Second Battle of the Jordan
| Second Transjordan attack on Shunet Nimrin and Es Salt | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Middle Eastern theatre of World War I | |||||||
 Prisoners captured during the 2nd Transjordan operations marching through Jerusalem May 1918 | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
| |||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Units involved | |||||||
|
60th (London) Division Anzac Mounted Division Australian Mounted Division Imperial Camel Corps Brigade Two Companies Patiala Infantry |
Fourth Army VIII Corps 3rd Cavalry Division Caucasus Cavalry Brigade 143rd Regiment 3rd and 46th Assault Companies 48th Division 703rd Infantry Battalion a storm battalion, a machine gun company and Austrian artillery | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| Unknown | 7,000 troops | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| 1,784 | Unknown | ||||||
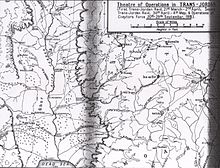
The Second Transjordan attack on Shunet Nimrin and Es Salt,[citation needed] officially known by the British as the Second action of Es Salt [1] and by others as the Second Battle of the Jordan,[2] was fought east of the Jordan River between 30 April and 4 May 1918, during the Sinai and Palestine Campaign of the First World War. The battle followed the failure of the First Transjordan attack on Amman fought at the beginning April.[1][3] During this second attack across the Jordan River, fighting occurred in three main areas. The first area in the Jordan Valley between Jisr ed Damieh and Umm esh Shert the Egyptian Expeditionary Force (EEF) defended their advanced position against an attack by units of the Seventh Army based in the Nablus region of the Judean Hills. The second area on the eastern edge of the Jordan Valley where the Ottoman Army garrisons at Shunet Nimrin and El Haud, on the main road from Ghoraniyeh to Amman were attacked by the 60th (London) Division many of whom had participated in the First Transjordan attack. The third area of fighting occurred after Es Salt was captured by the light horse brigades to the east of the valley in the hills of Moab, when they were strongly counterattacked by Ottoman forces converging on the town from both Amman and Nablus. The strength of these Ottoman counterattacks forced the EEF mounted and infantry forces to withdraw back to the Jordan Valley where they continued the Occupation of the Jordan Valley during the summer until mid September when the Battle of Megiddo began.
In the weeks following the unsuccessful First Transjordan attack on Amman and the First Battle of Amman, German and Ottoman Empire reinforcements strengthened the defences at Shunet Nimrin, while moving their Amman army headquarters moved forward to Es Salt. Just a few weeks later at the end of April, the Desert Mounted Corps again supported by the 60th (London) Division were ordered to attack the recently entrenched German and Ottoman garrisons at Shunet Nimrin and advance to Es Salt with a view to capturing Amman. Although Es Salt was captured, the attack failed despite the best efforts of the British infantry's frontal attack on Shunet Nimrin and the determined light horse and mounted rifle defences of the northern flank in the Jordan Valley. However, the mounted yeomanry attack on the rear of Shunet Nimrin failed to develop and the infantry attack from the valley could not dislodge the determined Ottoman defenders at Shunet Nimrin. By the fourth day of battle, the strength and determination of the entrenched German and Ottoman defenders at Shunet Nimrin, combined with the strength of attacks in the valley and from Amman in the hills, threatened the capture of one mounted yeomanry and five light horse brigades in the hills, defending Es Salt and attacking the rear of the Shunet Nimrin position, forcing a retreat back to the Jordan Valley.
