Portal:Pan-Africanism/Selected history/1

The history of Africa begins with the emergence of hominids, archaic humans and – at least 200,000 years ago – anatomically modern humans (Homo sapiens), in East Africa, and continues unbroken into the present as a patchwork of diverse and politically developing nation states. The earliest known recorded history arose in the Kingdom of Kush, and later in Ancient Egypt, the Sahel, the Maghreb and the Horn of Africa.
Following the desertification of the Sahara, North African history became entwined with the Middle East and Southern Europe while the Bantu expansion swept from modern day Cameroon (West Africa) across much of the sub-Saharan continent in waves between around 1000 BC and 0 AD, creating a linguistic commonality across much of the central and Southern continent.
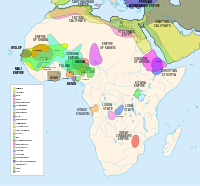
During the Middle Ages, Islam spread west from Arabia to Egypt, crossing the Maghreb and the Sahel. Some notable pre-colonial states and societies in Africa include the Ajuran Empire, D'mt, Adal Sultanate, Warsangali Sultanate, Kingdom of Nri, Nok culture, Mali Empire, Songhai Empire, Benin Empire, Oyo Empire, Ashanti Empire, Ghana Empire, Mossi Kingdoms, Mutapa Empire, Kingdom of Mapungubwe, Kingdom of Sine, Kingdom of Sennar, Kingdom of Saloum, Kingdom of Baol, Kingdom of Cayor, Kingdom of Zimbabwe, Kingdom of Kongo, Empire of Kaabu, Kingdom of Ile Ife, Ancient Carthage, Numidia, Mauretania, and the Aksumite Empire. At its peak, prior to European colonialism, it is estimated that Africa had up to 10,000 different states and autonomous groups with distinct languages and customs.
From the mid-7th century, the Arab slave trade saw Muslim Arabs enslave Africans. Following an armistice between the Rashidun Caliphate and the Kingdom of Makuria after the Second Battle of Dongola in 652 AD, they were transported, along with Asians and Europeans, across the Red Sea, Indian Ocean, and Sahara Desert.
