Portal:Andes
Portal maintenance status: (November 2018)
|
The Andes Portal

The Andes (/ˈændiːz/ AN-deez), Andes Mountains or Andean Mountain Range (Spanish: Cordillera de los Andes; Quechua: Anti) are the longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range is 8,900 km (5,530 mi) long and 200 to 700 km (124 to 435 mi) wide (widest between 18°S and 20°S latitude) and has an average height of about 4,000 m (13,123 ft). The Andes extend from South to North through seven South American countries: Argentina, Chile, Bolivia, Peru, Ecuador, Colombia, and Venezuela.
Along their length, the Andes are split into several ranges, separated by intermediate depressions. The Andes are the location of several high plateaus—some of which host major cities such as Quito, Bogotá, Cali, Arequipa, Medellín, Bucaramanga, Sucre, Mérida, El Alto, and La Paz. The Altiplano Plateau is the world's second highest after the Tibetan Plateau. These ranges are in turn grouped into three major divisions based on climate: the Tropical Andes, the Dry Andes, and the Wet Andes.
The Andes are the highest mountain range outside of Asia. The range's highest peak, Argentina's Aconcagua, rises to an elevation of about 6,961 m (22,838 ft) above sea level. The peak of Chimborazo in the Ecuadorian Andes is farther from the Earth's center than any other location on the Earth's surface, due to the equatorial bulge resulting from the Earth's rotation. The world's highest volcanoes are in the Andes, including Ojos del Salado on the Chile-Argentina border, which rises to 6,893 m (22,615 ft). (Full article...)
Selected articles
-
Image 1
Jirishanca is a 6,094-metre-high (19,993 ft) mountain in the Huayhuash mountain range in west central Peru, part of the Andes. Other sources cite a height of 6,125 metres (20,095 ft). It is the 10th highest peak in Peru and the third in the Huayhuash range (after Yerupajá and Siula Grande). Jirishanca translates as "hummingbird bill peak". (Full article...) -
Image 2
Mount Tarn is a small mountain located on the southernmost part of the Strait of Magellan, in Brunswick Peninsula, about 70 km south of Punta Arenas, Chile. It is in the southern extreme of continental Chile very close to Cape Froward, surrounded by historic places such as Fort Bulnes and Puerto del Hambre (Port Famine).
From the summit it is possible to see the Strait of Magellan, Dawson and Tierra del Fuego islands, and many other smaller ones; the Darwin Mountain Range, Mount Sarmiento, and most of the Brunswick Peninsula. (Full article...) -
Image 3

The yellow-tailed woolly monkey (Lagothrix flavicauda) is a New World monkey endemic to Peru. It is a rare primate species found only in the Peruvian Andes, in the departments of Amazonas and San Martin, as well as bordering areas of La Libertad, Huánuco, and Loreto. (Full article...) -
Image 4
Licancabur (Spanish pronunciation: [likaŋkaˈβuɾ]) is a prominent, 5,916-metre-high (19,409 ft) stratovolcano on the Bolivia–Chile border in the Central Volcanic Zone of the Andes. It is capped by a 400–500-metre (1,300–1,600 ft) wide summit crater which contains Licancabur Lake, a crater lake that is among the highest lakes in the world. There are no glaciers owing to the arid climate. Numerous plants and animal species live on the mountain. The volcanoes Sairecabur and Juriques are north and east of Licancabur, respectively.
