Ichma culture
This article needs to be updated. (January 2023) |
Ichma Kingdom Ichma | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1100–1469 | |||||||||
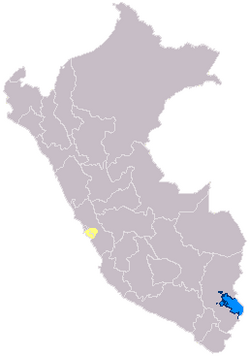 Domain of the Ichma or Ychsma people (in yellow) | |||||||||
| Location | Lima | ||||||||
| Capital | Pachacamac | ||||||||
| Government | Diarchy | ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
• Established | 1100 | ||||||||
• Disestablished | 1469 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
The Ichma kingdom (also written Ychma or Yschma, among other spellings) or Pachacamac kingdom[1][2] was a pre-Inca indigenous polity later absorbed by the Inca Empire and reorganized as a wanami (province). For the Inca it was known as Pachakamaq (Pachacamac), rather than its original name of Ishma.
The Ishmay Kingdom was located south of Lima, Peru in the Lurín River valley; it later spread north into the Rímac River's valley. The Ishma culture was formed around 1100 AD following the breakup of the Wari Empire. Ishma autonomy lasted until around 1469 when they were absorbed into the Incan Empire.[3]
Despite occupying a desert, the inhabitants of Ishma had a high standard of living, thanks to their expertise in devising multiple irrigation channels as far as the river waters could reach, to give life to an extensive orchard and forest.[4]
Onomastics
[edit]At least since the Spanish conquest, the name used for the ancient temple as well as the nearby area is Pachacamac (from the Quechua name of deity). According to some colonial sources, though, the Pachachamac name might have been given by Inca conquerors, and the previous name for both the place and the temple was Ichma.[5]
This latter toponym has great variation in colonial sources, including <Ychma>, <Yzma>, <Ychsmac>, <Ychsma>, <Ychima>, <Ychmay> and <Irma>.[5] The word was clearly part of Classical Quechua vocabulary, as colonial dictionaries have it, written as <yxma> or <ychma>, as a color term for red. Contemporary linguists interpret additional evidence as pointing to cinnabar as the primary referent of the term.[6][5] While colonial Quechua dictionaries point to [iʃma] or [itʃma] as Classical Quechua ponunciation for the color term, the <Irma> and <Ychsma> variants have been interpreted as evidence for a retroflex affricate sound, and for *[iʈʂma] as the original local pronunciation of the place name.[5]
Archaeologist Krysztof Makowski has proposed an Aymaran origin for Ichma, as an explanation for the existence of two placenames, as opposed to clearly Quechua Pachacamac.[7] This latter hypothesis has not been accepted by linguists.
Organization
[edit]The Ishma controlled coastal the valleys of Rimac and Lurin rivers in modern-day Lima, from the mouth—sea of the rivers to the middle valley or "Chaupi Yunga" (middle Yunga altitude, between 500 and 1200 meters of elevation).[8][9] Ishma territory reached up to the sanctuary of Mama located in Rimac (present-day Ricardo Palma) and the sites of Chontay and Sisicaya in Lurin at 1,000 meters above sea level.[8][10]
The Ishma were divided into two moiety administrative divisions or saya, these were the anan (upper) saya Ichma and luren (lower) saya Ichma.[11] On the coast, unlike the Andean highlands, the most important moiety often was that of luren (lurin) because it was linked to the sea.[4]
Each saya was in turn divided into unu or waranka subdivisions, which in turn were also divided into the anan and luren moieties,[12] The Ishma dominions of Lati, Surco (Sulco), Guatca, Rimac (Lima), and Maranga (Malanca) were located in the Rimac valley, while the dominions of Pachacamac (Ishma), Manchay, Quilcay (Quilcayuna), and Caringa were located in the Lurin valley.[8]
The city of Pachacamac, formerly known as Ishma before Inca conquest, was the capital of the Ishma kingdom and seat of its rulers.[13] Many Ishma ruins have been discovered along Lima's coast, however other than Pachacamac and a few other sites, there is no consensus on which the large majority sites could correspond to each domain, neither is known their physical distribution.[14] It has been proposed that the archaeological site of Pampa de Flores could be the head of Manchay dominion and residence of the Manchay ayllu (a subdivision of the waranka).[14]
History
[edit]
With the breakup of the Wari Empire, several small kingdoms and confederations were created. Over time, two cultures came to dominate the region, the Chancay culture to the north of Lima, and the Ishma culture to the south.
Is believed the Ishma people were an Aymara-speaking people that came to inhabit the coastal areas near Lima following the collapse of the Wari empire.
