RegreSSHion
| CVE identifier(s) | CVE-2024-6387 |
|---|---|
| Date patched | 1 July 2024 |
| Discoverer | Qualys Threat Research Unit (TRU) |
| Affected software | OpenSSH (8.5p1–9.7p1) |
RegreSSHion is a family of security bugs in the OpenSSH software that allows for an attacker to remotely execute code and gain potential root access on a machine running the OpenSSH Server.[1] [2] The vulnerability was discovered by the Qualys Threat Research Unit and was disclosed on July 1, 2024. It affected all prior versions of OpenSSH from 8.5p1 (March 3, 2021) to 9.7p1 (March 11, 2024) and was patched in release 9.8/9.8p1 on July 1, 2024.[3] Qualys reported identifying over 14 million public facing OpenSSH instances potentially vulnerable to the attack. [4] It affects glibc-based Linux systems; Windows and OpenBSD systems are not vulnerable to the attack.
Disclosure
[edit]The vulnerability was publicly disclosed by Qualys on July 1, 2024. Qualys reported disclosing the vulnerability to the OpenSSH developers on May 19, approximately two months prior, and reported notifying OpenWall on June 20, 2024.[5]
Vulnerability
[edit]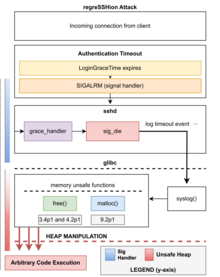
The regreSSHion vulnerability in OpenSSH results from a signal handler race condition in its server component (sshd). This issue is triggered when a client fails to authenticate within the LoginGraceTime period (default 120 seconds). When this timeout occurs, sshd's SIGALRM handler is called asynchronously, invoking functions that are not safe to use in signal handlers, such as syslog(). In versions < 4.4p1, an attacker could exploit the free() function during syslog() within the signal handler. However, in versions from 8.5p1 to 9.7p1, both the free() and malloc() functions are targeted.
This vulnerability is a regression of CVE-2006-5051, reintroduced in OpenSSH 8.5p1 (October 2020) due to the accidental removal of a crucial directive that had mitigated the earlier vulnerability. The directive transformed unsafe calls into a safe _exit(1) call.[5]
Affected versions
[edit]Note: The following versions are referring to the upstream versions. Checking the versions shipped by e.g. linux Distros is not enough to validate it being vulnerable or not as many have backported fixes to older versions. E.g. Debian's OpensSSH version 9.7p1-7[6] and Rocky Linux's OpenSSH version 8.7p1-38.4[7] are also NOT Vulnerable.
| Legend: | Vulnerable | Not Vulnerable |
|---|
| Release | Status | Date |
|---|---|---|
| < 4.4p1 | Vulnerable if not patched against CVE-2006-5051 or CVE-2008-4109 | Before Sep. 27th, 2006 |
| 4.4p1 ≤ OpenSSH < 8.5p1 | Not vulnerable due to presence of mitigation directive | Sep. 27th, 2006 - Mar. 3rd, 2021 |
| 8.5p1 ≤ OpenSSH < 9.8p1 | Vulnerable again because the directive was removed | Mar. 3rd, 2021 - Jul. 1st, 2024 |
| ≥ 9.8p1 | Patched officially | After Jul. 1st, 2024 |
Terminology
[edit]According to Qualys, the bug was named "regreSSHion" as a reference to a regression bug affecting OpenSSH.[3][4]
References
[edit]- ^ "RegreSSHion: Remote Unauthenticated Code Execution Vulnerability in OpenSSH server". July 2024.
- ^ ""RegreSSHion" vulnerability in OpenSSH gives attackers root on Linux". 2 July 2024.
- ^ a b "OpenSSH Release Notes". OpenSSH. Retrieved 16 July 2024.
- ^ a b "regreSSHion: Remote Unauthenticated Code Execution Vulnerability in OpenSSH server". Qualys Community. Qualys. Retrieved 16 July 2024.
- ^ a b c "Qualys Technical Details". Qualys. Retrieved 16 July 2024.
- ^ "Package: openssh | Debian Sources". sources.debian.org. Retrieved 2024-07-26.
- ^ "import openssh-8.7p1-38.el9_4.4 (ebf2263f) · Commits · staging / rpms / openssh · GitLab". GitLab. 2024-07-10. Retrieved 2024-07-26.
