Urban planning of Barcelona

The urban planning of Barcelona developed in accordance with the historical and territorial changes of the city, and in line with other defining factors of public space, such as architecture, urban infrastructure and the adaptation and maintenance of natural spaces, parks and gardens.
The urban evolution of Barcelona has been constant since its foundation in Roman times to the present day, although since the nineteenth century it has been accentuated thanks to the Eixample plan and the aggregation of neighboring municipalities. Until the nineteenth century the city was constrained by its medieval walls as it was considered a military square, so its growth was limited. The situation changed with the demolition of the walls and the donation to the city of the fortress of the Citadel, which led to the expansion of the city across the adjacent plain, a fact that was reflected in the Eixample project drawn up by Ildefons Cerdà, which was the largest territorial expansion of Barcelona. Another significant increase in the area of the Catalan capital was the annexation of several municipalities adjoining Barcelona between the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, which led to a Plan of Connections (Spanish: Plan de Enlaces) drawn up in 1903. Subsequently, urban development was marked by the increase in population due to immigration from other parts of Spain, which led to various urban projects such as the Regional Plan of 1953 or the Metropolitan General Plan of 1976. Likewise, the adaptation of the urban space of the city has been favored between the 19th and 21st centuries by various events held in the city, such as the Universal Exposition of 1888, the International Exposition of 1929, the International Eucharistic Congress held in 1952, the 1992 Summer Olympics, the 1992 Summer Paralympics and the Universal Forum of Cultures of 2004.
Urban development in recent years and the commitment to design and innovation, as well as the linking of urban planning with ecological values and sustainability, have made the Catalan capital one of the leading European cities in the field of urban planning, a fact that has been recognized with numerous awards and distinctions, such as the Prince of Wales Award for Urban Planning from Harvard University (1990) and the Royal Gold Medal from the Royal Institute of British Architects (RIBA) in 1999. The work carried out and the awards received have led to talk of a "Barcelona Model" of urban planning, which has served as a guide for numerous cities that have embarked on similar paths.[1]
Geography and location
[edit]
Barcelona, capital and largest city of the autonomous community of Catalonia, is located in the Spanish Levant, on the Mediterranean coast. Its geographical location is between 41°16' and 41°30' north latitude and between 1°54' and 2°18' east longitude.[2] With an area of 102.16 km², it is situated on a plain about 11 km long and 6 km wide, bounded on its sides by the sea and by the Collserola mountain range —with the summit of Tibidabo (516.2 m) as its highest point—, as well as by the deltas of the Besós and Llobregat rivers. Above the coastline and separating the city from the Llobregat delta is the mountain of Montjuïc (184.8 m).[3] Also, from the Collserola mountain range, several hills that follow a line parallel to the coastal range rise up on the plain: the hills of La Peira (133 m), La Rovira (261 m), El Carmel (267 m), Creueta del Coll (249 m), El Putget (181 m) and Monterols (121 m).[4]
The plain of Barcelona is not uniform, but has several undulations caused by the many torrents that once crossed the land, and also has a uniform slope from the sea to the Collserola mountain range, with an ascent of about 260 m.[5] It is crossed by several faults, mainly the one that separates the Collserola mountain range from the hills that come forward in the plain, with a northeast-southwest orientation, and the one that separates the mountain of Montjuic from the coast.[6] The terrain is formed by a substrate of slate and granitic formations, as well as clays and limestones.[7] The coast was formerly occupied by tidal marshes and salt-water lagoons, which disappeared as the coastline advanced thanks to the sediments provided by the rivers and streams that flowed into the beach; it is estimated that since the sixth century BC, the coastline has been able to advance about 5 km.[8] The area of the plain was formerly crossed by numerous torrents and streams, which were grouped into three fluvial sectors: Horta stream in the area near the Besòs river (or eastern area); the Blanca stream and the Gornal torrent in the Llobregat area (or western area); and, in the central area of the plain, a group of streams coming from the southern slope of Tibidabo, such as the Sant Gervasi, Vallcarca, Magòria and Collserola streams.[9]
The climate is Mediterranean, with mild winters thanks to the protection that the orography of the terrain offers to the plain, which is sheltered from the north winds. The temperature usually ranges between 9.5 °C and 24.3 °C, on average. Rainfall is low, about 600 mm per year, and most of the precipitation occurs in spring and autumn. This scarcity meant that in the past numerous works had to be carried out to supply water to the city, including wells, canals and irrigation ditches. The vegetation of the area consists mainly of pines and evergreen oaks, and undergrowth of heather, laurestine, arbutus and climbing plants. In the past, both rainfed and irrigated agriculture was practiced —mainly vineyards and cereals—, although nowadays almost the entire surface area is built up.[10]
Barcelona, capital of the Barcelonès region and of the province of Barcelona, is the most important urban center in Catalonia in demographic, political, economic and cultural terms. It is the seat of the autonomous government and the Parliament of Catalonia, as well as the provincial deputation, the archbishopric and the IV Military Region, and has a port, an airport and an important network of railroads and roads.[11] With a population of 1,604,555 inhabitants in 2015,[12] it is the second most populous city in Spain after Madrid, and the eleventh most populous in the European Union.[13]
Administrative divisions
[edit]
Barcelona is divided into 10 districts and 73 neighborhoods:
- Ciutat Vella (4.49 km², 100 685 inhabitants): corresponds to the old core of the city, the one derived from the Roman and medieval periods, plus the Barceloneta neighborhood, created in the eighteenth century. This area received much immigration from the rest of Spain during the nineteenth and twentieth centuries, settled mainly in the neighborhoods of Sant Pere and Raval; it has continued to do so during the twenty-first century, although with immigrants from other countries. This district has the oldest and lowest socioeconomic level population in the city, although in the new millennium a slow process of gentrification has begun in parallel to the urban development plans carried out in the district. Being the oldest part of the city, it has numerous monuments and architectural works of interest, making it an important focus of tourist attraction. On the other hand, it houses the most important institutions of the city, such as the City Hall or the Generalitat de Catalunya.[14]
- Eixample (7.46 km², 263,565 inhabitants): this district arose from the expansion of the old city after the demolition of the walls, thanks to the Cerdá Plan drawn up by Ildefons Cerdà. It is a densely populated district, since in its beginnings it was mainly a residential area where wealthy families stayed after leaving the old part of the city. The social level, however, has stabilized, and today corresponds mainly to the middle class. Even so, it is an important focus of tourist attraction, especially due to the presence of modernist architectural works, which has encouraged trade and the installation in the area of major commercial brands.[15]
- Sants-Montjuïc (21.35 km², 180,824 inhabitants): includes the old town of Sants, annexed to Barcelona in 1897, together with the land of Montjuïc mountain, which makes it the largest district of the city; it also includes the Zona Franca. It has a low population density, and its rate of population of foreign origin exceeds the average. It has a high percentage of green area, thanks mainly to the presence of the Montjuic mountain, as well as industrial land.[16]
- Les Corts (6.08 km², 81,200 inhabitants): it comes from the old town of Les Corts de Sarrià, added to the city in 1897, with a probable origin in a medieval masia. It was an eminently agricultural area, which in the mid-nineteenth century experienced a significant urban growth with the construction of the area called Corts Noves. The population is mainly autochthonous, and stands out for its high rate of young people. The majority is middle class, although the Pedralbes neighborhood stands out as one of the most exclusive in the city. Its main economic activity is in the tertiary sector, and it is home to numerous financial institutions and office centers.[17]
- Sarrià-Sant Gervasi (20.09 km², 145,761 inhabitants): it comes from the union of two former municipalities, Sarrià and Sant Gervasi de Cassoles. It is one of the largest districts, especially because it includes a large part of the Collserola mountain range. It is also the district with the lowest population density, mainly because it is a high status residential area, with a predominance of single-family houses. The economy is dominated by quality facilities, as well as private schools and health centers. Its population has the highest rate of higher education and technical and managerial professionals, as well as autochthonous residents, while the foreign population is dominated by the European Union.[18]
- Gràcia (4.19 km², 120,273 inhabitants): has its origins in the old village of Gràcia, incorporated into the city in 1897. It was an agricultural area, which in the early nineteenth century began to forge an urban and industrial fabric. It has one of the highest population densities in the city, since its old center is characterized by narrow streets and tightly packed houses. Its population has a high percentage of elderly people and, although the level of education is above average, most are of lower-middle social class.[19]
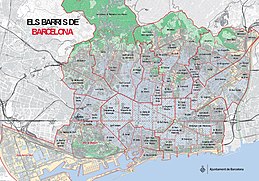
Neighborhoods of Barcelona. - Horta-Guinardó (11.96 km², 166,950 inhabitants): comes from the old town of Horta, added in 1904, to which the Guinardó district, formerly belonging to Sant Martí de Provençals, was added administratively. It was an agricultural area and summer residences, which received numerous immigrants, especially in the first two thirds of the twentieth century. Being a peripheral area, it has a low population density, with a predominance of young and lower-middle class population. During the years of massive immigration, it was an area of strong real estate speculation.[20]
- Nou Barris (8.04 km², 164,516 inhabitants): is the most recently created district, on land segregated from Sant Andreu de Palomar. It is a peripheral area with a majority immigrant population, which also suffered from strong real estate speculation and even suffered from shantyism and self-construction, and which for a long time has suffered from a significant lack of assistance, infrastructure and basic services, which have been mitigated in recent times. The majority of the population is working class and has low purchasing power.[21]
- Sant Andreu (6.56 km², 145,983 inhabitants): corresponds to the former municipality of Sant Andreu de Palomar, annexed in 1897. It was an agricultural and milling area until the mid-nineteenth century, when numerous industries began to settle. On the other hand, in the mid-twentieth century it received a strong wave of immigration, which was received in neighborhoods of cheap houses and residential estates, such as the Bon Pastor and Baró de Viver. In recent times it has experienced a certain revitalization thanks to commercial activities such as the location of the La Maquinista center or the urbanization of the surroundings of La Sagrera Station to accommodate the arrival of the AVE high-speed train.[22]
- Sant Martí (10.80 km², 232,629 inhabitants): it comes from the old town of Sant Martí de Provençals, added in 1897. Like the previous one, it was an agricultural and milling area, until the arrival of the Industrial Revolution when numerous factories were installed in the area; however, in recent decades it has suffered a process of deindustrialization, replaced by economic activities more based on new technologies, especially after the location of the so-called 22@ district. This district also welcomed a large immigrant population. Thanks to the 1992 Olympic Games, it underwent a process of renovation of the entire waterfront, where the Olympic Village was located.[23]
Historical evolution
[edit]
The administrative division has varied over time. The first delimitation was established in 1389, when the city was divided into four quarters: Framenors, Pi, Mar and Sant Pere. This division was made by establishing a grid with the Plaça del Blat as the geometric center, with the separation of the northern and southern quarters set in the ancient Roman cardo maximus. This separation already showed the social difference between the different parts of the city: Framenors was an aristocratic neighborhood, Pi was residential and civil service, Sant Pere was industrial and commercial, and Mar was popular and religious, since it housed most of the convents and monasteries. In the 15th century, another quarter, Raval, was added, establishing a division that lasted until the 18th century.[24]
In 1769 a reform was made by which five quarters were created, each subdivided into eight neighborhoods: I-Palacio included the port and the new neighborhood of Barceloneta; II-San Pedro was an eminently industrial area; III-Audiencia corresponded to the center of the city; IV-Casa de la Ciudad was a mostly residential area; and V-Raval included the land west of La Rambla.[25]
Numerous divisions were made in the 19th century, most of them for political reasons, since the districts also marked the electoral districts. The most notable were those of 1837, in which the city was divided into four districts (Lonja, San Pedro, Universidad and San Pablo); and that of 1878, after the demolition of the walls, in which 10 districts were established: I-La Barceloneta, II-Borne, III-Lonja, IV-Atarazanas, V-Hospital, VI-Audiencia, VII-Instituto, VIII-Universidad, IX-Hostafranchs and X-Concepción.[26]
Between the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, several neighboring municipalities were added to the city (Sants, Les Corts, Sant Gervasi de Cassoles, Gràcia, Sant Andreu de Palomar, Sant Martí de Provençals, Sant Joan d'Horta, Sarrià); a new administrative reorganization was then carried out, again with 10 districts: I-Barceloneta and Pueblo Nuevo, II-San Pedro, III-Lonja and Audiencia, IV-Concepción, V-Atarazanas and Hospital, VI-Universidad, VII-Sans, Las Corts and Hostafranchs, VIII-Gracia and San Gervasio, IX-Horta and Sant Andreu de Palomar, X-Sant Martí de Provençals.[27]
In 1933 a new reformulation was made, also with ten districts: I-Barceloneta, II-Poble Sec and Montjuïc, III-Sarrià, Vallvidrera and Sant Gervasi, IV- Sant Pere and Dreta de l'Eixample, V-Raval, VI-Esquerra de l'Eixample, VII-Sants, Les Corts and Hostafrancs, VIII-Gràcia, IX-Horta, Sant Andreu del Palomar, Sagrera and Camp de l'Arpa, X-Sant Martí de Provençals, Clot and Poblenou. These districts were expanded in 1949 with two more: XI-Les Corts and XII-Sagrada Família.[28]
In 1984 the current division into ten districts was approved, established with the aim of decentralizing the City Council, transferring competencies to the new consistories. The new districts were established with maximum respect for their historical and morphological identity, but also seeking a practical and functional delimitation that would guarantee the residents a wide range of services. In general, an attempt was made to respect the old demarcations coming from the old city, its expansion and the aggregated municipalities, although some areas varied with respect to their historical belonging: Pedralbes, previously belonging to Sarrià, passed to Les Corts; Vallcarca, before Horta, was incorporated to Gràcia; El Guinardó, originally from Sant Martí, was added to Horta; and the new district of Nou Barris was segregated from Sant Andreu.[29]
The last reform was carried out in 2006, this time aimed at establishing the neighborhoods that make up each district, with the objective of improving the distribution of facilities and proximity services.[30] Seventy-three neighborhoods were established, stipulated according to historical, cultural and social criteria, although the decision was not without controversy, mainly due to the fragmentation of some historical neighborhoods defended as units by the neighborhood associations: thus, for example, from the neighborhood of El Clot was segregated El Camp de l'Arpa; from Sants was segregated the neighborhood of Badal; Esquerra de l'Eixample was divided between La Nova and L'Antiga Esquerra de l'Eixample; and Poblenou was fragmented into five neighborhoods. Similarly, some neighborhood units were not satisfied with their aspirations to become neighborhoods, such as Can Caralleu, Penitents, Torre Melina or El Polvorí.
Ancient city
[edit]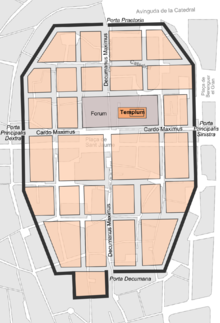
Barcelona was founded by Roman colonizers in the first century BC with the name of Barcino.[note 1] Originally, it was a small walled city which took the urban form of castrum initially, and later oppidum, seated on the Mons Taber (16.9 meters above sea level), a small hill located on the site of the current Plaça de Sant Jaume. The maximum splendor of the Roman period took place during the second century, with a population that must have ranged between 3500 and 5000 inhabitants.[31]
The main reason for the choice of a small promontory near the coast to build the city was its natural harbor, although the alluvium of the torrents and the sedimentation of sand from the coastal currents would make the port's draught difficult.[32] The center of the city was the forum, the central square dedicated to public life and business. It was located at the confluence of the cardus maximus (Llibreteria and Call streets) and the decumanus maximus (Bisbe, Ciutat and Regomir streets), approximately in the center of the walled enclosure.[33] From this center, the city followed an orthogonal layout, with square or rectangular blocks, following a grid layout based on two main axes: a horizontal axial order (northwest-southwest) and a vertical one (southeast-northeast), which would mark the future layout of the city, and would be collected by Ildefonso Cerdá in his Plan de Eixample of 1859.[34]
The Romans were great experts in architecture and civil engineering, and provided the territory with roads, bridges, aqueducts and an urban design with a rational layout and basic services, such as sewerage.[35] The enclosure of Barcino was walled, with a perimeter of 1.5 km, which protected a space of 10.4 ha.[36] The first wall of the city, of simple construction, began to be built in the first century B.C. It had few towers, only in the corners and at the gates of the walled perimeter. However, the first incursions by Franks and Alemanni from the 250s onwards made it necessary to reinforce the walls, which were enlarged in the 4th century. The new wall was built on the foundations of the first, and consisted of a double wall of 2 meters, with a space in the middle filled with stone and mortar. The wall consisted of 74 towers about 18 meters high, most of which were rectangular in base.[37]
Of the rest of the urban elements preserved from the Roman period, it is worth mentioning the necropolis, a group of tombs located outside the walled area, in the current Plaça de la Vila de Madrid: it has more than 70 tombs from the second and third centuries, discovered by chance in 1954.[38] There are also remains of two aqueducts that carried water to the city, one of them from the Collserola mountain range, to the northwest, and another from the north, taking water from the Besós river; both joined in front of the decuman gate of the city —currently the Plaça Nova—.[39]
After the fall of the Roman Empire and until the formation of the Catalan counties, there were several conquests and the passage of successive civilizations, from the Visigoths and Arabs to a period of integration into the Carolingian Empire. This period was marked by the reuse of the Roman city and the use of its urban structure, which did not undergo significant changes. A noteworthy aspect of this period is its consideration as a military stronghold, which will lead it to acquire hegemony over other surrounding cities and become the capital of its territory.[40] The colonization of the surrounding countryside also began at this time, within a system of feudal structure, as well as a certain suburbanization began, with the appearance of the first suburbs.[41]
Middle Ages
[edit]
At this time Barcelona was constituted as a county and later became part of the Crown of Aragon and the political and economic center of the Principality of Catalonia, becoming an important maritime and commercial axis of the Mediterranean Sea. The city grew from the primitive urban core —what is now the Gothic Quarter— and, in the 14th century, the Raval district emerged. Barcelona had about 25,000 inhabitants at that time.[42]
Medieval Barcelona arose from the reconstruction of the city after its near destruction by Almanzor in 985, starting again as the main nucleus of the structure and the wall from Roman times.[43] The city underwent numerous changes as a center of political and religious power, a center of trade and craft production, and as the nexus of a new and complex network of social and institutional relations. Thus, the city acquired an autonomy of its own, a singularity within the surrounding territory, becoming the center of a hinterland that would mark the organization of the modern city.[44]
The progressive increase in the size of the city, and its increasing urban, social and economic complexity, led to the creation of a specific system of government for the administration of the city, the Council of One Hundred (1265). This entity operated in a field of action that went from Montcada to Molins de Rei, and from Castelldefels to Montgat. Among other things, it was responsible for the supply of food and water, the maintenance of roads, the census of the population and territorial demarcation. It also established the first urban building patterns, known as Consuetuds de Santacilia and promulgated by James I.[45]