Background
[edit]The German and Ottoman forces won victories at the first and second battles of Gaza in March and April 1917. But from the last day of October 1917 to the end of the year, the German, Austrian and Ottoman Empires endured a series of humiliating defeats in the Levant, culminating in the loss of Jerusalem and a large part of southern Palestine to the Egyptian Expeditionary Force (EEF). From just north of the Ottoman frontier with Egypt they were defeated at Gaza, at Sheria and at Beersheba, resulting in a retreat to Jaffa and the Judean Hills.[4] The Ottoman Army was again forced to retreat, this time from Capture of Jericho by General Edmund Allenby's force in February 1918.[5]
In late March and early April, German and Ottoman forces defeated Major Generals John Shea and Edward Chaytor's force at the first Transjordan attack. The Ottoman Fourth Army's VIII Corps' 48th Division with the 3rd and 46th Assault Companies and the German 703rd Infantry Battalion successfully defended Amman against the attack by the Anzac Mounted Division with the 4th (Australian and New Zealand) Battalion Imperial Camel Corps Brigade,[6][7] reinforced by infantry from the 181st Brigade, 60th (London) Division.[8][9]
The objective of the First Transjordan operations had been to disable the Hejaz Railway near Amman by demolishing viaducts and tunnels. As Shea's force moved forward, Shunet Nimrin on the main road from Ghoraniyeh to Es Salt and Amman and the town of Es Salt were captured by the infantry and mounted force. While Es Salt was garrisoned by infantry from the 60th (London) Division, two brigades of Chaytor's Anzac Mounted Division (later reinforced by infantry and artillery) continued on to Amman. The operations had only been partly successful by the time large numbers of German and Ottoman reinforcements forced a withdrawal back to the Jordan. The only territorial gains remaining in the EEF's control were the Jordan River crossings at Ghoraniyeh and Makhadet Hajlah, where pontoon bridges had been built and a bridgehead established on the eastern bank.[10][11][12] With their lines of communication seriously threatened by attacks in the Jordan Valley, Shea's and Chaytor's forces withdrew to the Jordan Valley, by 2 April 1918, maintaining the captured bridgeheads.[13]
On 21 March, Erich Ludendorff launched the German spring offensive on the Western Front, coinciding with the start of the first Transjordan attack; overnight the Palestine theatre of war went from the British government's first priority to a "side show."[14] Because of the threat to Allied armies in Europe, 24 battalions – 60,000 mostly-British soldiers – were sent to Europe as reinforcements. They were replaced by Indian infantry and cavalry from the British Indian Army.[2][15][16]
The large troop movements these withdrawals and reinforcements required caused a substantial reorganisation of the EEF.[17] Until September, when Allenby's force would be completely reformed and retrained, it would not be in a position to successfully attack both the Transjordan on the right and the Plain of Sharon on the left as well as continuing to hold the centre in the Judean Hills. In the meantime, it seemed essential to occupy the Transjordan to establish closer ties with Britain's important Arab ally, Feisal and the Hejaz Arabs. Until direct contact was made, Allenby could not completely support this force and he knew that if Feisal was defeated, German and Ottoman forces could turn the whole length of the EEF's right flank. This would make their hard-won positions shaky all the way to Jerusalem, and could result in a humiliating withdrawal, possibly to Egypt. Apart from the extremely important military ramifications of such a loss of captured territory, the political fallout could include a negative effect on the Egyptian population, upon whose cooperation the British war effort relied heavily.[18] Allenby hoped that a series of attacks into the hills of Moab could turn Ottoman attention away from the Plain of Sharon, north of Jaffa on the Mediterranean coast, to the important railway junction at Daraa which, if captured by T. E. Lawrence and Feisal, would seriously dislocate the Ottoman railway and lines of communication in Palestine.[17][19]
Prelude
[edit]After the withdrawal from Amman, the British infantry continued operations in the Judean Hills, launching unsuccessful attacks towards Tulkarem between 9 and 11 April with the aim of threatening Nablus.[20] Also on 11 April, the Ottoman 48th Infantry Division, reinforced by eight squadrons and 13 battalions, unsuccessfully attacked the Anzac Mounted Division and the Imperial Camel Corps Brigade, supported in turn by the 10th Heavy Battery and 301st Brigade Royal Field Artillery, in and near the Jordan Valley, at the Ghoraniyeh and Aujah bridgeheads and on Mussallabeh hill.[21][22][23] Between 15 and 17 April, Allenby's Hejaz Arab force attacked Ma'an with partially successful results.[24]

To support the Hejaz Arab attacks at Ma'an, Lieutenant-General Philip W. Chetwode tried to divert German and Ottoman attention away from them, encourage further operations against Amman, and attract more German and Ottoman reinforcements to Shunet Nimrin instead. He ordered Chaytor to lead an attack on 18 April against the strongly entrenched Shunet Nimrin garrison of 8,000 with a force that included an attached infantry brigade the 180th and the Anzac Mounted Division, supported by a heavy and siege artillery batteries. Also, two battalions from the 20th Indian Brigade held the Ghoraniyeh bridgehead.[25] Then on 20 April Allenby ordered Lieutenant-General Harry Chauvel of the Desert Mounted Corps to destroy the force at Shunet Nirmin and capture Es Salt with two mounted divisions and an infantry division.[26][27][28][29]
