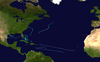
Hurricane Barry (1983)
 Barry making landfall in Northern Mexico on August 28 | |
| Meteorological history | |
|---|---|
| Formed | August 23, 1983 |
| Dissipated | August 29, 1983 |
| Category 1 hurricane | |
| 1-minute sustained (SSHWS/NWS) | |
| Highest winds | 80 mph (130 km/h) |
| Lowest pressure | 986 mbar (hPa); 29.12 inHg |
| Overall effects | |
| Fatalities | None |
| Damage | Minimal |
| Areas affected | Florida, Texas and Mexico |
| IBTrACS | |
Part of the 1983 Atlantic hurricane season | |
Hurricane Barry was a moderate tropical cyclone that caused minor damage in Florida, Texas, and Mexico in late August 1983. Barry was the fourth tropical depression, second named storm and second hurricane of the inactive 1983 Atlantic hurricane season. Developing out of a tropical wave on August 23, Barry quickly strengthened off the coast of Florida, reaching an initial peak intensity with winds of 60 mph (95 km/h). However, increased wind shear caused the storm to weaken to a tropical depression before making landfall near Melbourne, Florida, the next morning. Traveling almost due west, the storm regenerated and became a hurricane on August 28. The storm made landfall on the northern Mexican coastline later that day at peak intensity. Rapid weakening followed shortly after and the storm dissipated the next day. The storm had only minor effects in the United States but destroyed hundreds of homes and left over 400 homeless in northern Mexico. Despite the damage, there were no reports of fatalities or injuries.
Meteorological history
[edit]
Tropical storm (39–73 mph, 63–118 km/h)
Category 1 (74–95 mph, 119–153 km/h)
Category 2 (96–110 mph, 154–177 km/h)
Category 3 (111–129 mph, 178–208 km/h)
Category 4 (130–156 mph, 209–251 km/h)
Category 5 (≥157 mph, ≥252 km/h)
Unknown
The origins of Hurricane Barry can be traced to a tropical wave which moved off the western coast of Africa on August 13, 1983. Strong wind shear in the North Atlantic hurricane basin prevented significant development of the system as it traveled towards the west-northwest. Little convection was associated with the disturbance as a result of the shear. While approaching the Bahamas on August 22, an upper-level trough moved away from the system, which led to a decrease in the wind shear.[1] The disturbance then entered this environment and spawned an area of low pressure which intensified. On August 23, the low had become sufficiently organized to be declared Tropical Depression Four. Later that day, the depression quickly strengthened into a tropical storm and was given the name Barry by the National Hurricane Center (NHC).[2][3] About 12 hours after becoming a tropical storm, Barry reached its initial peak intensity with winds of 60 mph (95 km/h).[4]
Barry then began a westerly course towards central Florida. However, wind shear began to increase, causing the system to weaken. The NHC downgraded the storm back to a tropical depression on August 25.[2] Barry made landfall near Melbourne, Florida the same morning with winds of 35 mph (55 km/h).[4] After crossing Florida, the depression traveled towards the west-southwest due to a strong upper-level flow. On August 27, Barry became sufficiently organized to be reclassified as a tropical storm while located in the central Gulf of Mexico. The re-strengthening was the result of decreased wind shear and more favorable conditions over the Gulf. The storm continued to become better organized as it traveled nearly due west towards Mexico. At 1200 UTC the next day, Barry was upgraded to a hurricane while located about 75 mi (120 km) southeast of Brownsville, Texas. The hurricane continued to intensify until it made landfall about 35 mi (55 km) south-southeast of Brownsville[2] at peak intensity with winds of 80 mph (130 km/h).[4] The storm quickly weakened after landfall and dissipated the next day over northern Mexico.[2]
Preparations
[edit]
United States
[edit]Several watches and warnings were issued along the Florida and Texas coastlines as a result of Barry.[5] The first was a gale warning from Jupiter Inlet, Florida to Savannah, Georgia on August 24 at 1900 UTC. The warning was discontinued from St. Augustine to Savannah the next day. The next was a gale warning issued for Brownsville, Texas to Port O'Connor, Texas on August 27. This was upgraded into a hurricane warning as Barry strengthened a few hours later, and then extended to Mansfield. The warning was discontinued by late August 28.[5] Over 4,000 people were evacuated from South Padre Island in preparation of Hurricane Barry.[6] Several thousand people were evacuated from beaches in Port Aransas on August 27 as Barry approached. An estimated 700 people took refuge in shelters set up in Brownsville and 800 people fled to schools, which were being used as temporary shelters, in Harlingen. An additional 2,000 residents evacuated from Harlingen. Shelters were also opened in San Benito, Santa Rosa, and Los Fresnos.[7] Offshore, several oil platforms were evacuated in the Gulf of Mexico.[8]