During medieval times Barcelona had a Jewish quarter, the Call, located between the current streets of Ferran, Banys Nous, Palla and Bisbe. Founded in 692, it survived until its destruction in 1391 in a xenophobic assault. It was separated from the rest of the city by a wall, and had two synagogues (Mayor, now a museum, and Menor, now the parish church of Sant Jaume), baths, schools and hospitals.[46]
Outside the city walls, the plain of Barcelona was devoted to agriculture, especially dedicated to supplying the city: it was known as the hort i vinyet de Barcelona ("orchard and vineyard"), which produced fruit, vegetables and wine, in an area between the streams of Horta and Sants, and between the Collserola mountain range, Puig Aguilar and Coll de Codines to the sea.[47] This agricultural development was consolidated with the construction, in the middle of the 10th century —and probably by Count Miró— of two canals that directed the waters of the Llobregat and Besòs rivers to the vicinity of the city: the Besòs canal was known as Rec Comtal or Regomir, and was parallel to the Strata Francisca, a road that was a variant of the ancient Roman Via Augusta, and was built by the Franks to better bring the city closer to the center of the Carolingian Empire.[48]
Once the danger of Muslim incursions was over, the first settlements outside the city walls were established. Various population centers (vila nova) were created, generally around churches and monasteries: this was the case around the church of Santa Maria del Mar, where a neighborhood of port character was created; likewise around the church of Sant Cugat del Rec, of an agrarian character; the neighborhood of Sant Pere around Sant Pere de les Puelles; the neighborhood of El Pi arose around the church of Santa Maria del Pi; that of Santa Anna next to the church of the same name; the neighborhood of Arcs settled around the Portal del Bisbe; and the Mercadal, around the market of Portal Major. The Raval neighborhood (Catalan for "suburb"), initially a suburb populated by orchards and some religious buildings, such as the monastery of Sant Pau del Camp (914), the church of Sant Antoni Abat (1157), the convent of the Carmelites Calçats (1292), the priory of Nazareth (1342) or the monastery of Montalegre (1362), was also formed little by little.[49]

The creation of these new neighborhoods made it necessary to extend the walled perimeter, so in 1260 a new wall was built from Sant Pere de les Puelles to the Drassanes, facing the sea. The new section was 5100 m long and covered an area of 1.5 km². The enclosure had eighty towers and eight new gates, among which were several enclaves of relevance today, such as the Portal de l'Àngel, the Portaferrissa or La Boqueria.[50] A network of fortifications was also built in the urban periphery for the defense of the city, such as the castle of the Port, in Montjuïc; those of Martorell and Castellví de Rosanes, at the entrance of the Llobregat river; those of Eramprunyà (Gavà) and Castelldefels in the delta of the same river; and that of Montcada at the entrance of the Besòs river.[51]
The medieval urban fabric was marked by different areas of influence, from the aristocracy and institutional power, through the bishopric and religious orders, to the guilds and the various trade associations. The network of streets was irregular, and the squares were mere widenings of the streets, or plots of land derived from the demolition of a house, which were usually used to store wheat, wool or coal. The houses were usually of the "artisan type", with a first floor for the workshop and one or two floors for living, generally measuring 4 m wide and 10–12 m deep, sometimes with a small vegetable garden at the back. The larger buildings were either churches or palaces, along with some institutional buildings, such as the Casa de la Ciutat, seat of the Consell de Cent —later City Hall— or the Palau de la Generalitat de Catalunya, seat of the homonymous political institution of the Principality, as well as a hospital —such as the Santa Creu— or buildings such as the Llotja or the Drassanes.[52]

In 1209, one of the first private urban planning operations in the city took place, the opening of Montcada street, thanks to the concession made by Peter II to Guillem Ramon de Montcada; a wide, straight street was laid out, running from the Bòria to the sea, and was occupied by large stately residences.[53] Another of the few urban planning processes of this period was the opening of the Plaça Nova, next to the Episcopal Palace and near the cathedral of Barcelona, carried out in 1355 thanks to the demolition of several houses and the reuse of the Bishop's orchard.[54]
Between the 14th and 15th centuries, the continuous urban growth led to a new extension of the walled enclosure, with the construction of the Raval wall, in the western part of the city, which covered an area of 218 ha, with a perimeter of 6 km. The new urban enclosure started at the Drassanes, following the current ring roads of Sant Pau, Sant Antoni, Universitat and Sant Pere, going down the current Passeig de Lluís Companys to the monastery of Santa Clara —in the current Citadel Park—, and to the sea, along the current Avinguda Marquès del l'Argentera. Currently only the Portal de Santa Madrona, in the Drassanes, is still preserved.[55]
With the extension of the wall, a long avenue known as La Rambla, occupied mainly by religious institutions, was left within the city walls. It was then proceeded to its urbanization, which was completed in 1444. In its day it was the widest space in the city, dedicated to strolling, leisure or the installation of occasional markets. Deeply reformed between the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries, today it is one of the most emblematic places of the city.[56]
Finally, it is worth noting that during the Middle Ages an extensive network of roads emerged in the plain of Barcelona that connected the city with the various suburbs and villages in the vicinity, as well as other points of interest: farmhouses (Melina tower road), mills (Verneda road), quarries (Creu dels Molers road), bleaching meadows (Teulat road), churches or chapels (Sant Llàtzer road), fountains (Font dels Ocellets road), etc.[57]
Early Modern Age
[edit]
In this period Barcelona and Catalonia became part of the Hispanic Monarchy, which arose from the dynastic union of the crowns of Castile and Aragon. It was a time of alternation between periods of prosperity and economic crisis, especially due to plague epidemics in the sixteenth century and social and military conflicts such as the Reapers' War and the War of Succession between the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries, although in the latter century the economy rebounded thanks to the opening of trade with America and the beginning of the textile industry. The city was still confined within its walls —the only expansion was on the beach, in the neighborhood of La Barceloneta— despite the fact that by the end of the period it had almost 100,000 inhabitants.[42]
This period was not one of excessive urban reforms, since the loss of Barcelona's capital status meant that large-scale projects were not carried out. In the first half of the 16th century, the sea wall was built, where the bastions of Llevant, Torre Nova, Sant Ramon and Migdia were placed.[58] Otherwise, the main urban reform was in the area around the cathedral, where the Plaça de la Seu was opened, in front of the main portal of the cathedral (1546), as well as the Plaça de San Iu, with a space cut out of the Grand Royal Palace.[59]

During the 15th and 16th centuries, an artificial port was built to finally meet the needs of the important mercantile center that was Barcelona: paradoxically, during the period of splendor of Catalan trade in the Mediterranean, Barcelona did not have a port prepared for the port volume that was common in the city. The old port at the foot of Montjuïc had been abandoned, and the city had only the beach to receive passengers and goods. Deep-draught ships had to unload by means of boats and rope lads (bastaixos). Finally, in 1438, royal permission was obtained to build a port: first, a ship loaded with stones was sunk to serve as a base for the wall that connected the beach to the island of Maians; the wall was reinforced in 1477 and lengthened in the form of a breakwater in 1484. In the mid-16th century, the port was enlarged in response to the campaign launched by Charles I against Tunisia. At the end of the century, the quay had a length of 180 m by 12 m wide.[60]
With the construction of the port, the seafront between Pla de Palau and La Rambla was embanked, thus urbanizing the Passeig del Mar, now Passeig de Colom.[61] At this time the water supply and sewage system was also improved, and for its maintenance the figure of the mestre de les fonts ("master of the fountains") was instituted, in charge of the care of mines, fountains and gutters.[62]
In the 17th century, the city wall was extended again with the construction of five new gates (Sant Sever, Tallers, Sant Antoni, Sant Pau and Santa Madrona, the latter a reconstruction of the 14th century one). Streets were also paved, sewers were installed, drinking water fountains were built and improvement works were carried out in the port.[63]

In the eighteenth century the Principality of Catalonia and Barcelona itself saw much of its autonomy truncated with the victory of Philip V in the War of Succession: the Nueva Planta Decree (1716) eliminated the Generalitat, the Corts and the Consell de Cent, which were replaced by a military government, and the municipal jurisdiction was reduced to the city, losing the area of influence that the Consell de Cent had in the metropolitan area. In this period there was a notable demographic increase, and the economy was progressively industrialized, until it led to the so-called Industrial Revolution.[64]

The arrival of the Bourbons generated a series of military engineering works, such as the castle of Montjuïc and the fortress of the Citadel.[65] For the construction of the Citadel (1715-1751), 1200 houses in the Ribera neighborhood were demolished, leaving 4500 people homeless and without compensation, and the Rec Comtal was diverted.[66] The work of Jorge Próspero de Verboom, it was a pentagonal walled bastion, with a protective moat and an esplanade of 120 m between the walls and the surrounding buildings. Demolished in the Revolution of 1868, on its perimeter was installed the park of the Citadel.[67]
There were also two new military roads that crossed the plain of Barcelona: the Mataró road —coincident with the current Pere IV street— and the Creu Coberta road, which connected with the Madrid road —current streets of Hostafrancs and Sants—.[57]
In 1753, the construction of the neighborhood of La Barceloneta began at the initiative of the Marquis of La Mina. Located on a small peninsula of land reclaimed from the sea, its layout was designed by the engineer Pedro Martín Cermeño, with a grid of orthogonal streets and blocks of houses of elongated plan, which is a clear example of academic baroque urbanism.[68] In this neighborhood was located in 1772 the Clock Tower, the first lighthouse of the city; it was followed by the Llobregat in 1845 and Montjuïc in 1925.[69]
In 1771, the Edicto de obreria was approved, a municipal ordinance aimed at controlling private works in the city, which involved the regulation of the alignment of houses according to the layout of the streets, as well as the supervision of aspects such as the paving of the streets, the sewage system, the numbering of houses, etc. This edict established for the first time the obligation to request a building permit, accompanied by a report and the payment of the respective fees. Likewise, in 1797 a height limit was established for all buildings.[70] During this century there was a change in the typology of private buildings, which went from the "artisan house" of the medieval type to the "multi-family house" with a collective staircase, which definitively separated work from residence.[71]

Between 1776 and 1778 the redevelopment of La Rambla was carried out, an ancient torrent that during the Middle Ages marked the western boundary of the city, which had been populated since the 16th century, mainly by theaters and convents. At this time the inner wall was demolished, the buildings were realigned and a new landscaped promenade, in the style of the French boulevard, was designed.[72] The paseos of Sant Joan and Gràcia were also planned, although they were not built until the turn of the century for the former and 1820-1827 for the latter.[73] Likewise, the street of the Count of the Assault —currently New Street of La Rambla— (1778-1789) was laid out, named after Francisco González de Bassecourt, captain general of Catalonia, who had the initiative to create the street.[74] In 1797 the Paseo Nuevo or Paseo de la Explanada was also created, located next to the military Citadel, a wide avenue lined with poplars and elms and decorated with ornamental fountains, which for a time was the main green space of the city, but disappeared in the urbanization works of the park of the Citadel.[75]
During the eighteenth century, the Born and Boqueria markets were established as the only two general supply markets, and in 1752 aspects such as weights and measures for the marketing of food products, in addition to coal, were regulated.[76]
19th Century
[edit]
In this period there was a great economic revitalization, linked primarily to the textile industry, which in turn led to a Catalan cultural renaissance. Between 1854 and 1859, the city walls were demolished, allowing the city to expand, under a project called the Eixample, drawn up by Ildefons Cerdà in 1859. After the revolution of 1868, the Citadel was also demolished and the land transformed into a public park. The population grew, especially thanks to immigration from the rest of Spain, reaching 400,000 inhabitants by the end of the century.[77]
Although chintz printing was well established in Barcelona since the 18th century, the industrial era proper began with the founding in 1832 of the Bonaplata Factory, founded by Josep Bonaplata. In 1849 the complex La España Industrial, owned by the Muntadas brothers, was opened in Sants. The textile industry grew steadily until a crisis in 1861, caused by the shortage of cotton due to the American Civil War. The metallurgical industry was also gaining importance, boosted by the creation of the railroad and steam navigation. In 1836 the Nueva Vulcano foundry opened in La Barceloneta and, in 1841, La Barcelonesa began, one of the predecessors of La Maquinista Terrestre y Marítima (1855), one of the most important factories in the history of Barcelona.[78]
Industrialization brought about important changes in the urban planning of the city, due to the new needs of the economic sectors of the capitalist system, which required a strong concentration of labor and auxiliary services. Barcelona thus underwent an important leap to modernity, characterized by three factors: the population migration from the countryside to the city, the link between industrial and urban developments, and a better articulation of the territory through a wide network of roads and railroads, which will lead Barcelona to become a colonizing metropolis of its territorial environment.[79]