Licancabur formed on top of ignimbrites produced by other volcanoes and it has been active during the Holocene. Three stages of lava flows emanated from the edifice and have a young appearance. Although no historical eruptions of the volcano are known, lava flows extending into Laguna Verde have been dated to 13,240 ± 100 before present and there may be residual heat in the mountain. The volcano has primarily erupted andesite, with small amounts of dacite and basaltic andesite. (Full article...) -
Image 5Parinacota, K'isi K'isini, Pomerape, Laram Q'awa, Patilla Pata and Sajama (l-r) as seen from NASA space shuttle
Laram Q'awa (Aymara larama blue, q'awa little river, ditch, crevice, fissure, gap in the earth, "blue brook" or "blue ravine", Hispanicized spellings Laram Khaua, Larancagua) is a 5,182-metre-high (17,001 ft) mountain in the Andes. According to the Bolivian IGM map 1:50,000 'Nevados Payachata Hoja 5739-I' it is situated on Bolivian terrain in the La Paz Department, Pacajes Province (Charaña Municipality), at the border with Chile. It lies north-west of the mountains Kunturiri, Phaq'u Q'awa and another mountain on the border named Laram Q'awa (Laram Khaua). One of three different rivers of this area called Kunturiri (Condoriri) originates north-east of the mountain near Phaq'u Q'awa. It flows in a bow along the northern slopes of Laram Q'awa towards Chile. (Full article...) -
Image 6
Cerro Macá is a stratovolcano located to the north of the Aisén Fjord and to the east of the Moraleda Channel, in the Aysén del General Carlos Ibáñez del Campo Region of Chile. This glacier-covered volcano lies along the regional Liquiñe-Ofqui Fault Zone.
Cerro Macá is a relatively small volcano with a volume of only 39 cubic kilometres (9.4 cu mi). It has a summit elevation of approximately 2,300 m above sea level and features glaciers that in 2011 covered an area of 27.62 square kilometres (10.66 sq mi). The edifice is partially eroded and a sector collapse is probably the origin of a large steep sided depression in the summit area. Pyroclastic cones with associated lava flows are found on its southwestern flank but also on the other slopes of the volcano, as far down as sea level and in the Bahia Aysen. (Full article...) -
Image 7Pico Bonpland as seen from the Pico Humboldt
Pico Bonpland is Venezuela's fourth-highest peak, at 4,883 metres above sea level. It is located in the Sierra Nevada de Merida, in the Venezuelan Andes of (Mérida State). The peak with its sister peak Pico Humboldt, and the surrounding páramos are protected by the Sierra Nevada National Park. The name of the peak is in honor of Aimé Bonpland, although he never visited the Venezuelan Andes.
The glaciers located in the Bonpland were the result from Merida glaciation in the Pleistocene. By 2011 they had all disappeared. (Full article...) -
Image 8
Puracé is an andesitic stratovolcano located in the Puracé National Natural Park in the Cauca Department, Colombia. It is part of the North Volcanic Zone of the Andean Volcanic Belt. The volcano is located at the intersection of the Coconucos and Morras Faults.
It is one of the most active volcanoes in Colombia. Large explosive eruptions occurred in 1849, 1869, 1885, 1949, 1950, 1956, and 1957. There were about a dozen eruptions in the 20th century, the most recent being in 1977. On this occasion, volcanic ash was deposited 7 kilometres (4.3 mi) away. Fumaroles were seen near the summit in 1990, and hot springs emerged from some of the lower slopes. (Full article...) -
Image 9

Lake Junin (IPA: [xuˈnin]; Spanish Lago Junín, named after the nearby town of Junin) or Chinchaycocha (possibly from Quechua chincha, chinchay north, northern, chinchay ocelot, qucha lake, lagoon, "northern lake" or "ocelot lake") is the largest lake entirely within Peruvian territory. Even though Lake Titicaca has a much larger area, its eastern half is located on Bolivian territory. Lake Junin is an important birdwatching destination in the country. (Full article...) -
Image 10
Yerupajá is a mountain of the Huayhuash mountain range in west central Peru, part of the Andes. It is located at Áncash, Bolognesi Province, Lauricocha Province. At 6,635 metres (21,768 ft) (other sources: 6,617 m (21,709 ft)) it is the second-highest in Peru and the highest in the Huayhuash mountain range. The summit is the highest point in the Amazon River watershed, and was first reached in 1950 by Jim Maxwell and Dave Harrah, and its northern peak (Yerupajá Norte) in 1968 by the Wellingtonian Roger Bates and Graeme Dingle. Many visitors consider Yerupajá to be the most spectacular peak in South America.
