Second Punic War, but the Romans also aimed to destroy the Barcid Empire in Iberia and prevent major Punic allies from linking up with forces in Italy.
Over the years, Rome had expanded along the southern Iberian coast until in 211 BC it captured the city of Saguntum. Following two major military expeditions to Iberia, the Romans finally crushed Carthaginian control of the peninsula in 206 BC, at the Battle of Ilipa, and the peninsula became a Roman province known as Hispania. From 206 BC onwards the only opposition to Roman control of the peninsula came from within the native Celtiberian tribes themselves, whose disunity prevented their security from Roman expansion.[127]
Following two small-scale rebellions in 197 BC,[128] in 195–194 BC war broke out between the Romans and the Lusitani people in the Lusitanian War, in modern-day Portugal.[129] By 179 BC, the Romans had mostly succeeded in pacifying the region and bringing it under their control.[128]
About 154 BC,[128] a major revolt was re-ignited in Numantia, which is known as the First Numantine War,[127] and a long war of resistance was fought between the advancing forces of the Roman Republic and the Lusitani tribes of Hispania. The praetor Servius Sulpicius Galba and the proconsul Lucius Licinius Lucullus arrived in 151 BC and began the process of subduing the local population.[130] In 150 BC, Galba betrayed the Lusitani leaders he had invited to peace talks and had them killed, ingloriously ending the first phase of the war.[130]
The Lusitani revolted again in 146 BC under a new leader called Viriathus,[128] invading Turdetania (southern Iberia) in a guerrilla war.[131] The Lusitanians were initially successful, defeating a Roman army at the Battle of Tribola and going on to sack nearby Carpetania,[132] and then besting a second Roman army at the First Battle of Mount Venus in 146 BC, again going on to sack another nearby city.[132] In 144 BC, the general Quintus Fabius Maximus Aemilianus campaigned successfully against the Lusitani, but failed in his attempts to arrest Viriathus.
In 144 BC, Viriathus formed a league against Rome with several Celtiberian tribes[133] and persuaded them to rise against Rome too, in the Second Numantine War.[134] Viriathus' new coalition bested Roman armies at the Second Battle of Mount Venus in 144 BC and again at the failed Siege of Erisone.[134] In 139 BC, Viriathus was finally killed in his sleep by three of his companions who had been promised gifts by Rome.[135] In 136 and 135 BC, more attempts were made to gain complete control of the region of Numantia, but they failed. In 134 BC, the Consul Scipio Aemilianus finally succeeded in suppressing the rebellion following the successful Siege of Numantia.[136]
Since the Roman invasion of the Iberian Peninsula had begun in the south in the territories around the Mediterranean controlled by the Barcids, the last region of the peninsula to be subdued lay in the far north. The Cantabrian Wars or Astur-Cantabrian Wars, from 29 BC to 19 BC, occurred during the Roman conquest of these northern provinces of Cantabria and Asturias. Iberia was fully occupied by 25 BC and the last revolt put down by 19 BC[137]
Macedon, the Greek poleis, and Illyria (215–148 BC)
[edit]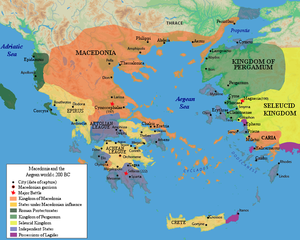
Rome's preoccupation with its war with Carthage provided an opportunity for Philip V of the kingdom of Macedon in northern Greece to attempt to extend his power westward. Philip sent ambassadors to Hannibal's camp in Italy, to negotiate an alliance as common enemies of Rome.[138][139] However, Rome discovered the agreement when Philip's emissaries, along with emissaries from Hannibal, were captured by a Roman fleet.[138] Desiring to prevent Philip from aiding Carthage in Italy and elsewhere, Rome sought out land allies in Greece to fight a proxy war against Macedon on its behalf and found partners in the Aetolian League of Greek city-states,[139] the Illyrians to the north of Macedon and the Attalid kingdom of Pergamon[140] and the city-state of Rhodes,[140] which lay across the Aegean from Macedon.[141]
The First Macedonian War saw the Romans involved directly in only limited land operations. When the Aetolians sued for peace with Philip, Rome's small expeditionary force, with no more allies in Greece, was ready to make peace. Rome had achieved its objective of pre-occupying Philip and preventing him from aiding Hannibal.[141] A treaty was drawn up between Rome and Macedon at Phoenice in 205 BC which promised Rome a small indemnity,[125] formally ending the First Macedonian War.[142]
Macedon began to encroach on territory claimed by several other Greek city states in 200 BC and these pleaded for help from their newfound ally Rome.[143] Rome gave Philip an ultimatum that he must submit Macedonia to being essentially a Roman province. Philip, unsurprisingly, refused and, after initial internal reluctance for further hostilities,[144] Rome declared war against Philip in the Second Macedonian War.[143] In the Battle of the Aous Roman forces under Titus Quinctius Flamininus defeated the Macedonians,[145] and in a second larger battle under the same opposing commanders in 197 BC, in the Battle of Cynoscephalae,[146] Flamininus again beat the Macedonians decisively.[145][147] Macedonia was forced to sign the Treaty of Tempea, in which it lost all claim to territory in Greece and Asia, and had to pay a war indemnity to Rome.[148]
Between the second and third Macedonian wars Rome faced further conflict in the region due to a tapestry of shifting rivalries, alliances and leagues all seeking to gain greater influence. After the Macedonians had been defeated in the Second Macedonian War in 197 BC, the Greek city-state of Sparta stepped into the partial power vacuum in Greece. Fearing the Spartans would take increasing control of the region, the Romans drew on help from allies to prosecute the Roman-Spartan War, defeating a Spartan army at the Battle of Gythium in 195 BC.[148] They also fought their former allies the Aetolian League in the Aetolian War,[149] against the Istrians in the Istrian War,[150] against the Illyrians in the Illyrian War,[151] and against Achaia in the Achaean War.[152]
Rome now turned its attentions to Antiochus III of the Seleucid Empire to the east. After campaigns as far abroad as Bactria, India, Persia and Judea, Antiochus moved to Asia Minor and Thrace[153] to secure several coastal towns, a move that brought him into conflict with Roman interests. A Roman force under Manius Acilius Glabrio defeated Antiochus at the Battle of Thermopylae[147] and forced him to evacuate Greece:[154] the Romans then pursued the Seleucids beyond Greece, beating them again in naval battles at the Battle of the Eurymedon and Battle of Myonessus, and finally in a decisive engagement of the Battle of Magnesia.[154][155]
In 179 BC Philip died[156] and his talented and ambitious son, Perseus of Macedon, took his throne and showed a renewed interest in Greece.[157] He also allied himself with the warlike Bastarnae,[157] and both this and his actions in Greece possibly violated the treaty signed with the Romans by his father or, if not, certainly was not "behaving as [Rome considered] a subordinate ally should".[157] Rome declared war on Macedonia again, starting the Third Macedonian War. Perseus initially had greater military success against the Romans than his father, winning the Battle of Callicinus against a Roman consular army. However, as with all such ventures in this period, Rome responded by simply sending another army. The second consular army duly defeated the Macedonians at the Battle of Pydna in 168 BC[156][158] and the Macedonians, lacking the reserve of the Romans and with King Perseus captured,[159] duly capitulated, ending the Third Macedonian War.[160]
The Fourth Macedonian War, fought from 150 BC to 148 BC, was the final war between Rome and Macedon and began when Andriscus usurped the Macedonian throne. The Romans raised a consular army under Quintus Caecilius Metellus, who swiftly defeated Andriscus at the Second battle of Pydna.
Under Lucius Mummius, Corinth was destroyed following a siege in 146 BC, leading to the surrender and thus conquest of the Achaean League (see Battle of Corinth).
Late (147–30 BC)
[edit]Jugurthine War (112–105 BC)
[edit]Rome had, in the earlier Punic Wars, gained large tracts of territory in Africa, which they consolidated in the following centuries.[161] Much of that land had been granted to the kingdom of Numidia, a kingdom on the north African coast approximating to modern Algeria, in return for its past military assistance.[162] The Jugurthine War of 111–104 BC was fought between Rome and Jugurtha of Numidia and constituted the final Roman pacification of Northern Africa,[163] after which Rome largely ceased expansion on the continent after reaching natural barriers of desert and mountain. In response to Jugurtha's usurpation of the Numidian throne,[164] a loyal ally of Rome since the Punic Wars,[165] Rome intervened. Jugurtha impudently bribed the Romans into accepting his usurpation[166][167][168] and was granted half the kingdom. Following further aggression and further bribery attempts, the Romans sent an army to depose him. The Romans were defeated at the Battle of Suthul[169] but fared better at the Battle of the Muthul[170] and finally defeated Jugurtha at the Battle of Thala,[171][172] the Battle of Mulucha,[173] and the Battle of Cirta (104 BC).[174] Jugurtha was finally captured not in battle but by treachery,[175][176] ending the war.[177]
Resurgence of the Celtic threat (121 BC)
[edit]Memories of the sack of Rome by Celtic tribes from Gaul in 390/387 BC, had been made into a legendary account that was taught to each generation of Roman youth, were still prominent despite their historical distance. In 121 BC, Rome came into contact with the Celtic tribes of the Allobroges and the Arverni, both of which they defeated with apparent ease in the First Battle of Avignon near the Rhone river and the Second Battle of Avignon, the same year.[178]
New Germanic threat (113–101 BC)
[edit]The Cimbrian War (113–101 BC) was a far more serious affair than the earlier clashes of 121 BC. The Germanic tribes of the Cimbri[179] and the Teutons or Teutones[179] migrated from northern Europe into Rome's northern territories,[180] where they clashed with Rome and her allies.[181] The Cimbrian War was the first time since the Second Punic War that Italia and Rome itself had been seriously threatened, and caused great fear in Rome.[181] The opening action of the Cimbrian War, the Battle of Noreia in 112 BC, ended in defeat and near disaster for the Romans. In 105 BC the Romans were defeated at the Battle of Arausio and was the costliest Rome had suffered since the Battle of Cannae. After the Cimbri inadvertently granted the Romans a reprieve by diverting to plunder Iberia,[182] Rome was given the opportunity to carefully prepare for and successfully meet the Cimbri and Teutons[180] in the Battle of Aquae Sextiae[182] (102 BC) and the Battle of Vercellae[182] (101 BC) where both tribes were virtually annihilated, ending the threat.
Internal unrest (135–71 BC)
[edit]The extensive campaigning abroad by Rome, and the rewarding of soldiers with plunder from those campaigns, led to the trend of soldiers becoming increasingly loyal to their commanders rather than to the state, and a willingness to follow their generals in battle against the state.[183] Rome was plagued by several slave uprisings during this period, in part because in the past century vast tracts of land had been given to veterans who farmed by use of slaves and who came to greatly outnumber their Roman masters. In the last century BC, at least twelve civil wars and rebellions occurred. This pattern did not break until Octavian (later Caesar Augustus) ended it by becoming a successful challenger to the Senate's authority, and was made princeps (emperor).