During this century, the municipal ordinances that began with the Edicto de obrería (Workmen's Edict) were consolidated: in 1814, the Pregón de policía urbana (Proclamation of Urban Police) established in 84 articles all the provisions on civil building, maintenance of public spaces and various regulations on security and public order. In 1839, the Bando general de buen gobierno (General Good Governance Charter) renewed and expanded these provisions and, among other things, regulated the relationship between the width of streets and the height of buildings. On the other hand, the law of 8 January 1845 established the City Council's own attributions in various aspects such as urban planning, regulating the sanitary conditions of public spaces, as well as the conditioning of streets, squares and markets.[80] In 1856 the first Ordenanzas Municipales (Municipal Ordinances) were approved, which brought together and expanded previous provisions, within an urban code that contemplated for the first time all aspects of civic and institutional relations in the city. For the first time, building permits were required to include an interior layout plan. These ordinances soon became obsolete due to the new Eixample plan, until in 1891 new ones were drawn up that took into account the new specificities of the expansion and new links in the city. Among other things, the area of occupation of the plots was increased from 50% —established in the Cerdà Plan of 1859— to 70%.[81]
Among the main urban planning actions of these years were the opening of Calle de Fernando (Ferran) in 1827, between La Rambla and the Plaza de San Jaime (Sant Jaume), with a later continuation towards the Borne with the streets of Jaime I (Jaume I) (1849–53) and Princesa (1853).[82] In 1833 the expansion of the Pla de Palau began, which was then the nerve center of the city, with the presence of the Royal Palace, the Llotja and the Aduana. The square was enlarged and the Portal de Mar was built (1844-1848), a monumental gateway to Barceloneta from the old quarter, the work of Josep Massanès, which was demolished in 1859 along with the city walls.[83] Massanès was also the author of a widening plan in 1838 that was never completed, which included the triangle between Canaletes, Plaça de la Universitat and Plaça Urquinaona, and which already sketched what would become Plaça de Catalunya, located in the center of the triangle.[84]

Another factor that favored the urban planning of these years was the confiscation of 1836, which left numerous plots of land that were built on or converted into public spaces, such as La Boqueria and Santa Catalina markets, the Gran Teatro del Liceo (Liceu) and two squares designed by Francesc Daniel Molina i Casamajó: the Plaça Reial and the Plaça del Duc de Medinaceli.[note 2]
Similarly, the new sanitary provisions enacted at this time led to the disappearance of numerous parish cemeteries, whose plots were developed as new public squares: thus, squares such as Santa Maria, del Pi, Sant Josep Oriol, Sant Felip Neri, Sant Just, Sant Pere and San Jaime (Sant Jaume) came into being.[85] The latter became the political heart of the city, since the Barcelona City Council and the Generalitat de Catalunya were located there.[86] On the other hand, the disappearance of the parish cemeteries led to the creation of a new cemetery located outside the city, the cemetery of the East or Pueblo Nuevo (Poblenou), based on a project of 1773 but which was built mainly between 1813 and 1819. It was followed in 1883 by the Southwest or Montjuic cemetery, while already in the 20th century, the North or Collserola cemetery was built (1969).[87]
In 1842, one of the clearest factors of modernity derived from new scientific advances, the gas lighting, began. The first illuminated streets were La Rambla, Fernando Street and the Plaza de San Jaime, specifically with gas produced by dry distillation of black coal (town gas). That year the Sociedad Catalana para el Alumbrado por Gas (Catalan Society for Gas Lighting) was created, renamed in 1912 as Catalana de Gas y Electricidad. In 1856, gas was successfully applied to domestic stoves and heaters.[88]

One of the major factors in the dynamization of the city as the capital of a large metropolitan area was the arrival of the railroad: in 1848, the first railroad line in peninsular Spain left from Barcelona, connecting Barcelona with the town of Mataró. The stations of Francia (1854), Sants (1854) and Norte (1862) were then created. The Catalan capital became the center of a railway network in the shape of an 8 —the so-called "Catalan eight"— formed by two rings that intersected in the city. In the 1880s there were already links with France, Madrid, Zaragoza and Valencia, in addition to the rest of the Catalan provincial capitals. Two companies operated at that time: Ferrocarril del Norte and MZA (Madrid-Zaragoza-Alicante), integrated in 1941 in RENFE.[89]
The city's first fire and police services also appeared at this time. In 1843 the Guardia Urbana de Barcelona was created, in charge of the defense of public safety; in 1938 they also assumed control of traffic and urban circulation.[90] On the other hand, in 1849 the Sociedad de Socorro Mutuo contra Incendios (Mutual Fire Aid Society) emerged, a private company that in 1865 was replaced by the Sociedad de Extinción de Incendios y Salvamento de Barcelona (Barcelona 's Fire Extinguishing and Rescue Company), he first public fire department managed by the City Council. Its first chief was the architect Antoni Rovira i Trias, and its first firehouse was the Casa de Comunes Depósitos (House of Common Warehousess) which was followed by multiple firehouses throughout the city. In 1908, animal-drawn vehicles were replaced by motor vehicles, and in 1913 the figure of the firefighter, until then casual, was professionalized.[91]

In the middle of the century, the Diputation of Barcelona took charge of establishing new road layouts in the Barcelona plain: the Sarrià road (now Sarrià Avenue), designed by Ildefons Cerdà and built between 1850 and 1853; the road from Sants to Les Corts (1865-1867); and the road from Sagrera to Horta (1871), now Garcilaso Street.[57] In these years, the port, increasingly important as a source of raw materials —especially cotton and coal—, was improved with the construction of a new wharf and the dredging of the port by the engineer José Rafo, who presented his project in 1859.[92]
On the other hand, in 1855 the telegraph service began, with a network of radial character centered in Madrid, which from 1920 was extended peripherally with Valencia, Seville and A Coruña. Controlled by the State, the service was incorporated into the postal service, creating the Dirección General de Correos y Telégrafos (General Directorate of Posts and Telegraphs).[93]
It should also be noted that the first public parks appeared in the nineteenth century, as the increase in urban environments due to the phenomenon of the Industrial Revolution, often in conditions of environmental degradation, made it advisable to create large urban parks and gardens, which were paid for by the public authorities, thus giving rise to public gardening —until then preferably private— and landscape architecture.[94] The first public garden in Barcelona was created in 1816: the General's Garden, an initiative of Captain General Francisco Javier Castaños; it was located between the present Marqués de la Argentera avenue and the Citadel, in front of where today is the station of Francia, and had an area of 0.4 ha, until it disappeared in 1877 during the development of the park of the Citadel.[95] At this time several gardens were installed on Passeig de Gràcia: in 1848 the Tívoli Gardens were created, between Valencia and Consell de Cent streets; and in 1853 the so-called Jardín de los Campos Elíseos, with a garden, a lake with boats, a theater and an amusement park with roller coasters, were located between Aragon and Roussillon streets. These gardens disappeared a few years later with the urbanization of Passeig de Gràcia.[96]
Expansion of Barcelona (Example)
[edit]
In the middle of the century a transcendental event took place that completely changed the physiognomy of the city; the demolition of the walls. During the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries, the population grew steadily (from 34,000 inhabitants at the beginning of the eighteenth century to 160,000 in the mid-nineteenth century), which led to an alarming increase in population density (850 inhabitants per hectare), endangering the health of the citizens. However, due to its status as a stronghold, the central government opposed the demolition of the walls. A strong popular outcry began, led by Pedro Felipe Monlau, who in 1841 published the memoir ¡Abajo las murallas! (Down with the walls!) in which he defended their destruction to prevent diseases and epidemics. Finally, in 1854, permission was granted for their demolition, which gave the way out for the territorial expansion of the city.[97]
In 1859 the City Council appointed a commission to promote a competition for urban expansion projects, which was won by Antoni Rovira i Trias; however, the Ministry of Development intervened and imposed the project of Ildefons Cerdà, author of a topographic plan of the Barcelona plan and a demographic and urbanistic study of the city (1855). The Cerdà Plan (Plan de los alrededores de la ciudad de Barcelona y del proyecto para su mejora y ampliación, 1859) instituted an orthogonal layout between Montjuic and the Besòs, with a system of straight northwest-southeast oriented streets, 20 meters wide, cut by other southwest-northeast oriented streets parallel to the coast and the Collserola mountain range. Cerdà had planned to build on only two sides and leave the other spaces for gardens, although this point was not fulfilled and finally practically all the buildable land was used; the buildings were designed with an octagonal floor plan characteristic of the Eixample, with chamfers that favored circulation.[98] The plan called for the construction of several main avenues: Diagonal, Meridiana, Paral·lel, Gran Via and Passeig de Sant Joan, as well as several large squares at their intersections: Tetuan, Glòries, Espanya, Verdaguer, Letamendi and Universitat. It also foresaw the opening of three large avenues in the old part of the city: two that would connect the Eixample with the coast (Muntaner and Pau Claris) and another perpendicular one that would connect the Citadel with Montjuic (avenida de la Catedral).[99] It also contemplated a series of new ring roads that would circumvent the old city, in the place left by the walls: the ring roads of San Pablo, San Antonio, Universitat and Sant Pere.[100]

Cerdá's project was quite innovative for the time, especially with regard to the delimitation of green spaces and service areas, taking into account both functional, recreational and welfare aspects. The buildings were to have a height of 16 meters (first floor and four floors), and a depth of 10 to 20 meters. The distribution of the Eixample was to be in sectors of 20 x 20 blocks, divided into districts of 10 x 10 and neighborhoods of 5 x 5. Each neighborhood was to have a church, a civic center, a school, a day care center, a nursing home and other welfare centers, while each district was to have a market and each sector a park. It also had industrial and administrative facilities, and in the suburbs there was a slaughterhouse, a cemetery and three hospitals. However, most of these provisions did not come to fruition, due to the opposition of the City Council, annoyed by the imposition of Cerdà's plan as opposed to Rovira's, which had been approved in the competition, and also due to real estate speculation, which led to building the blocks on all sides and not only on the two sides planned by Cerdá.[101]
Cerdá accompanied his project with several memoirs and statistical studies in which he showed his urbanistic theory, developed in three main points: hygienism, based on his Monografía estadística de la clase obrera (Statistical monograph of the working class), where he criticizes the living conditions within the walled city in force until then —life expectancy was 38.3 years for the rich and 19.7 for the poor—, against which he proposes improvements in urban orientation according to factors such as climatology, as well as in the constructive elements; circulation, with a view to making public roads compatible between pedestrians and vehicular traffic, which led him to regulate the distribution of streets and to establish chamfers on all sides of the blocks to facilitate crossings; and the multipurpose design, with an urban layout that would be extrapolated both to spaces to be built and to those already existing, integrating the notions of "widening" and "reform", and that would give a hygienic and functional city, although this part of his project would not be carried out.[102]
It must be taken into account that in many cases the Cerdà plot was superimposed on suburban layouts already existing or under development, in addition to the fact that the towns bordering the city of Barcelona, which would be added in successive phases at the turn of the nineteenth century, had their own urban development projects. Among these layouts we must take into account the highways and rural roads, or the easements imposed by railroads, canals, irrigation ditches, torrents and other land features.[103]
A tangential aspect of the new layout was the question of toponymy, since the new urban grid designed by Cerdá included a series of new streets for which there was no tradition when it came to naming them. The naming of the new streets was entrusted to the writer Víctor Balaguer, who was inspired by the history of Catalonia: Thus, many streets are named after territories linked to the Crown of Aragon, such as Valencia, Mallorca, Aragon, Provence, Roussillon, Naples, Corsica, Sicily or Sardinia; with institutions such as the Catalan Courts, the Generalitat or the Consell de Cent; with characters such as Jaime Balmes, Enrique Granados, Buenaventura Carlos Aribau, Ramón Muntaner, Rafael Casanova, Pau Claris, Roger de Flor, Antoni de Villarroel, Roger de Lauria, Ausiàs March or the Count of Urgel; or battles and historical events such as Bailén, Lepanto, El Bruch or Caspe.[104]
- Projects of Expansion (Eixample)
-
Project by Francesc Soler i Glòria.
-
Project by Josep Fontserè i Mestre.
-
Project by Miquel Garriga i Roca
-
Project by Antoni Rovira i Trias.
Interior renovations
[edit]
The Cerdà Plan was developed mainly outside the city walls, due to real estate speculation, leaving aside the necessary improvements for the development of the old part of Barcelona. The need for a project of "interior renovations" was then raised, with the aim of modernizing the old core of the expanding city. One of the first was that of Miquel Garriga i Roca, author of a joint plan of alignments (1862), the first exhaustive plan of the city, at 1/250 scale. Garriga's project foresaw the realignment of streets as the basic method of a broad renovation of the city's interior, but the difficulty of its execution and the absence of expropriation mechanisms paralyzed this first project.[105]

A more elaborate project was carried out by Àngel Baixeras in 1878, who presented an expropriation bill to the Senate, which was approved in 1879. Baixeras' project envisaged a thorough remodeling of the old city, and its most outstanding aspect was the opening of three major thoroughfares —initially called A, B and C— to make the old city center more walkable, following Cerdà's old project. However, the project was not approved until 1895, and it still had to wait until 1908 for its execution, partially realized, since only the A road, renamed Vía Laietana, was built.[106]
It is also worth mentioning the introduction of the tramway for urban transport. In 1860 an omnibus line had been opened along La Rambla, but the slowness of the carriages made this means of transport not very viable. In 1872, rails were laid for its traction, which lightened the transport, with imperial model cars —of English origin—, pulled by two or four horses. The line was extended from the port (Drassanes) to the village of Gracia, and later from the Drassanes to La Barceloneta. One of the first lines to operate was the English Barcelona Tramways Company Limited. In 1899 the streetcars were electrified.[107]

During these years, street furniture also grew, especially since the appointment in 1871 of Antoni Rovira i Trias as head of Buildings and Ornamentation of the City Council, as well as his successor, Pere Falqués, who made a special effort to combine aesthetics and functionality for this type of urban adornments. The increase of elements such as lampposts, fountains, benches, kiosks, railings, planters, mailboxes and other public services was favored by the rise of the iron industry, which allowed their mass production and resulted in greater strength and durability.[108]