During the first Transjordan attack on Amman, the high country had still been in the grip of the wintry wet season, which badly degraded roads and tracks in the area making the movements of large military units extremely difficult. Just a few weeks later, with the rainy season over, movement was considerably easier, but the main road via Shunet Nimrin was heavily entrenched by the Ottoman army and could no longer be used to move on Es Salt; Chauvel's mounted brigades were forced to rely on secondary roads and tracks.[30]
Plans
[edit]Allenby's ambitious overall concept was to capture a great triangle of land with its tip at Amman, its northern line running from Amman to Jisr ed Damieh on the Jordan River and its southern line running from Amman to the north shore of the Dead Sea.[17][31] He ordered Chauvel to make bold and rapid marches, in an attempt to develop the attack into the total overthrow of the whole of the German and Ottoman forces. Allenby confirmed, "As soon as your operations have gained the front Amman–Es Salt, you will at once prepare for operations northward, with a view to advancing rapidly on Daraa." Chauvel's instructions included the optimistic assessment that it was unlikely that the defenders would risk withdrawing troops from the main battlefront in the Judean Hills to reinforce Shunet Nimrin.[31][32]

During the first Transjordan attack reinforcements from Nablus in the Judean Hills crossed the Jordan River to attack the northern flank, threatening the supply lines of Shea's force.[33][34] This area, together with the infantry frontal attack on Shunet Nimrin, saw the first stage of the second operation; capturing Jisr ed Damieh, Es Salt and Madaba would allow a base for advances to the Hejaz railway at Amman and the railway junction at Daraa.[31][32]
The Jisr ed Damieh crossing was on the main Ottoman lines of communication from the Ottoman Eighth Army headquarters at Tulkarem to the Ottoman Seventh Army headquarters at Nablus via the Wadi Fara and to the north from Beisan and Nazareth. The German and Ottoman forces at all these places could quickly and easily move reinforcements and supplies to the Fourth Army at Es Salt and on to Amman by crossing the Jordan River at this ford.[35][36]
Chauvel planned to control this strategically vital crossing and secure the left flank by first moving the Imperial Camel Corps Brigade from the Auja bridgehead to take control of the fords south of Jisr ed Damieh from the western side of the river. Second, the 4th Light Horse Brigade, Australian Mounted Division, would advance up the valley to take control of the road from Jisr ed Damieh to Es Salt. With this important flank secure, the 60th (London) Division under Shea was to make a frontal attack on Shunet Nimrin from the Jordan Valley while the Anzac and Australian Mounted Divisions commanded by Chaytor and Henry West Hodgson moved north up the Jordan Valley to capture the Jisr ed Damieh. After he left one brigade at Jisr ed Damieh as flank guard, covered from the west bank by the Imperial Camel Corps Brigade, the remaining brigades would move up the road to Es Salt, capture the village and launch a second attack on Shunet Nimrin from the rear.[37][38][39] One brigade of the Anzac Mounted Division was attached to the Australian Mounted Division, while the remainder of the Anzac Mounted Division formed the reserve.[39]
Problems
[edit]Planning for both the first and second Transjordan operations optimistically assumed Ottoman reinforcements would not leave the Judean Hills and cross the river, which would have disastrous effects on the operations.[31][32][40][Note 1] Neither Chauvel, nor Shea the commander of the 60th (London) Division, were keen on the second Transjordan operations.[29][41][Note 2]
Chauvel considered the operation impracticable, believing he lacked sufficient striking power and supply capacity.[42] On 26 April Chauvel explained his supply problems in detail to General Headquarters (GHQ) and asked to postpone operations against Amman and Jisr ed Damieh. In reply GHQ said they would take Chauvel's points into account before ordering any further advance, but also that the first stage, clearing the country up to the Madaba – Es Salt – Jisr ed Damieh line, would go ahead.[41]
The men of the 60th (London) Division had suffered greatly only a few weeks before during the first Transjordan operations, particularly during the attack on Amman, and had had little time to recover between attacks. Further, tackling the 5,000 strongly entrenched Ottomans around Shunet Nimrin, put on the alert by Chetwode's attack on 18 April, would be a chilling prospect.[29][41]
Chetwode later said that the first and second Transjordan attacks were "the stupidest things he [Allenby] ever did."[17] Chauvel had no confidence in the promised Arab support Allenby relied on. The attack on Shunet Nirmin relied heavily on the Beni Sakhr's ability to capture and hold Ain es Sir to cut the German and Ottoman supply line to Shunet Nimrin.[37][42]
Beni Sakhr
[edit]I have had some local fights; but I am no longer pushing North. The Arabs are doing well, East of Jordan; and I have been helping them by forcing the Turks to keep a big force of all arms opposite my bridgehead on the Jordan. I hope soon to send a considerable mounted force across the Jordan, gain permanent touch with the Arabs and deny to the Turks the grain harvest of the Salt–Madaba area. They depend largely on this grain supply.
