Hourglass figure

The hourglass figure is one of four traditional female body shapes described by the fashion industry; the other shapes are the rectangle, inverted triangle, and spoon (or pear). The hourglass shape is defined by a woman's body measurements – the circumference of the bust, waist and hips. Hourglass body shapes have a wide bust, a narrow waist, and wide hips with a similar measurement to that of the bust. This body shape is named for its resemblance to that of an hourglass, where the upper and lower half are wide and roughly equal while the middle is narrow in circumference, making the overall shape wide-narrow-wide.
Women who exhibit the hourglass figure have been shown to be more admired, which can put pressure on women whose body shapes are noticeably different to strive to achieve the hourglass figure. This can lead to body dissatisfaction which can cause eating disorders in (often young) women from all over the globe.[1]
Structure
[edit]The so-called "gynecoid" pelvis, is low and wide, and has a wide pubic arch.[2] This shape is considered ideal for childbirth, because women who have it can more easily deliver a child.[3] Tall women are less likely to have the gynecoid pelvis shape.[3] Ethnic variation has also been found, as East Asian women are more likely to have the gynecoid pelvis shape than White women.[4]
Evolution of female body shape
[edit]It has been proposed by scientists that the evolutionary reason for the female body shape is due in part to this sexual selection. Sex-typical body shapes (a man's muscular physique and a woman's hourglass figure) are an outcome of evolutionary adaptation for reproductive fitness because they convey information about gene quality, health and fertility, which are important elements for mate selection.[5]
Holly Dunsworth has criticised the common assumption that female body shapes evolved for the above reasons. She suggests that although sexual dimorphism may partly explain women's body shapes, they likely also reflect adaptation to reproduction and locomotion.[2] One study found that, during pregnancy, a woman's body is transformed so it is properly able to carry the baby. To prevent the center of gravity in a woman's body from being off balance, it is believed that evolution could have favored fat deposits in the gluteal region and the thighs.[6]
A systematic review of multiple studies found that age and sex were the factors most strongly correlated with waist-hip ratio. These authors wrote that there is not enough evidence to conclude that a low WHR is a sign for health, fertility or better reproductive success.[7]
Data from 1996-2005 indicated that women with larger waist circumferences had a higher risk of dying.[8]
Body shape and hormones
[edit]Sex hormones can influence body shape. Estrogen decreases fat accumulation to the abdominal region, and stimulates fat growth in the lower body.[9]
Estrogen also widens the internal structure of the pelvis (giving it the "gynecoid" shape), while the hormone relaxin causes the muscles and tendons of the pelvis to loosen, resulting in more expansion of the pelvis, increased mobility, and the so-called thigh gap.[2]
In women, high estrogen levels are associated with pelvic width, while low estrogen levels are associated with a large waist circumference.[10] Heavier women tend to have lower estrogen levels, and higher levels of androgens.[10]
History
[edit]
The hourglass figure ideal has long been documented in a variety of cultures. In ancient Greek and Egyptian artwork, sculptures of women typically feature small waists and wide hips, while in Indian and African artwork, the waist-to-hip ratios for female statues are even more pronounced.[11] In Africa's lower Niger region, a traditional Bamana song describes an ideal young woman:
A well-formed girl is never disdained, Namu....Her breasts completely fill her chest, Namu....Her buttocks stand out firmly behind her.... Look at her slender, young bamboo-like waist...[12]
In Europe, the first representations of truly fashionable women appear in the 14th century. Between the 14th and 16th centuries in northern Europe, bulging bellies were deemed desirable, however the rest of the figure was generally thin. This is most easily visible in paintings of nudes from the time. When looking at clothed images, the belly is often visible through a mass of otherwise concealing, billowing, loose robes. Since the stomach was the only visible anatomical feature, it became exaggerated in nude depictions while the rest of the body was de-emphasized. This was true in southern Europe around the time of the renaissance. Though the classical aesthetic was being revived and studied, the art produced in the time period was influenced by both factors. This resulted in a beauty standard that reconciled the two aesthetics by using classically proportioned figures who had non-classical amounts of flesh and soft, padded skin.[citation needed] In the nude paintings of the 17th century, such as those by Rubens, the naked women appear quite fat. Upon closer inspection however, most of the women have fairly normal figures- Rubens has simply painted their flesh with more flab and rolls than otherwise of that period. This may be a reflection of the female style of the day: a long, cylindrical, corseted gown with rippling satin accents. Thus Rubens' women have a tubular figure with excess flab.