There have been only a few successful ascents of the peak because it is one of the hardest Andean high peaks to climb. The most popular route is the southwest face. The approach is normally made from Huaraz southwards via Chiquián and Jahuacocha. (Full article...) -
Image 11

The Puracé National Natural Park (Spanish: Parque Nacional Natural Puracé) is a national park located in the Andean region of Colombia, southeast of the city of Popayán in the Cordillera Central range. Its main feature is the active stratovolcano Puracé, one of Colombia's most active volcanoes. Four of the country's most important rivers originate within the area: Magdalena River, Cauca River, Japurá River and Patía River. (Full article...) -
Image 12Lanín as seen from Mamuil Malal Pass
Lanín is an ice-clad, cone-shaped stratovolcano on the border of Argentina and Chile. It forms part of two national parks: Lanín in Argentina and Villarrica in Chile. As a part of the flag and anthem of the Argentine province of Neuquén, it serves as a symbol for the region. Although the date of its last eruption is not known, it is estimated to have occurred within the last 10,000 years. Following the 1906 Valparaíso earthquake a local newspaper reported the volcano to have erupted, but a work published in 1917 by Karl Sapper disputed this.
The ascent is regulated by the management of Argentine National Parks and the Argentine National Gendarmerie and is technically relatively simple but has a much higher level of exposure than the neighbouring volcanoes. The nearest towns, usually employed as a base for climbers, are Pucón in Chile and Junín de los Andes in Argentina. (Full article...) -
Image 13
El Altar or Capac Urcu (possibly from Kichwa kapak principal, great, important / magnificence, urku mountain) is an extinct volcano on the western side of Sangay National Park in Ecuador, 170 km (110 mi) south of Quito, with a highest point of 5,319 m (17,451 ft). Spaniards named it so because it resembled two nuns and four friars listening to a bishop around a church altar. In older English sources it is also called The Altar. (Full article...) -
Image 14View of Tronador mountain from Mascardi Lake, Argentina
Tronador (Spanish: Cerro Tronador) is an extinct stratovolcano in the southern Andes, located along the border between Argentina and Chile, near the Argentine city of Bariloche. The mountain was named Tronador (Spanish for "Thunderer") by locals in reference to the sound of falling seracs. With an altitude of 3,470 metres (11,380 ft), Tronador stands more than 1,000 m above nearby mountains in the Andean massif, making it a popular mountaineering destination. Located inside two national parks, Nahuel Huapi in Argentina and Vicente Pérez Rosales in Chile, Tronador hosts a total of eight glaciers, which are currently retreating due to warming of the upper troposphere. (Full article...) -
Image 15

The royal cinclodes (Cinclodes aricomae) is a Critically Endangered passerine bird in the Furnariinae subfamily of the ovenbird family Furnariidae. It is found in Bolivia and Peru. (Full article...) -
Image 16
The hooded mountain tanager (Buthraupis montana) is a species of bird in the tanager family Thraupidae. It is the only member of the genus Buthraupis. This yellow, blue and black tanager is found in forest, woodland and shrub in the Andean highlands of Bolivia, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, and Venezuela. At 23 centimetres (9.1 in) and 85 grams (3.0 oz), it is one of the largest tanagers (second in weight only to the white-capped tanager). (Full article...) -
Image 17
Pico Humboldt is Venezuela's second highest peak, at 4,925 metres above sea level. It is located in the Sierra Nevada de Merida, in the Venezuelan Andes of (Mérida State). The peak, its sister peak Pico Bonpland, and the surrounding páramos are protected by the Sierra Nevada National Park. The mountain is named after German explorer and naturalist Alexander von Humboldt. (Full article...) -
Image 18
Reventador is an active stratovolcano which lies in the eastern Andes of Ecuador. It lies in a remote area of the national park of the same name, which is Spanish for "exploder". Since 1541, it has erupted over 25 times, although its isolated location means that many of its eruptions have gone unreported.
