Portal:Paleontology/DYK
Appearance
Did you know...

- ... that in the first scientific study of fossils in English, William Martin speculated that horn coral (pictured) was a kind of bamboo and said another fossil was not a small crocodile tail?
- ... that the extinct ants Azteca alpha carried larvae of the nematode Formicodiplogaster myrmenema?
- ... that fossils of the extinct snakefly family Mesoraphidiidae are known mainly from the Northern Hemisphere?
- ... that Acteosaurus tommasinii, a species of aquatic lizard from the upper Cretaceous is similar to mosasauroids and modern snakes?
- ... that the last common ancestor of bilaterian animals has been reconstructed as a tiny worm with a combined mouth and anus?

- ... that the extinct Eocene butterfly Prodryas persephone (pictured) from the Florissant Fossil Beds is the best preserved fossil lepidopteran discovered to date?
- ...that despite being known from many specimens, the fossil Fuxianhuia remains one of the most controversial Cambrian arthropods?
- ... that paleobotanist Shya Chitaley named an extinct plant species for Cleveland's bicentennial and also had an extinct plant species named for her?
- ... that Araneagryllus is named from a combination of the Latin aranea meaning "spider" and gryllus meaning "cricket"?
- ... that fossil specimens of the extinct scorpionfly family Dinopanorpidae, which includes Dinopanorpa and Dinokanaga, sometimes have preserved dark with light to clear color patterning?

- ... that the extinct ant Zigrasimecia tonsora (pictured) is named from the Latin words "tonsor" meaning barber and "oris" meaning mouth?
- ...that the fossil of Ichthyornis (pictured) discovered by Benjamin Franklin Mudge was the first bird recognized to possess teeth?
- ... that "color markings", considered rare among fossil crabs, have been found on Avitelmessus?
- ... that Alexander Wetmore assessed the extinct Eonessa anaticula as being an ancient type of duck, possibly due to its fossil's resemblance to the modern Oxyura jamaicensis?
- ... that Peltandra primaeva was the first fossil record for the genus Peltandra when described in 1977?

- ... that it is all but impossible to match up species known by leaves with those known by trunks in the prehistoric cycad-like genus Cycadeoidea?
- ... that the fossil stick insect Eoprephasma was described from two isolated forewings?
- ... that the practice of insect husbandry by ants is at least 15 million years old?
- ... that a fossil of the extinct monitor lizard Saniwa preserves cartilage, scales, and even a wind pipe?
- ...that a fossil specimen of Pelagosaurus was found with the remains of a Leptolepis in its stomach?

- ... that the extinct sweat bee genus Nesagapostemon is known from a single 9.9-millimetre (0.39 in) female specimen?
- ... that unlike its closest living relatives, lemurs and lorisoids, Djebelemur from Eocene Africa probably lacked a toothcomb?
- ... that Krijn is the common name for the first Neanderthal discovered in the Netherlands?
- ... that seeds of the fossil yew genus Diploporus are larger than Taxus seeds and smaller than Torreya seeds?
- ... that the fossil bivalve Emiliodonta shared its name with a coccolithophore for about a decade?

- ... that the discovery of the extinct golden silk orb-weaver species Nephila jurassica extended the fossil record of the genus by 130 million years?
- ... that the fossil ant genus Yantaromyrmex (pictured) is found in four amber deposits in Europe?
- ... that members of the extinct bivalve genus Hemiconcavodonta are unique in the subfamily Concavodontinae in that their teeth point in two directions?
- ... that the shortest fossil termite bug is Termitaradus avitinquilinus?
- ... that Acer castorrivularis is one of five extinct maples from the Eocene Beaver Creek flora in Montana?

- ... that within the United States, dinosaur fossils (example pictured) have been found in Alabama, Alaska, Arizona, Arkansas, California, Colorado, Connecticut, Delaware, Georgia, Idaho, Iowa, Kansas, Louisiana, Maryland, Massachusetts, Minnesota, Mississippi, Missouri, Montana, Nebraska, Nevada, New Jersey, New Mexico, New York, North Carolina, North Dakota, Oklahoma, Oregon, Pennsylvania, South Carolina, South Dakota, Tennessee, Texas, Utah, Virginia, Washington, D.C., and Wyoming, but not in Florida, Hawaii, Illinois, Indiana, Kentucky, Maine, Michigan, New Hampshire, Ohio, Rhode Island, Vermont, Washington, West Virginia, or Wisconsin?
- ... that Ekgmowechashala was the only North American genus of primate during the Late Oligocene?
- ... that lice from mummified guinea pigs and mites preserved in amber while feeding on spiders have provided evidence for researchers in the field of paleoparasitology?

- ... that in addition to some isolated teeth and a jaw fragment, the Mesozoic mammals of Madagascar include the most complete mammalian skeleton known from the Mesozoic of Gondwana?
- ... that the extinct Neocorynura electra, found in Dominican amber, is the only known species of Neocorynura "sweat bee" from the Greater Antilles?
- ... that the fossil sawfly species Eriocampa tulameenensis was found along the Canadian Pacific rail line near Princeton, British Columbia?
- ... that a single spoon-shaped lower jaw belonging to the goniopholidid crocodyliform Sunosuchus is the most well preserved fossil found from the Phu Kradung Formation in Thailand?
- ... that although it was first classified as a reptile, the extinct genus Batropetes (restoration pictured) is now known to be a microsaur amphibian?

- ... that Mary Buckland, a scientific illustrator, took a year-long geological tour as a honeymoon with her husband William Buckland?
- ... that the extinct ant Agroecomyrmex duisburgi (head pictured) was first described in 1868?
- ... that the entire Arostropsis weevil genus is known from only one specimen, which is 45 million years old?
- ... that over the course of the history of stegosaur research, their iconic back plates have been thought to function as armor plating, to regulate body temperature, or to attract mates?
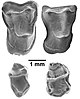
- ... that Mesotherium ("middle beast") (skull pictured) was so named because its discoverer believed it was an intermediate between rodents and pachyderms?

- ...that Mauisaurus was the largest plesiosaur to roam New Zealand waters and that it gets its name from the Māori god Maui?
- ... that Jaggermeryx naida was named in honor of Mick Jagger due to its large, sensitive lips?
- ... that Dactylosaurus lived in the Middle Triassic period during the Anisian faunal stage of central Europe?
- ... that Bambolinetta was probably the only duck species to propel itself underwater with its wings, like a penguin?
- ...that the prehistoric marine reptile Excalibosaurus (pictured) was named after King Arthur's sword because of the sword-like appearance of its upper jaw?

- ... that the extinct ant Anochetus lucidus is named for its shiny exoskeleton?
- ... that the recently described extinct penguin Inkayacu from the Eocene of Peru is postulated to have had gray and reddish brown feathers, unlike the black and white feathers of living penguins?
- ... that Ocepeia (pictured), a 60-million-year-old afrotherian mammal, is named after a Moroccan mining company?
- ...that although related to modern filter feeding baleen whales, the recently discovered prehistoric whale Janjucetus had large serrated teeth implying that it fed on large fish or even sharks?
- ... that seeds of the extinct tree Eucommia montana are found from British Columbia to Colorado?

- ... that paleontologists have discovered the fossilized eggs of cephalopods, fishes, and reptiles, with some dinosaur eggs (pictured) being preserved with pathological shell deformities?
- ... that Electrinocellia peculiaris is named for the Latin "electrum" meaning amber, "Inocellia", the type genus for Inocelliidae, and "peculiaris" for the enigmatic nature of the species?
- ... that Adolf Carl Noé challenged disbelief in the possibility of North American coal balls (example pictured) by presenting a wheelbarrow full of them?
- ... that the extinct New Zealand Musk Duck was becoming more sedentary than its closest relative, the Australian Musk Duck?
- ... that the Cretaceous Malagasy mammal Lavanify is most closely related to a species from India?

- ... that microbial mats increase our understanding of evolution by helping to preserve soft-bodied organisms and soft parts of hard-shelled animals?
- ... that the fossil bee Anthophorula persephone is named for a Greek goddess?
- ...that the discovery of Icadyptes salasi, a prehistoric five-foot-tall penguin in Peru, has caused scientists to reconsider the timeline of penguin evolution?
- ... that the Cretaceous snakefly Necroraphidia arcuata takes its name, in part, from the Latin word for "bent" and the Greek word for "dead"?
- ... that the fossil maple Acer taurocursum is named for its type locality, the "Bull Run flora"?