While the corset continued to be fashionable into the 18th century, it shortened, became more conical, and consequently began to emphasize the waist. It also lifted and separated the breasts as opposed to the 17th century corsets which compressed and minimized the breasts. Consequently, depictions of nude women in the 18th century tend to have a very narrow waist and high, distinct breasts, almost as if they were wearing an invisible corset. La maja desnuda is a clear example of this aesthetic. The 19th century maintained the general figure of the 18th century. Examples can be seen in the works of many contemporary artists, both academic artists, such as Cabanel, Ingres, and Bouguereau, and impressionists, such as Degas, Renoir, and Toulouse-Lautrec. As the 20th century began, the rise of athletics resulted in a drastic slimming of the female figure. This culminated in the 1920s flapper look, which has informed modern fashion ever since.[citation needed] The last 100 years envelop the time period in which that overall body type has been seen as attractive, though there have been small changes within the period as well.
From the 1920s onward, the overall silhouette of the ideal woman's body slimmed down substantially. There was dramatic flattening of the entire body resulting in a more youthful aesthetic, and a pursuit of a more youthful ideal.[13]
Corsets
[edit]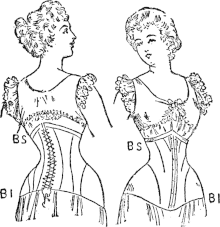
In the mid to late 1800s, during the Victorian era, the hourglass corset was used to accentuate the hourglass body shape that became popular and ideal. It accentuated a woman’s waist by compressing and reducing its size by force to allow a woman who had a straight figure to display the hourglass shape. Hourglass corset designs have varied throughout history, but the basic design and intention of the corset remained the same– the reduction of the waist line in order to create the ideal hourglass body shape where the bust and hips were similar in measurement while being much wider than the narrow waist. Even though the corsets of this time were able to give women the body of their dreams, it was also harmful and damaging to their bodies over time. This well-known historical attempt at changing a woman's body shape — corseting of the waist to make an hourglass figure — had lasting effects on the skeleton, deforming the ribs and misaligning the spine.[14]
Women's fashion
[edit]The return of the hourglass figure has been influenced by the many different roles women play at home and in the workplace. This reflects the fact that women in society have more control over what they look like than in years past. In the 1960s women celebrated liberation by wearing skimpy mini skirts, in the '70s bohemian fashion emerged thanks to the feminist movement, and in the '80s the fight for equality in the workplace led many women to choose attire that drew less attention to their bodies.[15]
Plus-size women in the fashion industry
[edit]The hourglass figure is perhaps the most iconic of the four major body shapes, as reflected by the fashion industry. Such fashion designers as Christian Dior have designed clothes with the female hourglass body shape in mind.[16] Fashion designers continue to design clothes to fit the hourglass body shape even though the body shapes of modern women are changing and becoming much more varied.[17] Even when plus-size is included in the fashion industry as well as being more commonly produced by clothing designers, the hourglass shape is a great influence on the design of plus-sized clothes. Models of plus size clothing retain the coveted hourglass figure, albeit larger than the models of regular clothing.[18] Research conducted in Britain by the University College London and the London College of Fashion found that less than 10% of women had an hourglass body shape.[17] The smooth and narrow waist continues to dominate in fashion designs meant to cater to plus-size women even when that particular body shape, the hourglass, is not commonly found.
Research
[edit]
Research indicates that men have a marked preference for women who have the hourglass figure. These studies found that this shape was even more highly preferred than breast size or facial features. While it is true that most men were initially drawn to a woman's cleavage, it was her hips and waist that were what they found the most attractive.[19] Scientists observed that the most desirable waist-to-hip ratio was 0.7—a waist that measures 70 percent of the circumference of the hips. Some examples of women who possess or have possessed the "perfect" body were Marilyn Monroe, Jessica Alba and Alessandra Ambrosio. A scientist on one of the studies speculated that the 0.7 ratio might signal female fertility.[19] One study showed that only about 8 percent of women have the sort of hourglass figure flaunted by curvaceous 1950s film stars such as Sophia Loren. Of 6,000 women's body shapes analyzed, 46 percent were described as rectangular, with the waist less than nine inches smaller than the hips or bust. Just over 20 percent of women were bottom-heavy "spoons"—pear shapes, with hips two inches larger than busts or more—, while almost 14 percent were "inverted triangles"—women whose busts were three or more inches bigger than their hips.[20]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Singh, Devendra. "An Evolutionary Theory of Female Physical Attractiveness" (PDF). Fields of Psychology.