Between 135 BC and 71 BC there were three Servile Wars against the Roman state; the third, and most serious,[184] may have involved the revolution of 120,000[185] to 150,000[186] slaves. Additionally, in 91 BC the Social War broke out between Rome and its former allies in Italy,[187][188] collectively known as the Socii, over the grievance that they shared the risk of Rome's military campaigns, but not its rewards.[180][189][190] Despite defeats such as the Battle of Fucine Lake, Roman troops defeated the Italian militias in decisive engagements, notably the Battle of Asculum. Although they lost militarily, the Socii achieved their objectives with the legal proclamations of the Lex Julia and Lex Plautia Papiria, which granted citizenship to more than 500,000 Italians.[189]
The internal unrest reached its most serious stage in the two civil wars or marches upon Rome by the consul Lucius Cornelius Sulla at the beginning of 82 BC. In the Battle of the Colline Gate at the very door of the city of Rome, a Roman army under Sulla bested an army of the Roman senate and its Samnite allies.[191] Whatever the merits of his grievances against those in power of the state, his actions marked a watershed of the willingness of Roman troops to wage war against one another that was to pave the way for the wars of the triumvirate, the overthrowing of the Senate as the de facto head of the Roman state, and the eventual endemic usurpation of power by contenders for the emperor-ship in the later Empire.
Conflicts with Mithridates (89–63 BC)
[edit]Mithridates the Great was the ruler of Pontus,[192] a large kingdom in Asia Minor, from 120 to 63 BC. He is remembered as one of Rome's most formidable and successful enemies who engaged three of the most prominent generals of the late Roman Republic: Sulla, Lucullus, and Pompey the Great. In a pattern familiar from the Punic Wars, the Romans came into conflict with him after the two states' spheres of influence began to overlap. Mithridates antagonised Rome by seeking to expand his kingdom,[192] and Rome for her part seemed equally keen for war and the spoils and prestige that it might bring.[192][193] After conquering western Anatolia (modern Turkey) in 88 BC, Roman sources claim that Mithridates ordered the killing of the majority of the 80,000 Romans living there.[194] In the subsequent First Mithridatic War, the Roman general Lucius Cornelius Sulla forced Mithridates out of Greece proper after the Battle of Chaeronea and later Battle of Orchomenus but then had to return to Italy to answer the internal threat posed by his rival Marius; consequently, Mithridates VI was defeated but not destroyed. A peace was made between Rome and Pontus, but this proved only a temporary lull.
The Second Mithridatic War began when Rome tried to annex Bithynia as a province. In the Third Mithridatic War, first Lucius Licinius Lucullus and then Pompey the Great were sent against Mithridates.[195] Mithridates was finally defeated by Pompey in the night-time Battle of the Lycus.[196] After defeating Mithridates, Pompey invaded Caucacus, subjugated the Kingdom of Iberia and established Roman control over Colchis.
Campaign against the Cilician pirates (67 BC)
[edit]The Mediterranean had at this time fallen into the hands of pirates,[196] largely from Cilicia.[197] Rome had destroyed many of the states that had previously policed the Mediterranean with fleets, but had failed to step into the gap created.[198] The pirates had seized the opportunity of a relative power vacuum and had not only strangled shipping lanes but had plundered many cities on the coasts of Greece and Asia,[197] and had even made descents upon Italy itself.[199] After the Roman admiral Marcus Antonius Creticus (father of the triumvir Marcus Antonius) failed to clear the pirates to the satisfaction of the Roman authorities, Pompey was nominated his successor as commander of a special naval task force to campaign against them.[195][196] It supposedly took Pompey just forty days to clear the western portion of the western Mediterranean of pirates,[197][200] and restore communication between Iberia, Africa, and Italy. Plutarch describes how Pompey first swept their craft from the Mediterranean in a series of small actions and through the promise of honouring the surrender of cities and craft. He then followed the main body of the pirates to their strongholds on the coast of Cilicia, and destroyed them there in the naval Battle of Korakesion.[196]
Caesar's early campaigns (59–50 BC)
[edit]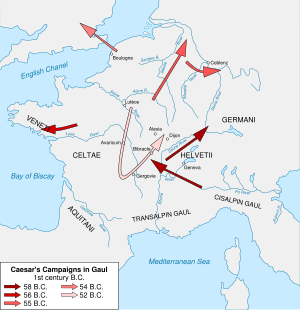
During a term as praetor in Iberia, Pompey's contemporary Julius Caesar of the Roman Julii clan defeated the Calaici and Lusitani in battle.[201] Following a consular term, he was then appointed to a five-year term as Proconsular Governor of Transalpine Gaul (current southern France) and Illyria (the coast of Dalmatia).[201][202] Not content with an idle governorship, Caesar strove to find reason to invade Gaul, which would give him the dramatic military success he sought.[203] To this end he stirred up popular nightmares of the first sack of Rome by the Gauls and the more recent spectre of the Cimbri and Teutones.[203] When the Helvetii and Tigurini[201] tribes began to migrate on a route that would take them near (not into)[204] the Roman province of Transalpine Gaul, Caesar had the barely sufficient excuse he needed for his Gallic Wars, fought between 58 BC and 49 BC.[205] After slaughtering the Helvetii tribe,[206] Caesar prosecuted a "long, bitter and costly"[207] campaign against other tribes across the breadth of Gaul, many of whom had fought alongside Rome against their common enemy the Helvetii,[204] and annexed their territory to that of Rome. Plutarch claims that the campaign cost a million Gallic lives.[208] Although "fierce and able"[207] the Gauls were handicapped by internal disunity and fell in a series of battles over the course of a decade.[207][209]
Caesar defeated the Helvetii in 58 BC at the Battle of the Arar and Battle of Bibracte,[210] the Belgic confederacy known as the Belgae at the Battle of the Axona,[201][206] the Nervii in 57 BC at the Battle of the Sabis,[201][211] the Aquitani, Treviri, Tencteri, Aedui and Eburones in unknown battles,[206] and the Veneti in 56 BC.[206] In 55 and 54 BC he made two expeditions to Britain.[206][212] In 52 BC, following the Siege of Avaricum and a string of inconclusive battles,[213] Caesar defeated a union of Gauls led by Vercingetorix[214] at the Battle of Alesia,[215][216] completing the Roman conquest of Transalpine Gaul. By 50 BC, the entirety of Gaul lay in Roman hands.[215] Caesar recorded his own accounts of these campaigns in Commentarii de Bello Gallico ("Commentaries on the Gallic War").
Gaul never regained its Celtic identity, never attempted another nationalist rebellion, and remained loyal to Rome until the fall of the Western Empire in 476 AD. However, although Gaul itself was to thereafter remain loyal, cracks were appearing in the political unity of Rome's governing figures – partly over concerns over the loyalty of Caesar's Gallic troops to his person rather than the state[207] – that were soon to drive Rome into a lengthy series of civil wars.
Triumvirates, Caesarian ascension, and revolt (53–30 BC)
[edit]By 59 BC an unofficial political alliance known as the First Triumvirate was formed between Gaius Julius Caesar, Marcus Licinius Crassus, and Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus to share power and influence.[217] It was always an uncomfortable alliance given that Crassus and Pompey intensely disliked one another. In 53 BC, Crassus launched a Roman invasion of the Parthian Empire. After initial successes,[218] he marched his army deep into the desert;[219] but here his army was cut off deep in enemy territory, surrounded and slaughtered[206] at the Battle of Carrhae[220][221] in "the greatest Roman defeat since Hannibal"[222] in which Crassus himself perished.[223] The death of Crassus removed some of the balance in the Triumvirate and, consequently, Caesar and Pompey began to move apart. While Caesar was fighting against Vercingetorix in Gaul, Pompey proceeded with a legislative agenda for Rome that revealed that he was at best ambivalent towards Caesar[224] and perhaps now covertly allied with Caesar's political enemies. In 51 BC, some Roman senators demanded that Caesar would not be permitted to stand for Consul unless he turned over control of his armies to the state, and the same demands were made of Pompey by other factions.[225][226] Relinquishing his army would leave Caesar defenceless before his enemies. Caesar chose Civil War over laying down his command and facing trial.[225] The triumvirate was shattered and conflict was inevitable.
Pompey initially assured Rome and the senate that he could defeat Caesar in battle should he march on Rome.[227][228] However, by the spring of 49 BC, when Caesar crossed the Rubicon river with his invading forces and swept down the Italian peninsula towards Rome, Pompey ordered the abandonment of Rome.[227][228] Caesar's army was still under-strength, with certain units remaining in Gaul,[227] but on the other hand Pompey himself only had a small force at his command, and that with uncertain loyalty having served under Caesar.[228] Tom Holland attributes Pompey's willingness to abandon Rome to waves of panicking refugees as an attempt to stir ancestral fears of invasions from the north.[229] Pompey's forces retreated south towards Brundisium,[230] and then fled to Greece.[228][231] Caesar first directed his attention to the Pompeian stronghold of Iberia[232] but following campaigning by Caesar in the Siege of Massilia and Battle of Ilerda he decided to attack Pompey in Greece.[233][234] Pompey initially defeated Caesar at the Battle of Dyrrachium in 48 BC[235] but failed to follow up on the victory. Pompey was decisively defeated in the Battle of Pharsalus in 48 BC[236][237] despite outnumbering Caesar's forces two to one.[238] Pompey fled again, this time to Egypt, where he was murdered[196][239] in an attempt to ingratiate the country with Caesar and avoid a war with Rome.[222][236]
Pompey's death did not see the end of the civil wars since initially Caesar's enemies were manifold and Pompey's supporters continued to fight on after his death. In 46 BC Caesar lost perhaps as much as a third of his army when his former commander Titus Labienus, who had defected to the Pompeians several years earlier, defeated him at the Battle of Ruspina. However, after this low point Caesar came back to defeat the Pompeian army of Metellus Scipio in the Battle of Thapsus, after which the Pompeians retreated yet again to Iberia. Caesar defeated the combined forces of Titus Labienus and Gnaeus Pompey the Younger at the Battle of Munda in Iberia. Labienus was killed in the battle and the Younger Pompey captured and executed.
| "The Parthians began to shoot from all sides. They did not pick any particular target since the Romans were so close together that they could hardly miss...If they kept their ranks they were wounded. If they tried to charge the enemy, the enemy did not suffer more and they did not suffer less, because the Parthians could shoot even as they fled...When Publius urged them to charge the enemy's mail-clad horsemen, they showed him that their hands were riveted to their shields and their feet nailed through and through to the ground, so that they were helpless either for flight or for self-defence." |
| Plutarch on the Battle of Carrhae[240] |
Despite his military success, or probably because of it, fear spread of Caesar, now the primary figure of the Roman state, becoming an autocratic ruler and ending the Roman Republic. This fear drove a group of senators naming themselves The Liberators to assassinate him in 44 BC.[241] Further civil war followed between those loyal to Caesar and those who supported the actions of the Liberators. Caesar's supporter Mark Antony condemned Caesar's assassins and war broke out between the two factions. Antony was denounced as a public enemy, and Octavian was entrusted with the command of the war against him. In the Battle of Forum Gallorum Antony, besieging Caesar's assassin Decimus Brutus in Mutina, defeated the forces of the consul Pansa, who was killed, but Antony was then immediately defeated by the army of the other consul, Hirtius. At the Battle of Mutina Antony was again defeated in battle by Hirtius, who was killed. Although Antony failed to capture Mutina, Decimus Brutus was murdered shortly thereafter.