In the 1880s the installation of electric lighting began, which gradually replaced the gas lighting on public roads. In 1882 the first street lamps were placed in the Plaça de Sant Jaume, and between 1887 and 1888 La Rambla and Passeig de Colom were electrified. However, the generalization of electric light did not take place until the beginning of the 20th century, with the invention of the light bulb, and it was not completed until 1929.[109]
Another service that emerged at the end of the century was the telephone. The first telephone communication in the whole peninsula took place in Barcelona, in 1877, between the Montjuic castle and the fortress of the Citadel —in the process of dismantling but still housing a garrison—. That same year the first interurban transmission between Barcelona and Girona was carried out by the company Dalmau i Fills, pioneer in the installation of lines in Barcelona. In 1884 the state monopoly of the service was established, but two years later the company Sociedad General de Teléfonos de Barcelona (General Telephone Society of Barcelona) was authorized to operate it, which was later absorbed by the Compañía Peninsular de Teléfonos (Peninsular Telephone Company). In 1925 the service was nationalized by the dictatorship of Primo de Rivera, and the Compañía Telefónica Nacional de España (National Telephone Company of Spain) was created. In 1897 there were 2479 telephones in the city, a figure that grew progressively: in 1917 there were about 10 .00, in 1930 26 .00, in 1960 200 .00, in 1985 750 .00 and in 2000 there were 850 .00 telephones.[110]
It should also be noted that in the last third of the century numerous supply markets were built, many of them made of iron, a fashionable element in the architecture of the time. The markets of Born (1872-1876), Sant Antoni (1872-1884), Hostafrancs (1881), La Barceloneta (1884), Concepción (1887-1888), Llibertat (1888-1893), Clot (1884-1889), Unió (1889), Gràcia (1892) and Sants (1898-1913) were built in this way.[76]
1888 Universal Exposition
[edit]
At the end of the century, an event was held that had a great economic, social, urban, artistic and cultural impact on the city: the Universal Exposition of 1888. It took place between 8 April and 9 December 1888, and was held in the park of the Citadel, a land formerly belonging to the Army and won for the city in 1868. The incentive of the fair events led to the improvement of the infrastructure of the entire city, which took a huge leap towards modernization and development.[111]
The remodeling project of the Citadel Park was commissioned to Josep Fontserè in 1872, who designed extensive gardens for the recreation of the citizens, and together with the green area he planned a central square and a ring road, as well as a monumental fountain and various ornamental elements, two lakes and a wooded area, as well as various auxiliary buildings and infrastructures, such as the Born market, a water reservoir —currently the library of the Pompeu Fabra University—, a slaughterhouse, an iron bridge over the railroad lines and several service sheds.[112] He also designed the urbanization of the new sector of the Born, composed of a hundred plots of land, which would present a common stylistic stamp, although it was finally only partially realized.[113]
In addition to the Citadel, the Salón de San Juan (now Passeig de Lluís Companys), a long avenue 50 meters wide that served as the entrance to the Exposition, at the beginning of which was located the Arc de Triomf, designed by Josep Vilaseca, was remodeled. This promenade featured wrought iron balustrades, pavement mosaics and large lampposts, all designed by Pere Falqués.[114] Most of the buildings and pavilions built for the Exposition disappeared after its completion, although the Castle of the Three Dragons and the Martorell Museum (both integral parts of the Museum of Natural Sciences of Barcelona), the Orangery and the Umbraculum survived, while part of the park grounds were later occupied by the Barcelona Zoo.
Numerous works and improvements were carried out throughout the city for the event: the urbanization of the entire seafront of the city was completed, between the Citadel Park and the Rambles, through the remodeling of the Passeig de Colom and a new pier, the Fusta; the urbanization of the Plaça de Catalunya began, a process that would culminate in 1929 thanks to another Exposition, the International Exhibition of Electrical Industries; Riera d'en Malla was covered, giving rise to the Rambla de Catalunya; Avenue of Paral·lel was begun; and Passeig de Sant Joan was extended towards Gràcia and Gran Via de les Corts Catalanes towards the west.[115] The Golondrinas, pleasure boats that left in front of the statue of Columbus and offered a promenade to visitors, were also installed and still remain.[116]

From the end of the century it is worth mentioning Pere Garcia Fària's project to regulate the city's sewage system (Proyecto de saneamiento del subsuelo de Barcelona: alcantarillado, drenaje, residuos urbanos, 1891). It was a project that placed special emphasis on hygienism, with innovative criteria that are still in force today: it established a visitable sewerage network, 80 cm wide by 170 cm high, maintained by a municipal brigade that still performs its functions. It is a unitary system for rainwater and wastewater, which works mainly by gravity —except for a few small pumping stations— making it necessary to have large collectors in the lower part of the city. Thanks to this project, the sewerage network was extended in a few years from 31.2 km to 212 km.[117] Around this time, the streets also began to be urbanized with tiled sidewalks and cobblestone roadways, replaced in the 1960s by asphalt.[118]
It should also be noted that during the nineteenth century the increase in population and new industrial needs led to an increase in water consumption, which required a larger water collection and distribution network. Thus, at the end of the century a new pipeline was built from Dosrius (Maresme), with a 17 km gallery and a 37 km aqueduct that brought water to the city. The first marketing companies appeared then, the main one of which was the Sociedad General de Aguas de Barcelona (AGBAR), created in 1882.[119]
On the other hand, the increase in population between the nineteenth and twentieth centuries led to the creation of new hospitals to serve the population of the new districts of the city: the Hospital Clínico y Provincial (1895-1906) and the Hospital de la Santa Creu i Sant Pau (1902-1930), a monumental modernist-style complex designed by Lluís Domènech i Montaner. Later, the hospitals of Esperança (1924), the Red Cross (1924), the Military (1924) and the Hospital del Mar (1931) were created, while in 1955 the Hospital Universitari Vall d'Hebron, one of the main health referents of Catalonia, was inaugurated.[120]
During these years the Eixample was progressively urbanized, first thanks to private initiative and the so-called Sociedades de Fomento (Development societies), and from 1892 with the appearance of the Comisiones Especiales de Ensanche (Special Commissions for the Eixample) arising from the new Eixample Law of 1892. This law was based on the Law of Forced Expropriation of 1879, and developed a management system with public and private participation. The urbanization process used to have several phases: filling the area, parceling the land, installation of services such as sewerage, running water and lighting, and construction of buildings. Most houses used to be rented: the owner reserved the second floor (planta noble) and rented the others.[121]
20th Century
[edit]
The 20th century was conditioned by the convulsive political situation, with the end of the monarchy in 1931 and the arrival of the Second Republic, which ended with the Civil War and was replaced by Franco's dictatorship, until the reestablishment of the monarchy and the arrival of democracy. Socially, this century saw the massive arrival of immigration to the city, with the consequent increase in population: if in 1900 there were 530 000 inhabitants, in 1930 they had almost doubled (1 009 000 hab), to reach between 1970 and 1980 the maximum peak (1 754 900) and by the end of the century to 1 500 000 inhabitants.[122]
With the turn of the century, a new political scenario opened up, marked by the loss of the colonies in America and Asia and the rise of the Regionalist League, led by politicians such as Francesc Cambó, Enric Prat de la Riba and the architect Josep Puig i Cadafalch, who expressed their desire to place Barcelona on the international front line, at the level of cities such as Paris, New York, Berlin or Vienna. It is the model of the "Imperial Barcelona" proposed by Prat de la Riba, or the "Nova París del Migdia" (New Paris of the Midday) commented by Puig i Cadafalch. In this sense, projects for the improvement of infrastructures, railroads, transport and equipment, the creation of a free port, the attention to the needs of an increasingly industrialized society, the search for mechanisms to accommodate the increase in population and to satisfy aspects hitherto little attended to, such as education, culture and green spaces, all arise in this sense.[123]
Municipal Aggregations and Plan of Connections
[edit]The beginning of the century was marked by the geographical expansion of the city: in 1897 Barcelona annexed six neighboring towns, until then independent: Sants, Les Corts, San Gervasio de Cassolas, Gràcia, Sant Andreu de Palomar and Sant Martí de Provençals.[note 3] Likewise, in 1904, Sant Joan d'Horta was annexed; in 1921, Sarrià and Santa Creu d'Olorda (a small piece of land in Collserola segregated from Molins de Rei); in 1924, Collblanc and the Marina de Hospitalet, where the Zona Franca was created; and, in 1943, Bon Pastor and Baró de Viver, segregated from Santa Coloma de Gramenet. The city grew from 15.5 km² to 77.8 km², and from a population of 383,908 to 559,589.[124]

The annexation of the new municipalities raised the need for a plan to connect the city, which was put out to public tender in 1903 (Concurso Internacional sobre anteproyectos de enlaces de la Zona de Ensanche de Barcelona y los pueblos agregados entre sí y con el resto del término municipal de Sarrià y Horta; "International Competition on preliminary projects to connect to each other the Barcelona Eixample Area and the towns added and with the rest of the municipality of Sarrià and Horta"), in which the French town planner Léon Jaussely was the winner. The integration of the new aggregated municipalities with Barcelona and between them was sought, with a predominance of the organizational aspects over the expansive ones, in an attempt to reformulate the Cerdà Plan, badly seen by the modernist generation.[125] The Jaussely Plan was based on a structural scheme, with a differentiated treatment of the various urban fabrics, which recalls the Beaux-Arts type layouts in vogue in the international environments of the time.[126] His proposal was based mainly on three criteria: a road scheme of main axes (five radial roads and two ring roads), the zoning of activities and the systematization of green spaces.[127] The project envisaged large road infrastructures (boulevards, large squares, promenades, diagonals), parks and gardens, rail links —with underground interior lines—, public and collective buildings at the central points of the road layout, facilities and service areas. The project was only partially realized, and in 1917 it was reformulated with the so-called Romeu-Porcel Plan;[80] however, the innovative nature of its ideas left a deep mark and inspired Barcelona's urban planning for much of the century.[128]

The most important action in these years was the opening of the Via Laietana, which connected the Eixample with the sea, projected with the letter A in the Plan Baixeras of 1878. The works were finally carried out in 1908, with joint financing between the City Council and the Banco Hispano Colonial (Hispanic Colonial Bank), the first concerted operation in Barcelona.[129] The new road was designed with the desire to create an avenue with a uniform appearance, so most of the buildings are of noucentista appearance, with some influence of the Chicago School.[130] Criticism of the works for the opening of this road, which involved numerous demolitions of houses —some buildings of artistic value were moved—,[note 4] paralyzed the construction of the other two roads planned by Baixeras, although later some punctual interventions were made in these places, according to the projects of Antoni Darder (1918), Joaquim Vilaseca (1932, Plan de Reforma, urbanización y enlace entre los puntos singulares del Casco Antiguo; "Renovation, urbanization and linkage plan between the singular points of the Old Town") and Soteras-Bordoy (1956, Plan parcial de Ordenación del Casco Antiguo de Barcelona; "Partial Plan for the Development of the Old Town of Barcelona").[106] [note 5]

Also in the early years of the century the slopes of Tibidabo were urbanized, with a wide avenue linking the avenue of San Gervasio with the mountain, which was occupied by single-family houses in the style of the English garden cities.[note 6][131] For transportation, a tramway was installed on the avenue and a funicular to ascend to the top of the mountain (1901), where the Tibidabo Amusement Park was located.[132] In 1906, the Vallvidrera funicular was also opened.[133]
An interesting urbanization project was that of the Can Muntaner estate (1900-1914), at the foot of Mount Carmel, in the neighborhood of La Salut, also designed as a garden city of single-family houses. The promoter was the industrialist Eusebi Güell, and the architect Antoni Gaudí was in charge of the layout. The project was unsuccessful, as only two plots were sold, and in 1926 the land was ceded to the City Council and converted into a park, known today as Park Güell.[134]

During the first years of the century the port was enlarged, with a project elaborated by Julio Valdés and carried out between 1905 and 1912: the eastern dock was extended and a counter dock and the inner docks were built. These works gave the port practically its current physiognomy, except for the construction of the south dock and the inner dock in 1965.[135]
The turn of the century brought the general electrification of the city, both public and private. In 1911 the company Barcelona Traction Light and Power —better known as La Canadiense— was founded, which was committed to the use of the hydraulic resources of the Pyrenees, building reservoirs in Tremp (1915) and Camarassa (1920). It also built the Fígols and Sant Adrià de Besòs thermal power stations. Thanks to electrification, Barcelona began to stand out in sectors such as metallurgy, chemistry and automobiles, consolidating itself as an industrial and commercial center.[136]
During the first decade of the century, public urinals called vespasianas were installed, made of metal with a circular body with a capacity for six people, above which rose a hexagonal section for advertising, topped by a little dome. In the 1910s they were removed, and in the future it was established that all urinals had to be underground.[140][137]

During these years the tramway network was extended, thanks to companies such as Les Tramways de Barcelone Société Anonyme. The expansion of the city with the aggregation of the adjoining municipalities increasingly required a wide and fast transport network, whose progress was favored by the electrification of the streetcars, a fact that also lowered their cost and allowed the service to become more popular: from seven million passengers in 1900 it went to 17 million in 1914.[138]
At the beginning of the century the first buses also appeared: in 1906 the first line was created between Plaça de Catalunya and Plaça de Trilla, in Gràcia, operated by the company La Catalana, with five Brillié-Schneider cars. The service was suppressed in 1908 due to protests from the tramway companies, for which it was clear competition, but in 1916 some suburban lines appeared, running between Barcelona and Sant Just Desvern, Santa Coloma de Gramenet, Hospitalet, Badalona, El Prat, Sant Boi de Llobregat, Gavà and Sant Climent de Llobregat. In 1922, city buses were reestablished, in charge of the Compañía General de Autobuses de Barcelona (General Bus Company of Barcelona, CGA), which was later absorbed by Tranvías de Barcelona, (Tramways of Barcelona) which went on to operate both transports.[139]
Also at this time the first taxis appeared: in 1910 the first 21 vehicles were licensed; in 1920 there were already a thousand taxis, with 64 stops throughout the city. In 1928 the green light was incorporated as a "free" signal, and in 1931 the color black and yellow was established as the city's distinguishing color.[140]