The Ishma people inhabited Pachacamac and continued the growth and influence of the city. The Ishma people constructed at least 16 pyramids in Pachacamac, and built or remodeled more structures in the Lima area. Among these are Huaca Huantille in the Magdalena del Mar district, Huaca Mateo Salado in Lima's district of Pueblo Libre, Huaca San Borja in the San Borja District, and Huaca Casa Rosada, Huaca Huantinamarca and Huaca San Miguel in the San Miguel District. Additionally, archeological sites in Puruchuco and Cajamarquilla have been ascribed to the Ichma people.[3]
Archaeology
[edit]A number of cultural and human remains have been discovered in various Ichma sites. In the Huaca Huantille, at least 9 mummies have been discovered, buried with ceramic items and jewelry crafted from copper, silver, and gold.[15] In 2012, excavation in the Pachacamac site yielded a burial chamber with more than 80 mummified remains, and a dozen infant remains. Along with the skeletons, this site also contained various artifacts, including ceramic wares, jewellery, and animal remains.[16]
As Luisa Diaz Arriola mentions: "The ethnohistorical narratives made by the Spaniards from 1533 AD, when they arrived in Pachacamac, are enriching but have a bias. They are what the informants wanted to tell, and reflect what the Spaniards of the 16th century considered important to record about those ancient inhabitants of Lima. The chronicles recorded religious beliefs, the importance of the deity Pachacamac and his kin, inter-valley relations, the existence of curacazgos, the coastal ecosystems, the irrigation schemes, among other aspects. But this information is insufficient to know all the dimensions of a past pre-colonial society. Archaeology has direct contact with the material remains left by the ychsma."[17]
Collapse of the Ichma
[edit]When the Inca Empire expanded into this region, the cultures of the Ichma and the Chancay people, along with smaller cultures, were absorbed into the Inca Empire.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Mora, César Gálvez; Rochietti, Ana (2018-03-20). Patrimonio cultural del Perú: Humanidad andina (in Spanish). Eduvim. ISBN 9789876992206.
- ^ (Rostworowski, 1989: 71, 1992: 77)
- ^ a b "Lima History, the Chancay and Ichma Culture". www.limaeasy.com. Archived from the original on 2012-07-31. Retrieved 2012-05-25.
- ^ a b Soriano, Valdemar Espinoza (2014). "La etnia Ishma (Ychsma, Ichma, Ichmay)" [The ethnic Ishma (Ychsma, Ichma, Ichmay)]. Investigaciones Sociales (in Spanish). 18 (32): 117–159. doi:10.15381/is.v18i32.10950. ISSN 1818-4758.
- ^ a b c d Cerrón-Palomino, Rodolfo (2008). Voces del Ande: ensayos sobre onomástica andina. Colección estudios andinos (in Spanish) (1. ed.). Lima, Perú: Fondo Editorial de la Pontificia Universidad Católica del Perú. pp. 178–179. ISBN 978-9972-42-856-2.
- ^ Torero, Alfredo (2005). Idiomas de los Andes: lingüística e historia. Filología, lingüística (2a ed.). Lima: Ed. Horizonte. pp. 139–140. ISBN 978-9972-699-38-2.
- ^ Makowski, Krzysztof (March 2015). "Pachacamac—Old Wak'a or Inka Syncretic Deity?: Imperial Transformation of the Sacred Landscape in the Lower Ychsma (Lurín) Valley". The Archaeology of Wak'as: Explorations of the Sacred in the Pre-Columbian Andes: 127–166.
- ^ a b c Salazar, Casas; Lizbeth, Lyda (2017). "La zona de Carapongo como expresión física de una entidad política, durante el período de los Reinos y Señoríos Tardíos". Universidad Nacional Mayor de San Marcos. Archived from the original on 2019-10-26. Retrieved 2019-09-17.
- ^ Román Godines, Oscar (2013). "El paisaje de Nieve Nieve: la chaupi yunga del Lurín". Ministerio de Cultura.
- ^ (Rostworowski, 1976, 1989; Espinoza, 1963, 1964, 1983).
- ^ Vallejo, Francisco; Díaz, Luisa (2002-04-09). "Armatambo y el dominio incaico en el valle de Lima". Boletín de Arqueología PUCP (6): 355–374. doi:10.18800/boletindearqueologiapucp.200201.014. ISSN 2304-4292.
- ^ Makowski, Krzysztof (2002-04-09). "Arquitectura, estilo e identidad en el Horizonte Tardío: el sitio de Pueblo Viejo-Pucará, valle de Lurín". Boletín de Arqueología PUCP (6): 137–170. doi:10.18800/boletindearqueologiapucp.200201.007. ISSN 2304-4292.
The site, located between 400 and 600 meters above sea level in a loma ecozone on the left bank of the river, could have been the main habitation center of the Caringa of Huarochiri, one of the Caringa moieties of the unu of Luren.
- ^ Díaz, Luisa; Vallejo, Francisco (2004). "VARIACIONES CULTURALES EN EL VALLE DE LIMA DURANTE LA OCUPACIÓN INCAICA / CULTURAL VARIATIONS IN LIMA VALLEY DURING THE INKA PERIOD". Chungara: Revista de Antropología Chilena. 36 (2): 295–302. doi:10.4067/S0717-73562004000200004. ISSN 0716-1182. JSTOR 27802272.
- ^ a b Marcone Flores, Giancarlo (2004-12-01). "Cieneguilla a la llegada de los Incas Aproximaciones desde la historia ecológica y la arqueológica". Bulletin de l'Institut français d'études andines (in Spanish). 33 (3): 715–734. doi:10.4000/bifea.5330. ISSN 0303-7495.
- ^ "Pre-Incan Mummies found in Lima". infosurhoy.com. Archived from the original on 2013-01-26. Retrieved 2012-05-25.
- ^ "Temple of Doom: Scientists Discover peruvian Tomb Filled with Mummies, Infants". Time. 2012-05-24. Retrieved 2012-05-25.
- ^ Díaz Arriola, Luisa (2022). Los ychsma. Habitantes prehispánicos de Lima (PDF) (in Spanish). Municipalidad de Lima. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2022-12-27. Retrieved 2023-01-27.