Octavian betrayed his party, and came to terms with Caesarians Antony and Lepidus and on 26 November 43 BC the Second Triumvirate was formed,[242] this time in an official capacity.[241] In 42 BC Triumvirs Mark Antony and Octavian fought the indecisive Battle of Philippi with Caesar's assassins Marcus Brutus and Cassius. Although Brutus defeated Octavian, Antony defeated Cassius, who committed suicide. Brutus also committed suicide shortly afterwards.
Civil war flared again when the Second Triumvirate of Octavian, Lepidus and Mark Antony failed just as the first had almost as soon as its opponents had been removed. The ambitious Octavian built a power base and then launched a campaign against Mark Antony.[241] Together with Lucius Antonius, Mark Antony's wife Fulvia raised an army in Italy to fight for Antony's rights against Octavian but she was defeated by Octavian at the Battle of Perugia. Her death led to partial reconciliation between Octavian and Antony who went on to crush the army of Sextus Pompeius, the last focus of opposition to the second triumvirate, in the naval Battle of Naulochus.
As before, once opposition to the triumvirate was crushed, it started to tear at itself. The triumvirate expired on the last day of 33 BC and was not renewed in law and in 31 BC, war began again. At the Battle of Actium,[243] Octavian decisively defeated Antony and Cleopatra in a naval battle near Greece, using fire to destroy the enemy fleet.[244]
Octavian went on to become Emperor under the name Augustus[243] and, in the absence of political assassins or usurpers, was able to greatly expand the borders of the Empire.
Empire
[edit]Imperial expansion (40 BC – 117 AD)
[edit]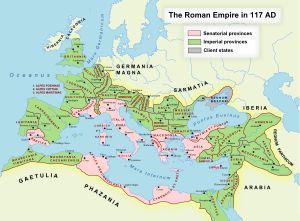
Secured from internal threats, Rome achieved great territorial gains in both the East and the West. In the West, following humiliating defeats at the hands of the Sugambri, Tencteri and Usipetes tribes in 16 BC,[245] Roman armies pushed north and east out of Gaul to subdue much of Germania. The Pannonian revolt in 6 AD[245] forced the Romans to cancel their plan to cement their conquest of Germania.[137][246][247] Despite the loss of a large army almost to the man of Varus' famous defeat at the hands of the Germanic leader Arminius in the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest in 9 AD,[248][249][250] Rome recovered and continued its expansion up to and beyond the borders of the known world. Roman armies under Germanicus pursued several more campaigns against the Germanic tribes of the Marcomanni, Hermunduri, Chatti,[251] Cherusci,[252] Bructeri,[252] and Marsi.[253] Overcoming several mutinies in the armies along the Rhine,[254] Germanicus defeated the Germanic tribes of Arminius in a series of battles culminating in the Battle of the Weser River.[255]
After Caesar's preliminary low-scale invasions of Britain,[256][257] the Romans invaded in force in 43 AD,[258] forcing their way inland through several battles against British tribes, including the Battle of the Medway,[258] the Battle of the Thames, the Battle of Caer Caradoc and the Battle of Mona.[259] Following a general uprising[260][261] in which the Britons sacked Colchester,[262] St Albans[263] and London,[263][264] the Romans suppressed the rebellion in the Battle of Watling Street[265][266] and went on to push as far north as central Scotland in the Battle of Mons Graupius.[267][268] Tribes in modern-day Scotland and Northern England repeatedly rebelled against Roman rule and two military bases were established in Britannia to protect against rebellion and incursions from the north, from which Roman troops built and manned Hadrian's Wall.[269]
On the continent, the extension of the Empire's borders beyond the Rhine hung in the balance for some time, with the emperor Caligula apparently poised to invade Germania in 39 AD, and Cnaeus Domitius Corbulo crossing the Rhine in 47 AD and marching into the territory of the Frisii and Chauci.[270] Caligula's successor, Claudius, ordered the suspension of further attacks across the Rhine,[270] setting what was to become the permanent limit of the Empire's expansion in this direction.[2]
| "Never was there slaughter more cruel than took place there in the marshes and woods, never were more intolerable insults inflicted by barbarians, especially those directed against the legal pleaders. They put out the eyes of some of them and cut off the hands of others; they sewed up the mouth of one of them after first cutting out his tongue, which one of the barbarians held in his hand, exclaiming At last, you viper, you have ceased to hiss!." |
| Florus on the loss of Varus' force[271] |
Further east, Trajan turned his attention to Dacia, an area north of Macedon and Greece and east of the Danube that had been on the Roman agenda since before the days of Caesar[272][273] when they had beaten a Roman army at the Battle of Histria.[274] In 85 AD, the Dacians had swarmed over the Danube and pillaged Moesia[275][276] and initially defeated an army the Emperor Domitian sent against them,[277] but the Romans were victorious in the Battle of Tapae in AD 88 and a truce was drawn up.[277]
Emperor Trajan recommenced hostilities against Dacia and, following an uncertain number of battles,[278] defeated the Dacian general Decebalus in the Second Battle of Tapae in 101 AD.[279] With Trajan's troops pressing towards the Dacian capital Sarmizegethusa, Decebalus once more sought terms.[280] Decebalus rebuilt his power over the following years and attacked Roman garrisons again in 105 AD. In response Trajan again marched into Dacia,[281] besieging the Dacian capital in the Siege of Sarmizegethusa, and razing it to the ground.[282] With Dacia quelled, Trajan subsequently invaded the Parthian empire to the east, his conquests taking the Roman Empire to its greatest extent. Rome's borders in the east were indirectly governed through a system of client states for some time, leading to less direct campaigning than in the west in this period.[283]
The Kingdom of Armenia between the Black Sea and Caspian Sea became a focus of contention between Rome and the Parthian Empire, and control of the region was repeatedly gained and lost. The Parthians forced Armenia into submission from 37 AD[284] but in 47 AD the Romans retook control of the kingdom and offered it client kingdom status. Under Nero, the Romans fought a campaign between 55 and 63 AD against the Parthian Empire, which had again invaded Armenia. After gaining Armenia once more in 60 AD and subsequently losing it again in 62 AD, the Romans sent Gnaeus Domitius Corbulo in 63 AD into the territories of Vologases I of Parthia. Corbulo succeeded in returning Armenia to Roman client status, where it remained for the next century.
Year of the Four Emperors (69 AD)
[edit]In 69 AD, Marcus Salvius Otho, governor of Lusitania, had the Emperor Galba murdered[285][286] and claimed the throne for himself.[287][288] However, Vitellius, governor of the province of Germania Inferior, had also claimed the throne[289][290] and marched on Rome with his troops.[287][288] Following an inconclusive battle near Antipolis,[291] Vitellius' troops attacked the city of Placentia in the Assault of Placentia, but were repulsed by the Othonian garrison.[290][292]
Otho left Rome on March 14, and marched north towards Placentia to meet his challenger. In the Battle of Locus Castorum the Othonians had the better of the fighting,[293] and Vitellius' troops retreated to Cremona. The two armies met again on the Via Postunia, in the First Battle of Bedriacum,[294] after which the Othonian troops fled back to their camp in Bedriacum,[295] and the next day surrendered to the Vitellian forces. Otho decided to commit suicide rather than fight on.[296]
Meanwhile, the forces stationed in the Middle East provinces of Judaea and Syria had acclaimed Vespasian as emperor[294] and the Danubian armies of the provinces of Raetia and Moesia also acclaimed Vespasian as emperor. Vespasian's and Vitellius' armies met in the Second Battle of Bedriacum,[294][297] after which the Vitellian troops were driven back into their camp outside Cremona, which was taken.[298] Vespasian's troops then attacked Cremona itself,[299] which surrendered.
Under pretence of siding with Vespasian, Civilis of Batavia had taken up arms and induced the inhabitants of his native country to rebel.[294][300] The rebelling Batavians were immediately joined by several neighbouring German tribes including the Frisii. These forces drove out the Roman garrisons near the Rhine and defeated a Roman army at the Battle of Castra Vetera, after which many Roman troops along the Rhine and in Gaul defected to the Batavian cause. However, disputes soon broke out amongst the different tribes, rendering co-operation impossible; Vespasian, having successfully ended the civil war, called upon Civilis to lay down his arms, and on his refusal his legions met him in force, defeating him[276] in the Battle of Augusta Treverorum.
Jewish revolts (66–135 AD)
[edit]The First Jewish-Roman War, sometimes called The Great Revolt, was the first of three major rebellions by the Jews of Judaea against the Roman Empire.[301] According to Fergus Millar, the revolt represents "the best-attested series of operations by the Roman army in the entire history of the Empire."[302] Judaea, an independent kingdom under the Hasmoneans, fell into a civil war in which Pompey intervened, conquering Jerusalem in 63 BC.[303][304] The territory gradually transformed into a client kingdom before eventually becoming a directly governed province.[305] Jewish anger towards Rome grew due to the incompetent and often harsh rule of successive governors[306][307][308] coupled with Roman insensitivity[309] – Tacitus says disgust and repulsion[310] – towards their religion. This discontent was further fueled by ethnic tensions between Jews and pagans,[311][308] economic and social issues,[308] and aspirations for national independence.[312][313] The spark came in 66 AD, when violence broke out in Jerusalem after the Roman governor seized a large amount of money from the Temple and killed many;[314] this act led to an open uprising against Rome. Cestius Gallus, the Roman governor of Syria, attempted to quell the revolt but withdrew after initial engagements in Jerusalem,[315][316][317] with his force decisively ambushed and annihilated in the Battle of Beth-Horon, losing a contingent equivalent to a legion.[315][318][317] By this point, the revolt attracted greater attention from Rome and Emperor Nero appointed general Vespasian to crush the rebellion.[319][320] Vespasian led his forces in a methodical clearance of the areas in revolt. By the year 68 AD, Jewish resistance in the Galilee had been crushed, with the Romans besieging and destroying rebel strongholds such as Yodfat[321] and Gamla.[322] In 70 AD, Titus succeeded Vespasian and, using a force significantly larger than the one deployed for the Roman invasion of Britain,[323] managed to take Jerusalem after a long siege, during which the Temple was razed.[324] The city was systematically destroyed,[325][326] with much of its population massacred or enslaved.[327] Roman forces continued to suppress remaining resistance, culminating in the Siege of Masada in 73 AD.[328][329] The Flavian dynasty leveraged the victory to solidify its claim to imperial rule. This was achieved through a triumph in Rome (the only one celebrating the subjugation of an existing province's population),[330] the minting of Judaea Capta coins,[331] and the construction of commemorative monuments[332] such as the Arch of Titus.[333]

Circa 115 AD, a series of revolts broke out among Jewish diaspora communities in the eastern provinces of the Roman Empire while Trajan was engaged in his Parthian campaign.[334] The revolts, which came to be known as the Diaspora Revolt, erupted nearly simultaneously in Egypt, Libya, and Cyprus.[335] Marcius Turbo, a leading general, was sent to quell the uprisings in Egypt and Libya,[336] while Lusius Quietus handled Jewish unrest in Mesopotamia and Judaea (the "Kitos War").[337] The uprisings were largely suppressed by late 117 AD, just before Trajan's death, resulting in the annihilation and expulsion of Jewish communities in Egypt, Libya, and Cyprus.[338]
In 132 AD, the Bar Kokhba revolt emerged as the final major Jewish uprising against Roman authority and the last bid for Jewish independence in Judaea. The immediate triggers of the revolt, still debated by scholars, include Hadrian's establishment of the pagan colony Aelia Capitolina on the ruins of Jerusalem and his prohibition of circumcision.[339] Led by Simon bar Kokhba, the Jews initially succeeded in creating a brief independent state. However, the Romans assembled six full legions with auxiliaries and other elements from up to six additional legions, all under the command of Sextus Julius Severus, that effectively crushed the revolt by 135 AD.[340] This suppression caused extensive devastation across Judaea, leading to massive loss of life, widespread displacement, and enslavement, while also inflicting heavy casualties on Roman forces. After the revolt, the province was renamed Syria Palaestina, and Jews were subjected to harsh religious restrictions.[341]
Struggle with Parthia (114–217 AD)
[edit]By the 2nd century AD the territories of Persia were controlled by the Arsacid dynasty and known as the Parthian Empire. Due in large part to their employment of powerful heavy cavalry and mobile horse archers, Parthia was the most formidable enemy of the Roman Empire in the east. As early as 53 BC, the Roman general Crassus had invaded Parthia, but he was killed and his army was defeated at the Battle of Carrhae. In the years following Carrhae, the Romans were divided in civil war and hence unable to campaign against Parthia. Trajan also campaigned against the Parthians from 114 to 117 AD and briefly captured their capital Ctesiphon, putting the puppet ruler Parthamaspates on the throne. However, rebellions in Babylonia and the Jewish revolts in Judaea made it difficult to maintain the captured province and the territories were abandoned.
A revitalised Parthian Empire renewed its assault in 161 AD, defeating two Roman armies and invading Armenia and Syria. Emperor Lucius Verus and general Gaius Avidius Cassius were sent in 162 AD to counter the resurgent Parthia. In this war, the Parthian city of Seleucia on the Tigris was destroyed and the palace at the capital Ctesiphon was burned to the ground by Avidius Cassius in 164 AD. The Parthians made peace but were forced to cede western Mesopotamia to the Romans.[342]
In 197 AD, Emperor Septimius Severus waged a brief and successful war against the Parthian Empire in retaliation for the support given to a rival for the imperial throne Pescennius Niger. The Parthian capital Ctesiphon was sacked by the Roman army, and the northern half of Mesopotamia was restored to Rome.
Emperor Caracalla, the son of Severus, marched on Parthia in 217 AD from Edessa to begin a war against them, but he was assassinated while on the march.[343] In 224 AD, the Parthian Empire was crushed not by the Romans but by the rebellious Persian vassal king Ardashir I, who revolted, leading to the establishment of Sassanid Empire of Persia, which replaced Parthia as Rome's major rival in the East.
Throughout the Parthian wars, tribal groups along the Rhine and Danube took advantage of Rome's preoccupation with the eastern frontier (and the plague that the Romans suffered from after bringing it back from the east) and launched a series of incursions into Roman territories, including the Marcomannic Wars.
Struggle with Germanic tribes (163–378 AD)
[edit]
After Varus' defeat in Germania in the 1st century, Rome had adopted a largely defensive strategy along the border with Germania, constructing a line of defences known as limes along the Rhine. Although the exact historicity is unclear, since the Romans often assigned one name to several distinct tribal groups, or conversely applied several names to a single group at different times, some mix of Germanic peoples, Celts, and tribes of mixed Celto-Germanic ethnicity were settled in the lands of Germania from the 1st century onwards. The Cherusci, Bructeri, Tencteri, Usipi, Marsi, and Chatti of Varus' time had by the 3rd century either evolved into or been displaced by a confederacy or alliance of Germanic tribes collectively known as the Alamanni,[344] first mentioned by Cassius Dio describing the campaign of Caracalla in 213 AD.
In around 166 AD, several Germanic tribes pushed across the Danube, striking as far as Italy itself in the Siege of Aquileia in 166 AD,[342] and the heartland of Greece in the Sack of Eleusis.[342]
Although the essential problem of large tribal groups on the frontier remained much the same as the situation Rome faced in earlier centuries, the 3rd century saw a marked increase in the overall threat,[345][346] although there is disagreement over whether external pressure increased,[344] or Rome's ability to meet it declined.[347] The Carpi and Sarmatians whom Rome had held at bay were replaced by the Goths and likewise the Quadi and Marcomanni that Rome had defeated were replaced by the greater confederation of the Alamanni.[348]
The assembled warbands of the Alamanni frequently crossed the limes, attacking Germania Superior such that they were almost continually engaged in conflicts with the Roman Empire, whilst Goths attacked across the Danube in battles such as the Battle of Beroa[349] and Battle of Philippopolis in 250 AD[349] and the Battle of Abrittus in 251 AD,[349] and both Goths and Heruli ravaged the Aegean and, later, Greece, Thrace and Macedonia.[348][350] However, their first major assault deep into Roman territory came in 268 AD. In that year the Romans were forced to denude much of their German frontier of troops in response to a massive invasion by another new Germanic tribal confederacy, the Goths, from the east. The pressure of tribal groups pushing into the Empire was the result of a chain of migrations with its roots far to the east:[351] Huns from the Russian steppe attacked the Goths,[352][353][354] who in turn attacked the Dacians, Alans and Sarmatians at or within Rome's borders.[355] The Goths first appeared in history as a distinct people in this invasion of 268 AD when they swarmed over the Balkan peninsula and overran the Roman provinces of Pannonia and Illyricum and even threatened Italia itself.
The Alamanni seized the opportunity to launch a major invasion of Gaul and northern Italy. However, the Visigoths were defeated in battle that summer near the modern Italian-Slovenian border and then routed in the Battle of Naissus[356] that September by Gallienus, Claudius and Aurelian, who then turned and defeated the Alemanni at the Battle of Lake Benacus. Claudius' successor Aurelian defeated the Goths twice more in the Battle of Fanum Fortunae[356] and the Battle of Ticinum.[356] The Goths remained a major threat to the Empire but directed their attacks away from Italy itself for several years after their defeat. By 284 AD, Gothic troops were serving on behalf of the Roman military as federated troops.[357]

The Alamanni on the other hand resumed their drive towards Italy almost immediately. They defeated Aurelian at the Battle of Placentia in 271 AD but were beaten back for a short time after they lost the battles of Fano and Pavia later that year. They were beaten again in 298 AD at the battles of Lingones and Vindonissa but fifty years later they were resurgent again, making incursions in 356 AD at the Battle of Reims,[358] in 357 AD at the Battle of Strasbourg,[359] in 367 AD at the Battle of Solicinium and in 378 AD at Battle of Argentovaria. In the same year the Goths inflicted a crushing defeat on the Eastern Empire at the Battle of Adrianople,[360][361] in which the Eastern Emperor Valens was massacred along with tens of thousands of Roman troops.[362]
At the same time, Franks raided through the North Sea and the English Channel,[363] Vandals pressed across the Rhine, Iuthungi against the Danube, Iazyges, Carpi and Taifali harassed Dacia, and Gepids joined the Goths and Heruli in attacks round the Black Sea.[364] At around the same time, lesser-known tribes such as the Bavares, Baquates and Quinquegentanei[357] raided Africa.[364]
At the start of the 5th century, the pressure on Rome's western borders was growing intense. However, it was not only the western borders that were under threat: Rome was also under threat both internally and on its eastern borders.
Usurpers (193–394 AD)
[edit]
An army that was often willing to support its general over its emperor, meant that if commanders could establish sole control of their army, they could usurp the imperial throne from that position. The so-called Crisis of the Third Century describes the turmoil of murder, usurpation and in-fighting that followed the murder of the Emperor Alexander Severus in 235 AD.[365] However, Cassius Dio marks the wider imperial decline as beginning in 180 AD with the ascension of Commodus to the throne,[366] a judgement with which Gibbon concurred,[367] and Matyszak states that "the rot ... had become established long before" even that.[366]
Although the crisis of the 3rd century was not the absolute beginning of Rome's decline, it nevertheless did impose a severe strain on the empire as Romans waged war on one another as they had not done since the last days of the Republic. Within the space of a single century, twenty-seven military officers declared themselves emperors and reigned over parts of the empire for months or days, all but two meeting with a violent end.[344][368] The time was characterized by a Roman army that was as likely to be attacking itself as it was an outside invader, reaching a low point around 258 AD.[369] Ironically, while it was these usurpations that led to the breakup of the Empire during the crisis, it was the strength of several frontier generals that helped reunify the empire through force of arms.
The situation was complex, often with three or more usurpers in existence at once. Septimius Severus and Pescennius Niger, both rebel generals declared to be emperors by the troops they commanded, clashed for the first time in 193 AD at the Battle of Cyzicus, in which Niger was defeated. However, it took two further defeats at the Battle of Nicaea later that year and the Battle of Issus the following year, for Niger to be destroyed. Almost as soon as Niger's usurpation had been ended, Severus was forced to deal with another rival for the throne in the person of Clodius Albinus, who had originally been allied to Severus. Albinus was proclaimed emperor by his troops in Britain and, crossing over to Gaul, defeated Severus' general Virius Lupus in battle, before being in turn defeated and killed in the Battle of Lugdunum by Severus himself.
After this turmoil, Severus faced no more internal threats for the rest of his reign,[370] and the reign of his successor Caracalla passed uninterrupted for a while until he was murdered by Macrinus,[370] who proclaimed himself emperor. Despite Macrinus having his position ratified by the Roman senate, the troops of Varius Avitus declared him to be emperor instead, and the two met in battle at the Battle of Antioch in 218 AD, in which Macrinus was defeated.[371] However, Avitus himself, after taking the imperial name Elagabalus, was murdered shortly afterwards[371] and Alexander Severus was proclaimed emperor by both the Praetorian Guard and the senate who, after a short reign, was murdered in turn.[371] His murderers were working on behalf of the army who were unhappy with their lot under his rule and who raised in his place Maximinus Thrax. However, just as he had been raised by the army, Maximinus was also brought down by them and despite winning the Battle of Carthage against the senate's newly proclaimed Gordian II, he too was murdered[372] when it appeared to his forces as though he would not be able to best the next senatorial candidate for the throne, Gordian III.
Gordian III's fate is not certain, although he may have been murdered by his own successor, Philip the Arab, who ruled for only a few years before the army again raised a general, Decius, by their proclamation to emperor, who then defeated Philip in the Battle of Verona.[373] Several succeeding generals avoided battling usurpers for the throne by being murdered by their own troops before battle could commence. The lone exception to this rule was Gallienus, emperor from 260 to 268 AD, who confronted a remarkable array of usurpers, most of whom he defeated in pitched battle. The army was mostly spared further infighting until around 273 AD, when Aurelian defeated the Gallic usurper Tetricus in the Battle of Chalons. The next decade saw an incredible number of usurpers, sometimes three at the same time, all vying for the imperial throne. Most of the battles are not recorded, due primarily to the turmoil of the time, until Diocletian, a usurper himself, defeated Carinus at the Battle of the Margus and became emperor.
Some small measure of stability again returned at this point, with the empire split into a Tetrarchy of two greater and two lesser emperors, a system that staved off civil wars for a short time until 312 AD. In that year, relations between the tetrarchy collapsed for good and Constantine I, Licinius, Maxentius and Maximinus jostled for control of the empire. In the Battle of Turin Constantine defeated Maxentius, and in the Battle of Tzirallum, Licinius defeated Maximinus. From 314 AD onwards, Constantine defeated Licinius in the Battle of Cibalae, then the Battle of Mardia, and then again at the Battle of Adrianople, the Battle of the Hellespont and the Battle of Chrysopolis.
Constantine then turned upon Maxentius, beating him in the Battle of Verona and the Battle of Milvian Bridge in the same year. Constantine's son Constantius II inherited his father's rule and later defeated the usurper Magnentius in first the Battle of Mursa Major and then the Battle of Mons Seleucus.
Successive emperors Valens and Theodosius I also defeated usurpers in, respectively, the Battle of Thyatira, and the battles of the Save and the Frigidus.
Struggle with the Sassanid Empire (230–363 AD)
[edit]After overthrowing the Parthian confederacy,[344][374] the Sassanid Empire that arose from its remains pursued a more aggressive expansionist policy than their predecessors[375][376] and continued to make war against Rome. In 230 AD, the first Sassanid emperor attacked Roman territory first in Armenia and then in Mesopotamia[376] but Roman losses were largely restored by Severus within a few years.[375] In 243 AD, Emperor Gordian III's army retook the Roman cities of Hatra, Nisibis and Carrhae from the Sassanids after defeating the Sassanids at the Battle of Resaena[377] but what happened next is unclear: Persian sources claim that Gordian was defeated and killed in the Battle of Misikhe[378] but Roman sources mention this battle only as an insignificant setback and suggest that Gordian died elsewhere.[379]
Certainly, the Sassanids had not been cowed by the previous battles with Rome and in 253 AD the Sassanids under Shapur I penetrated deeply into Roman territory several times, defeating a Roman force at the Battle of Barbalissos[379] and conquering and plundering Antiochia in 252 AD following the Siege of Antiochia.[374][379] The Romans recovered Antioch by 253 AD,[380] and Emperor Valerian gathered an army and marched eastward to the Sassanid borders. In 260 AD at the Battle of Edessa the Sassanids defeated the Roman army[380] and captured the Roman Emperor Valerian.[374][376]
By the late 3rd century, Roman fortunes on the eastern frontier improved dramatically. During a period of civil upheaval in Persia, emperor Carus led a successful campaign into Persia essentially uncontested, sacking Ctesiphon in 283 AD. During the reign of the Tetrarchy, emperors Diocletian and Galerius brought a decisive conclusion to the war, sacking Ctesiphon in 299 AD and expanding the Roman eastern frontier dramatically with the Treaty of Nisibis. The treaty brought lasting peace between Rome and the Sassanids for almost four decades until the end of Constantine the Great's reign. In 337 AD, Shapur II broke the peace and began a 26-year conflict, attempting with little success to conquer Roman fortresses in the region. After early Sassanid successes including the Battle of Amida in 359 AD and the Siege of Pirisabora in 363 AD,[381] Emperor Julian met Shapur in 363 AD in the Battle of Ctesiphon outside the walls of the Persian capital.[381] The Romans were victorious but were unable to take the city, and were forced to retreat due to their vulnerable position in the middle of hostile territory. Julian was killed in the Battle of Samarra during the retreat, possibly by one of his own men.[381]
There were several future wars, although all brief and small-scale, since both the Romans and the Sassanids were forced to deal with threats from other directions during the 5th century. A war against Bahram V in 420 AD over the persecution of the Christians in Persia led to a brief war that was soon concluded by treaty and in 441 AD a war with Yazdegerd II was again swiftly concluded by treaty after both parties battled threats elsewhere.[382]
Collapse of the Western Empire (402–476 AD)
[edit]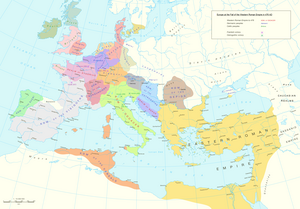
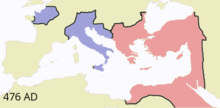
Many theories have been advanced in way of explanation for decline of the Roman Empire, and many dates given for its fall, from the onset of its decline in the 3rd century[383] to the fall of Constantinople in 1453.[384] Militarily, however, the Empire finally fell after first being overrun by various non-Roman peoples and then having its heart in Italy seized by Germanic troops in a revolt. The historicity and exact dates are uncertain, and some historians do not consider that the Empire fell at this point.
The Empire became gradually less Romanised and increasingly Germanic in nature: although the Empire buckled under Visigothic assault, the overthrow of the last Emperor Romulus Augustus was carried out by federated Germanic troops from within the Roman army rather than by foreign troops. In this sense had Odoacer not renounced the title of Emperor and named himself "King of Italy" instead, the Empire might have continued in name. Its identity, however, was no longer Roman – it was increasingly populated and governed by Germanic peoples long before 476 AD. The Roman people were by the 5th century "bereft of their military ethos"[385] and the Roman army itself a mere supplement to federated troops of Goths, Huns, Franks and others fighting on their behalf.
Rome's last gasp began when the Visigoths revolted around 395 AD.[386] Led by Alaric I,[387] they attempted to seize Constantinople,[388] but were rebuffed and instead plundered much of Thrace in northern Greece.[387][389] In 402 AD they besieged Mediolanum, the capital of Roman Emperor Honorius, defended by Roman Gothic troops. The arrival of the Roman Stilicho and his army forced Alaric to lift his siege and move his army towards Hasta (modern Asti) in western Italy, where Stilicho attacked it at the Battle of Pollentia,[390][391] capturing Alaric's camp. Stilicho offered to return the prisoners in exchange for the Visigoths returning to Illyricum but upon arriving at Verona, Alaric halted his retreat. Stilicho again attacked at the Battle of Verona[392] and again defeated Alaric,[393] forcing him to withdraw from Italy.
In 405 AD, the Ostrogoths invaded Italy itself, but were defeated. However, in 406 AD an unprecedented number of tribes took advantage of the freezing of the Rhine to cross en masse: Vandals, Suevi, Alans and Burgundians swept across the river and met little resistance in the Sack of Moguntiacum and the Sack of Treviri,[394] completely overrunning Gaul. Despite this grave danger, or perhaps because of it, the Roman army continued to be wracked by usurpation, in one of which Stilicho, Rome's foremost defender of the period, was put to death.[395]
It is in this climate that, despite his earlier setback, Alaric returned again in 410 AD and managed to sack Rome.[396][397][398] The Roman capital had by this time moved to the Italian city of Ravenna,[399] but some historians view 410 AD as an alternative date for the true fall of the Roman Empire.[400] Without possession of Rome or many of its former provinces, and increasingly Germanic in nature, the Roman Empire after 410 AD had little in common with the earlier Empire. By 410 AD, Britain had been mostly denuded of Roman troops,[401][402] and by 425 AD was no longer part of the Empire,[387] and much of western Europe was beset "by all kinds of calamities and disasters",[403] coming under barbarian kingdoms ruled by Vandals, Suebians, Visigoths and Burgundians.[404]
| "The fighting became hand-to-hand, fierce, savage, confused and without the slightest respite.... Blood from the bodies of the slain turned a small brook which flowed through the plain into a torrent. Those made desperately thirsty by their injuries drank water so augmented with blood that in their misery it seemed as though they were forced to drink the very blood which had poured from their wounds" |
| Jordanes on the Battle of the Catalaunian Plains[405] |
The remainder of Rome's territory—if not its nature—was defended for several decades following 410 AD largely by Flavius Aëtius, who managed to play off each of Rome's barbarian invaders against one another. In 435 AD he led a Hunnic army against the Visigoths at the Battle of Arles, and again in 436 AD at the Battle of Narbonne. In 451 AD he led a combined army, including his former enemy the Visigoths, against the Huns at the Battle of the Catalaunian Plains,[406][407][408] where Aëtius managed to halt the Hunnic onslaught. However, Concordia, Altinum, Mediolanum,[409] Ticinum,[409] and Patavium were sacked, and the Huns returned a year later. After brutally razing Aquileia, the Huns continued to move towards Rome. It was at this point that Pope Leo I managed to convince Attila to leave.
Despite being the only clear champion of the Empire at this point, Aëtius was slain by the Emperor Valentinian III's own hand 2 years afterwards, leading Sidonius Apollinaris to observe, "I am ignorant, sir, of your motives or provocations; I only know that you have acted like a man who has cut off his right hand with his left".[410]
Carthage, the second largest city in the empire, was lost along with much of North Africa in 439 AD to the Vandals,[411][412] and the fate of Rome seemed sealed. By 476 AD, what remained of the Empire was completely in the hands of federated Germanic troops and when they revolted, led by Odoacer and deposed the Emperor Romulus Augustus[413] there was nobody to stop them. Odoacer happened to hold the part of the Empire around Italy and Rome but other parts of the Empire were ruled by Visigoths, Ostrogoths, Franks, Alans and others. The Empire in the West had fallen,[404][413] and its remnant in Italy was no longer Roman in nature. The Eastern Roman Empire and the Goths continued to fight over Rome and the surrounding area for many years, though by this point Rome's importance was primarily symbolic.
See also
[edit]Citations
[edit]- ^ Trigger, Understanding Early Civilizations, p. 240
- ^ a b Luttwak, The Grand Strategy of the Roman Empire, p. 38
- ^ Goldsmith, An Estimate of the Size and Structure of the National Product of the Early Roman Empire, p. 263
- ^ Johnson, The Dream of Rome, p. 8
- ^ Goldsworthy, In the Name of Rome, p. 15
- ^ Goldsworthy, In the Name of Rome, p. 31
- ^ Goldsworthy, The Punic Wars, p. 96
- ^ Pennell, Ancient Rome, first page of Chapter III.
- ^ Grant, The History of Rome, p. 23
- ^ Pennell, Ancient Rome, Ch. IX, para. 3
- ^ Ronald Syme, following G. M. Hirst, has argued for 64 BC–12 AD. For a presentation on the dates see Livy.
- ^ Florus, Epitome of Roman History, Book 1, ch. 1
- ^ Florus, Epitome of Roman History, Book 1, ch. 2
- ^ a b c Cassius Dio, The Roman History, Vol. 1, VII, 6
- ^ Florus, Epitome of Roman History, Book 1, ch. 3
- ^ Florus, Epitome of Roman History, Book 1, ch. 4
- ^ Pennell, Ancient Rome, Ch. V, para. 1
- ^ Grant, The History of Rome, p. 21
- ^ Livy, The Rise of Rome, p. 13
- ^ Livy, The Rise of Rome, p. 3
- ^ Cassius Dio, The Roman History, Vol. 1, VII, 9; Livy, Ab urbe condita, 1:10–13
- ^ Livy, Ab urbe condita, 1:35
- ^ "The Cholas"" University of Madras"K. A. Nilakanta Sastri
- ^ Livy, Ab urbe condita, 1:38
- ^ Livy, Ab urbe condita, 1.42
- ^ Livy, Ab urbe condita, 1.50–52
- ^ Fasti Triumphales
- ^ Livy Ab urbe condita 1.53–55
- ^ Livy Ab urbe condita 1.55
- ^ Livy, Ab urbe condita, 1.57
- ^ Livy, Ab urbe condita, 1.57–60
- ^ Grant, The History of Rome, p. 33
- ^ a b Florus, Epitome of Roman History, Book 1, ch. 9
- ^ a b Grant, The History of Rome, p. 32
- ^ Livy, Ab urbe condita, 2.6–7
- ^ Livy, Ab urbe condita, 2.9–13
- ^ a b Florus, The Epitome of Roman History, Book 1, ch. 11
- ^ a b Grant, The History of Rome, p. 38
- ^ a b Grant, The History of Rome, p. 37
- ^ Livy, The Rise of Rome, p. 89
- ^ Grant, The History of Rome, p. 41
- ^ a b c Florus, The Epitome of Roman History, Book 1, ch. 12
- ^ Cassius Dio, The Roman History, Vol. 1, VII, 17
- ^ Cassius Dio, The Roman History, Vol. 1, VII, 16
- ^ a b c The Enemies of Rome, p. 13
- ^ Livy, The Rise of Rome, p. 96
- ^ a b Grant, The History of Rome, p. 42
- ^ Cassius Dio, The Roman History, Vol. 1, VII, 20
- ^ Grant, The History of Rome, p. 39
- ^ Pennell, Ancient Rome, Ch. II
- ^ Koepke, Nikola; Baten, Joerg (1 April 2008). "Agricultural specialization and height in ancient and medieval Europe". Explorations in Economic History. 45 (2): 127–146. doi:10.1016/j.eeh.2007.09.003.
- ^ a b c d e f Grant, The History of Rome, p. 44
- ^ a b c d e Florus, The Epitome of Roman History, Book 1, ch. 13
- ^ a b c Pennell, Ancient Rome, Ch. IX, para. 2
- ^ Livy, The Rise of Rome, p. 329
- ^ Lane Fox, The Classical World, p. 283
- ^ Livy, The Rise of Rome, p. 330
- ^ Appian, History of Rome, The Gallic Wars, §1
- ^ Livy, History of Rome, Book 5, Chapter 49.
- ^ Pennell, Ancient Rome, Ch. IX, para. 4
- ^ Pennell, Ancient Rome, Ch. IX, para. 23
- ^ a b c d Florus, The Epitome of Roman history, Book 1, ch. 16
- ^ Lane Fox, The Classical World, p. 282
- ^ Pennell, Ancient Rome, Ch. IX, para. 8
- ^ a b Grant, The History of Rome, p. 48
- ^ a b Pennell, Ancient Rome, Ch. IX, para. 13
- ^ Grant, The History of Rome, p. 49
- ^ Pennell, Ancient Rome, Ch. IX, para. 14
- ^ a b c Grant, The History of Rome, p. 52
- ^ a b Lane Fox, The Classical World, p. 290
- ^ Grant, The History of Rome, p. 53
- ^ Grant, The History of Rome, p. 77
- ^ a b Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 14
- ^ a b c d e f Grant, The History of Rome, p. 78
- ^ Cantor, Antiquity, p. 151
- ^ Pennell, Ancient Rome, Ch. X, para. 6
- ^ a b c d e Florus, The Epitome of Roman history, Book 1, ch. 18
- ^ Lane Fox, The Classical World, p. 304
- ^ a b Lane Fox, The Classical World, p. 305
- ^ a b c Grant, The History of Rome, p. 79
- ^ Cassius Dio, The Roman history, Vol. 1, VIII, 3
- ^ Pennell, Ancient Rome, Ch. X, para. 11
- ^ a b c Lane Fox, The Classical World, p. 306
- ^ Lane Fox, The Classical World, p. 307
- ^ Pennell, Ancient Rome, Ch. XI, para. 1
- ^ a b Grant, The History of Rome, p. 80
- ^ a b Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 16
- ^ Sallust, The Jugurthine War, XIX
- ^ a b c Cantor, Antiquity, p. 152
- ^ Goldsworthy, The Punic Wars, p. 13
- ^ Goldsworthy, The Punic Wars, p. 68
- ^ Cassius Dio, The Roman History, Vol. 1, VIII, 8
- ^ Pennell, Ancient Rome, Ch. XII, para. 14
- ^ Lane Fox, The Classical World, p. 309
- ^ Goldsworthy, The Punic Wars, p. 113
- ^ Goldsworthy, The Punic Wars, p. 84
- ^ Goldsworthy, The Punic Wars, p. 86
- ^ a b Goldsworthy, The Punic Wars, p. 87
- ^ Goldsworthy, The Punic Wars, p. 88
- ^ Lane Fox, The Classical World, p. 310
- ^ Goldsworthy, The Punic Wars, p. 90
- ^ Goldsworthy, The Punic Wars, p. 128
- ^ Florus, The Epitome of Roman history, Book 2, ch. 3
- ^ Florus, The Epitome of Roman history, Book 2, ch. 4
- ^ Goldsworthy, In the Name of Rome, p. 29
- ^ Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 25
- ^ Pennell, Ancient Rome, Ch. XIII, para. 15
- ^ a b c d e Cantor, Antiquity, p. 153
- ^ Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 27
- ^ a b Goldsworthy, In the Name of Rome, p. 30
- ^ Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 29
- ^ Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 31
- ^ Polybius, The Histories, 243
- ^ Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 34
- ^ Polybius, The Histories, 263
- ^ Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 36
- ^ Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 38
- ^ Liddell Hart, Scipio Africanus, p. xiii
- ^ Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 40
- ^ Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 41
- ^ Pennell, Ancient Rome, Ch. XV, para. 24
- ^ Goldsworthy, The Punic Wars, p. 338
- ^ a b Goldsworthy, The Punic Wars, p. 339
- ^ a b Florus, The Epitome of Roman history, Book 2, ch. 15
- ^ a b Cantor, Antiquity, p. 154
- ^ Goldsworthy, The Punic Wars, p. 12
- ^ a b c Florus, The Epitome of Roman history, Book 2, ch. 17
- ^ a b c d Grant, The History of Rome, p. 122
- ^ Pennell, Ancient Rome, Ch. XX, para. 2
- ^ a b Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 54
- ^ Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 56
- ^ a b Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 57
- ^ Pennell, Ancient Rome, Ch. XX, para. 4
- ^ a b Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 58
- ^ Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 61
- ^ Grant, The History of Rome, p. 123
- ^ a b Luttwak, The Grand Strategy of the Roman Empire, p. 8
- ^ a b Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 47
- ^ a b Grant, The History of Rome, p. 115
- ^ a b Grant, The History of Rome, p. 116
- ^ a b Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 48
- ^ Goldsworthy, In the Name of Rome, p. 71
- ^ a b Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 49
- ^ Goldsworthy, In the Name of Rome, p. 72
- ^ a b Goldsworthy, In the Name of Rome, p. 73
- ^ Grant, The History of Rome, p. 117
- ^ a b Lane Fox, The Classical World, p. 325
- ^ a b Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome. p. 51
- ^ Florus, The Epitome of Roman history, Book 2, ch. 9
- ^ Florus, The Epitome of Roman history, Book 2, ch. 10
- ^ Florus, The Epitome of Roman history, Book 2, ch. 13
- ^ Florus, The Epitome of Roman history, Book 2, ch. 16
- ^ Pennell, Ancient Rome, Ch. XVII, para. 1
- ^ a b Grant, The History of Rome, p. 119
- ^ Lane Fox, The Classical World, p. 326
- ^ a b Grant, The History of Rome, p. 120
- ^ a b c Goldsworthy, In the Name of Rome, p. 75
- ^ Goldsworthy, In the Name of Rome, p. 92
- ^ Lane Fox, The Classical World, p. 328
- ^ Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 53
- ^ Luttwak, The Grand Strategy of the Roman Empire, p. 9
- ^ Sallust, The Jugurthine War, V
- ^ Santosuosso, Storming the Heavens, p. 29
- ^ Sallust, The Jugurthine War, XII
- ^ Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 64
- ^ Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 65
- ^ Florus, The Epitome of Roman history, Book 3, ch. 1
- ^ Sallust, The Jugurthine War, XIII
- ^ Sallust, The Jugurthine War, XVIII
- ^ Sallust, The Jugurthine War, LII
- ^ Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 69
- ^ Sallust, The Jugurthine War, LXXVI
- ^ Sallust, The Jugurthine War, XCIV
- ^ Sallust, The Jugurthine War, CI
- ^ Grant, The History of Rome, p. 153
- ^ Sallust, The Jugurthine War, CXIII
- ^ Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 71
- ^ Grant, The History of Rome, p. 152
- ^ a b Appian, History of Rome, §6
- ^ a b c Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 75
- ^ a b Santosuosso, Storming the Heavens, p. 6
- ^ a b c Florus, The Epitome of Roman history, Book 3, ch. 3
- ^ Santosuosso, Storming the Heavens, p. 39
- ^ Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 77
- ^ Appian, Civil Wars, 1, 117
- ^ Santosuosso, Storming the Heavens, p. 43
- ^ Grant, The History of Rome, p. 156
- ^ Lane Fox, The Classical World, p. 351
- ^ a b Cantor, Antiquity, p. 167
- ^ Santosuosso, Storming the Heavens, p. 30
- ^ Grant, The History of Rome, p. 161
- ^ a b c Florus, The Epitome of Roman history, Book 3, ch. 5
- ^ Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 76
- ^ Grant, The History of Rome, p. 158
- ^ a b Lane Fox, The Classical World, p. 363
- ^ a b c d e Plutarch, Lives, Pompey
- ^ a b c Florus, The Epitome of Roman history, Book 3, ch. 6
- ^ Grant, The History of Rome, p. 165
- ^ Holland, Rubicon, p. 170
- ^ Cicero, Pro Lege Manilia, 12 or De Imperio Cn. Pompei (in favour of the Manilian Law on the command of Pompey), 66 BC.
- ^ a b c d e Plutarch, Lives, Caesar
- ^ Santosuosso, Storming the Heavens, p. 58
- ^ a b Goldsworthy, In the Name of Rome, p. 187
- ^ a b Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 117
- ^ Goldsworthy, In the Name of Rome, p. 191
- ^ a b c d e f Florus, The Epitome of Roman history, Book 3, ch.10
- ^ a b c d Cantor, Antiquity, p. 162
- ^ Santosuosso, Storming the Heavens, p. 48
- ^ Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 116
- ^ Santosuosso, Storming the Heavens, p. 59
- ^ Goldsworthy, In the Name of Rome, p. 201
- ^ Santosuosso, Storming the Heavens, p. 60
- ^ Goldsworthy, In the Name of Rome, p. 204
- ^ Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 78
- ^ a b Santosuosso, Storming the Heavens, p. 62
- ^ Goldsworthy, In the Name of Rome, p. 212
- ^ Cantor, Antiquity, p. 168
- ^ Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 133
- ^ Plutarch, Lives of the Noble Grecians and Romans, p. 266
- ^ Goldsworthy, In the Name of Rome, p. 213
- ^ Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 79
- ^ a b Cantor, Antiquity, p. 169
- ^ Goldsworthy, In the Name of Rome, p. 271
- ^ Goldsworthy, In the Name of Rome, p. 214
- ^ a b Goldsworthy, In the Name of Rome, p. 215
- ^ Lane Fox, The Classical World, p. 398
- ^ a b c Holland, Rubicon, p. 299
- ^ a b c d Goldsworthy, In the Name of Rome, p. 216
- ^ Holland, Rubicon, p. 298
- ^ Holland, Rubicon, p. 303
- ^ Lane Fox, The Classical World, p. 402
- ^ Goldsworthy, In the Name of Rome, p. 217
- ^ Julius Caesar, The Civil War, 81–92
- ^ Goldsworthy, In the Name of Rome, p. 218
- ^ Goldsworthy, In the Name of Rome, p. 220
- ^ a b Goldsworthy, In the Name of Rome, p. 227
- ^ Lane Fox, The Classical World, p. 403
- ^ Holland, Rubicon, p. 312
- ^ Lane Fox, The Classical World, p. 404
- ^ Plutarch, Life of Crassus, XXIII–V
- ^ a b c Cantor, Antiquity, p. 170
- ^ Goldsworthy, In the Name of Rome, p. 237
- ^ a b Luttwak, The Grand Strategy of the Roman Empire, p. 7
- ^ Cassius Dio, The Roman History: The Reign of Augustus, p. 61
- ^ a b Goldsworthy, In the Name of Rome, p. 244
- ^ Luttwak, The Grand Strategy of the Roman Empire, p. 37
- ^ Grant, The History of Rome, p. 208
- ^ Goldsworthy, In the Name of Rome, p. 245
- ^ Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 159
- ^ Clunn, In Quest of the Lost Legions, p. xv
- ^ Tacitus, The Annals, Book 1, ch, 56
- ^ a b Tacitus, The Annals, Book 1, ch. 60
- ^ Santosuosso, Storming the Heavens, p. 143–144
- ^ Goldsworthy, In the Name of Rome, p. 248
- ^ Goldsworthy, In the Name of Rome, p. 260
- ^ Churchill, A History of the English Speaking Peoples, p. 1
- ^ Lane Fox, The Classical World, p. 379
- ^ a b Churchill, A History of the English Speaking Peoples, p. 4
- ^ Churchill, A History of the English-Speaking Peoples, p. 5
- ^ Tacitus, Annals 14.29–39, Agricola 14–16
- ^ Dio Cassius, Roman History, 62.1–12
- ^ Churchill, A History of the English-Speaking Peoples, p. 6
- ^ a b Churchill, A History of the English-Speaking Peoples, p. 7
- ^ Welch, Britannia: The Roman Conquest & Occupation of Britain, 1963, p. 107
- ^ Tacitus, Annals, 14.37
- ^ Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 189
- ^ Fraser, The Roman Conquest Of Scotland: The Battle Of Mons Graupius AD 84
- ^ Churchill, A History of the English-Speaking Peoples, p. 9
- ^ Churchill, A History of the English-Speaking Peoples, p. 10
- ^ a b Goldsworthy, In the Name of Rome, p. 269
- ^ Clunn, In Quest of the Lost Legions, p. 303
- ^ Goldsworthy, In the Name of Rome, p. 322
- ^ Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 213
- ^ Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 215
- ^ Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 216
- ^ a b Luttwak, The Grand Strategy of the Roman Empire, p. 53
- ^ a b Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 217
- ^ Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 219
- ^ Luttwak, The Grand Strategy of the Roman Empire, p. 54
- ^ Goldsworthy, In the Name of Rome, p. 329
- ^ Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 222
- ^ Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 223
- ^ Luttwak, The Grand Strategy of the Roman Empire, p. 39
- ^ Tacitus, The Annals, Book 2, ch, 3
- ^ Tacitus, The Histories, Book 1, ch. 41
- ^ Plutarch, Lives, Galba
- ^ a b Luttwak, The Grand Strategy of the Roman Empire, p. 51
- ^ a b Lane Fox, The Classical World, p. 542
- ^ Tacitus, The Histories, Book 1, ch. 57
- ^ a b Plutarch, Lives, Otho
- ^ Tacitus, The Histories, Book 1, ch. 14–15
- ^ Tacitus, The Histories, Book 1, ch. 22
- ^ Tacitus, The Histories, Book 1, ch, 26
- ^ a b c d Luttwak, The Grand Strategy of the Roman Empire, p. 52
- ^ Tacitus, The Histories, Book 1, ch. 44
- ^ Tacitus, The Histories, Book 1, ch. 49
- ^ Tacitus, The Histories, Book 3, ch. 18
- ^ Tacitus, The Histories, Book 3, ch. 25
- ^ Tacitus, The Histories, Book 3, ch. 31
- ^ Lane Fox, The Classical World, p. 543
- ^ Goldsworthy, In the Name of Rome, p. 294
- ^ Millar 1995, p. 70.
- ^ Goodman 1987, p. 9.
- ^ Safrai & Stern 1974, p. 216.
- ^ Cohen 2014, pp. 3–4.
- ^ Price 1992, p. 12.
- ^ Smallwood 1976, p. 284.
- ^ a b c Cohen 2014, p. 4.
- ^ Goodman 1987, pp. 1–2.
- ^ Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 194
- ^ Freyne 2002, p. 47.
- ^ Gabba 1999, p. 152.
- ^ McLaren 2011, p. 141.
- ^ Smallwood 1976, p. 289–291.
- ^ a b Goldsworthy, In the Name of Rome, p. 295
- ^ Price 1992, p. 11.
- ^ a b Millar 1995, p. 71.
- ^ Mason 2016, p. 281.
- ^ Millar 1995, pp. 71–72.
- ^ Smallwood 1976, p. 306.
- ^ Rogers 2022, p. 230.
- ^ Rogers 2022, pp. 258–259.
- ^ Millar 2005, p. 101.
- ^ Goldsworthy, In the Name of Rome, p. 292
- ^ Rogers 2022, p. 368.
- ^ Price 2011, p. 409.
- ^ Davies 2023, pp. 100–101.
- ^ Santosuosso, Storming the Heavens, p. 146
- ^ Luttwak, The Grand Strategy of the Roman Empire, p. 3
- ^ Millar 1995, p. 79.
- ^ Magness 2012, pp. 166–167.
- ^ Goodman 2004, p. 17.
- ^ Millar 2005, pp. 113–114.
- ^ Pucci Ben Zeev 2006, p. 93–94.
- ^ Pucci Ben Zeev 2006, p. 102.
- ^ Pucci Ben Zeev 2006, p. 96–98.
- ^ Pucci Ben Zeev 2006, p. 100–101.
- ^ Schwartz 2004, pp. 79–80.
- ^ Eshel 2006, p. 106.
- ^ Eshel 2006, pp. 123, 126.
- ^ Eshel 2006, pp. 125–127.
- ^ a b c Grant, The History of Rome, p. 273
- ^ Grant, The History of Rome, p. 279
- ^ a b c d Luttwak, The Grand Strategy of the Roman Empire, p. 128
- ^ Luttwak, The Grand Strategy of the Roman Empire, p. 146
- ^ Grant, The History of Rome, p. 282
- ^ Luttwak, The Grand Strategy of the Roman Empire, p. 150
- ^ a b Luttwak, The Grand Strategy of the Roman Empire, p. 147
- ^ a b c Jordanes, The Origins and Deeds of the Goths, 103
- ^ Jordanes, The Origins and Deeds of the Goths, 108
- ^ Gibbon, The Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire, p. 624
- ^ Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 270
- ^ Grant, The History of Rome, p. 322
- ^ Jordanes, The Origins and Deeds of the Goths, 121
- ^ Santosuosso, Storming the Heavens, p. 196
- ^ a b c Grant, The History of Rome, p. 285
- ^ a b Jordanes, The Origins and Deeds of the Goths, 110
- ^ Goldsworthy, In the Name of Rome, p. 344
- ^ Goldsworthy, In the Name of Rome, p. 345
- ^ Ammianus Marcellinus, Historiae, book 31.
- ^ Jordanes, The Origins and Deeds of the Goths, 138.
- ^ Gibbon, The Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire, p. 534
- ^ Grant, The History of Rome, p. 284
- ^ a b Luttwak, The Grand Strategy of the Roman Empire, p. 149
- ^ Grant, The History of Rome, p. 280
- ^ a b Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 226
- ^ Gibbon, The Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire, p. 113
- ^ Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 227
- ^ Gibbon, The Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire, p. 133
- ^ a b Gibbon, The Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire, p. 129
- ^ a b c Gibbon, The Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire, p. 130
- ^ Gibbon, The Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire, p. 131
- ^ Gibbon, The Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire, p. 135
- ^ a b c Grant, The History of Rome, p. 283
- ^ a b Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 234
- ^ a b c Luttwak, The Grand Strategy of the Roman Empire, p. 151
- ^ Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 235
- ^ Shapur, Deeds of the God-Emperor Shapur
- ^ a b c Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 236
- ^ a b Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 237
- ^ a b c Goldsworthy, In the Name of Rome, p. 358
- ^ Procopius, History of the Wars, Book 1, Pt 1, Ch. 2
- ^ Goldsworthy, In the Name of Rome, p. 361
- ^ Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 231
- ^ Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 285
- ^ Jordanes, The Origins and Deeds of the Goths, 147
- ^ a b c Procopius, History of the Wars, Book 3, Pt 1, Ch. 2
- ^ Gibbon, The Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire, p. 551
- ^ Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 260
- ^ Gibbon, The Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire, p. 563
- ^ Jordanes, The Origins and Deeds of the Goths, 154
- ^ Gibbon, The Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire, p. 565
- ^ Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 263
- ^ Grant, The History of Rome, p. 324
- ^ Grant, The History of Rome, p. 327
- ^ Jordanes, The Origins and Deeds of the Goths, 156
- ^ Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 267
- ^ Gibbon, The Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire, p. 589
- ^ Gibbon, The Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire, p. 587
- ^ Wood, In Search of the First Civilizations, p. 177
- ^ Gibbon, The Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire, p. 560
- ^ Churchill, A History of the English-Speaking Peoples, p. 16
- ^ Churchill, A History of the English-Speaking Peoples, p. 17
- ^ a b Santosuosso, Storming the Heavens, p. 187
- ^ Jordanes, History of the Goths, 207
- ^ Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, p. 276
- ^ Gibbon, The Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire, p. 489
- ^ Jordanes, The Origins and Deeds of the Goths, 197
- ^ a b Jordanes, The Origins and Deeds of the Goths, 222
- ^ Gibbon, The Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire, ch. 35
- ^ Gibbon, The Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire, p. 618
- ^ Procopius, History of the Wars, Book 3, Pt 1, Ch. 4
- ^ a b Jordanes, The Origins and Deeds of the Goths, 243
Bibliography
[edit]Primary sources
[edit]- Julius Caesar (1869). . Trans. William Alexander McDevitte and W. S. Bohn. New York: Harper & Brothers – via Wikisource. (print: Penguin Books, 1976, (tr. Jane Mitchell), ISBN 0-14-044187-5)
- Julius Caesar (1869). . Trans. William Alexander McDevitte and W. S. Bohn. New York: Harper & Brothers – via Wikisource.