In the 1920s, urban transport was improved with the construction of the Barcelona Metro. Work began in 1920 with the installation of two lines: line 3 (Lesseps-Liceo), inaugurated in 1924, and line 1 (Cataluña-Bordeta), put into service in 1926. The network was progressively expanded, and today Barcelona has 12 lines. Initially it was operated by three companies: Gran Metropolitano de Barcelona (L3), Metropolitano Transversal (L1) and Ferrocarril de Sarrià a Barcelona (now Ferrocarrils de la Generalitat de Catalunya);[141] the first two merged in 1957 into the company Ferrocarril Metropolitano de Barcelona, which together with the bus company Transportes de Barcelona formed in 1979 the company Transportes Metropolitanos de Barcelona (TMB).[142]
It should also be noted that during the first decades of the century, public schooling was greatly boosted, thanks above all to the initiative of the City Council, the Provincial Deputation and the Commonwealth of Catalonia. In 1922, the City Council created the Patronat Escolar, which promoted secular, bilingual education and pedagogical renovation,[143] and promoted an ambitious plan of school buildings, including those built in noucentista style by Josep Goday (Ramon Llull, Collaso i Gil, Lluís Vives, Milà i Fontanals, Baixeras and Pere Vila schools).[144] After the Civil War, public education was taken over by the central government, until the arrival of democracy, when the competences were transferred to the Generalitat.[145]
In these years, increasing importance was also given to the question of green spaces, which was raised in 1926 by Nicolau Maria Rubió i Tudurí, director of the Parks and Gardens Service of Barcelona: with the text El problema de los espacios libres (The problem of open spaces), presented at the XI Congreso Nacional de Arquitectos (XI National Congress of Architects), he proposed the placement of a series of green spaces in the form of concentric semicircles between the Besòs and Llobregat rivers, all along the Collserola mountain range, with small enclaves in the inner part of the city in the style of the London squares.[146] He proposed four levels for the city: interior parks, among which would be the Citadel and Montjuïc, as well as three smaller ones (Letamendi, Sagrada Família and Glòries); suburban parks, among which would be the Hippodrome, Turó Park, Turó Gil, Font del Racó, Vallcarca, Guinardó and Park Güell; exterior parks (Llobregat, Pedralbes, Vallvidrera, Tibidabo, Sant Medir, Horta and Besòs); and the Collserola nature reserve. Rubió's project was not executed, except in small portions, but little by little the city was gaining green land: from 1910 to 1924 it went from 72 ha to 450 ha.[147]
1929 International Exposition
[edit]
In 1929 the International Exposition was held in Montjuïc. For this event the entire area of the Plaça dEspanya, the avenue of Queen Maria Christina and the mountain of Montjuïc was urbanized, and the pavilions that currently house the Barcelona Fair were built. One of the main architects of the project was Josep Puig i Cadafalch, and it was one of the main test beds of noucentisme, the successor style to modernisme.[148] The Exposition took place from 19 May 1929 to 15 January 1930, over an area of 116 ha, and cost 180 million pesetas.[149]
On the occasion of the Exposition, a large part of the Montjuic mountain was landscaped, with a project by Jean-Claude Nicolas Forestier and Nicolau Maria Rubió i Tudurí, who created an ensemble of marked Mediterranean character and classicist taste: the Laribal, Miramar and Greek Theater gardens were thus created.[150]
As in 1888, the 1929 Exposition had a great impact on the city's urban development, not only in the area of Montjuïc, but also throughout the city: the squares of Tetuan, Urquinaona and Letamendi were landscaped; the Marina bridge was built; Plaça de Catalunya was urbanized; Diagonal was extended to the west and Gran Vía to the southwest, as well as the promenades of Gràcia and Sant Joan in the sections around Gràcia. Various public works were also carried out: street asphalting and sewerage were improved, public toilets were installed, and the replacement of gas lighting with electric lighting was completed.[151]

Finally, the city's communications were improved, with the construction in the 1920s of the Prat Airport, the renovation of the France Station, the improvement of connections with the suburbs, the elimination of level crossings within the city, the burying of the train tracks in the urban interior —in streets such as Aragó, Balmes and Via Augusta— and the electrification of public streetcars.[152] A funicular railway was also built to reach the top of the mountain —with a second section to ascend to the castle which was replaced by a cable car in 1970—, as well as a cable car to access the mountain from the port of Barcelona, a work by Carles Buïgas that was inaugurated in 1931 due to a delay in the works.[153][154]
All these public works led to a strong demand for employment, causing a large increase in immigration to Barcelona from all parts of Spain. This increase in population led to the construction of several working-class neighborhoods of "cheap houses", such as the Eduardo Aunós group in Montjuic (now disappeared), the Ramon Albó group in Horta (now Can Peguera) and the Milans del Bosch (now Bon Pastor) and Baró de Viver groups in Besós.[155] However, one of its worst effects was the rise of shantyism, since many of the immigrants who could not have access to housing resorted to self-construction, with precarious buildings made of scrap materials (cane, wood, brass), in single spaces for the family of about 25 m². In 1930 there were about 15,000 barracks in Barcelona, mainly in Sant Andreu, Montjuïc mountain and the beaches of Barceloneta and Poblenou, where neighborhoods such as Pequín, La Perona and Somorrostro are still remembered.[156]
In 1929, the first traffic lights were installed to regulate vehicular traffic: the first was located at the intersection of Balmes and Provenza streets, and by the end of the year there were ten operating throughout the city, regulated by agents of the Guardia Urbana. The Civil War meant a halt in the installation of traffic lights, which was reactivated in the 1950s. The first synchronization took place in 1958, in Via Laietana. In 1984 the Traffic Control Center was opened, which in 2004 controlled 1,500 traffic light crossings.[157]
Second Republic and the Macià Plan
[edit]
The arrival of the Second Republic and the grant of self-government to Catalonia favored the creation of various urban development projects in a city that by 1930 had reached one million inhabitants and was deficient in infrastructure, housing, transport and facilities such as schools and hospitals.[158] In 1932 the autonomous government of Catalonia, the Generalitat, commissioned the brothers Nicolau and Santiago Rubió i Tudurí to develop a zoning project for the Catalan territory (Regional Planning), which would be the first attempt at joint planning of all the lands of the Principality. The project included a region of Barcelona, which included the plain of the city, the Baix Llobregat and the group of towns around the Tibidabo mountain.[80] The Regional Plan included all the considerations about the territory, both urban and natural, as well as in aspects such as agriculture and livestock, mining, industry, tourism, health and culture.[159]
Another territorial structuring project was carried out in 1936, the Territorial Division of Catalonia, based on a work commissioned by the Generalitat in 1932 to Pau Vila. The project sought a spatial organization based on administrative public services, which resulted in a division into 9 regions and 38 comarques. Barcelona became the capital of the Barcelonès comarca, which included Hospitalet de Llobregat, Badalona, Santa Coloma de Gramenet and Sant Adrià de Besòs. At that time, Catalonia had an area of 32 049 km², 2 920 748 inhabitants and 1070 municipalities.[160]

During these years an interesting urban planning project was generated, the Macià Plan (1932-1935), elaborated by the architects of GATCPAC, with Josep Lluís Sert at the head, in collaboration with the French rationalist architect Le Corbusier. The project envisaged a functional distribution of the city with a new geometric order, through large vertebral axes and with a new maritime façade defined by Cartesian skyscrapers, in addition to the improvement of facilities and services, the promotion of public housing and the creation of a large park and leisure center next to the Llobregat delta.[161]

The Plan presented Barcelona as a political and administrative capital, with a working-class and functional character, which would be structured in different areas: a residential zone, a financial and industrial zone, a civic and service zone, and a recreational zone, which included parks and gardens and beaches; connectiobs, communications and transport were also studied in detail. The backbone would be the Gran Via de les Corts Catalanes, a 600 m wide strip that would run from the Llobregat to the Besòs. The Meridiana and Paral·lel avenues were also promoted, which would converge at the port, where a city or business center would be located, moving the port facilities to the Zona Franca. For the residential area, they proposed the creation of 400 x 400 m modules —equivalent to nine blocks of the Eixample— with large housing complexes and social facilities. The recreational area was conceived through green spaces located in these residential modules and in a large strip of land in the coastal area, between Barceloneta and Poblenou, as well as the creation of a vast complex for leisure called Ciutat de Repòs i Vacances (Rest and Vacation City), which would be located on the beaches of Viladecans, Gavà and Castelldefels.[162]
Although the Macià Plan was not put into practice, its innovative and avant-garde design made it one of the landmarks of Barcelona urban planning, along with the Cerdà and Jaussely plans. Some of its aspects inspired the city's urban planning in the democratic period and the 1992 Summer Olympics bidding project, especially in terms of the recovery of the seafront as a space intended for leisure, as evidenced by the location of the Maremagnum shopping center on the Quai d'Espanya or the creation of the Poblenou area and the various parks that follow one after the other from this to the Diagonal Mar area.[163]
Also on the initiative of GATCPAC, the Pla de Sanejament del Casc Antic (Old Town Sanitation Plan) (1935-1937), which provided for the demolition of blocks considered unhealthy, a sponging of urban space and the creation of hygienic facilities, all supported by a strong public intervention, a fact that favored the decree in 1937, in the course of the Civil War, the municipalization of urban property.[164]
The GATCPAC also developed a workers' housing plan inspired by Le Corbusier's model of building à rédent, which was embodied in the Bloc house (1932-1936, Josep Lluís Sert, Josep Torres Clavé and Joan Baptista Subirana), an S-shaped housing complex of long, narrow blocks with a two-bay metal structure, with access to the dwellings through covered corridors. The outbreak of the Civil War cut short the dissemination of this project.[165]
In the 1930s the first pedestrian road signs appeared: the first ones were vertical, consisting of a white oval plate on a pole with the inscription "pedestrian crossing";[166] later, horizontal signs were placed, in the form of 10 x 30 cm metal plates, with a rough texture, placed on the asphalt in such a way that their protruding bands made cars slow down.[167]
Franco's dictatorship and the Comarcal Plan
[edit]
The years of the Franco dictatorship (1939-1975) were characterized by urban development, which consisted of the unbridled construction of cheap housing, mostly subsidized housing, to absorb immigration from the rest of Spain. In two decades it went from 1,280,179 inhabitants in 1950 to 1,745,142 in 1970.[168] However, although subsidized housing was encouraged, this did not stop speculation.[169] New housing was developed mostly on the periphery of the city —an area of about 2500 ha, twice the size of the Eixample—,[170] with three main models: suburban sprawl neighborhoods, marginal or self-construction urbanization neighborhoods, and mass housing estates.[171] The construction of housing was carried out, in many cases, without prior urban planning, and using cheap materials that, over the years, would cause various problems such as aluminosis. The construction fever caused the creation or expansion of new neighborhoods, such as El Carmel, Nou Barris, El Guinardó, Vall d'Hebron, La Sagrera, El Clot or El Poblenou.[172] The growth of the suburbs caused the uninterrupted connection with the neighboring municipalities (Santa Coloma de Gramenet, Badalona, Sant Adrià de Besòs, Hospitalet de Llobregat, Esplugues de Llobregat), which in turn grew enormously, a fact that led Mayor Porcioles to coin the concept of the "Great Barcelona."[173]
Real estate speculation was favored by the reform of the Municipal Ordinances carried out in 1942, which increased the height of buildings in relation to the width of the streets: in streets between 20 and 30 m (average width of the Eixample), heights of up to 24.40 m were allowed, equivalent to a first floor and six floors, while in streets over 30 m the height could reach 27.45 m (seven floors). This increase in buildability caused notable differences between buildings constructed at different times, and led to the presence of numerous party walls that disfigured the urban space, a problem that the city still suffers from despite several projects to remedy it, such as the Barcelona posa't guapa (Barcelona, make yourself pretty) campaign.[174]
The post-war urban renewal was led by the head of urban planning of the new authorities, Pedro Bidagor, who in 1945 promoted the creation of the Barcelona Provincial Planning Commission, responsible for drawing up a planning project for the city and its surroundings.[80] Thus arose the Regional Plan of 1953, developed by Josep Soteras, an attempt to integrate the city with neighboring municipalities in order to meet the strong demand for housing in the years of massive immigration, while trying to curb real estate speculation and improve the urban environment.[175] The Plan was accompanied by a legislative change, the Land and Urban Planning Law of 1956, which sought to bring rationality to urban development, although it encountered numerous difficulties in its application.[176] The project differentiated between zones of urban expansion, suburban or garden cities, applying a polarized distribution of the territory; thus, in Barcelona it identified three zones as areas of growth: Levante, Poniente and Diagonal Norte. It also reserved large areas for infrastructure, facilities and green spaces; among the latter, it emphasized the enclosure of the Collserola mountain range as a large central metropolitan park.[177]
Although it was not carried out in its entirety, various "partial plans" emerged from its initial approach, most of which yielded to the pressures of the land owners and tended towards the requalification of land: a 1971 study calculated a 1.8 multiplication of the population density of the partial plans with respect to the Comarcal of 1953.[178] The most relevant were those referring to the two ends of the Diagonal avenue, east and west: in the first the new neighborhoods of La Verneda and Besòs were created, while in the second the Zona Universitaria was projected and the neighborhoods of Les Corts and Collblanc were enlarged.[179]

The growth of the population and the appearance of new neighborhoods implied the construction of new markets for the supply of basic products: Sagrada Família (1944), Carme (1950), Sagrera (1950), Horta (1951), Vallvidrera (1953), Estrella (1954), Guinardó (1954), Tres Torres (1958), Bon Pastor (1960), Montserrat (1960), Mercè (1961), Corts (1961), Guineueta (1965), Ciutat Meridiana (1966), Felip II (1966), Sant Martí (1966), Besòs (1968), Sant Gervasi (1968), Carmel (1969), Vall d'Hebrón (1969), Port (1973), Provençals (1974), Lesseps (1974), Trinitat (1977) and Canyelles (1987).[180]
During these years, automobile traffic increased considerably, which led to the improvement of the city's road network: Meridiana Avenue was opened, the First Ring Road (Ronda del Mig) was built and the Second Ring Road was planned, the construction of subway parking lots was started and the freeway network was extended thanks to the 1962 arterial network project, with a set of radial highways starting from Barcelona in several axes (Vallès, Llobregat, Maresme).[181] The opening of three tunnels to cross the Collserola mountain range, at Vallvidrera, Tibidabo and Horta, was also proposed, of which only the first one was built, of which only the first phase was built between 1969 and 1976 and the second between 1982 and 1991; the Rovira tunnel was also built between 1983 and 1987, linking El Guinardó with El Carmel, which was supposed to link the Horta tunnel with the center of the city.[182]

In transportation, streetcars were replaced by buses, and the metro network was expanded; in 1941 trolleybuses appeared, which disappeared in 1968.[108] The water supply was also improved with the contribution coming from the Ter River, natural gas was introduced, and the electrical and telephone networks were renewed.[183]
In 1952 Barcelona hosted the XXXV International Eucharistic Congress, which allowed the development of a new neighborhood known as Congreso (Congrés), with a housing complex designed by Josep Soteras, Carles Marquès and Antoni Pineda.[184] The complex, of 16.5 ha, included a complex of 3,000 homes, 300 commercial premises, a church (parish of San Pío X) and various school, sports and cultural services and facilities, with alternating open and closed blocks.[185] In the rest of the city, several renovations were also carried out, such as the opening of the avenues of Príncipe de Asturias (now Riera de Cassoles) and Infanta Carlota (now Josep Tarradellas);[186] a monumental fountain was placed at the intersection of Gran Via de les Corts Catalanes and Passeig de Gràcia, the work of Josep Soteras;[187] and Calvo Sotelo square —currently Francesc Macià— was landscaped, with a project by Nicolau Maria Rubió i Tudurí.[188]
In 1957 the first section of the Paseo Marítimo was opened, an idea that had emerged in the 1920s but had not yet been developed, with a project by Enric Giralt i Ortet.[189] On the other hand, the housing deficit to accommodate the new immigration led to the enactment of the Social Urgency Plan of 1958, which led to the construction of large blocks of social housing in neighborhoods on the periphery, such as La Verneda, Torre Llobeta, La Trinitat and Verdum.[189]