- ^ a b c Dunsworth, Holly M. (2020). "Expanding the evolutionary explanations for sex differences in the human skeleton". Evolutionary Anthropology: Issues, News, and Reviews. 29 (3): 108–116. doi:10.1002/evan.21834. ISSN 1060-1538.
- ^ a b Cleveland Clinic medical professional (2023-03-10). "Gynecoid Pelvis: What It Means & Other Types". Cleveland Clinic. Retrieved 2024-06-19.
- ^ Cheung, R. Y. K.; Shek, K. L.; Chan, S. S. C.; Chung, T. K. H.; Dietz, H. P. (May 2015). "Pelvic floor muscle biometry and pelvic organ mobility in East Asian and Caucasian nulliparae". Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology. 45 (5): 599–604. doi:10.1002/uog.14656. ISSN 0960-7692. PMID 25175901.
- ^ Sim, Kyungok (2013). "The relationship between sex-typical body shape and quality indicators" (PDF). Journal of Social, Evolutionary, and Cultural Psychology. 7 (2): 97–120. doi:10.1037/h0099207.
- ^ Pawłowski, Bogusław; Grabarczyk, Marzena (2003). "Center of Body Mass and the Evolution of Female Body Shape". American Journal of Human Biology. 15 (2): 144–150. doi:10.1002/ajhb.10136. PMID 12621602. S2CID 42783231.
- ^ Bovet, Jeanne (2019). Jones, Alex L. (ed.). "Evolutionary Theories and Men's Preferences for Women's Waist-to-Hip Ratio: Which Hypotheses Remain? A Systematic Review". Frontiers in Psychology. 10: 1221. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2019.01221. ISSN 1664-1078. PMC 6563790. PMID 31244708.
- ^ Koster, A.; Leitzmann, M. F.; Schatzkin, A.; Mouw, T.; Adams, K. F.; van Eijk, J. Th. M.; Hollenbeck, A. R.; Harris, T. B. (2008-04-29). "Waist Circumference and Mortality". American Journal of Epidemiology. 167 (12). Oxford University Press (OUP): 1465–1475. doi:10.1093/aje/kwn079. ISSN 0002-9262. PMID 18417494.
- ^ Dixson, A.F. (2009). Sexual Selection and the Origins of Human Mating Systems. Oxford biology. OUP Oxford. p. 135. ISBN 978-0-19-955942-8. Retrieved 2024-06-19.
- ^ a b Ray, W.J. (2013). Evolutionary Psychology: Neuroscience Perspectives concerning Human Behavior and Experience. Core textbook. SAGE Publications. p. 281. ISBN 978-1-4129-9589-4. Retrieved 2024-06-19.
- ^ Lassek, William D.; Gaulin, Steven J. C. (2016-06-01). "What Makes Jessica Rabbit Sexy? Contrasting Roles of Waist and Hip Size". Evolutionary Psychology. 14 (2): 147470491664345. doi:10.1177/1474704916643459. ISSN 1474-7049. PMC 10481102.
In the Greek and Egyptian samples, the modal female WHR was 0.7, but in the Indian and African samples, it was 0.5 and 0.6, respectively. In all cases, half or more of the WHRs were below 0.7.
- ^ Smith, Merril D. (2014-09-08). Cultural Encyclopedia of the Breast. Rowman & Littlefield. p. 18. ISBN 978-0-7591-2332-8.
- ^ Whitaker, J. (2006). Service and Style: How the American Department Store Fashioned the Middle Class. St. Martin's Press. p. 291. ISBN 978-0-312-32635-7. Retrieved 2024-06-19.
- ^ "Here's How Corsets Deformed the Skeletons of Victorian Women". Forbes.
- ^ Coulson, Clare (2006-05-06). "The big new look? It's right behind you The ultra-skinny look is being challenged by the return of the hourglass figure. Clare Coulson reports on a dramatic change in the female silhouette". Daily Telegraph.
- ^ "hourglass figure type Archives - University of Fashion Blog". University of Fashion Blog. January 2017. Retrieved 2017-03-17.
- ^ a b "The shape of things to wear: scientists identify how women's figures". The Independent. 2005-11-21. Retrieved 2017-03-17.
- ^ "Why Is The Hourglass Figure The Only Celebrated Body Type In Plus Size Fashion? | Stylish Curves". Stylish Curves. 2017-03-01. Retrieved 2017-03-17.
- ^ a b Hough, Andrew (2010-08-26). "Women with hourglass figures and perfect waists most attractive, study finds". Telegraph.co.uk. Retrieved 2017-05-04.
- ^ McCormick, Helen (2005-11-21). "The shape of things to wear: Scientists identify how women's figures have changed". Independent.co.uk.
