Serotonin–norepinephrine releasing agent
Appearance


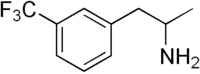
A serotonin–norepinephrine releasing agent (SNRA) is a type of drug which induces the release of serotonin and norepinephrine (and epinephrine) in the body and/or brain.
Only a few SNRAs are known, examples of which include norfenfluramine, (R)-MDMA, MBDB, and MDAI. Fenfluramine produces norfenfluramine as a major active metabolite and hence is an SNRA similarly. It was formerly used as an appetite suppressant for the treatment of obesity. (R)-MDMA, MBDB, and MDAI are entactogens.
A closely related type of drug is a serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI).
Mechanism of action
[edit]See also
[edit]- Monoamine releasing agent
- Serotonin releasing agent
- Norepinephrine releasing agent
- Serotonin–dopamine releasing agent
- Serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine releasing agent
References
[edit]
