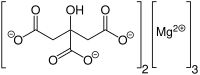
Magnesium citrate (3:2)
This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. (May 2023) |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Trimagnesium bis(2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate) | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.020.086 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H10Mg3O14 | |
| Molar mass | 451.113 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White powder |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Magnesium citrate (3:2) (3 magnesium atoms per 2 citrate molecules), also called trimagnesium dicitrate, trimagnesium citrate, or the ambiguous name magnesium citrate. The substance may come as anhydrous or hydrated salt with varying properties.
The anhydrous salt has good solubilty in water (~10% or more at 25°C) and contains 16.2% elemental magnesium by weight. Its taste is slightly bitter-alkaline.
The hydrated salt may have 3 to 14 molecules of water attached to it and has much lower solubility in water (2% or less at 25°C).[1] This form doesn't have any noticeable taste.
Commercially available are the anhydrous salt, as well as nonahydrate (with 9 molecules of water attached) and 14-hydrate.[2] The nonahydrate form contains 12% elemental magnesium by weight.
References
[edit]- ^ "Anhydrous trimagnesium citrate and its production". Google Patents. Retrieved 15 January 2025.
- ^ "Magnesium Salts from the Manufacturer". Dr. Paul Lohmann®. Retrieved 15 January 2025.
