User:Double sharp/Phosphorus
Forms of phosphorus Waxy white Light red Dark red and violet Black | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phosphorus | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˈfɒsfərəs/ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Allotropes | white, red, violet, black and others (see Allotropes of phosphorus) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | white, red and violet are waxy, black is metallic-looking | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Standard atomic weight Ar°(P) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abundance | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| in the Earth's crust | 5.2 (silicon = 100) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phosphorus in the periodic table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic number (Z) | 15 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group | group 15 (pnictogens) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Period | period 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Block | p-block | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electron configuration | [Ne] 3s2 3p3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrons per shell | 2, 8, 5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phase at STP | solid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point | white: 317.3 K (44.15 °C, 111.5 °F) red: ∼860 K (∼590 °C, ∼1090 °F)[3] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boiling point | white: 553.7 K (280.5 °C, 536.9 °F) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sublimation point | red: ≈689.2–863 K (≈416–590 °C, ≈780.8–1094 °F) violet: 893 K (620 °C, 1148 °F) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density (near r.t.) | white: 1.823 g/cm3 red: ≈2.2–2.34 g/cm3 violet: 2.36 g/cm3 black: 2.69 g/cm3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of fusion | white: 0.66 kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of vaporization | white: 51.9 kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar heat capacity | white: 23.824 J/(mol·K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vapor pressure (white)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
vapor pressure (red)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oxidation states | common: −3, +3, +5 −2,[4] −1,[4] 0,[5] +1,[4][6] +2,[4] +4[4] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electronegativity | Pauling scale: 2.19 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ionization energies |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Covalent radius | 107±3 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Van der Waals radius | 180 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Natural occurrence | primordial | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
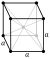
| Crystal structure | α-white: body-centered cubic (bcc) (cI232) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lattice constant | a = 1.869 nm (at 20 °C)[7] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
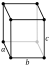
| Crystal structure | black: orthorhombic (oS8) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lattice constants | a = 0.33137 nm b = 1.0477 nm c = 0.43755 nm (at 20 °C)[7] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal conductivity | white: 0.236 W/(m⋅K) black: 12.1 W/(m⋅K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Magnetic ordering | white, red, violet, black: diamagnetic[8] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar magnetic susceptibility | −20.8×10−6 cm3/mol (293 K)[9] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bulk modulus | white: 5 GPa red: 11 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Number | 7723-14-0 (red) 12185-10-3 (white) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discovery | Hennig Brand (1669) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Recognised as an element by | Antoine Lavoisier[10] (1777) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Isotopes of phosphorus | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Phosphorus is a chemical element with symbol P and atomic number 15. It was first isolated by the alchemist Henning Brand in 1669, making it the first element to be discovered chemically.
Phosphorus is the second-lightest member of group 15 on the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. As an element, phosphorus exists in two major forms, white phosphorus and red phosphorus, but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Earth. With a concentration of 0.099%, phosphorus is the most abundant pnictogen in the Earth's crust. With few exceptions, minerals containing phosphorus are in the maximally oxidized state as inorganic phosphate rocks.
The first form of elemental phosphorus that was produced (white phosphorus, in 1669) emits a faint glow when exposed to oxygen – hence the name, taken from Greek mythology, Φωσφόρος meaning "light-bearer" (Latin Lucifer), referring to the "Morning Star", the planet Venus (or Mercury). The term "phosphorescence", meaning glow after illumination, originally derives from this property of phosphorus, although this word has since been used for a different physical process that produces a glow. The glow of phosphorus itself originates from oxidation of the white (but not red) phosphorus — a process now termed chemiluminescence. Together with nitrogen, arsenic, antimony, and bismuth, phosphorus is classified as a pnictogen.
Phosphorus is essential for life. Phosphates (compounds containing the phosphate ion, PO43−) are a component of DNA, RNA, ATP, and phospholipids. Elemental phosphorus was first isolated from human urine, and bone ash was an important early phosphate source. Phosphate mines contain fossils because phosphate is present in the fossilized deposits of animal remains and excreta. Low phosphate levels are an important limit to growth in some aquatic systems. The vast majority of phosphorus compounds produced are consumed as fertilisers. Phosphate is needed to replace the phosphorus that plants remove from the soil, and its annual demand is rising nearly twice as fast as the growth of the human population. Other applications include organophosphorus compounds in detergents, pesticides, and nerve agents.
- ^ "Standard Atomic Weights: Phosphorus". CIAAW. 2013.
- ^ Prohaska, Thomas; Irrgeher, Johanna; Benefield, Jacqueline; Böhlke, John K.; Chesson, Lesley A.; Coplen, Tyler B.; Ding, Tiping; Dunn, Philip J. H.; Gröning, Manfred; Holden, Norman E.; Meijer, Harro A. J. (2022-05-04). "Standard atomic weights of the elements 2021 (IUPAC Technical Report)". Pure and Applied Chemistry. doi:10.1515/pac-2019-0603. ISSN 1365-3075.
- ^ Phosphorus at the Encyclopædia Britannica
- ^ a b c d e Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 28. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ^ Wang, Yuzhong; Xie, Yaoming; Wei, Pingrong; King, R. Bruce; Schaefer, Iii; Schleyer, Paul v. R.; Robinson, Gregory H. (2008). "Carbene-Stabilized Diphosphorus". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 130 (45): 14970–1. doi:10.1021/ja807828t. PMID 18937460.
- ^ Ellis, Bobby D.; MacDonald, Charles L. B. (2006). "Phosphorus(I) Iodide: A Versatile Metathesis Reagent for the Synthesis of Low Oxidation State Phosphorus Compounds". Inorganic Chemistry. 45 (17): 6864–74. doi:10.1021/ic060186o. PMID 16903744.
- ^ a b Arblaster, John W. (2018). Selected Values of the Crystallographic Properties of Elements. Materials Park, Ohio: ASM International. ISBN 978-1-62708-155-9.
- ^ Lide, D. R., ed. (2005). "Magnetic susceptibility of the elements and inorganic compounds". CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (PDF) (86th ed.). Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press. ISBN 0-8493-0486-5.
- ^ Weast, Robert (1984). CRC, Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. Boca Raton, Florida: Chemical Rubber Company Publishing. pp. E110. ISBN 0-8493-0464-4.
- ^ cf. "Memoir on Combustion in General" Mémoires de l'Académie Royale des Sciences 1777, 592–600. from Henry Marshall Leicester and Herbert S. Klickstein, A Source Book in Chemistry 1400–1900 (New York: McGraw Hill, 1952)