The Zona Franca, an industrial sector located between the mountain of Montjuic, the port and the Llobregat, was also established at that time. The idea arose in 1900, due to the loss of the colonial market in Cuba, promoted by Fomento del Trabajo Nacional (National Labor Development) an entity that commissioned the project to Guillem Graell. However, bureaucratic obstacles, the outline of several projects that did not come to fruition and the Civil War delayed its construction until the 1960s, although then simply as an industrial estate, abandoning the concept of a zona franca. In addition to the industrial area itself, several residential neighborhoods were located in the sector, such as Casa Antúnez, Can Clos, La Vinya and Polvorín. In 1967, Mercabarna, a central wholesale food market that supplies the entire city, was established in the area. In 1993 the Zona d'Actividades Logísticas (Logistics Activities Zone) (ZAL), dedicated to post-production and pre-commercial activities, was also created in the area.[190]
Between 1957 and 1973, Josep Maria de Porcioles was mayor, a long term of office known as the "Porcioles era", which stood out in urban planning for its speculative rampage, favored by the Municipal Charter of 1960, which granted the City Council broad powers in many areas, including urban planning.[191] Porcioles created the Municipal Housing Board, whose developments included the creation of large housing estates, such as Montbau (1958-1961), Southwest Besòs (1959-1960) and Canyelles (1974).[192] Some of the urban development actions of this period were positive, such as the covering of Aragón street, the extension of the Gran Vía towards the Maresme, the adaptation of the seafront of Montjuic or the Barceloneta promenade; however, the speculative rampage of large real estate operations generated popular discontent that resulted in the so-called "urban social movements", which combined the discomfort generated by the degradation of the urban periphery with political protest against the Franco regime. Examples of this were the opposition to the new layout of Lesseps square caused by the opening of the First Ring Road (Ronda del Mig), or the reaction against the Partial Plan of Vallbona, Torre Baró and Trinitat, organized by a neighborhood association called Nueve Barrios (Nine Neighbourhoods) which later gave rise to the name of that new district of the city.[193]

Despite the rise of developmentalism, there were some attempts at urban reorganization, such as the Master Plan for the Metropolitan Area of Barcelona (1966), which sought to make profitability and urban construction compatible, although its guiding character did not lead to practical realization; and the so-called Plan Barcelona 2000 (1970), a somewhat utopian attempt to establish criteria for the future city, where the importance given to infrastructure predominates, while a realistic commitment was made to the disorderly nature of urban growth.[195] In the same 1970 a project for a Universal Exposition in 1982 emerged, which foresaw the opening of large avenues in the city, among them a vertical axis that would link Plaza de España with Vallès through the Vallvidrera tunnel, and a Gran Vía Norte formed with Josep Tarradellas street and the Travessera de Gràcia extended to Santa Coloma; all this was not finally realized.[196] In 1969 the Vilalta Plan for the construction of treatment plants for the treatment of the city's wastewater was also approved.[197]
Between 1964 and 1972 the Plan de la Ribera was developed, aimed at the urbanization of the city's eastern seafront, from Barceloneta to Besòs, an area of 225 ha. Prepared by Antoni Bonet i Castellana, it was based on the deindustrialization of the area, and proposed the creation of a megastructure of seven large blocks of 500 x 500 m of luxury housing. The project had a long administrative process, and was not included in the Regional Plan until 1970. However, in 1972 the Town Planning Department of the City Council requested a redrafting of the project, due to opposition from neighbors and professional associations, who denounced the speculation attempts of the companies that financed the project, so it was definitively paralyzed. However, over time the plan was recognized as an attempt to renew Barcelona's urban planning, in line with international trends such as urban renewal or renovation urbaine, and the renovation of the coast remained in the collective imagination, which was finally carried out on the occasion of the Olympic Games.[177]
Finally, during the dictatorship the actions in green spaces focused more on the maintenance and restoration of existing areas than on the creation of new spaces. In 1940 Lluís Riudor, the initiator of landscaping in Catalonia, was put in charge of Parks and Gardens.[198] His actions included the Austria Garden —located in the Park Güell enclosure—, the Monterols Park, the Cervantes Park, and various interventions in the Montjuïc mountain aimed at eliminating shantytowns, a project continued by his successor, Joaquim Casamor, with the creation of several thematic gardens, such as the Mossèn Costa i Llobera gardens, specialized in cacti and succulents, and the Mossèn Cinto Verdaguer gardens, dedicated to aquatic, bulbous and rhizomatous plants.[199] His work also included the Mirador del Alcalde and Joan Maragall gardens on Montjuic, located around the Albéniz Palacete; and, in the rest of Barcelona, the Putget, Guineueta and Villa Amelia parks.[200]
Democracy and the General Metropolitan Plan
[edit]
The end of the dictatorship and the advent of democracy brought a new era in the architectural and urban planning panorama of the city, which was increasingly immersed in international avant-garde trends. The new socialist councils of Narcís Serra (1979-1982) and Pasqual Maragall (1982-1997) were committed to urban planning and architecture as the city's hallmarks, and initiated an extensive program of urban reforms that culminated with the 1992 Olympic Games. The new public commitment was reflected in the increase of facilities such as schools, parks and gardens, roads and urban spaces, and civic, cultural and sports centers.[201]
A large part of the municipal actions consisted of the acquisition of urban land, a fact favored by the relocation of factories and industrial complexes that moved out of the city. This policy was favored by the new consistory, which appointed Oriol Bohigas as Urban Planning delegate, which began a period of strong public investment in the city that led to a radical change in the urban physiognomy and a new projection of Barcelona at international level, which came to fruition with the Olympic Games.[202]
Municipal actions in those years focused on reconstruction versus expansion, on public versus private initiative. Against the vision of the city as a unitary entity, the concept of the sum of realities was opposed, prioritizing attention to local needs. It sought to palliate both quantitative and qualitative deficits, in which each intervention in public space served as an engine of urban regeneration, compensating the peripheries with a "monumentalization" of their environment.[203]
One of the factors driving urban change was industrial restructuring, promoted by the Plan for the reindustrialization of the center of Barcelona, which resulted in the creation of an Zona d'Urgent Reindustrialització (Urgent Reindustrialization Zone) (ZUR). The new industrial development was based on factors such as R&D, and on the commitment to new technologies.[204]

The new urban planning was embodied in the General Metropolitan Urban Development Plan (1976), drafted by Joan Antoni Solans, an attempt to curb speculation and rehabilitate the most degraded urban spaces, placing special emphasis on social, welfare and cultural facilities. To this end, the Metropolitan Corporation of Barcelona was created, which included the capital and 26 surrounding municipalities. Three general lines of action were outlined: one of small-scale urban rehabilitation, such as the opening of streets and squares, the creation of parks and gardens and the restoration of buildings and artistic monuments; another of urban restructuring, focused on aspects such as road reorganization (ring roads), new central areas and land requalification; and another of morphological reorganization, which took the form of the current administrative division of the city into ten districts (1984), most of which coincided with the former municipalities attached to Barcelona.[205] One of the main tools for these interventions would be the Plans Especials de Reforma Interior (Special Plans of Interior Renovations) (PERI).[206]
However, the ambitious nature of the project, which reserved numerous areas for green spaces and intended to requalify others with a high population density, provoked countless lawsuits and claims, both from individuals and landowners, which delayed its execution and eventually left the project practically inoperative, a fact that was materialized with the dissolution of the Metropolitan Corporation in 1985 by the Generalitat de Catalunya.[207] Even so, its general guidelines have marked the urban planning actions of the late twentieth century and early twenty-first century.[208]
Between 1983 and 1989 the concept of "areas of new centrality" was developed, in search of a more polycentric and better connected city.[209] The aim was to decongest the center by promoting various sectors of the urban periphery, which should regenerate low-quality urban fabrics thanks to their intrinsic morphological qualities. Twelve areas were delimited: RENFE-Meridiana, Diagonal-Sarrià, Tarragona street, Cerdà square, Port Vell, Glòries square, Diagonal-Prim (future Fòrum area), Sant Andreu-Sagrera and four related to the Olympic Games: Montjuic, Diagonal-Zona Universitària, Vall d'Hebron and Carles I-Avinguda Icària (future Olympic Village).[210]

During this period, numerous stretches of the city's roads were improved, with wide and often landscaped avenues designed mainly for pedestrian traffic. Some examples are: Avinguda de Gaudí, Avinguda de Josep Tarradellas, Carrer Tarragona, the connection between the old Rambles and the Rambla de Catalunya, Passeig de Lluís Companys, Avinguda de la Reina Maria Cristina, Via Júlia and Rambla de Prim. Numerous squares were also opened and refurbished, in many cases also landscaped, such as those of Salvador Allende, Baixa de Sant Pere, Sant Agustí Vell, la Mercè, Sóller and Robacols.[211]
Among the sectoral plans developed during these years it is worth mentioning: those of Ciutat Vella, especially in the Raval, Santa Caterina and Barceloneta; that of Carmel; that of Gràcia, where several squares were urbanized (Sol, Virreina, Trilla, Diamant and Raspall, 1982-1985); and those of Sarrià, Sant Andreu and Poblenou.[212] Policies to promote affordable housing were also carried out, and in Eixample the recovery of the block courtyards as green areas or public services was sought.[213]
In 1988 the Pla Especial de Clavegueram de Barcelona (Special Sewerage Plan of Barcelona) (PECB) was approved, which remodeled the network of coastal sewers, eliminating practically half of the city's flood areas, while promoting the construction of breakwaters, which allowed the recovery of the city's beaches. The same purpose was served by the 1997 Pla Especial de Clavegueram de Barcelona (Special Sewerage Plan for Barcelona) (PECLAB), which boosted stormwater regulation reservoirs to prevent flooding.[197]
The arrival of democracy favored the creation of new green areas in the city. At this time gardening was closely linked to urban planning, with a concept that combined aesthetics with functionality, as well as recreational aspects, sports facilities and services for certain groups such as children or the elderly, as well as areas for dogs.[214] Numerous parks were converted from former municipal facilities, such as the Joan Miró park, built between 1980 and 1982 on the site of the former central slaughterhouse of Barcelona; or in industrial areas (Espanya Industrial park, 1981-1985; Pegaso park, 1982-1986; Clot park, 1982-1986) or former railway facilities (Sant Martí park, 1985; Estació del Nord park, 1988). The Creueta del Coll park (1981-1987), a work of the Martorell-Bohigas-Mackay team, was also established on the site of an old quarry.[95]
1992 Olympic Games
[edit]
Another of Barcelona's profound transformations came on the occasion of the 1992 Olympic Games. The event involved the remodeling of part of the mountain of Montjuïc, where the so-called Olympic Ring (1985-1992), designed by Carles Buxadé, Joan Margarit, Federico Correa and Alfons Milà,[215] a large enclosure located between the Olympic Stadium Lluís Companys and the Plaça d'Europa, which houses several sports facilities including the Palau Sant Jordi, was located.[216]
To accommodate the athletes, a new neighborhood was built, the Poblenou Olympic Village (1985-1992), with a general layout of the Martorell-Bohigas-Mackay-Puigdomènech team.[217] The planning of the Olympic Village was complex, and several aspects had to be adapted: the coastal railroad had to be buried; sewage treatment plants had to be built and the wastewater that had previously gone directly into the sea had to be channeled; a new port (Olympic Port) was built; new beaches were established and regenerated; and new road and transport axes were laid out, such as Avinguda d'Icària.[218] Several facilities were also installed in the area, such as the Telephone Exchange (1989-1992, Jaume Bach and Gabriel Mora) and the Meteorology Center (1990-1992, Álvaro Siza). On the other hand, the construction of two large skyscrapers (Hotel Arts and Torre Mapfre) changed the physiognomy of Barcelona.[219]

Another area of action was the Vall d'Hebron neighborhood, planned according to a project by Eduard Bru (1989-1991), which combined green areas with sports facilities. This area was the site of the Olympic Press Village (1989-1991), designed by Carlos Ferrater.[220]
The Olympic Games also led to the creation of new parks and gardens, such as the parks of Mirador del Migdia, Poblenou, Carles I and three designed by the firm Martorell-Bohigas-Mackay: the park of the Cascades, the Olympic Port and the park of Nova Icària.[221]
On the occasion of the Games, the Old port (Port Vell) was also remodeled, with a project by Jordi Henrich and Olga Tarrasó. The new space was dedicated to leisure, with the creation of the Maremagnum leisure center, connected to land by the Rambla de Mar, a pivoting bridge designed by Helio Piñón and Albert Viaplana.[222] For the event a Coastal Plan was also instituted with a view to the regeneration of the city's beaches, which had been quite eroded until then, and which were totally renovated and won for the enjoyment of the citizens. Beaches such as Sant Sebastià, Barceloneta, Nova Icària, Bogatell, Mar Bella and Nova Mar Bella were cleaned and filled with sand from the seabed, sewage treatment plants were built on the Besòs and Llobregat rivers and underwater reefs were placed to favor flora and fauna.[223] On the other hand, the Llobregat River was diverted in its final stretch 2.5 km to the south, thus allowing the port to be extended in that direction.[224]

Another urban planning action was in the Raval neighborhood, which was remodeled with a project by Jaume Artigues and Pere Cabrera, which consisted of the opening of the Rambla del Raval and the adequacy of the surroundings of the Plaça dels Àngels as a cultural center, where the Center of Contemporary Culture of Barcelona (1990-1993) and the Museum of Contemporary Art of Barcelona (1987-1996) were located.[225]
The Games also brought progress in the technological sector, with new infrastructures especially in the telecommunications sector: the Collserola (by Norman Foster) and Montjuïc (by Santiago Calatrava) communications towers were built, and 150 km of optical fiber cabling were installed in the city's subsoil.[226]
It should also be noted that the road infrastructure of the city was significantly expanded for the Games, especially with the creation of the ring roads, arranged as a ring road around the entire urban perimeter. The general planning was carried out between 1989 and 1992 by Josep Acebillo, technical director of the Municipal Institute for Urban Development, and Alfred Morales, coordinator of transport and circulation of the Barcelona City Council.[227] There are currently three ring roads: the Ronda de Dalt, the Ronda del Mig and the Ronda del Litoral; the first two ring roads circumvent Barcelona, while the Ronda del Mig (of the "middle") crosses the city and receives different names depending on the section (Passeig de la Zona Franca, Carrer de Badal, Rambla del Brasil, Gran Via de Carles III, Ronda del General Mitre, Travesera de Dalt and Ronda del Guinardó).[228]

On the other hand, there was a campaign to restore facades and monuments and to adapt dividing walls, called Barcelona posa't guapa (Barcelona make yourself pretty) (1986-1992), directed by Josep Emili Hernández-Cros, from the Heritage area of the City Council.[229]
The celebration of the Games was a challenge for the urban planning of the city, and was a platform for a determined strategic urban planning action, with a perfect harmony between social and economic agents, which led to a new projection of the city both nationally and internationally, and led to talk of a "Barcelona model" as an integrative project of urban reform that was exportable to other cities.[203]
The last years of the century were marked by the search for a more sustainable urban planning based on ecological criteria. This new awareness was reflected in the search for public spaces adapted to the environment and designed for the residents, with special emphasis on community facilities and services. These criteria were defined in particular at the Sustainable Barcelona Civic Forum, held in 1998.[230] One of the main achievements during these years in the interests of sustainability has been the commitment to the bicycle as a more environmentally friendly means of transport: in 1993 the first bicycle path was installed on Avinguda Diagonal, on a 3 km stretch;[231] since then the space allocated to bicycles has not stopped increasing, the use of which has also been favored by the creation in 2007 of a municipal bicycle rental company (Bicing), with several stopping points throughout the city.[232]
The turn of the century also saw an increase in multi-municipal projects, especially in terms of infrastructure and transport, such as the expansion of the port and the airport, the route of the AVE and the Plan for public transport, or the projects for the rehabilitation of the Llobregat and Besós deltas.[233] The Pla Director d'Infraestructures (Infrastructure Master Plan) (PDI) marked the expansion and improvement of public transport, with a Metro network covering the entire metropolitan area, the reintroduction of the tramway at both ends of the Diagonal (Baix Llobregat and Besòs), and the improvement of the bus network.[234]
21st Century
[edit]
With the turn of the century, the city continued to focus on innovation and design as projects for the future, together with the use of new technologies and a commitment to environmental sustainability. In 2000, the Urban Strategies Advisory Council was created to assist the City Council in urban planning and strategic decision making for the city and its surroundings. Initially it was composed of Oriol Bohigas, Dominique Perrault, Richard Rogers, Ramon Folch, Jordi Nadal and Antoni Marí.[120]
One of the first urban development projects of the new millennium was the creation of the 22@ district, thanks to a modification of the General Metropolitan Plan in 2000. Its objective is the reformulation of the industrial land in the El Poblenou neighborhood, a traditionally industrial sector that fell into decline at the end of the 20th century due to the relocation of most companies to land outside the city. The preservation of the productive business fabric of the area was then promoted, focusing on companies dedicated to new technologies, in line with the private sector and the day-to-day activities of the area. The area of action is 115 ha, which made it one of the areas of greatest urban renewal in Europe at the beginning of the 21st century.[235]