The largest historical eruption occurred in 2002. During that eruption, the plume from the volcano reached a height of 17 kilometres (11 mi) and pyroclastic flows proceeded to 7 kilometres (4.3 mi) from the cone. On March 30, 2007, the mountain ejected ash to a height of about 3.2 kilometres (2.0 mi). No injuries or damage were reported. Its most recent eruption began on 27 July 2008, and it has remained in continuing eruption status (intermittent eruptive events without a break of 3 months or more) as of 15 October 2021. (Full article...) -
Image 19

Coropuna is a dormant compound volcano located in the Andes mountains of southeast-central Peru. The upper reaches of Coropuna consist of several perennially snowbound conical summits, lending it the name Nevado Coropuna in Spanish. The complex extends over an area of 240 square kilometres (93 sq mi) and its highest summit reaches an altitude of 6,377 metres (20,922 ft) above sea level. This makes the Coropuna complex the third-highest of Peru. Its thick ice cap is the most extensive in Earth's tropical zone, with several outlet glaciers stretching out to lower altitudes. Below an elevation of 5,000 metres (16,000 ft), there are various vegetation belts which include trees, peat bogs, grasses and also agricultural areas and pastures.
The Coropuna complex consists of several stratovolcanoes. These are composed chiefly of ignimbrites and lava flows on a basement formed by Middle Miocene ignimbrites and lava flows. The Coropuna complex has been active for at least five million years, with the bulk of the current cone having been formed during the Quaternary. Coropuna has had two or three Holocene eruptions 2,100 ± 200 and either 1,100 ± 100 or 700 ± 200 years ago which generated lava flows, plus an additional eruption which may have taken place some 6,000 years ago. Current activity occurs exclusively in the form of hot springs. (Full article...) -
Image 20

The guanaco (/ɡwɑːˈnɑːkoʊ/ ghwuah-NAH-koh; Lama guanicoe) is a camelid native to South America, closely related to the llama. Guanacos are one of two wild South American camelids; the other species is the vicuña, which lives at higher elevations. (Full article...) -
Image 21Illimani is a mountain in the Khari Khari mountain range of the Bolivian Andes, about 5,030 m (16,503 ft) high. It is situated south-east of Potosí in the Potosí Department, Tomás Frías Province, Potosí Municipality. Illimani lies south-west of the mountain Uma Jalanta, north-east of Challwiri Lake and north of Illimani Lake. (Full article...)
-
Image 22
Chumpe (possibly from chumpi Jaqaru for corn with yellow seeds and Quechua for belt; or ch'umpi Jaqaru for red and Quechua for brown), is a mountain in the north of the Pariacaca mountain range in the Andes of Peru, about 5,200 metres (17,060 ft) high. It is situated in the Junín Region, Yauli Province, in the districts of Huay-Huay and Yauli District. Chumpe lies east of Lake Pumacocha. The mining town of San Cristóbal is situated at its feet. (Full article...) -
Image 23
The Junin grebe (Podiceps taczanowskii), also known as Junin flightless grebe or puna grebe, is a species of grebe endemic to Lake Junin in the Andean highlands of Junin in west-central Peru. An endangered species, the current population is estimated at 300–400 individuals, including 140–320 adults. (Full article...) -
Image 24Chinchilla lanigera at the Wrocław Zoo in Poland
Chinchilla refers to either of two species (Chinchilla chinchilla and Chinchilla lanigera) of crepuscular rodents of the parvorder Caviomorpha, and are native to the Andes mountains in South America. They live in colonies called "herds" at high elevations up to 4,270 m (14,000 ft). Historically, chinchillas lived in an area that included parts of Bolivia, Peru and Chile, but today, colonies in the wild are known only in Chile. Along with their relatives, viscachas, they make up the family Chinchillidae. They are also related to the chinchilla rat.