Mexico
[edit]In the Mexican city of Matamoros, located south of Brownsville, Texas, Captain Manuel Leon Lopez warned residents about the approaching hurricane through radio messages. Many people were seen leaving coastal villages and heading further inland.[7] Mexican officials raised the alert level to stage three due to the threat of Barry.[9]
Impact and aftermath
[edit]
United States
[edit]Rainfall around 1 in (25 mm) were reported around Lake Okeechobee, 3 inches (76.2 mm) around the Orlando area and 1 in (25 mm) in the Miami area. The peak rainfall was 3.01 in (76 mm) in Wauchula, Florida.[10] Roads with poor drainage in Key West, Florida were flooded after the area received 1.5 in (38.1 mm) of rain.[11] Barry also affected the launch of the Space Shuttle Challenger, whose third mission was scheduled for August 30. NASA (National Aeronautics and Space Administration) did not have time to return the shuttle to the hangar in time for the storm and had the shuttle ride out the storm on the launch pad.[12] The only rainfall reported in Texas by Barry was 1-inch (25 mm) around San Antonio.[10] Along the Texas coast, beach erosion was caused from waves that were 1 to 2 feet (0.30 to 0.61 m) higher than normal.[6] Winds were gusting in excess of 50 mph (85 km/h) off the South Padre Island coast.[6] Near Brownsville, a possible tornado knocked down power lines, leaving an estimated 6,000 people without power.[9]
Mexico
[edit]No casualties were reported from Barry. However, 30 fishing boats were sunk in Mexico and several hundred homes were destroyed. The rainfall from the hurricane was considered to be relief from drought conditions in parts of northern Mexico.[2] A storm surge of 3 to 4 feet (0.91 to 1.22 m) was recorded in Mexican fishing villages. Over 400 people were made homeless and there was a major loss of shrimping nets.[6] At least ten people were left homeless in the town of El Mezquital. Homes in Santa Teresa sustained some damage but none were destroyed.[8] Only one person was injured by the storm after shards from a broken window hit the child.[13] Following the storm, General Jesus Ponce de Leon Rodriguez went to survey the damage in Tamaulipas along with a medical team.[7]
See also
[edit]- List of Texas hurricanes (1980–present)
- Other storms of the same name
- List of Category 1 Atlantic hurricanes
- Hurricane Bret (1999) – A Category 4 hurricane that impacted similar areas
- Hurricane Claudette (2003) – A Category 1 hurricane that also impacted South Texas
- Hurricane Erika (2003) – A Category 1 hurricane that took a similar path
References
[edit]- ^ Robert A. Case and Harold P. Gerrish (May 1984). "Atlantic Hurricane Season of 1983" (PDF). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved February 14, 2009.
- ^ a b c d e National Hurricane Center (1983). "Preliminary Report: Hurricane Barry – Page 1 – Storm History". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved February 14, 2009.
- ^ Staff Writer (August 24, 1983). "Tropical Storm Barry Heading for Cocoa Beach". The Deseret News. Retrieved February 14, 2009.[permanent dead link]
- ^ a b c National Hurricane Center (1983). "Preliminary Report: Hurricane Barry – Page 3 – Preliminary Best Track". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved February 14, 2009.
- ^ a b National Hurricane Center (1983). "Preliminary Report: Hurricane Barry – Page 4 – Watches and Warnings". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved April 3, 2007.
- ^ a b c d National Hurricane Center (1983). "Preliminary Report: Hurricane Barry – Page 2 – Meteorological Statistics and Impact". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved April 3, 2007.
- ^ a b c "Hurricane Barry Loses Punch in Mexico". Pittsburgh Post-Gazette. Associated Press. August 29, 1983. Retrieved February 14, 2009.[permanent dead link]
- ^ a b "Hurricane Fizzles Before Reaching Populated Areas Along Texas Coast". The Post-Standard. Associated Press. August 29, 1983. Retrieved February 14, 2009.
- ^ a b United Press International (August 29, 1983). "Barry Blows Out of South Texas". Logansport Pharos-Tribune.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|url=(help) - ^ a b David Roth (2007). "Tropical Cyclone Rainfall: Hurricane Barry". Hydrometeorogical Prediction Center. Retrieved February 2, 2007.
- ^ Staff Writer (August 26, 1983). "Rain Transforms Street Into Lake". The Miami Herald. Retrieved February 3, 2007.
- ^ Staff Writer (August 25, 1983). "NASA Secures Shuttle As Storm Heads for Cape Canaveral". The Miami Herald. Retrieved February 3, 2007.
- ^ "About 400 Homeless After Hurricane Barry". The Paris News. Associated Press. August 30, 1983.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|url=(help)
External links
[edit]