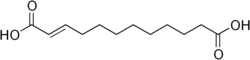
Traumatic acid
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(2E)-Dodec-2-enedioic acid | |
| Other names
(E)-Dodec-2-enedioic acid
Dodec-2-enedioic acid trans-Traumatic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.026.382 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H20O4 | |
| Molar mass | 228.288 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 166 to 167 °C (331 to 333 °F; 439 to 440 K) |
| Boiling point | 150 to 160 °C (302 to 320 °F; 423 to 433 K) at 0.001 mmHg |
| Sparingly soluble | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Traumatic acid is a monounsaturated dicarboxylic acid that occurs naturally in plants. The compound was first isolated from wounded bean plants by American chemists James English Jr. and James Frederick Bonner and Dutch scientist Arie Jan Haagen-Smit in 1939.[2] Traumatic acid is a potent wound healing agent in plants ("wound hormone") that stimulates cell division near a trauma site to form a protective callus and to heal the damaged tissue. It may also act as a growth hormone, especially in inferior plants (e.g. algae). Traumatic acid is biosynthesized in plants by non-enzymatic oxidation of traumatin (12-oxo-trans-10-dodecenoic acid), another wound hormone.
At normal conditions, traumatic acid is a solid, crystalline, water-insoluble substance. The salts and esters of traumatic acid are called traumatates.
Traumatic acid is used as an intermediate in prostaglandin synthesis. It is also a constituent of some pharmaceutical products, such as the odontostomatologic gel Restomyl, due to its mucosal re-epithelialization activity.