The chinchilla has the densest fur of all extant terrestrial mammals, with around 20,000 hairs per square centimeter and 50 hairs growing from each follicle. The chinchilla is named after the Chincha people of the Andes, who once wore its dense, velvet-like fur and ate their meat. By the end of the 19th century, chinchillas had become quite rare after being hunted for their notably soft fur. Most chinchillas currently used by the fur industry for clothing and other accessories are farm-raised. Domestic chinchillas descended from C. lanigera are sometimes kept as pets, and may be considered a type of pocket pet. (Full article...) -
Image 25
Sierra Nevada, also known as Sierra Nevada de Lagunas Bravas, is a major ignimbrite-lava dome complex which lies in both Chile and Argentina in one of the most remote parts of the Central Andes.
Activity in the complex started in Argentina and formed two stratovolcanoes. Later, 12 or more vents formed, some with craters up to 400 metres (1,300 ft) wide. Lava flows up to 7 kilometres (4.3 mi) long with flow ridges are also found. It covers a total area of 225 km2. Radiometric dating has yielded ages of 1.7 ± 0.4 to 0.431 ± 0.012 million years ago, a lava flow from the neighbouring Azufrera Los Cuyanos volcano that is sometimes considered part of Sierra Nevada is 140,000 years old. Together with Cerro el Condor and Peinado it forms the Culampaja line, a line of volcanoes that reaches Cerro Blanco. Strong seismic attenuation is observed beneath Sierra Nevada. Hydrothermally altered rocks in Sierra Nevada may be the source of sulfate and arsenic in the Juncalito and Negro rivers, and heat sources for regional hot springs. The snowline in the area lies at 5,800 metres (19,000 ft) altitude at Cumbre del Laudo. (Full article...)
Did you know...
- ... that the 1930s Polish Andean expeditions have been credited with several first ascents and the tracing of a new route to the summit of Aconcagua, the Andes' highest peak?
Need help?
Do you have a question about Andes that you can't find the answer to?
Consider asking it at the Wikipedia reference desk.
General images
-
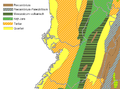
Image 3Syncline next to Nordenskjöld Lake in Torres del Paine National Park. The syncline formed during the Andean orogeny. (from Andean orogeny)
-
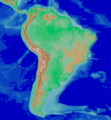
Image 4Topographic map of the Andes by the NASA. The southern and northern ends of the Andes are not shown. The Bolivian Orocline is visible as a bend in the coastline and the Andes lower half of the map. (from Andean orogeny)
-
Image 5Aerial view of Valle Carbajal in the Tierra del Fuego. The Andes range is about 200 km (124 mi) wide throughout its length, except in the Bolivian flexure where it is about 640 kilometres (398 mi) wide.
-
Image 7Central Andes (from Andes)
-
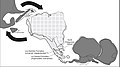
Image 10Map of a north-south sea-parallel pattern of rock ages in western Colombia. This pattern is a result of the Andean orogeny. (from Andean orogeny)
-
Image 11Peruvian farmers sowing maize and beans (from Andes)
-
Image 15Paleogeography of the Late Cretaceous South America. Areas subject to the Andean orogeny are shown in light grey while the stable cratons are shown as grey squares. The sedimentary formations of Los Alamitos and La Colonia that formed in the Late Cretaceous are indicated. (from Andean orogeny)
-
Image 16A male Andean cock-of-the-rock, a species found in humid Andean forests and the national bird of Peru (from Andes)
-
Image 17Pacha Mama Ceremony (from Andean agriculture)
-
Image 18Irrigating land in the Peruvian Andes (from Andes)
-
Image 19Huayna Potosí, Bolivia (from Andes)
-
Image 20Pico Humboldt at sunset (from Andes)
-
Image 21The seaward tilting of the sedimentary strata of Salto del Fraile Formation in Peru was caused by the Andean orogeny. (from Andean orogeny)
-
Image 25Mashua tubers (from Andean agriculture)
-
Image 27Ulluco: Common crop of the Andean region (from Andean agriculture)
-
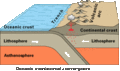
Image 28Simplified sketch of the present-situation along most of the Andes (from Andean orogeny)
-
Image 30Bolivian Andes (from Andes)
Subcategories
Related portals
Subtopics
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus