Cabomba haynesii
| Cabomba haynesii | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Order: | Nymphaeales |
| Family: | Cabombaceae |
| Genus: | Cabomba |
| Species: | C. haynesii
|
| Binomial name | |
| Cabomba haynesii | |
| Synonyms[2] | |
|
Cabomba piauhiensis f. albida Fassett | |
Cabomba haynesii is a species of aquatic plant in the family Cabombaceae native to the Caribbean, Central America, and South America.[2]
Description
[edit]Vegetative characteristics
[edit]Cabomba haynesii is an aquatic, rhizomatous, long-stemmed herb with both submerged and floating leaves.[3] The pilose, green to red stems with red papillae at the nodes[4][5] have two vascular bundles.[4] The dissected, oppositely arranged, petiolate, submerged leaves[3] are 0.5-0.9 cm long, and 1.4-1.8 cm wide. The glabrous petiole is 0.5-0.8 mm long.[6]
Generative characteristics
[edit]The pinkish-purple to white,[7] 1–1.5 cm wide flowers with 1.5-1.8 cm long pedicels[6] float on the water surface, or extend beyond it.[3] The base of the petals is auriculate. The flowers have 3 (5) stamens and (1–) 2 (–3) carpels.[7] The oblong to ovoid seeds are 1.8-2.5 mm long, and 1-2 mm wide.[4]
Taxonomy
[edit]It was first described as Cabomba piauhiensis f. albida Fassett by Norman Carter Fassett in 1953. Later, it was described as the new species Cabomba haynesii Wiersema by John Harry Wiersema in 1989.[8][2][3] The type specimen was collected by J. Steiner, C. von Chong, and H. Kennedy[3][9] in the Chagres River in Gamboa, Panama on the 8th of February 1973.[3]
Hybridisation
[edit]It has been speculated that Cabomba haynesii may be a result of a hybridisation event involving Cabomba palaeformis and Cabomba furcata.[10]
Etymology
[edit]The specific epithet haynesii honours Robert R. Haynes.[3]
Ecology
[edit]Habitat
[edit]In Brazil, it is found in seasonally flooded lagoons,[5] or in temporary or permanent standing bodies of water.[6] It can occur in slightly brackish water.[7]
Conservattion
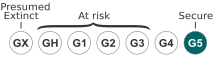
[edit]The NatureServe conservation status is G5 Secure.[1]
References
[edit]- ^ a b Cabomba haynesii. (n.d.). NatureServe. Retrieved November 21, 2024, from https://explorer.natureserve.org/Taxon/ELEMENT_GLOBAL.2.149365/Cabomba_haynesii
- ^ a b c "Cabomba haynesii Wiersema". Plants of the World Online. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. Retrieved 4 October 2024.
- ^ a b c d e f g Wiersema, J. H. (1989). A new species of Cabomba (Cabombaceae) from tropical America. Annals of the Missouri Botanical Garden, 76(4), 1167-1168.
- ^ a b c Pellegrini, M.O.O. Cabombaceae in Flora e Funga do Brasil. Jardim Botânico do Rio de Janeiro. Available at:<https://floradobrasil.jbrj.gov.br/FB34569>. consulta.publica.uc.citacao.acesso.em04 Oct. 2024
- ^ a b Lima, C. T. D., & Gil, A. D. S. B. (2016). Flora das cangas da Serra dos Carajás, Pará, Brasil: Cabombaceae. Rodriguésia, 67, 1273-1276.
- ^ a b c Matias, L. Q., & Nascimento, H. P. D. (2021). Flora of Ceará, Brazil: Cabombaceae. Rodriguésia, 72, e00592019.
- ^ a b c WFO (2024): Cabomba haynesii Wiersema. Published on the Internet;http://www.worldfloraonline.org/taxon/wfo-0000705668. Accessed on: 21 Nov 2024
- ^ Fassett, N. C. (1953). A Monograph of Cabomba. Castanea, 18(4), 116–128. http://www.jstor.org/stable/4031558
- ^ Cabomba haynesii | International Plant Names Index. (n.d.). Retrieved October 4, 2024, from https://www.ipni.org/n/938414-1
- ^ Wilson, C. E., Darbyshire, S. J., & Jones, R. (2007). The biology of invasive alien plants in Canada. 7. Cabomba caroliniana A. Gray. Canadian Journal of Plant Science, 87(3), 615-638.