- Julius Caesar (1869). . Trans. William Alexander McDevitte and W. S. Bohn. New York: Harper & Brothers – via Wikisource.
- Julius Caesar (1869). . Trans. William Alexander McDevitte and W. S. Bohn. New York: Harper & Brothers – via Wikisource.
- Cassius Dio. The Roman History at Project Gutenberg (print: Penguin Books, 1987, ISBN 0-14-044448-3)
- Florus (1889). . Trans. John Selby Watson. London: George Bell & Sons – via Wikisource.
- Livy (1905). . Trans. Canon Roberts – via Wikisource. (print: Book 1 as The Rise of Rome, Oxford University Press, 1998, ISBN 0-19-282296-9)
- Jordanes. The Origin and Deeds of the Goths at Project Gutenberg
- Plutarch. . Trans. John Dryden – via Wikisource. (print: Jacques Amyot and Thomas North (tr.), Plutarch, Lives of the Noble Grecians and Romans, Southern Illinois University Press, 1963, ISBN 0-404-51870-2 )
- Polybius: The Rise of the Roman Empire at LacusCurtius (print: Harvard University Press, 1927. (Translation by W. R. Paton), unknown ISBN
- Procopius. . Trans. Henry Bronson Dewing – via Wikisource.
- Sallust. Conspiracy of Catiline and the Jurgurthine War at Project Gutenberg (print: John Carew Rolfe (tr.), Sallust, Loeb Classical Library, 1940, ISBN 0-674-99128-1 )
- Tacitus (1876). . Trans. Alfred John Church & William Jackson Brodribb. New York: Random House, Inc. – via Wikisource.
- Tacitus (1876). . Trans. Alfred John Church & William Jackson Brodribb. New York: Random House, Inc. – via Wikisource. (print: Penguin Books, 1975, ISBN 0-14-044150-6)
Secondary and tertiary sources
[edit]- John Bagnall Bury: History of the Later Roman Empire at LacusCurtius, 1889
- Cantor, Norman. Antiquity, Perennial Press, 2004, ISBN 0-06-093098-5
- Chaliand, Gérard. (ed.), The Art of War in World History, University of California Press, 1994, ISBN 0-520-07964-7
- Churchill, Winston. A History of the English-Speaking Peoples, Cassell, 1998, ISBN 0-304-34912-7
- Clunn, Tony. In Quest of the Lost Legions, Arminius Publishing, 1999, ISBN 0-9544190-0-6
- Cohen, Shaye J. D. (2014). From Maccabees To Mishnah (3rd ed.). Louisville, Kentucky: Westminster John Knox Press. ISBN 978-0-664-23904-6.
- Davies, Gwyn (2023). "Stamping Out the Embers: Roman "Mopping-Up" Operations at the End of the First Jewish Revolt". In Mizzi, Dennis; Grey, Matthew; Rassalle, Tine (eds.). Pushing Sacred Boundaries in Early Judaism and the Ancient Mediterranean. Supplements to the Journal for the Study of Judaism. Vol. 208. Brill. pp. 100–127. doi:10.1163/9789004540828_005. ISBN 978-9-004-54082-8.
- Ferrill, Arther. The Fall of the Roman Empire: The Military Explanation, Thames and Hudson, 1988, ISBN 0-500-27495-9
- Fraser, James. The Roman Conquest Of Scotland: The Battle Of Mons Graupius AD 84, Tempus Publishing, 2005, ISBN 0-7524-3325-3
- Freyne, Sean (2002). "The Revolt from a regional perspective". In Berlin, Andrea M.; Overman, J. Andrew (eds.). The First Jewish Revolt: Archaeology, History, and Ideology. London and New York: Routledge. pp. 43–55. ISBN 978-0-415-62024-6.
- Gabba, Emilio (1999). "The social, economic and political history of Palestine 63 BCE–CE 70". In Horbury, William; Davies, W. D.; Sturdy, John (eds.). The Early Roman Period. The Cambridge History of Judaism. Vol. 3. Cambridge University Press. pp. 94–167. ISBN 9781139053662.
- Edward Gibbon. The Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire at Project Gutenberg (print: Penguin Books, 1985, ISBN 0-14-043189-6)
- Goldsmith, Raymond W. (8 March 2005). "An Estimate of the Size and Structure of the National Product of the Early Roman Empire". Review of Income and Wealth. 30 (3): 263–288. doi:10.1111/j.1475-4991.1984.tb00552.x.
- Goldsworthy, Adrian (2004). In the Name of Rome: The Men Who Won the Roman Empire. London: Weidenfeld & Nicolson. ISBN 0-297-84666-3.
- Goldsworthy, Adrian (2001). The Punic Wars. London: Cassell Military. ISBN 0-304-35284-5.
- Goldsworthy, Adrian. The Complete Roman Army, Thames and Hudson, 2003, ISBN 0-500-05124-0
- Goodman, Martin (1987). The Ruling Class of Judaea: The Origins of the Jewish Revolt against Rome, A.D. 66–70. Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511552656. ISBN 9780511552656.
- Goodman, Martin (2004). "Trajan and the Origins of Roman Hostility to the Jews". Past & Present (182): 3–29. doi:10.1093/past/182.1.3. JSTOR 3600803 – via JSTOR.
- Grant, Michael (1993). The History of Rome (Revised ed.). London: Faber.
- Hanson, Victor Davis. Carnage and Culture, Hanson Press, 2002, ISBN 0-385-72038-6
- Harkness, Albert. The Military System Of The Romans, University Press of the Pacific, 2004, ISBN 1-4102-1153-3
- Heather, Peter. The Fall of the Roman Empire: A New History, Macmillan Publishers, 2005, ISBN 0-330-49136-9
- Holland, Tom. Rubicon, Little Brown, 2003, ISBN 0-316-86130-8
- Johnson, Boris (2006). The Dream of Rome. HarperPress. ISBN 0-00-722441-9.
- Arnold Hugh Martin Jones, The Later Roman Empire, Johns Hopkins University Press, 1964, ISBN 0-8018-3285-3
- Robin Lane Fox, The Classical World, Penguin Books, 2005, ISBN 0-14-102141-1
- B. H. Liddell Hart, Scipio Africanus, Da Capo Press, 1994, ISBN 0-306-80583-9
- Luttwak, Edward N. (1976). The Grand Strategy of the Roman Empire From the First Century CE to the Third. Baltimore & London: Johns Hopkins University Press.
- Magness, Jodi (2012). The Archaeology of the Holy Land: From the Destruction of Solomon's Temple to the Muslim Conquest. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1-139-01383-3.
- Philip Matyszak, The Enemies of Rome, Thames and Hudson, 2004, ISBN 0-500-25124-X
- Theodor Mommsen. The History of Rome at Project Gutenberg
- Millar, Fergus (1995). The Roman Near East: 31 BC–AD 337. Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-77886-3.
- Millar, Fergus (2005). "Last Year in Jerusalem: Monuments of the Jewish War in Rome". In Edmondson, Jonathan; Mason, Steve; Rives, James (eds.). Flavius Josephus and Flavian Rome. Vol. 3. Oxford University Press. pp. 101–128. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199262120.003.0006. ISBN 978-0-199-26212-0.
- Pennell, Robert Franklin (2004) [1894]. Ancient Rome: From the earliest times down to 476 A. D. (Revised ed.). Boston, Chicago: Allyn and Bacon, Project Gutenberg. Archived from the original on September 24, 2015.
- Rodgers, Nigel. The Roman Army: Legions, Wars and Campaigns: A Military History of the World's First Superpower From the Rise of the Republic and the Might of the Empire to the Fall of the West , Southwater, 2005, ISBN 1-84476-210-6
- Henry William Frederick Saggs, Civilization Before Greece and Rome, Yale University Press, 1989, ISBN 0-300-05031-3
- Antonio Santosuosso, Storming the Heavens: Soldiers, Emperors and Civilians in the Roman Empire, Westview Press, 2001, ISBN 0-8133-3523-X
- Trigger, Bruce G (2003). Understanding Early Civilizations: A Comparative Study. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-82245-9.
- Kerkeslager, Allen (2006). "The Jews in Egypt and Cyrenaica, 66–c. 235 CE". In Katz, Steven T. (ed.). The Late Roman-Rabbinic Period. The Cambridge History of Judaism. Vol. 4th. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-77248-8.
- Eshel, Hanan (2006). "The Bar Kochba Revolt, 132–135". In Katz, Steven T. (ed.). The Late Roman-Rabbinic Period. The Cambridge History of Judaism. Vol. 4th. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-77248-8.
- Horbury, William (1996). "The Beginnings of the Jewish Revolt under Trajan". In Schäfer, Peter (ed.). Geschichte–Tradition–Reflexion: Festschrift für Martin Hengel zum 70 Geburstag. Vol. 1. Tübingen: Cambridge University Press.
- Price, Jonathan (2024). "Historiography in the Time of Stasis: Reflections on the Nationalistic Uprisings in Judea/Palestine". In Czajkowski, Kimberley; Friedman, David A. (eds.). Looking In, Looking Out: Jews and Non-Jews in Mutual Contemplation. Supplements to the Journal for the Study of Judaism. Vol. 212. Leiden and Boston: Brill. pp. 15–37. doi:10.1163/89004685055. ISBN 978-9-004-68503-1.
- Mason, Steve (2016). A History of the Jewish War: AD 66–74. Key Conflicts of Classical Antiquity. Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/CBO9781139020718. ISBN 978-1-139-02071-8.
- McLaren, James S. (2011). "Going to War against Rome: The Motivation of the Jewish Rebels". In Popović, Mladen (ed.). The Jewish Revolt against Rome: Interdisciplinary Perspectives. Brill. pp. 129–153. doi:10.1163/9789004216693_007. ISBN 978-9-004-21668-6.
- Pucci Ben Zeev, Miriam (2006). "The Uprisings in the Jewish Diaspora, 116–117". In Katz, Steven T. (ed.). The Late Roman-Rabbinic Period. The Cambridge History of Judaism. Vol. 4th. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-77248-8.
- Rogers, Guy MacLean (2022). For the Freedom of Zion: The Great Revolt of Jews against Romans, 66–74 CE. Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-300-24813-5.
- Safrai, Samuel; Stern, Menachem (1974). The Jewish People in the First Century. Vol. 1. Brill. ISBN 978-9-004-27500-3.
- Schwartz, Seth (2004). "Historiography on the Jews in the 'Talmudic Period' (70–640 ce)". In Martin, Goodman (ed.). The Oxford Handbook of Jewish Studies. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-199-28032-2.
- Smallwood, E. Mary (1976). "The Jewish Revolt of A.D. 115–117". The Jews under Roman Rule from Pompey to Diocletian. SBL Press. ISBN 978-90-04-50204-8.
- Michael Wood, In Search of the First Civilizations, BBC Books, 1992, ISBN 0-563-52266-6
- George Patrick Welch, Britannia: The Roman Conquest & Occupation of Britain, Hale, 1963, OCLC 676710326


