Parapaguridae
Appearance
| Parapaguridae | |
|---|---|
| |
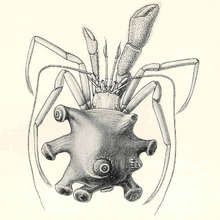
| Parapagurus pilosimanus | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Malacostraca |
| Order: | Decapoda |
| Suborder: | Pleocyemata |
| Infraorder: | Anomura |
| Superfamily: | Paguroidea |
| Family: | Parapaguridae S. I. Smith, 1882 [1] |
The Parapaguridae are a family of marine hermit crabs from deep waters. Instead of carrying empty gastropod shells like other hermit crabs, they carry colonies of dozen or more sea anemones or zoanthids.[2] Some genera, such as Bivalvopagurus and Tylaspis, do not inhabit shells.[3] The following genera are included:[4]
- Bivalvopagurus Lemaitre, 1993
- †Mutotylaspis Fraaije, Mychko, Barsukov & Jagt, 2023
- Oncopagurus Lemaitre, 1996
- Paragiopagurus Lemaitre, 1996
- Parapagurus Smith, 1879
- Probeebei Boone, 1926
- Strobopagurus Lemaitre, 1989
- Sympagurus Smith, 1883
- Tsunogaipagurus Osawa, 1995
- Tylaspis Henderson, 1885
- Typhlopagurus de Saint Laurent, 1972
References
[edit]- ^ J. W. Martin & G. E. Davis (2001). An Updated Classification of the Recent Crustacea (PDF). Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County. pp. 132 pp.
- ^ Poore, Gary C. B. (2004). Marine Decapod Crustacea of Southern Australia: A Guide To Identification. Csiro Publishing. p. 279. ISBN 9780643069060.
- ^ Patsy A. McLaughlin & Rafael Lemaitre (1997). "Carcinization in the Anomura – fact or fiction? I. Evidence from adult morphology". Contributions to Zoology. 67 (2): 79–123. doi:10.1163/18759866-06702001.
- ^ Patsy McLaughlin & Michael Türkay (2011). Lemaitre R, McLaughlin P (eds.). "Parapaguridae". World Paguroidea & Lomisoidea Database. World Register of Marine Species. Retrieved November 16, 2012.
External links
[edit] Data related to Parapaguridae at Wikispecies
Data related to Parapaguridae at Wikispecies