- ... that the extinct ant Aphaenogaster sommerfeldti was first described in 1868?
- ... that the late Miocene whale Joumocetus shimizui is the third oldest Cetotheriid known?
- ... that paleontologist Gerta Keller theorizes that dinosaurs did not become extinct until 300,000 years after the Chicxulub meteor, though she agrees that "I'm sure the day after, they had a headache"?
- ... that a petroleum geologist named William Warren Orcutt began collecting fossils from the La Brea Tar Pits in 1901, bringing the site to the attention of the scientific community?
- ... that the extinct maple Acer ivanofense is known from four Alaskan fossils?

- ... that one species of the extinct Eocene bulldog ant Ypresiomyrma reached up to 25 millimetres (0.98 in) in length?
- ... that the discovery of the fossil of Shenshou, a squirrel-like early mammal from the Tiaojishan Formation, pushed the origin of mammals back to the Late Triassic, 220 million to 200 million years ago?
- ... that Gustava Aigner made the first discovery of graptolites in the northern greywacke zone of the Alps, with her former fellow student, Ida Peltzmann, who named two species for her?
- ... that the extinct sumac Rhus rooseae was described from fossils over 35 million years old?
- ... that the clawless lobster Tricarina is known from a single fossil, obtained from an oil well 3,852 m (12,638 ft) below ground in western Iran?

- ... that the parareptile Eunotosaurus (restoration pictured) was once widely accepted as a transitional form between turtles and their prehistoric ancestors?
- ... that the extinct incense-cedar Calocedrus huashanensis is one of only three conifers found in the Ningming Formation?
- ...that corals, graptolites, brachiopods and trilobites are frequently used as index fossils?
- ... that the discovery of Babakotia radofilai, an extinct species of sloth lemur, helped to resolve the relationship between the indriids, sloth lemurs, and monkey lemurs?
- ... that researchers have identified the pictured life form which no longer lives on this planet?

- ... that multiple Leptocleidus skeletons have been found preserved as gemstone quality opal over the course of the history of plesiosaur research?
- ... that the ant Aphaenogaster avita was described from a fossil found in 1969?
- ... that the early Eocene maple species Acer douglasense is the second-oldest maple known from Alaska?
- ... that the extinct trapdoor spiders Baltocteniza and Electrocteniza were both identified from specimens in Baltic amber?
- ... that the Qaisracetus, a genus of extinct early whales, was named after a tribe in Pakistan?

- ... that the Late Eocene marine Hoko River Formation is noted for producing crab, gastropod, cephalopod, and wood fossils?
- ... that the extinct ant Acanthognathus poinari had jaws like its modern relatives?
- ... that the extinct Gigantoproductus giganteus was the largest known species of brachiopod?
- ... that the extinct ant Attopsis was fossilized in what may have been a lagoon?
- ... that the Klondike Mountain Formation has fossil hot springs and is a lagerstätten?

- ...that the prehistoric mammal Yanoconodon (pictured) was a Eutriconodont, a group of early, ancestral mammals that in some cases, grew so big they were able to eat small dinosaurs?
- ... that the Ordovician age bivalve Villicumia has overlapping teeth seen in few other bivalves?
- ... that the cretaceous subfamily Sphecomyrminae has not been included in several recent phylogenetic studies of the ant family?
- ... that the type specimen of the extinct bulldog ant Macabeemyrma ovata is the fossilized remains of an adult queen preserved in shale?
- ... that Rugosodon eurasiaticus is the oldest known species of multituberculata, the most successful lineage of mammals in history?
- ... that dental similarities in Afrotarsius, an African fossil primate, and Afrasia, a newly described fossil primate from Myanmar, add support to the hypothesis that simians first evolved in Asia?
- ... that the Mojokerto child was so unexpectedly old that it was discussed in a Time Magazine cover story?
- ... that Archaeoindris (pictured), a recently extinct giant lemur from Madagascar, was the largest known lemur, comparable in size to a male gorilla?
- ... that four-eyed harvestmen known as Tetrophthalmi once roamed the Earth?
- ... that the fossil ant Apterostigma eowilsoni had good stereoscopic vision but poor side vision?

- ... that the many examples of extinct 48-million year old bat genus Palaeochiropteryx (life restoration pictured) found in the Messel lake may have drowned after being rendered unconscious in flight by poisonous volcanic gases?
- ... that fossils of the temnospondyl amphibian Kourerpeton were notoriously discovered in the window of a barber's shop in Arizona?
- ... that the extinct snakefly Agulla protomaculata is the only snakefly described from the Green River Formation?
- ... that the extinct mason bee species Anthidium exhumatum and Anthidium scudderi are known from the Eocene Florissant Formation in Colorado?
- ... that fossil collectors often call Polyptychoceras vancouverensis the "paperclip ammonite" or the "candy cane", due to its shape?

- ... that members of the extinct bivalve family Bakevelliidae have shells made from rectangular calcium prisms and mother of pearl?
- ... that the extinct arum family plants Petrocardium and Montrichardia aquatica are known only from the Paleocene Cerrejón Formation rainforest in Colombia?
- ... that the Early Permian microsaur Rhynchonkos (pictured) shares many similarities with Eocaecilia, and may be an ancestor of caecilians?
- ...that Fossil Cycad National Monument, established in South Dakota in 1922, was withdrawn as a national monument in 1956 because all of the visible fossils had been stolen?
- ... that before modern paleontology came about, fossils of Encrinus went by a number of names in Germany, including "sun wheels", "Saint Boniface's pennies", and "witches' money"?

- ... that the extinct snakefly Amarantoraphidia ventolina is named for air beings of the Cantabrian mythologies?
- ... that the extinct Jamaican Flightless Ibis developed unique club-like wings that could be used as a flail?
- ... that over 200 fossils of Aphaenogaster mayri were known when the species was described in 1930?
- ... that the extinct Argentinian bivalve Cuyopsis symmetricus was named for the symmetry of its rectangular shells?
- ... that Andiva (fossil pictured), an enigmatic animal that lived 555 millions of years ago, perhaps had a convex carapace?
- ...that Ornatifilum is likely to be the oldest known fossil fungus?
- ... that Carnufex is an extinct relative of crocodiles that lived 231 million years ago in North Carolina?
- ...that Megazostrodon (pictured) is widely accepted as being one of the first mammals to have appeared on Earth?
- ...that Lantian Man, who was discovered in China in 1963, preceded Peking Man by several hundred thousand years?
- ... that the type specimen of Scolosaurus seriously injured its discoverer, who was excavating it when it fell on him?

- ...that the extinct crocodile-like Prionosuchus is the largest amphibian known to have existed?
- ...that the Choristodera are extinct reptiles that lived during the time of the dinosaurs and have a skull structure similar to that of the modern day Gharial?
- ... that the extinct plant species Eucommia jeffersonensis and Eucommia rolandii were both described from fossils in 1997?
- ... that the extinct snakefly Alavaraphidia is known from a single female trapped in amber (pictured)?
- ... that the extinct maple section Torada is only known from the three Eocene species A. stonebergae, A. toradense, and A. washingtonense?

- ... that the shrimp-like 510-million-year-old arthropod Waptia (artist's restoration pictured) was named after two mountains?
- ... that the early dinosaur-like animal Lagerpeton was only 70 cm (28 in) long?
- ... that the extinct monitor lizard Ovoo gurvel has "mystery bones" in its skull?
- ... that the extinct termite bug Termitaradus dominicanus is divided into fourteen brown lobes?
- ... that the extinct arachnid Attercopus was once considered as the world's oldest spider?

- ... that the extinct termite Prostylotermes is known from a female, male, and two eggs?
- ... that Archaeomarasmius, Aureofungus, Coprinites, Palaeoagaracites, and Protomycena are the only five genera of agaric mushrooms known from the fossil record?
- ... that the extinct, Miocene age, maple Acer browni ranged from southern Oregon to the north shore of the Haida Gwaii?
- ... that the extinct sweat bee Augochlora leptoloba is known from a single specimen now in a private collection in Turin, Italy?
- ... that Appianoporites, Margaretbarromyces, and Quatsinoporites are all fossil fungi from Vancouver Island, British Columbia?

- ... that the extinct witchalder Fothergilla malloryi (pictured) is the oldest confirmed member of the genus Fothergilla?
- ... that the flat-headed crocodilian relative Aegisuchus had a circular projection on top of its skull that may have served as an eyespot in mating displays?
- ... that the early Oligocene maple, Acer ashwilli, is known from only eight places in Oregon?
- ... that the extinct Eocene parasitic wasp Brevivulva electroma (pictured) was named from the Greek words meaning "short amber wrapper"?
- ... that the distinct fauna of the Kirtlandian includes the dinosaur Pentaceratops sternbergii?

- ... that Leurospondylus ultimus was so named as it was originally thought to be the last occurrence of a plesiosaur?
- ... that the leaves of two species of the fossil plant genus Banksieaeformis resemble those of the living Banksia serrata?
- ... that the extinct Actinidia oregonensis was the first kiwi relative described from North America?
- ... that the extinct rove beetle genus Ektatotricha is known from 15 beetles trapped in Cretaceous amber from Myanmar?
- ... that UA 8699, a broken molar from the Cretaceous of Madagascar, may be the only Mesozoic marsupial from the southern continents?
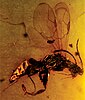
- ... that the wasp Deinodryinus velteni (pictured) is one of only three Deinodryinus species described from the fossil record?
- ... that the extinct snakefly genera Lebanoraphidia and Iberoraphidia are both named for the regions they were found in?
- ... that Canadian paleontologist Scott D. Sampson hosted the four episode nature documentary series Dinosaur Planet for the Discovery Channel in 2003?
- ...that the type specimen of Dromicosuchus had damage to its jaw and neck that may have been inflicted by the teeth of the large carnivore it was found underneath?
- ... that unlike living rorqual whales, the late Miocene genus Plesiobalaenoptera was probably not capable of ram feeding?

- ... that highlights from the history of troodontid research include the discovery that troodontids (example pictured) were among the brainiest dinosaurs?
- ... that a fossil of the Middle Permian therocephalian Blattoidealestes represents the oldest record of multicuspid teeth among theriodonts, the ancestors of mammals?
- ...that Archaeopotamus is the oldest well-identified genus of hippos, having lived 7.5 million to 1.8 million years ago?
- ...that the enigmatic Ediacaran biota (fossil pictured) have been classified into every major group of lifeforms, including their own kingdom?
- ... that the extinct lacewing Ainigmapsychops takes part of its name from the Greek word for enigma?

- ... that to support his claim that Java Man was the "missing link", discoverer Eugène Dubois argued that it looked like a "giant gibbon"?
- ... that the extinct pine Pinus driftwoodensis was first described from a permineralized conifer cone in chert?
- ... that the fossil mantidfly Dicromantispa moronei was first described from a single specimen in a private collection?
- ... that unlike other Eocene crocodilians found in Zamora, Spain, the extinct genus Duerosuchus was primarily a fish eater?
- ... that Megalictis ferox, a species of extinct predatory mustelid, resembled a modern wolverine but with three times the body mass?

- ...that the Burgsvik beds, a geological formation exposed on Gotland, Sweden, contain the only fossil euglenid ever discovered?
- ...that the extinct species of Edaphodon, a type of rabbitfish related to the shark, grazed along the bottom of the ocean like land-dwelling herbivores do now?
- ... that the Paleocene Alaskan maple Acer alaskense was described from a fossil leaf that may be atypical for the species?
- ... that Termitaradus protera was the first termite bug found in amber?
- ... that Hyptia deansi is the only fossil ensign wasp described from Mexican amber?

- ... that the largest known ovules produced by any non-flowering seed-plant came from the Medullosales (fossilized leaves pictured), an order of extinct seed ferns?
- ... that the Late Cretaceous crocodile relative Simosuchus (restoration pictured) ate plants and had a pug-nosed snout?
- ...that though no fossil grasses have been discovered, the earliest-known grassland ecosystem, the 30+ million-year-old Tinguiririca fauna of Chile, can be detected through the grazers' teeth?
- ... that the extinct hangingfly genera Formosibittacus, Jurahylobittacus, and Mongolbittacus are only known from the Middle Jurassic of China?
- ... that the extinct legume Hymenaea allendis is the second Hymenaea species described from Mexican amber?

- ... that unlike living species of the genus, the extinct ant Gesomyrmex pulcher is from Germany rather than Asia?
- ... that the earliest known account of Lebanese fossils is attributed to Herodotus?
- ... that the Makauwahi Cave has been described as "...maybe the richest fossil site in the Hawaiian Islands, perhaps in the entire Pacific Island region"?
- ... that Tzaganosuchus fossils were first discovered during a joint paleontological expedition by the Soviet Union and Mongolia?
- ... that the extinct earwig Toxolabis was preserved with two earwig nymphs?

- ...that the extinct marine reptile Kaganaias is the only ancient aquatic scaled reptile to be found in Asia?
- ... that the extinct maple Acer dettermani is only known from the flank of a volcano?
- ... that the only known specimen of the extinct spider Palaeoperenethis is in the Royal Ontario Museum?
- ... that the first four specimens of the fossil earwig Zigrasolabis are all preserved in the same piece of amber?
- ... that a small fetus is preserved in the holotype fossil of the extinct stingray Asterotrygon?

- ...that the Stag-moose (Cervalces scotti) went extinct about 11,500 years ago, part of a mass extinction of large North American mammals toward the end of the most recent ice age?
- ... that the only known specimen of the extinct planthopper Glisachaemus jonasdamzeni is preserved with a parasitic mite?
- ... that the plesiosaur Bathyspondylus was first described in 1982 from a specimen collected in 1774?
- ... that the dinosaur Wendiceratops (pictured) was named for fossil hunter Wendy Sloboda, who then had it tattooed on her arm in celebration?
- ... that the extinct Miocene hickory Carya washingtonensis is known from over 50 nuts found as a rodent cache within a petrified stump?

- ... that the bioluminescent crustacean Vargula hilgendorfii, named after Franz Hilgendorf, was used as a light source by Japanese soldiers in World War II?
- ... that unusual archosauromorph reptile Teraterpeton from the Late Triassic of Nova Scotia had nostril openings in its skull that were longer than its eye sockets?
- ... that Stephen Jay Gould once called Donald Prothero "the best punctuated equilibrium researcher on the West Coast"?
- ... that the only known specimen of the early crocodile relative Stegomosuchus was kept in the discoverer's yard for several years before being given over for study?
- ...that the discovery of the dinosauromorph Dromomeron, from the Late Triassic of New Mexico, indicates that dinosaurs did not rapidly replace their close relatives?

- ... that the first described fossil of Anochetus dubius is surrounded by a brownish bacterial growth?
- ... that amber fossils of ants carrying the extinct mealybug genus Electromyrmococcus represent the oldest record of symbiosis between mealybugs and Acropyga ants?
- ... that Aquila bullockensis, an extinct species of bird, is the oldest known true eagle from Australia?
- ... that the extinct hazel species Corylus johnsonii (fruit pictured) resembles three modern hazels found in China?
- ... that the recently discovered Eocypselus rowei may be ancestral to both hummingbirds and swifts?

- ... that the Cretaceous terrestrial crocodilian Araripesuchus is known from five distinct species, two from Africa and the other three from South America?
- ... that Plesiopithecus, a fossil primate from the late Eocene in Egypt, closely resembles the aye-aye of Madagascar and raises questions about the evolutionary history of lemurs?
- ... that the extinct moth Epiborkhausenites is noted for having very similar color patterning to the living species Tubuliferola josephinae and Hofmannophila pseudospretella?
- ... that the extinct amphibian Cryobatrachus (restoration pictured) was discovered in the Transantarctic Mountains of Antarctica?
- ... that fossils from the Paleocene-age Cerrejón Formation in Colombia are the earliest record of Neotropical rainforests?

- ... that the extinct sandfly species Lutzomyia adiketis is host to the Paleoleishmania species P. neotropicum?
- ... that Xylolaemus sakhnovi was the first of its genus described from the fossil record?
- ... that the type specimen of the extinct tortoise beetle Denaeaspis is only 6.04 millimetres (0.238 in) long?
- ... that the type specimen of the extinct whip scorpion Graeophonus carbonarius was originally identified as a species of dragonfly?
- ... that paleoecologist Heinz Lowenstam discovered that living organisms can produce magnetite within their bodies?

- ... that the extinct crocodilian Arenysuchus was part of the first evolutionary radiation of crocodyloids?
- ... that Kairuku grebneffi, an extinct species of penguin, was nearly 1.5 metres (4.9 ft) long and weighed 50% more than modern Emperor Penguins?
- ... that highlights from the history of ceratopsian research include the discovery of the iconic Triceratops (skeletal mount pictured), spike-frilled Styracosaurus, and vast bonebeds preserving thousands of Centrosaurus?
- ... that Frederic Brewster Loomis uncovered vertebrate fossils that were still exhibited at Amherst College's Beneski Museum of Natural History almost a century later?
- ... that the fossil yew Taxus masonii was described from fifteen fossils collected from 1942 to 1989?

- ... that biological anthropologist David Tab Rasmussen enjoyed working in the Neotropics because it allowed him to study both primates and birds, his two favorite subjects?
- ...that naturalist Remington Kellogg used his time serving in France during World War I to collect specimens for universities in the United States?
- ... that the extinct buthid scorpion Uintascorpio was first placed in the family Vaejovidae?
- ...that Cetartiodactyla is a hypothesis based on DNA that suggests whales and hippos are related?
- ... that the fossil maple species Acer kenaicum was suggested to be an ancestor of silver maples?

- ...that Archiinocellia is noted to be the only snakefly fossil genus from British Columbia and one of only two from Canada?
- ... that the extinct wasps Dryinus grimaldii and Dryinus rasnitsyni are distinguishable by the modified claws on their front legs?
- ... that the cat gap is a period in the fossil record (cat illustration pictured) of approximately 25 to 17 million years ago in which there were few cats or cat-like species?
- ... that the extinct horsetail Equisetum thermale grew in Jurassic hot springs?
- ... that Lepidotus was a genus of prehistoric fish that existed from the Late Triassic (Rhaetic) to the middle Cretaceous (Cenomanian)?

- ... that the extinct ant Anochetus corayi was the first Anochetus species described from a fossil?
- ... that the extinct fir species Abies milleri, known from Early Eocene fossils (pictured) found in Ferry County, Washington, is considered the oldest confirmed record for the fir genus?
- ... that the stems in the pseudo-trunk of the extinct fern Tempskya decayed as the plant matured, leaving a layer of adventitious roots behind?
- ... that this month celebrates the 100th anniversary of the discovery of the main Burgess Shale locality?
- ... that the extinct lacewing Undulopsychopsis (fossil pictured) is the only psychopsid to have wavy wings?

- ... that major discoveries in the history of ceratosaur research include horned predators like Ceratosaurus (pictured), Majungasaurus, and Carnotaurus, as well as a bonebed of the projecting-toothed Masiakasaurus?
- ... that Yongjiacaris represents the second report of freshwater caridean shrimp from the Mesozoic era?
- ... that the extinct rose family member Neviusia dunthornei is one of only three known Neviusia species?
- ...that William King Gregory, a leading authority on vertebrate evolution and the preeminent expert on human dentition, was initially taken in by the Piltdown Man, a hoax which was purported to be an early human?
- ... that as recently as 500 years ago, the island of Madagascar was inhabited by giant lemurs, referred to as subfossil lemurs, that weighed between 10 and 200 kg (22 and 441 lb)?

- ... that the Cretaceous ant Haidomyrmodes mammuthus is named for the similarity between its mandible shape and mammoth tusks?
- ... that the fossil scorpion fly Holcorpa was described in 1878 but the family Holcorpidae not until 1989?
- ... that the possibly extinct wall crab spider species Garcorops jadis was named for C.S. Lewis' Jadis, the White Witch?
- ... that the oldest known member of the mayfly family Neoephemeridae is the Eocene species Neoephemera antiqua?
- ... that Entropezites, Mycetophagites, and Palaeoagaracites present the oldest evidence of fungal parasitism and hyperparasitism by other fungi in the fossil record?

- ... that although the first Callawayasaurus fossil was discovered in 1962, it was not until 1999 that they were recognized as a separate genus?
- ... that Nanoraphidia electroburmica, known from a fossil in amber, is the smallest known snakefly species, living or extinct?
- ... that it may not be possible to determine what ?Oryzomys pliocaenicus is?
- ... that the paleobotanists David P. Penhallow and Chester A. Arnold both published studies on the extinct water-fern Azolla primaeva?
- ... that the name Ginkgo dissecta was first coined in 1974 but not formalized until 2002?

- ... that the broad-fronted moose was probably the largest species of deer that has ever existed?
- ... that the Eocene maple Acer clarnoense is not found in the Clarno Formation even though the species was named after it?
- ... that the extinct Pliocene pine Pinus matthewsii is thought to have been a colonizing tree?
- ... that Ambondro, which lived in Madagascar about 167 million years ago, is the oldest known mammal with modern, tribosphenic molars?
- ... that the Late Triassic archosauromorph Uatchitodon is the earliest known venomous reptile?

- ... that the extinct ant Anochetus ambiguus has a spiny petiole?
- ... that French paleontologist Charles Lamberton scathingly rebutted a theory claiming that some extinct, giant lemurs were aquatic and that one of them was an "arboreal-aquatic acrobat"?
- ... that shartegosuchid crocodyliforms made up an endemic Central Asian Mesozoic fauna that existed after the breakup of Pangaea?
- ... that a new dinosaur (pictured) discovered in North and South Dakota has been nicknamed the "chicken from hell"?
- ... that Manot 1, a skull discovered in the Manot Cave in Israel, provides evidence that modern humans lived side-by-side with Neanderthals?

- ... that the fossil genus Astreptolabis (pictured) is one of four described Burmese amber earwigs?
- ... that Xinjiangtitan is a 32-metre sauropod dinosaur from Xinjiang in China?
- ... that a fossil of the extinct sea scorpion Eurypterus (restoration pictured) was once thought to be a catfish?
- ... that the extinct brown lacewing Cretomerobius is known from both the Cretaceous and Eocene?
- ... that the 45,000-year-old remains of Ust'-Ishim man are the oldest modern human genome to be fully sequenced to date?

- ... that the Devonian stem tetrapod Tinirau clackae, transitional between fish and land vertebrates, was named after the half-human half-fish character Tinirau in Polynesian legend?
- ... that the extinct wasp Deinodryinus areolatus is one of two Deinodryinus species known from Baltic amber?
- ... that the pterosaur genus Carniadactylus was originally classified under the species name Eudimorphodon rosenfeldi?
- ... that Leptofoenus pittfieldae is the only species of Leptofoenus documented from the West Indies and the only member of Leptofoenus in the fossil record?
- ... that the ammonite Hildoceras bifrons (pictured) has been used as an index fossil to help identify the age of rocks?

- ...that the Natural History Museum of Berlin is home to the largest mounted dinosaur in the world, a Brachiosaurus (or Giraffatitan); and the most exquisitely preserved specimen of the earliest known bird, the Archaeopteryx?
- ... that Charles Darwin's final scientific book discussed the formation of mould through the action of earthworms?
- ... that during the MN 4 zone, the saber-toothed cat Prosansanosmilus first appeared in Europe?
- ... that Appianoporites, Margaretbarromyces, and Quatsinoporites are all fossil fungi from Vancouver Island, British Columbia?
- ... that Ororaphidia and Styporaphidia are the oldest snakeflies known from China, dating from the Middle Jurassic?

- ...that although no fossils of the extinct Malagasy Hippopotamus have been dated within the last 1,000 years, villagers in Madagascar described a similar creature still alive as recently as 1976?
- ... that one species of the extinct bivalve Similodonta was found in 108.90 metres (357.3 ft) down a Welsh borehole?
- ... that the hypercarnivorous crocodyliform Stratiotosuchus (pictured) from the Late Cretaceous of Brazil occupied the niche of top predator in the absence of theropod dinosaurs?
- ... that the extinct fly Schwenckfeldina archoica has spines on its genitalia?
- ... that 57 million-year-old Altiatlasius from Morocco may be the oldest fossil primate yet found, despite a molecular estimate that places the last common ancestor of primates at 90 million years ago?

- ... that the king of gore (skull pictured) and the monstrous murderer lived in Utah 80 and 75 million years ago respectively?
- ... that species of the Cambrian bivalve Tuarangia lived near the continents of Baltica and East Gondwana?
- ... that a fossil of Concavodonta described in 1843 has been lost?
- ... that the extinct paddlefish Paleopsephurus was first described from the Cretaceous Hell Creek Formation?
- ... that the Triassic archosaur Poposaurus walked on two legs like some dinosaurs, but was more closely related to crocodiles?

- ... that Decuriasuchus may be the first known archosaur to exhibit group behavior?
- ... that out of about 20,000 Clarno Formation fossils, only 5 were from the extinct dogwood Cornus clarnensis?
- ... that Scottish naturalist Ramsay Heatley Traquair received the Royal Medal of the Royal Society in 1907 for his work on fossil fish?
- ... that the extinct ant Anochetus exstinctus was described from only two of the three fossils known to the species author?
- ... that the extinct Cuban condor Gymnogyps varonai may have fed on ground sloths?

- ...that fossil Thelodont fish (depiction pictured) surprised scientists by showing that stomachs evolved before jaws?
- ... that the identification of azibiids, a type of fossil primate including Azibius, as either strepsirrhine or haplorine weighs heavily on the African or Asian origins of primates?
- ... that a fossil plesiosaur skull named Kimmerosaurus may be the missing head of a Colymbosaurus?
- ... that fossils of the extinct reptile Acallosuchus were found in a cigar box in 1983?
- ... that fossils of the extinct hazelnut relative Coryloides were informally identified as palm nuts first?

- ... that the Miocene maple Acer traini may be the same species as the living Douglas Maple (fruits pictured)?
- ...that the discovery of Lazarussuchus showed that choristoderes, a type of aquatic reptile, had not gone extinct in the Eocene, but persisted for millions of years after?
- ... that the limestone quarries near Ein Yabrud in the Judean Mountains have produced the only fossils for the extinct snakes Pachyrhachis and Haasiophis?
- ...that the discovery of Archaeamphora longicervia, the first known carnivorous plant, suggests that flowering plants should have originated much earlier than previously thought?
- ... that the remains of the armoured dinosaur Europelta were uncovered in a coal mine in Spain in 2011?

- ... that a revolution in burrowing marks the base of the Cambrian period, and is followed by the Cambrian explosion of animal diversity?
- ... that the extinct Chamaecyparis eureka is the oldest confirmed member of the genus Chamaecyparis?
- ... that when first described, the extinct bird Cruschedula was thought to be a "dry-land" penguin?
- ... that Puppigerus, an extinct sea turtle, had a specialized jaw structure which kept it from accidentally inhaling water?
- ...that Kirill Eskov named a genus from the Linyphiidae spider family discovered by him in 1988 after Kikimora, a female spirit in Slavic mythology?

- ... that both Fordilla and Pojetaia, Cambrian members of the extinct bivalve family Fordillidae, are part of the Turkish small shelly fauna?
- ... that, being a descendant of Pliohippus, Astrohippus is not considered to be an ancestor to modern horses?
- ... that the ichnogenus Chondrites (pictured) can be used as an indicator of anoxia in sediments?
- ... that the extinct plant species Eucommia jeffersonensis and Eucommia rolandii were both described from fossils in 1997?
- ... that, when described, the brown lacewing species Wesmaelius mathewesi was the most ancient member of its subfamily?

- ... that the extinct wasp Deinodryinus? aptianus has antennae similar to only two other Deinodryinus species?
- ... that the extinct Miocene age maple Acer smileyi has been classified as closely related to the living Acer nipponicum (pictured)?
- ... that Rhachitomi, a group of temnospondyl amphibians, was established as a clade in 2013?
- ... that the diminutive pterosaur Arcticodactylus from Greenland had a wingspan of only 24 centimetres (9.4 in)?
- ... that the extinct Eocene maple species Acer rousei is a possible ancestor to the vine maple?

- ... that Gerobatrachus is considered to be a missing link that supports the hypothesis offered by cladistics, that frogs and salamanders had a common ancestor?
- ...that Sacisaurus was named for a one-legged Brazilian elf, as the first skeleton was found missing a leg?
- ... that the fossil pelican Pelecanus schreiberi from North Carolina was possibly the largest species of pelican ever?
- ... that among fossils found at Koonwarra, Victoria are those of horseshoe crabs, ginkgo and gnetophytes?
- ... that the fossil ant Azteca eumeces is one of two Azteca species found in Dominican amber?

- ... that the Permian therocephalian Glanosuchus, an early relative of mammals, may have been warm-blooded?
- ... that at least one species of the extinct termites Parastylotermes (fossil pictured) was found in the Calico Mountains?
- ... that Siats, named after a man-eating monster, is the geologically youngest North American allosauroid yet discovered?
- ... that the extinct trilobite Bumastus (artist's rendition pictured) was named after its resemblance to large grapes?
- ... that the sloth lemurs of the genus Mesopropithecus were once thought to be indriids due to the similarities between their skulls and those of living sifakas?

- ... that the Paleocene Ginkgo cranei is the first fossil Ginkgo to be described from Tertiary "seeds"?
- ... that the extinct plant genus Dillhoffia can't be placed into a flowering plant family at this time?
- ... that Jurellana tithonia, dating from the Jurassic, is the earliest known porcelain crab?
- ...that Polar dinosaurs could have walked to Australia, because during the early Cretaceous the continent of Australia was still linked to Antarctica?
- ... that it has been suggested the extinct palm genus Palaeoraphe was restricted to the Greater Antilles?

- ... that Titanoceratops was known from an almost complete skeleton that was assigned to Pentaceratops, and that the two were only distantly related?
- ...that Pachycheilosuchus, an Early Cretaceous crocodile relative, was less than a meter (3.3 ft) long and had an armored neck?
- ... that the moth lacewing Elektrithone is the first member of its family found in Baltic amber?
- ... that the fossil ant Aphaenogaster donisthorpei was once part of the Samuel Hubbard Scudder insect collection?
- ... that although the giant fossa, formerly one of the top carnivores of Madagascar, is thought to be extinct, there is some anecdotal evidence of very large living fossas?

- ... that the ant Aphaenogaster amphioceanica (pictured) is in the same amber fossil as six Pseudarmadillo cristatus woodlice?
- ... that Paleodictyon nodosum made use of a new source of energy not dependent on the Sun?
- ... that Australornis is the first early Paleocene bird fossil discovered from New Zealand that is not a penguin?
- ... that ants of the extinct genus Haidomyrmex could possibly open their mandibles to almost twice their head size?
- ... that with a 150-millimetre (5.9 in) wingspan, Sinomeganeura is small for the Griffenfly family Meganeuridae, known for species with spans over 700 millimetres (28 in)?

- ... that highlights from the history of hadrosaur research include the first dinosaur fossils to be mounted in a museum, the colossal Shantungosaurus, and Maiasaura nesting grounds in Montana?
- ... that the family placement for the fossil moth genus Dominickus was not noticed until entomologist Norman Tindale was looking at pictures of modern moths from Australia?
- ... that the extinct Lotus Nelumbo aureavallis is known from Eocene rocks in western North Dakota?
- ... that, in one study on the aetosaur Redondasuchus, the orientation of a diagram in the paper may have contributed to the misidentification of its holotype as a left scute rather than a right?
- ... that Augustasaurus' name comes from the mountain range of northwestern Nevada, where its fossilized bones were first discovered?

- ... that only one side of the extinct parasitic wasp Neanaperiallus is visible in its sole fossilized specimen?
- ... that the fossil relative of the House Sparrow Passer predomesticus is known only from two upper jaw bones?
- ... that of the three described species in the Eocene bulldog ant genus Avitomyrmex, one species is known only from worker caste individuals?
- ... that the extinct Crocodylus thorbjarnarsoni from the Pliocene and Pleistocene of Kenya was the largest true crocodile and may have eaten early human ancestors?
- ... that historical therizinosaur research misinterpreted these unusual bird-like herbivorous dinosaurs as giant turtles, semiaquatic fish-eaters, and tree-climbing insectivores?

- ... that the fossil horse Scaphohippus became extinct when tectonic barriers between the Great Plains and Great Basin of North America disappeared about 13 million years ago?
- ... that the extinct Phlebotominae sandfly Pintomyia falcaorum is known only from Miocene age Dominican amber found on Hispaniola?
- ... that oviraptorosaurs were thought to be egg-eaters after the discovery of Oviraptor on a nest of presumed Protoceratops eggs, until the nest was recognized as belonging to Oviraptor itself?
- ... that the Paleozoic monoplacophoran Pilina unguis was twice as large as any known living monoplacophoran?
- ... that coal balls are not made of coal?

- ... that Aquilops ("eagle face") is the most ancient definite neoceratopsian discovered in North America?
- ... that the recently described genus Koilamasuchus from the Early Triassic of Argentina is the best-known early archosauriform in South America?
- ... that fossils of Yelovichnus were initially believed to be the feeding trails of other organisms?
- ... that, together with Platychelys, Pleurosternon is one of the few fossil genera with characteristics of both modern turtle suborders?
- ... that the extinct ant Anochetus brevidentatus was the second Anochetus species described from Dominican amber?

- ... that extinct diadectid reptiliomorphs (life restoration pictured) were the first large herbivorous land animals?
- ... that unlike its modern-day relative the gharial, the extinct crocodilian Aktiogavialis lived in saltwater?
- ...that in 1902, 23-year-old British archaeozoologist Dorothea Bate discovered a new species of dwarf elephant in a cave on the island of Cyprus?
- ... that the only close modern relative to the fossil ant Eulithomyrmex is Tatuidris?
- ... that the powerful teeth and jaws of Heliopithecus may have played a key role in the spread of Hominoids from Africa into Eurasia, 17 million years ago?

- ... that the extinct parasitic wasp genus Aspidopleura is known from only two fossils found in Baltic amber?
- ... that the extinct mantidfly Feroseta prisca has bristle-covered pterostigma?
- ...that Jan Czerski (pictured), exiled to Siberia after the January Uprising, became a self-taught scientist and Siberian explorer, thrice decorated with the gold medal by the Russian Geographical Society?
- ... that seeds of the extinct Paleocene pine Pinus peregrinus are most similar to those of the modern red pine and tropical pine?
- ... that the extinct fern Wessiea is known from Miocene fossils found at the "Ho ho" locality in Yakima County, Washington?

- ... that the extinct termite Zophotermes ashoki is named after a "sage of Indian paleontology"?
- ... that the extinct North American Oligocene-age vulture Phasmagyps may be the oldest New World vulture?
- ... that leaves of the fossil maple Acer palaeorufinerve resemble the living redvein maple?
- ... that the extinct planthopper Tainosia quisqueyae was named for the Taíno people and Hispaniola?
- ... that the extinct bivalve subfamily Praenuculinae can be told apart from its sister subfamily by looking at teeth?

- ... that Kulindroplax is the first known mollusk showing an unambiguous combination of exterior shells and a worm-like body?
- ... that the name for the extinct birch family genus Kardiasperma is from the Greek words for "heart" and "seed"?
- ... that the fossil ant genus Archiponera is known from a single pair of fossils described in 1930?
- ... that Algeripithecus, a 46–50 million year old fossil primate, was once crucial for the African origins of simians (monkeys and apes), but now suggests African origins for lemurs and lorisoids?
- ... that at the time of description, the extinct Tilia johnsoni (pictured) was the oldest basswood macrofossil occurrence?

- ... that the extinct Hydriomena? protrita was the first geometer moth to be described from the American fossil record?
- ... that the moth lacewing genus Principiala is known for three, possibly four, fossils?
- ... that the discovery of 189 fossils of the mid-Cambrian Odontogriphus thrust it into the centre of a heated debate about the evolution of molluscs, annelids and brachiopods?
- ... that the paleobotanists David P. Penhallow and Chester A. Arnold both published studies on the extinct water-fern Azolla primaeva?
- ... that fossils of extinct giant cicadas (pictured) were once misidentified as the oldest known butterflies?

- ... that the large prehistoric amphibian Cyclotosaurus had a skull up to 70 cm long?
- ... that the extinct Canadian redwood Metasequoia foxii was described from over 10,000 fossils?
- ... that siltstone deposits have allowed three-dimensional fossils of the extinct mushroom crinoid to be excavated from Indiana?
- ... that highlights from the history of tyrannosaur research include the first carnivorous dinosaur known to walk bipedally, the giant Tyrannosaurus rex, and feathered taxa from China like Yutyrannus?
- ... that the extinct Eocene maple Acer republicense is known from only one fossil seed?
- ... that Aegirocassis is the earliest example of massive filter-feeder animals discovered?
- ... that the extinct ants Azteca alpha carried larvae of the nematode Formicodiplogaster myrmenema?
- ... that small shells of Trigonoconcha are triangular?
- ... that lemurs (pictured) are primates that evolved and diversified on the island of Madagascar after arriving there at least 56 million years ago on a raft of vegetation?
- ... that the fossil ant genus Yantaromyrmex (pictured) is found in four amber deposits in Europe?

- ... that the extinct parasitic wasp Metapelma archetypon is thought to have preyed upon wood-boring beetles?
- ... that blade-like teeth in the extinct mammalian family Ferugliotheriidae may have evolved into molar-like teeth in the Sudamericidae?
- ... that the extinct planthopper Emiliana was described from a single 47 million year old wing?
- ... that Entropezites, Mycetophagites, and Palaeoagaracites present the oldest evidence of fungal parasitism and hyperparasitism by other fungi in the fossil record?
- ... that Obamadon was an extinct lizard that was named after President Barack Obama as a tribute to his "role model of good oral hygiene for the world"?

- ... that wings of the extinct moth lacewing Allorapisma are most similar to a Cretaceous genus from Brazil?
- ... that the rauisuchian Tsylmosuchus is known from strata in Russia that are early Olenekian in age, making it one of the earliest archosaurs?
- ... that malacologist Myra Keen was called the "First Lady of Malacology"?
- ... that the nearest living relatives of Eosacantha, a fossil tortoise beetle from Colorado, are found in Africa, tropical Asia, and Australia?
- ... that when the extinct forester moth Neurosymploca? oligocenica was described, a second fossil was known but unavailable for study?

- ... that the 150-million-year-old ink of the extinct, squid-like Belemnotheutis (artist's rendition pictured) was used to draw a picture that paleontologists called "the ultimate self portrait"?
- ... that Archaeomarasmius, Aureofungus, Coprinites, and Protomycena are the only four genera of agaric mushrooms known from the fossil record?
- ... that although the first two fossils of Indraloris to be found were misidentified as a carnivoran and a loris, it is in fact a member of the extinct adapiform primates?
- ... that the extinct Itilochelys is one of only three known fossil cheloniid sea turtle taxa found in the Volgograd Region?
- ... that fossils of Eucommia constans are the youngest and most southerly examples of Eucommia in North America?
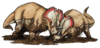
- ... that the Hilda mega-bonebed is Canada's largest dinosaur bonebed, preserving thousands of the horned dinosaur Centrosaurus apertus across an area of 2.3 square kilometers?
- ... that the oldest association between Trypanosoma, which causes Chagas disease, and its vector, the assassin bug Triatoma, is found in Triatoma dominicana and Trypanosoma antiquus?
- ... that the extinct crocodile Rimasuchus often preyed on large mammals, including early humans?
- ... that the first described fossil of Aphaenogaster mersa (illustrated) had a white mold coating?
- ... that Tilly Edinger founded paleoneurology?

- ... that Arizonasaurus had a large sail along its back made of the spines on its vertebrae?
- ... that Carletonomys, a rodent related to modern rice rats, is known only from one incomplete upper jaw from over 1 million year old silt deposits in Argentina?
- ... that Urocyon progressus, a species of extinct fox, was formally described after two bones and a tooth were found?
- ... that the scorpionfly family Eorpidae has a single genus, Eorpa, described in 2013?
- ... that based on its skull anatomy, the small Early Jurassic crocodile relative Dibothrosuchus (reconstruction pictured) probably had a keen sense of hearing and was vocal like modern crocodiles?

- ... that the extinct sweat bee genus Oligochlora contains six species all known from the Dominican amber deposits on Hispaniola?
- ... that Riojasuchus was an ornithosuchid that is known from four skeletons and lived about 217 to 215 million years ago?
- ... that the extinct ant Pristomyrmex rasnitsyni is the first member of its genus found in Europe?
- ... that the extinct species Agulla mineralensis is the first North American snakefly to be described from Neogene fossils?
- ... that the amber entombing the extinct ant Haidoterminus cippus (pictured) was preserved in a lagoon or saltwater marsh?

- ...that the largest sea turtles ever to have swum the oceans belonged to the family Protostegidae?
- ... that the extinct ant-like stone beetle Kachinus, found in Cretaceous amber, is similar in appearance to the modern genus Paraneseuthia?
- ... that at just over 18 millimetres (0.71 in), Fibla carpenteri is the largest species of snakefly known from amber?
- ... that Aenigmastacus, a fossil crayfish from Canada, belongs to a family only otherwise known from the Southern Hemisphere?
- ... that the extinct pseudoscorpion Pseudogarypus synchrotron is named for the synchrotron imaging equipment?

- ... that the extinct Pliocene dolphin Australodelphis from the Vestfold Hills of Antarctica has been described as an example of convergent evolution with whales?
- ... that the extinct sawfly Pseudosiobla cambelli is one of three species of Pseudosiobla known from the fossil record?
- ... that the extinct ant Afromyrma petrosa was found over a diamond mine?
- ... that Shantungosuchus, a small, primitive crocodile from the Cretaceous period, was terrestrial instead of aquatic?
- ... that the rove beetle Diochus electrus is the first definite member of the subfamily Staphylininae from the fossil record?

- ... that the ancient snakefly Cantabroraphidia was the first snakefly described from the El Soplao ambers?
- ... that the recently described notosuchian crocodyliform Pakasuchus had molar-like teeth that were as complex as those of carnivorous mammals?
- ... that a group of Late Permian mammal relatives called Nanictidopidae (restoration pictured) may have eaten fruit because their small teeth were unsuitable for grinding most plant material?
- ... that the Red Deer Cave people are the youngest prehistoric people discovered who do not appear similar to modern humans?
- ... that the extinct ant Anochetus conisquamis is noted for having a nipple-shaped spine?

- ... that a new species of the extinct ant Archimyrmex was described in 2012?
- ... that although the prehistoric shark Nanocetorhinus is named for the resemblance of its teeth to miniature Cetorhinus teeth, there is no evidence the two genera are closely related?
- ... that the only male "sweat bee" to have been documented from Dominican amber is the type specimen for the extinct Eickwortapis?
- ...that the evolution of sex is a major puzzle of evolutionary biology, due to the so-called two-fold cost of sex?
- ...that Endre Berner, Bjørn Føyn, Carl Jacob Arnholm, Eiliv Skard, Harald K. Schjelderup and Anatol Heintz were among the professors at the University of Oslo who were arrested by Nazis during World War II?

- ...that unlike most plesiosaurs, Leptocleidus once lived in shallow lagoon environments and likely visited brackish and fresh water systems such as the mouths of rivers?
- ... that seeds of the extinct tree Eucommia eocenica have been found with latex covered fossils?
- ... that Mastotermes electromexicus was the first giant northern termite described from the New World?
- ...that the extinct Australian dromornithids, which included the largest birds known, are related to ducks and geese?
- ... that cycloids are believed to have been driven to extinction when crabs spread across their territory?

- ... that the Stonerose fossil site contains the earliest known records of Rosaceae, the rose family?
- ... that the paleobotanists David P. Penhallow and Chester A. Arnold both published studies on the extinct water-fern Azolla primaeva?
- ... that the fossil big-headed fly Priabona is named for the age of the rocks in which it was found?
- ...that the Silurian Lau extinction event caused the Earth to temporarily return to a condition similar to how it was before multicellular life evolved?
- ... that the extinct ant Gesomyrmex germanicus was described from only four fossils?

- ... that species in the fossil ant genus Myrmeciites are named for Hercules, Goliath, and a river?
- ... that Tory Member of Parliament Admiral Theobald Jones (1790–1868) was a member of the Geological Society of London and kept a large collection of Carboniferous fishes?
- ... that the type specimen of the extinct nutmeg yew Torreya clarnensis is located in Florida?
- ... that the ants Anonychomyrma samlandica and A. geinitzi have been preserved in the same piece of amber?
- ... that highlights from the history of ornithomimosaur research include the ostrich-like Ornithomimus (skeletal mount pictured), an Archaeornithomimus bonebed in Mongolia, and the bizarre, giant-armed Deinocheirus?

- ... that the hypothesis that the pachycephalosaurian dinosaurs used their domed skulls in head-butting competitions was first proposed in a work of science fiction?
- ... that the extinct Protosialis casca is one of only two known alderflies from the West Indies?
- ... that the extinct ant species Apterostigma electropilosum was described from a solitary fossil in amber?
- ... that the extinct species Trochodendron drachuckii is known from a single Eocene fossil found near Cache Creek, British Columbia?
- ... that Protostephanus was the first extinct wasp genus in the family Stephanidae to be described from a fossil?

- ... that the extinct ant Acanthostichus hispaniolicus is the only Acanthostichus species found in the West Indies?
- ... that the Miocene ant Acropyga glaesaria is one of the oldest examples of trophobiosis?
- ...that the barnacle Megabalanus can reach 7 cm in length?
- ... that a new family of predatory cockroaches, named Manipulatoridae, has been discovered from amber found in the Hukawng Valley of Myanmar?
- ... that members of the extinct bivalve genus Hemiconcavodonta are unique in the subfamily Concavodontinae in that their teeth point in two directions?

- ... that Orsten, fossil-bearing lagerstätten in Sweden and elsewhere, are called "stinking stones" from organic content that has been preserved since the Cambrian Period?
- ... that the extinct fern species Osmunda wehrii was named in honor of Northwest school painter and amateur paleobotanist Wesley C. Wehr?
- ... that fossils of the extinct bivalve family Praenuculidae have been found on every continent except Antarctica?
- ...that prehistoric frog Beelzebufo may have grown to over 40 cm (16 in)* (size comparison pictured), larger than any living frogs, and is called "the Frog from Hell" by the media?
- ... that the Jurassic crocodile relative Phyllodontosuchus had two types of teeth; one type resembled those of some herbivorous dinosaurs, indicating it may not have been a strict carnivore?

- ... that unlike modern Sassafras, which are deciduous, the extinct species Sassafras hesperia (fossil pictured) may have been evergreen?
- ... that the fordilloid Camya asy is one of four accepted Cambrian bivalves?
- ... that the Ph.D dissertation of taphonomist Kay Behrensmeyer suggested that sauropods were terrestrial?
- ... that the big-headed fly Metanephrocerus belgardeae expanded the known range for the genus to North America?
- ... that the original type specimens of the Electrostephanus fossils may have been burned up during World War II?

- ... that the Jurassic conifer Araucaria mirabilis (cone pictured) of Argentina may have been a primary food for sauropods?
- ... that a fossil flower of the extinct palm Roystonea palaea shows damage possibly made by a bat or bird?
- ... that highlights from the history of ankylosaur research include one of the first dinosaurs ever discovered and a dinosaur with armored eyelids?
- ...that American lions were probably cave lions who crossed the Bering land bridge into Alaska?
- ... that Kendallina, a genus of trilobite, lived in North America during the Upper Cambrian?

- ... that the recently described synapsid Raranimus (pictured) is the most basal member of the order Therapsida, from which mammals are a descendant taxon?
- ... that the extinct sweat bee Halictus? savenyei was the first fossil bee from Canada to be described?
- ... that fossil specimens of the extinct scorpionfly family Dinopanorpidae, which includes Dinopanorpa and Dinokanaga, sometimes have preserved dark with light to clear color patterning?
- ... that the extinct snakefly genus Proraphidia is known from fossils found in Spain, England, and Kazakhstan?
- ... that remains of the recently described saber-toothed anomodont Tiarajudens were uncovered from a location in Brazil that was first found using Google Earth?

- ... that the extinct ant Asymphylomyrmex (pictured) was suggested to be a specialized group with no descendants?
- ... that fossils of the extinct legume Hymenaea mexicana show several types of insect feeding?
- ... that fossils of the extinct legume Hymenaea mexicana show several types of insect feeding?
- ... that the extinct Syndesus ambericus is the only stag beetle known from the Caribbean?
- ...that geologist T.H. Clark retired from McGill University in Quebec, Canada, at the age of 100, after teaching for 69 years?

- ...that the first Styxosaurus fossil to be discovered had about 250 stones in its stomach that it probably swallowed for ballast?
- ... that unlike the living golden-club Orontium aquaticum (pictured), the extinct species Orontium mackii may not have needed wetlands to grow?
- ... that an unnamed member of the extinct order Hupehsuchia exhibited an unusual form of polydactyly that is similar to that of some early tetrapods of the Devonian period?
- ... that the recently named trematopid temnospondyl Fedexia was named after the shipping service FedEx, which owned the land where the holotype specimen was found?
- ... that the name Pachylemur, now used for a type of extinct giant lemur, was first used as group name of primitive primates once considered intermediate between pachyderms and lemurs?

- ... that the extinct monkey lemurs, including Hadropithecus (pictured), were most closely related to modern indris and sifakas, as well as the extinct sloth lemurs?
- ... that over 16 million years ago, four species of parrot in the genus Nelepsittacus made their home in subtropical rainforest in what is now Otago, New Zealand?
- ... that Paul S. Martin and Paul Sidney Martin both worked as anthropologists at the University of Arizona in the early 1970s?
- ... that the extinct planthopper Ordralfabetix is named for a character from The Adventures of Asterix?
- ... that the Late Cretaceous madtsoiid snake Menarana had several adaptations for head-first burrowing, but its large size may have made burrowing difficult or impossible?

- ... that an anomalocaridid, a bizarre Cambrian organism, has been found 100 million years later, in the Devonian era?
- ... that the fossil crane fly Elephantomyia baltica is known from a single male in amber?
- ... that the fossil ant Aphaenogaster praerelicta is entombed in amber with three flies, two springtails, and a wasp?
- ... that with a forewing length of only 3.36 millimetres (0.132 in) Microberotha is one of the smallest known beaded lacewings to have been described?
- ... that the extinct crab Metacarcinus starri from Washington state is related to the graceful rock crab?

- ... that highlights from the history of ichthyosaur research (example pictured) include fossils of pregnant females, whale-sized ichthyosaurs from Nevada, and ichthyosaurs with swordfish-like jaws?
- ... that one species of the extinct wasp Palaeovespa fed caterpillars to its larvae?
- ... that humans living next to a lake at the Bouri Formation in Ethiopia 160,000 and 154,000 years ago butchered not only adult Hippopotamuses but also those that were newborn?
- ... that the fossil butterfly Prodryas persephone (engraving pictured) is so well preserved that individual wing scales can be seen?
- ... that wildfires have occurred on the Earth for over 420 million years?

- ... that it is unknown whether the dinosaur Nankangia was carnivorous or herbivorous?
- ... that Wushan Man, a species of Homo, was identified from a fossil jaw found south of the Yangtze River but is now thought to come from an extinct ape that lived in China two million years ago?
- ... that the extinct, Triassic, bivalve family Cassianellidae may have evolved from the family Bakevelliidae, which survived longer into the Eocene?
- ... that Pseudarmadillo tuberculatus was one of two Pseudarmadillo species described in 1984 from fossils in Dominican amber?
- ... that the recently named rhamphorhynchid Bellubrunnus (restoration pictured) from the Jurassic of Germany is the only known pterosaur to have wing tips that curved forward?
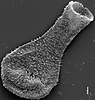
- ...that eighty years on, scientists are still debating whether the Palæozoic fossils known as Chitinozoans (SEM image pictured) represent plants, animals or eggs?
- ... that the extinct wasps Dryinus grimaldii and Dryinus rasnitsyni are distinguishable by the modified claws on their front legs?
- ... that only three possible fossils of the extinct ant Aphaenogaster oligocenica have been reported?
- ... that Calsoyasuchus valleyceps, an extinct crocodile relative from the Early Jurassic, has a deep groove in its skull from which its species name, "valley head", derives?
- ... that the wings of the extinct ant Aphaenogaster longaeva had "excessively delicate" hairs?

- ... that the Late Cretaceous madtsoiid snake Sanajeh preyed on hatchling sauropod dinosaurs at nesting sites in India?
- ... that the specific name of Tambachia trogallas, the type species of the trematopid temnospondyl Tambachia, refers to the Thuringian bratwurst that was frequently eaten by the describers of the species?
- ... that Tyrannasorus rex had wings and six legs?
- ... that the existence of a sea monster in Scotland has finally been proven?
- ... that Francisco Javier Muñiz was considered the first important naturalist from Argentina?

- ... that the Maxberg specimen, one of only 10 Archaeopteryx specimens ever found, has been lost since 1991?
- ... that the first Columbian mammoth (artist's restoration pictured) found at the Snowmastodon site, an Ice Age fossil dig near Denver, was initially dug out by a construction worker using a bulldozer?
- ... that the fossil moss Rhizomnium dentatum is preserved in the same amber block as two other mosses and part of a centipede?
- ... that the 500-million-year-old Cambrian predator Hurdia was thought to be a number of separate organisms for 100 years, until the complete animal was reconstructed in March 2009?
- ... that the extinct crocodyliform Sebecus (skull pictured) was named after Sebek, the ancient Egyptian crocodile god?

- ... that the 2.0-millimetre (0.079 in) long Nanotermes (pictured) are possibly the smallest adult termites known?
- ... that the extinct species Cornus piggae has fruits smaller than any other species in the dogwood subgenus of Cornus?
- ... that members of the fossil insect family Armaniidae have been described as "ant-like wasps"?
- ... that the extinct giant ant genus Formicium is known only from forewings found in Dorset, England and Tennessee, US?
- ... that the extinct spider Eoplectreurys is the oldest described genus of Haplogynae, predating spiders from Cretaceous amber in Jordan and Lebanon?

- ... that the extinct ant Burmomyrma rossi was missing its head when described?
- ... that out of the described snakefly specimens from the Florissant Formation, the Raphidia funerata holotype is the most complete?
- ... that Alanqa is a newly described pterosaur from Morocco which had a wingspan of up to six metres?
- ... that the extinct genus Paleopanax is one of the oldest reliable records for the ginseng family?
- ... that with a 20 million year fossil record, Acer chaneyi has the longest fossil record of the Western North American maples?

- ... that the primary leaf veins for the extinct plant Trochodendron nastae are palmate rather than being pinnate like those in the living Trochodendron aralioides?
- ... that the Early Cretaceous crocodilian relative Susisuchus was one of the first mesoeucrocodylians to have a segmented shield of bony osteoderms over its back, which allowed for greater flexibility while swimming?
- ... that the extinct griffenfly genus Bohemiatupus inhabited peat-mires?
- ... that the extinct rose species Stonebergia columbiana is named for its type locality of British Columbia?
- ... that the Miocene maple Acer latahense is most similar in appearance to the living Honshū maple?

- ... that fossils of 23 mammal species including mammoth, dire wolf, giant ground sloth, pre-historic bison, camel, and horse have been found at Fossil Lake in south central Oregon?
- ... that findings of Cylindroteuthis and other belemnites in Greenland suggest that an early form of the Gulf Stream existed as early as the Valanginian (Early Cretaceous)?
- ... that the type specimen of Kinkonychelys represents the first turtle skull described from the pre-Holocene era in Madagascar?
- ...that Castorocauda lutrasimilis, a recently described mammal relative that looked like an otter with a beaver's tail, evolved a semi-aquatic lifestyle 110 million years earlier than any other mammal-like animal?
- ... that the extinct earwig Tytthodiplatys is the oldest confirmed member of its family?

- ... that a fossilized dragon has been found in Poland?
- ... that T. Rex and the Crater of Doom details the development of the hypothesis that dinosaurs were wiped out by a meteor impact?
- ... that the shell of the extinct sea urchin Pelanechinus corallina was composed of separate groups of fused plates which resulted in its being flexible?
- ... that fossils of the extinct sumac Rhus malloryi (pictured) were first published in 1935?
- ... that although Atopodentatus had a fearsome set of teeth, it was a filter feeder and not a predator?

- ... that Dinocochlea was thought to be a giant snail shell or fossilised dinosaur dung but is actually a solidified worm's burrow?
- ... that the extinct stingray Heliobatis (pictured) has been found with up to three stings on its tail?
- ... that the extinct ant Anochetus intermedius had mandibles longer than its head?
- ... that Okmulgee State Park (pictured) in Oklahoma is one of only a few places in the world where the fossil coral Gymnophyllum wardi is found?
- ...that the prehistoric badger genus Chamitataxus lived during the Late Miocene and is considered the most primitive badger genus in North America?

- ... that Arthropleuridea is an extinct class of myriapods which includes, at over 2 meters long, the largest terrestrial arthropods that ever lived?

- ... that highlights from the history of dromaeosaurid research include a skeleton of Velociraptor preserved in combat with a Protoceratops, the gigantic Utahraptor, and tiny four-winged Microraptor?
- ... that the extinct lobe-finned fish Laccognathus embryi (reconstruction pictured) had fangs up to 3.8 cm (1.5 in) long?
- ...that ostracoderms are the earliest known vertebrate animals?
- ... that the extinct witch-hazel Langeria is named for American philosopher Susanne Langer?
- ... that the only fossil of the extinct moth Baltimartyria sat on a paleoentomologist's desk for a number of years before being described in 2011?

- ...that Repenomamus may have been the largest mammal in the Cretaceous period and is the only mammal known to have eaten non-avian dinosaurs?

- ... that unlike other stereospondyl amphibians, the Triassic Lydekkerina (restoration pictured) lived entirely on land?
- ... that the extinct Miocene redwood, Sequoiadendron chaneyi, is the probable ancestor to the giant sequoias in California?
- ...that Terminonatator ponteixensis is the type and only species described for Terminonatator, a genus of elasmosaurid plesiosaur from Late Cretaceous of Saskatchewan, Canada?
- ... that the extinct winter-hazel species Corylopsis readae was described from a single Ypresian fossil?

- ... that the Triassic reptile Vancleavea, which is specialized to live in the water, differs greatly from all other early archosauriforms?

- ... that the extinct Cretaceous wasp family Plumalexiidae is known from only the two Plumalexius type specimens found in New Jersey amber?

- ...that Santanachelys gaffneyi is the earliest known sea turtle?

- ... that the pattern of the veins on fossil leaves of the extinct golden-club Orontium wolfei confirm it as a member of the arum family?
- ... that the Albian 100-million-year-old fossil wasp Myanmymar (pictured) is only half a millimetre long?
- ... that the Permian amphibian Trimerorhachis either brooded young in its mouth or ate them?
- ... that the newly named extinct prawn Aciculopoda is the third unambiguous fossil decapod from before the Mesozoic?
- ... that the extinct ant Afropone was first described from fossils in kimberlite?

- ... that the discovery of the fossil giant ant Titanomyrma (pictured with a hummingbird) in Wyoming indicates that warmth-loving fauna spread through the north between Europe and America during hot spells in the Eocene?
... that highlights from 19th century ichnology include the discovery of protomammal tracks in England, dinosaur footprints in Massachusetts, and the mysterious hand-shaped Chirotherium tracks (pictured)?

- ... that during the 20th century, the first large-scale excavation of dinosaur footprints was undertaken in Texas for an exhibit at the American Museum of Natural History?

- ... that the New Zealand and the Chatham Coot were likely hunted to extinction by the Māori people?