One of the most outstanding events of the new millennium was the celebration of the 2004 Universal Forum of Cultures, which led to new urban changes in the city: the entire Besòs area, until then populated by old disused factories, was recovered, the entire Poblenou neighborhood was regenerated and the new Diagonal Mar neighborhood was built, while the city was provided with new parks and spaces for the leisure of the citizens.[236] The site was designed by Elías Torres and José Antonio Martínez Lapeña, with a 16-hectare multipurpose esplanade culminating at one end with a large photovoltaic panel, which became one of the emblems of the event.[237]
The urban planning of the new millennium has reinforced the polynuclear grid structure promoted since the 1990s, which has favored the emergence of new urban centers such as the Fòrum, 22@ and La Sagrera.[238] Currently the Plaça de les Glòries Catalanes is being remodeled, an important road axis where the undergrounding of automobile traffic is planned and the recovery of the land for public use.[239]

Communications have improved with the arrival of the high-speed train, which links the Catalan capital with Madrid and Paris; the Mediterranean Corridor, a strategic transport line between the peninsula and the European continent, is in the project. The port and El Prat airport have also been expanded, with the aim of making Barcelona the logistics hub of southern Europe. The metro network has been expanded, with the extension of several lines (3 and 5), and the creation of some new ones (9, 10 and 11), some of them fully automated. In 2012, an orthogonal rearrangement of the bus network was initiated, to create a bus rapid transit network.[240] The construction of a fourth ring road is also planned to improve communications in the metropolitan area,[241] as well as the connection between the Baix Llobregat and Besòs streetcars through Avinguda Diagonal.[242]
In recent years, numerous infrastructures have been installed in the city to facilitate pedestrian transit in high and inaccessible areas, mainly elevators and escalators. A clear example is the neighborhood of El Carmel, where in 2005 there was also a subsidence due to the extension works of line 5 of the subway, which caused the demolition of several buildings and the relocation of hundreds of neighbors.[243] As a result, the Generalitat declared El Carmel as an Àrea Extraordinària de Rehabilitació Integral (Extraordinary Area of Integral Rehabilitation) (AERI), with a program of intervention and promotion of public works, rehabilitation of buildings and improvement of public facilities.[244]
In terms of green spaces, the most recent projects include: the Central Park of Nou Barris (1997-2007), by Carme Fiol and Andreu Arriola, which in 2007 received the International Urban Landscape Award architecture prize in Frankfurt (Germany);[245] the Diagonal Mar Park (1999-2002), by Enric Miralles and Benedetta Tagliabue, a park of modern design where the presence of water stands out;[246] and the Poblenou Center Park (2008), by Jean Nouvel, divided into various thematic spaces, with an avant-garde design.[247] In 2016, the first large park for dogs was opened, a 700 m² space located in the Nou Barris district, which has a watering hole and play elements for pets.[248]
A new impetus for urban planning began in 2015 with the start of the drafting of the new Pla Director Urbanístic (Urban Master Plan) (PDU) for the Metropolitan Area of Barcelona, scheduled for approval in 2021. The PDU is intended to complement the 1976 General Metropolitan Plan in order to promote the urban and social transformation of the metropolitan area of the Catalan capital, made up of 36 municipalities and 3.5 million inhabitants.[249] The objectives of the new plan include: classifying metropolitan land and establishing criteria for urbanization, establishing building regulations, defining areas for urban transformation and their sustainable development, preserving the environment, respecting forest and agricultural land, and guaranteeing proper mobility of people and transport. According to Ramon Torra, manager of the Barcelona Metropolitan Area, "the PDU has two conceptual objectives: the definition of a metropolitan urban planning model that integrates the current diversity, is ecologically sustainable, economically efficient and socially cohesive; and the methods and tools necessary to carry it out."[250]
In September 2016, a pilot test was initiated for the adaptation of certain sets of city blocks as "superblocks", intermediate spaces between the block and the neighborhood, with restricted vehicle traffic to enhance pedestrian traffic, bicycle circulation and public transport, also gaining spaces for leisure and public facilities. The first test was carried out on a set of nine blocks in Poblenou, where vertical and horizontal signs were changed to mark the area. Traffic is prohibited in a straight line, so that vehicles can only turn at intersections, and is limited to 10 km/h. This leaves free the interior space between blocks, which will be used for public spaces, for which an ideas competition has been organized among architecture students.[251][252]
After this pilot test, a new phase of creating superblocks in the Eixample district began in 2020, with the aim of establishing 42 new green axes and squares within ten years, until 2030. The first axis of action would be Consell de Cent street, where the creation of four new agoras in Rocafort, Borrell, Enric Granados and Girona is planned. According to the forecast, one out of every three streets in the Eixample would give priority to pedestrianization and public and sustainable transport. In contrast to the pilot tests, this time it will be done by axes instead of blocks, with the subsequent creation of new plazas on intersecting axes. Private traffic will be restricted to residents, with a maximum speed of 10 km/h. A budget of 37.8 million euros is foreseen for these actions. Work is scheduled to start in 2022. These changes seek to comply with the objetivos de desarrollo sostenible (Sustainable Development Goals) (SDGs) promoted by the United Nations Organization.[253]
The COVID-19 pandemic that began in December 2019 worldwide led to various urban planning changes in the city, some temporary and others that became permanent. On 14 March 2020 the Spanish government decreed the entry into force of the state of alarm throughout the national territory, with the obligation of citizens to confine themselves to their homes except for essential services.[254] To keep their distance in order to avoid contagion, numerous spaces were set aside for pedestrians to pass through, at the expense of the roadways for vehicular traffic. These areas were marked with colored paint according to their use: blue for bicycles and yellow for pedestrians, together with the use of temporary elements such as bollards and concrete blocks. In many of these spaces, areas were set up as terraces for bars and restaurants, so that customers could drink outdoors, a space more conducive to avoiding contagion. These measures, initially conceived with an ephemeral character, were defined by the councilor of Urbanism, Janet Sanz, as "an example of tactical urbanism."[255] Over time, many of these temporary changes became permanent, such as the spaces enabled for terraces of hospitality establishments, which were regulated in September 2021 by a new ordinance that established new criteria for permanent street furniture, specifically seven new platform models to integrate the elements of such establishments (tables, chairs, umbrellas) in the surrounding space.[256]
See also
[edit]- Architecture of Barcelona
- City Council of Barcelona
- Fountains of Barcelona
- History of Barcelona
- Parks and gardens of Barcelona
- Public art in Barcelona
- Street names in Barcelona
Notes
[edit]- ^ Its full name was Colonia Iulia Augusta Faventia Paterna Barcino. (Barral i Altet et al. 2000, p. 44)
- ^ La Boquería market was built on the site of the Carmelite convent of San José, on La Rambla; the Liceu on the site of the convent of Nostr Senyora de la Bonaventura of the Trinitarians; the Plaça Reial on the site of the convent of the Caputxins of Santa Madrona; the Santa Caterina market replaced the convent of the same name; and the Plaça del Duc de Medinaceli was located on the site left by the convent of Sant Francesc. On the other hand, the Franciscan convent-college of Sant Buenaventura gave way to the Hotel Oriente; and on the convent-college of the Carmelites Calçats de Sant Àngel Màrtir a barracks of the Guardia Urbana de Barcelona was built. (Barral i Altet et al. 2000, p. XIV)
- ^ During the nineteenth century two aggregations took place: in 1836 the Hostafrancs neighborhood, belonging to Sants; and in 1848, some land in Sant Martí de Provençals where the cemetery of Poblenou was located. (AA. VV. 2006, p. 35)
- ^ Examples of this were: the Padellàs House (15th-16th centuries), moved to the Plaça del Rei, where it now houses the Museum of the History of Barcelona; and the Baroque facade of the church of Santa Marta (1737-1747), installed in one of the pavilions of the Hospital de la Santa Creu y Sant Pablou.
- ^ The B road was built partially and in different sectors: the Avinguda de les Drassanes (''Drassanes''), between the Plaça del Portal de la Pau and the Carrer Nova de la Rambla; and the Rambla del Raval, which connects with the previous one with the Carrer de Sant Olegari, and reaches the Carrer del Hospital, from which the plan foresaw a link with the Carrer de Muntaner, a section that has not been carried out. (AA. VV. 2006, p. 155) For its part, the C road was built between the squares Nueva and Antonio Maura, taking advantage of the spaces left by the destruction of several houses in some bombings during the Civil War, and was renamed Avenida de la Catedral in 1942. (AA. VV. 2006, p. 294)
- ^ At the beginning of the 20th century, the influence of Ebenezer Howard's theories on the garden-city, introduced by Cebrià de Montoliu through the magazine Civitas (1911-1919), was received. However, they were not very successful in Barcelona, except in the influence exerted on the construction of cheap houses in the 1920s. (AA. VV. 2006, p. 43)
References
[edit]- ^ Parraguez (2013, p. 16)
- ^ Carreras (1993, p. 29)
- ^ AA. VV. (1996, pp. 118–119)
- ^ AA. VV. (1991, p. 74)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, p. 139)
- ^ AA. VV. (1996, p. 118)
- ^ AA. VV. (1991, p. 62)
- ^ AA. VV. (1991, pp. 65–67)
- ^ AA. VV. (1991, p. 79)
- ^ AA. VV. (1991, pp. 88–90)
- ^ Barral i Altet et al. (2000, p. 66)
- ^ "Statistics of the Continuous Census as of 3 January 2015" (in Spanish). Archived from the original on 15 January 2009. Retrieved 28 January 2016.
- ^ "Ciudad" (in Spanish). Archived from the original on 17 January 2016. Retrieved 14 February 2016.
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, pp. 10–12)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, pp. 167–169)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, p. 120)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, pp. 95–100)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, pp. 125–127)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, pp. 10–13)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, pp. 55–59)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, pp. 249–250)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, pp. 97–101)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, pp. 109–111)
- ^ AA. VV. (1999, pp. 18–20)
- ^ AA. VV. (1999, p. 20)
- ^ AA. VV. (1999, p. 21)
- ^ AA. VV. (1999, p. 23)
- ^ "El término municipal de Barcelona queda dividido en doce distritos" (in Spanish). 21 July 1949. p. 12. Retrieved 15 November 2015.
- ^ AA. VV. (1999, pp. 29–30)
- ^ "División territorial" (in Spanish). Retrieved 19 October 2015.
- ^ AA. VV. (1998, pp. 46–48)
- ^ Busquets (2004, p. 25)
- ^ AA. VV. (1998, pp. 47–48)
- ^ Busquets (2004, pp. 29–30)
- ^ Azcárate Ristori, Pérez Sánchez & Ramírez Domínguez (1983, p. 79)
- ^ AA. VV. (1998, p. 47)
- ^ AA. VV. (1998, p. 61)
- ^ AA. VV. (1991, p. 218)
- ^ AA. VV. (1991, p. 215)
- ^ Busquets (2004, pp. 31–32)
- ^ Busquets (2004, p. 33)
- ^ a b Lecea et al. (2009, p. 29)
- ^ Busquets (2004, p. 34)
- ^ Busquets (2004, pp. 39–40)
- ^ Busquets (2004, pp. 40–42)
- ^ Rubio (2009, p. 19)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, p. 61)
- ^ AA. VV. (1992, p. 39)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, p. 58)
- ^ Roig (1995, pp. 16–17)
- ^ Busquets (2004, p. 46)
- ^ Busquets (2004, pp. 43–46)
- ^ Busquets (2004, pp. 46–47)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, p. 251)
- ^ Roig (1995, pp. 44–45)
- ^ Busquets (2004, pp. 68–71)
- ^ a b c AA. VV. (2006, p. 221)
- ^ AA. VV. (1998, p. 175)
- ^ Garriga (1986, pp. 92–93)
- ^ Roig (1995, p. 75)
- ^ Busquets (2004, p. 79)
- ^ Busquets (2004, p. 80)
- ^ AA. VV. (1998, pp. 197–198)
- ^ Busquets (2004, pp. 80–81)
- ^ AA. VV. (1998, pp. 226–228)
- ^ Roig (1995, pp. 86–87)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, p. 339)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, p. 145)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, p. 249)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, p. 272)
- ^ Busquets (2004, p. 91)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, p. 57)
- ^ Roig (1995, p. 91)
- ^ Triadó (1984, p. 220)
- ^ Villoro & Riudor (1984, p. 31)
- ^ a b AA. VV. (2006, p. 169)
- ^ Lecea et al. (2009, p. 73)
- ^ Roig (1995, pp. 103–105)
- ^ Busquets (2004, p. 101)
- ^ a b c d AA. VV. (2006, p. 206)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, pp. 272–273)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, p. 254)
- ^ Fontbona (1997, pp. 76–77)
- ^ Fontbona (1997, p. 53)
- ^ Fontbona (1997, p. 64)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, p. 106)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, pp. 302–304)
- ^ Roig (1995, p. 112)
- ^ Busquets (2004, p. 119)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, p. 28)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, p. 183)
- ^ Roig (1995, p. 106)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, p. 162)
- ^ Páez de la Cadena (1998, pp. 340–342)
- ^ a b "Història" (in Catalan). 11 February 2015. Retrieved 14 February 2016.
- ^ Villoro & Riudor (1984, pp. 38–41)
- ^ Roig (1995, p. 107)
- ^ Roig (1995, p. 120)
- ^ Roig (1995, pp. 120–121)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, p. 82)
- ^ Roig (1995, p. 121)
- ^ Busquets (2004, pp. 127–131)
- ^ Busquets (2004, p. 146)
- ^ Carreras (1993, p. 73)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, p. 63)
- ^ a b AA. VV. (2006, p. 64)
- ^ Roig (1995, p. 122)
- ^ a b AA. VV. (2006, p. 187)
- ^ Roig (1995, p. 142)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, pp. 161–162)
- ^ Roig (1995, pp. 130–131)
- ^ Garrut (1976, p. 10)
- ^ Busquets (2004, p. 156)
- ^ Garrut (1976, p. 27)
- ^ Busquets (2004, p. 163)
- ^ Roig (1995, p. 143)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, pp. 13–14)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, p. 260)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, p. 40)
- ^ a b AA. VV. (2006, p. 68)
- ^ Busquets (2004, p. 178)
- ^ Lecea et al. (2009, p. 127)
- ^ Busquets (2004, pp. 191–193)
- ^ Busquets (2004, p. 191)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, p. 97)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, p. 98)
- ^ Busquets (2004, pp. 193–194)
- ^ Montaner (2005, p. 65)
- ^ Busquets (2004, p. 198)
- ^ AA. VV. (1998, p. 317)
- ^ Montaner (2005, p. 64)
- ^ Miralles (2008, p. 155)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, p. 304)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, p. 42)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, p. 33)
- ^ Roig (1995, pp. 180–181)
- ^ "Urinari públic. Vespasiana. (1900's - 1910's)" (in Catalan). 21 March 2012. Retrieved 1 November 2015.
- ^ Roig (1995, p. 182)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, p. 115)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, pp. 156–157)
- ^ Roig (1995, p. 172)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, p. 182)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, p. 312)
- ^ AA. VV. (1998, p. 311)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, p. 192)
- ^ AA. VV. (2001, pp. 66–67)
- ^ Busquets (2004, p. 218)
- ^ Grandas (1988, pp. 194–196)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, pp. 234–235)
- ^ "Los Jardines de Laribal" (in Spanish). Retrieved 7 September 2013.
- ^ Grandas (1988, p. 41)
- ^ Grandas (1988, pp. 48–53)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, pp. 304–305)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, p. 178)
- ^ Hernàndez i Cardona (2001, p. 202)
- ^ Roig (1995, p. 209)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, p. 132)
- ^ Busquets (2004, p. 235)
- ^ Busquets (2004, p. 239)
- ^ Busquets (2004, pp. 241–242)
- ^ AA. VV. (1998, p. 319)
- ^ Roig (1995, pp. 210–211)
- ^ Roig (1995, p. 211)
- ^ Mercè Tatjer. "Las intervenciones urbanísticas en el centro histórico de Barcelona: de la Via Laietana a los nuevos programas de rehabilitación" (PDF) (in Spanish). Retrieved 1 October 2015.
- ^ Pla (2007, p. 134)
- ^ "Senyalització vertical de pas de vianants (1930's)" (in Catalan). 5 November 2016. Retrieved 9 November 2016.
- ^ "Senyalització horitzontal de passos de vianants (1930's)" (in Catalan). 8 November 2016. Retrieved 9 November 2016.
- ^ Roig (1995, p. 224)
- ^ Bahamón & Losantos (2007, p. 32)
- ^ Busquets (2004, p. 295)
- ^ Busquets (2004, p. 287)
- ^ Hernàndez i Cardona (2001, pp. 233–234)
- ^ Roig (1995, p. 225)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, p. 273)
- ^ Gausa, Cervelló & Pla (2002, p. K)
- ^ Busquets (2004, p. 317)
- ^ a b AA. VV. (2006, p. 17)
- ^ Busquets (2004, p. 318)
- ^ Roig (1995, p. 238)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, p. 170)
- ^ Busquets (2004, p. 284)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, p. 188)
- ^ Roig (1995, p. 226)
- ^ Gausa, Cervelló & Pla (2002, p. K2)
- ^ Lacuesta & González (1999, p. 52)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, pp. 66–67)
- ^ Lecea et al. (2009, p. 247)
- ^ Lecea et al. (2009, pp. 247–148)
- ^ a b Montaner (2005, p. 115)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, pp. 246–247)
- ^ Busquets (2004, p. 334)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, p. 43)
- ^ Busquets (2004, pp. 334–336)
- ^ Sacristán Arana, Irune. "La ciudad del (no) poder: barraquismo contemporáneo. El caso Barcelona" (PDF) (in Spanish). Retrieved 21 November 2015.
- ^ Gausa, Cervelló & Pla (2002, p. M)
- ^ Busquets (2004, p. 333)
- ^ a b AA. VV. (2006, p. 15)
- ^ AA. VV. (2001, p. 67)
- ^ Añon Feliú & Luengo (2003, pp. 80–85)
- ^ Gabancho (2000, p. 12)
- ^ Lacuesta & González (1999, p. 104)
- ^ Gausa, Cervelló & Pla (2002, p. N)
- ^ a b AA. VV. (2006, p. 207)
- ^ Busquets (2004, pp. 346–347)
- ^ Roig (1995, pp. 258–259)
- ^ Busquets (2004, p. 357)
- ^ Roig (1995, p. 258)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, p. 18)
- ^ Miralles & Sierra (2012, p. 9)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, pp. 75–76)
- ^ Busquets (2004, pp. 358–362)
- ^ Busquets (2004, pp. 364–370)
- ^ Busquets (2004, p. 372)
- ^ Añon Feliú & Luengo (2003, p. 34)
- ^ Miralles & Sierra (2012, p. 191)
- ^ Lacuesta & González (1999, pp. 152–153)
- ^ Gausa, Cervelló & Pla (2002, p. O15)
- ^ Busquets (2004, p. 396)
- ^ Gausa, Cervelló & Pla (2002, p. O16)
- ^ Gausa, Cervelló & Pla (2002, p. O28)
- ^ Añon Feliú & Luengo (2003, pp. 34–35)
- ^ Lacuesta & González (1999, pp. 174–175)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, p. 20)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, p. 80)
- ^ Bahamón & Losantos (2007, p. 47)
- ^ Roig (1995, p. 275)
- ^ Gausa, Cervelló & Pla (2002, p. O1)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, pp. 81–82)
- ^ Lacuesta & González (1999, p. 148)
- ^ Montaner (2005, p. 179)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, p. 177)
- ^ "Bicing" (in Catalan). Retrieved 18 October 2015.
- ^ Busquets (2004, p. 426)
- ^ Busquets (2004, p. 430)
- ^ AA. VV. (2006, p. 16)
- ^ Lecea et al. (2009, pp. 415–416)
- ^ Bahamón & Losantos (2007, p. 75)
- ^ Bahamón & Losantos (2007, p. 34)
- ^ "Barcelona planea ahora un gran parque en la plaza Glòries y que deje de ser nudo viario" (in Spanish). La Vanguardia. 17 January 2012. Retrieved 13 September 2013.
- ^ Márquez Daniel, Carlos (24 May 2012). "Barcelona revoluciona el bus" (in Spanish). Barcelona: El Periódico de Catalunya. Retrieved 27 November 2012.
- ^ "Fomento reanudará las obras del Cuarto Cinturón entre Olesa y Viladecavalls" (in Spanish). La Vanguardia. 18 February 2015. Retrieved 17 November 2015.
- ^ "Colau encarga una docena de estudios para conectar los tranvías por la Diagonal" (in Spanish). 20 minutos. 18 September 2015. Retrieved 17 November 2015.
- ^ Cia, Blanca (16 May 2007). "El hundimiento del metro del Carmel: la peor crisis" (in Spanish). Retrieved 12 March 2011.
- ^ Xalabarder, Maria. "Millora urbana del barri del Carmel (Barcelona) (2006)" (in Catalan). Archived from the original on 23 February 2016. Retrieved 14 February 2016.
- ^ Sánchez Vidiella (2008, p. 134)
- ^ Sánchez Vidiella & Zamora Mola (2011, pp. 322–333)
- ^ Jaume Fabre, Daniel Giralt-Miracle. "Parque del Centro del Poblenou" (in Spanish). Retrieved 14 January 2014.
- ^ "Barcelona abre su primer gran parque para perros en Nou Barris" (in Spanish). El Periódico. Retrieved 3 December 2016.
- ^ Vargas Llamas, Víctor (25 July 2017). "Fricción entre el AMB y la Generalitat por el plan urbanístico metropolitano" (in Spanish). El Periódico. Retrieved 8 February 2019.
- ^ "El futuro Plan Director Urbanístico del Área Metropolitana de Barcelona" (in Spanish). Retrieved 8 February 2019.
- ^ "La 'superilla' del Poblenou ya es una realidad" (in Spanish). El Periódico. Retrieved 5 September 2016.
- ^ "Superilles" (in Spanish). Retrieved 5 September 2016.
- ^ Márquez Daniel, Carlos. "La supermanzana inicia la conquista del Eixample" (in Spanish). El Periódico. Retrieved 11 November 2020.
- ^ "Real Decreto 463/2020, de 14 de marzo, por el que se declara el estado de alarma para la gestión de la situación de crisis sanitaria ocasionada por el COVID-19". Boletín Oficial del Estado (in Spanish) (67): 25390–25400. 14 March 2020.
- ^ Echarri, Miquel. "El código de colores con el que Barcelona ha empezado a sacar los coches de la ciudad" (in Spanish). El País. Retrieved 25 November 2021.
- ^ "Las terrazas ganadas durante la pandemia comienzan a ser definitivas" (in Spanish). Retrieved 25 November 2021.
Bibliography
[edit]- AA. VV. (1991), Història de Barcelona 1. La ciutat antiga (in Catalan), Barcelona: Enciclopèdia catalana, ISBN 84-7739-179-3
- AA. VV. (1992), Història de Barcelona 2. La formació de la Barcelona medieval (in Catalan), Barcelona: Enciclopèdia catalana, ISBN 84-7739-398-2
- AA. VV. (1996), Enciclopèdia Catalana Bàsica (in Catalan), Barcelona: Enciclopèdia catalana
- AA. VV. (1998), Art de Catalunya 3: Urbanisme, arquitectura civil i industrial (in Catalan), Barcelona: Edicions L'isard
- AA. VV. (1999), Els Barris de Barcelona I. Ciutat Vella, L'Eixample (in Catalan), Barcelona: Gran Enciclopèdia Catalana, ISBN 84-412-2768-3
- AA. VV. (2001), Gaudí. Hàbitat, natura i cosmos (in Catalan), Barcelona: Lunwerg, ISBN 84-7782-799-0
- AA. VV. (2006), Enciclopèdia de Barcelona 1. 22@ / Ciutat Meridiana (in Catalan), Barcelona: Gran Enciclopèdia Catalana, ISBN 84-412-1395-X
- AA. VV. (2006), Enciclopèdia de Barcelona 2. Ciutat Vella / Govern Militar (in Catalan), Barcelona: Gran Enciclopèdia Catalana, ISBN 84-412-1396-8
- AA. VV. (2006), Enciclopèdia de Barcelona 3. Gràcia / Petritxol (in Catalan), Barcelona: Gran Enciclopèdia Catalana, ISBN 84-412-1397-6
- AA. VV. (2006), Enciclopèdia de Barcelona 4. Pi / Zurich (in Catalan), Barcelona: Gran Enciclopèdia Catalana, ISBN 84-412-1398-4
- Añon Feliú, Carmen; Luengo, Mónica (2003), Jardines de España (in Spanish), Madrid: Lunwerg, ISBN 84-9785-006-8
- Azcárate Ristori, José María de; Pérez Sánchez, Alfonso Emilio; Ramírez Domínguez, Juan Antonio (1983), Historia del Arte (in Spanish), Madrid: Anaya, ISBN 84-207-1408-9
- Bahamón, Alejandro; Losantos, Àgata (2007), Barcelona. Atlas histórico de arquitectura (in Spanish), Barcelona: Parramón
- Barral i Altet, Xavier; Beseran, Pere; Canalda, Sílvia; Guardià, Marta; Jornet, Núria (2000), Guia del Patrimoni Monumental i Artístic de Catalunya, vol. 1 (in Catalan), Barcelona: Pòrtic, ISBN 84-7306-947-1
- Busquets, Joan (2004), Barcelona. La construcción urbanística de una ciudad compacta (in Spanish), Barcelona: Serbal, ISBN 84-7628-458-6
- Carreras, Carles (1993), Geografia urbana de Barcelona (in Catalan), Barcelona: Oikos-Tau, ISBN 84-281-0802-1
- Fontbona, Francesc (1997), Història de l'art català VI. Del neoclassicisme a la Restauració 1808-1888 (in Catalan), Barcelona: Edicions 62, ISBN 84-297-2064-2
- Gabancho, Patrícia (2000), Guía. Parques y jardines de Barcelona (in Spanish), Barcelona: Ajuntament de Barcelona, Imatge i Producció Editorial, ISBN 84-7609-935-5
- Garriga, Joaquim (1986), Història de l'art català IV. L'època del Renaixement, s. XVI (in Catalan), Barcelona: Edicions 62, ISBN 84-297-2437-0
- Garrut, Josep Maria (1976), L'Exposició Universal de Barcelona de 1888 (in Catalan), Barcelona: Ajuntament de Barcelona, Delegació de Cultura, ISBN 84-500-1498-0
- Gausa, Manuel; Cervelló, Marta; Pla, Maurici (2002), Barcelona: guía de arquitectura moderna 1860-2002 (in Spanish), Barcelona: ACTAR, ISBN 84-89698-47-3
- Grandas, M. Carmen (1988), L'Exposició Internacional de Barcelona de 1929 (in Catalan), Sant Cugat del Vallès: Els llibres de la frontera, ISBN 84-85709-68-3
- Hernàndez i Cardona, Francesc Xavier (2001), Barcelona, Història d'una ciutat (in Catalan), Barcelona: Llibres de l'Índex, ISBN 84-95317-22-2
- Lacuesta, Raquel; González, Antoni (1999), Barcelona, guía de arquitectura 1929-2000 (in Spanish), Barcelona: Gustavo Gili, ISBN 84-252-1801-2
- Lecea, Ignasi de; Fabre, Jaume; Grandas, Carme; Huertas, Josep M.; Remesar, Antoni; Sobrequés, Jaume (2009), Art públic de Barcelona (in Catalan), Barcelona: Ayuntamiento de Barcelona y Àmbit Serveis Editorials, ISBN 978-84-96645-08-0
- Miralles, Roger (2008), Barcelona, arquitectura modernista y noucentista 1888-1929 (in Spanish), Barcelona: Polígrafa, ISBN 978-84-343-1178-7
- Miralles, Roger; Sierra, Pau (2012), Barcelona, arquitectura contemporánea 1979-2012 (in Spanish), Barcelona: Polígrafa, ISBN 978-84-343-1307-1
- Montaner, Josep Maria (2005), Arquitectura contemporània a Catalunya (in Catalan), Barcelona: Edicions 62, ISBN 84-297-5669-8
- Páez de la Cadena, Francisco (1998), Historia de los estilos en jardinería (in Spanish), Madrid: Istmo, ISBN 84-7090-127-3
- Parraguez, Nicolás (2013), Modelo Barcelona de espacio público y diseño urbano. El mobiliario urbano en la cualificación del espacio público (in Spanish), Barcelona: Universitat de Barcelona, ISBN 978-84-7739-179-1
- Pla, Maurici (2007), Catalunya. Guia d'arquitectura moderna 1880-2007 (in Catalan), Sant Lluís (Menorca): Triangle, ISBN 978-84-8478-007-6
- Roig, Josep L. (1995), Historia de Barcelona (in Catalan), Barcelona: Primera Plana S.A., ISBN 84-8130-039-X
- Rubio, Albert (2009), Barcelona, arquitectura antigua (siglos I-XIX) (in Spanish), Barcelona: Polígrafa, ISBN 978-84-343-1212-8
- Sánchez Vidiella, Àlex (2008), Atlas de arquitectura del paisaje (in Spanish), Barcelona: Loft, ISBN 978-84-92463-27-5
- Sánchez Vidiella, Àlex; Zamora Mola, Francesc (2011), Paisatgisme urbà. Barcelona (in Catalan), Barcelona: Ajuntament de Barcelona, ISBN 978-84-9850-355-5
- Triadó, Joan Ramon (1984), Història de l'art català V. L'època del Barroc, s. XVII-XVIII (in Catalan), Barcelona: Edicions 62, ISBN 84-297-2204-1
- Villoro, Joan; Riudor, Lluís (1984), Guia dels espais verds de Barcelona. Aproximació històrica (in Catalan), Barcelona: La Gaia Ciència, ISBN 84-7080-207-0