Envoys from the Bedouin Beni Sakhr tribe, camped on the plateau about 20 miles (32 km) east of Ghoraniyeh, informed Allenby that they had 7,000 men concentrated at Madaba who could cooperate in a British advance on the east bank of the Jordan River. But due to supplies they would need to disperse to distant camping grounds by the first week in May. They assured Allenby that as soon as the Hejaz Arabs arrived, they would join them.[38][44]
The attacks on Shunet Nimrin and Es Salt were planned for about the middle of May, after the promised Indian cavalry divisions arrived.[45] But Allenby accepted the Beni Sakhr offer and brought the date for operations forward by two weeks, in the hope that the 7,000 Beni Sakhr would make up for the Indian cavalry. The Beni Sakhr offer to join the Hejaz Arabs was also enticing because these two groups together might be able to hold Es Salt and Shunet Nimrin permanently, making it unnecessary for Allenby's force to garrison the Jordan Valley over the summer period.[27][45]
The change in timing rushed preparations for the operations, which were hasty and imperfect as a result.[46] The original instructions for the second Transjordan operations contained only a general statement that considerable help might be counted on from the Beni Sakhr and that Chauvel should keep in close touch with them.[32] GHQ had no clear idea of the capabilities of the Beni Sakhr, but GHQ fitted them into Chauvel's battle and Allenby ordered Chauvel to attack on 30 April. All this happened without asking the opinion of either T. E. Lawrence or Captain Hubert Young, Lawrence's liaison officer with the Beni Sakhr, who was aware that the leader of the Arabs around Madaba was both perplexed and frightened by GHQ's reaction to his envoys.[32] Lawrence was in Jerusalem during the Shunet Nimrin and Es Salt operations and claimed no knowledge of the Beni Sakhr, or their leader.[47]
British Empire aircraft flying over the plains around Madaba saw large numbers of Bedouin ploughing their fields and grazing their animals, until they decamped across the Hejaz railway when attack on Shunet Nimrin began.[48]
Defending forces
[edit]At this time the headquarters of the German commander in chief of the Ottoman armies in Palestine, Otto Liman von Sanders, was at Nazareth. The headquarters of the Ottoman Seventh and Eighth Armies remained at Nablus and Tulkarem.[49][50][Note 3] The Ottoman Fourth Army's headquarters moved forward from Amman to Es Salt after the first Transjordan attack. The Fourth Army headquarters was defended by three companies.[31]
In the hills of Moab beyond the Jordan, Ottoman forces were at least two thousand stronger than British GHQ estimated.[51] Amman was held by two or three battalions, possibly the German 146th Regiment's 3/32nd, 1/58th, 1/150th Battalions.[dubious – discuss][31][52] a Composite Division, a German infantry company and an Austrian artillery battery.[52][53] To the east of the Jordan River the main Ottoman force of 5,000 held Shunet Nimrin with 1,000 defending Es Salt.[54] The Ottoman VIII Corps, Fourth Army, commanded by Ali Fuad Bey defended Shunet Nimrin, comprising the 48th Division, a Composite Division (made up of a variety of known units), a German infantry company and an Austrian artillery battery.[52][53]
After the first Transjordan attack on Amman, the 3rd Cavalry Division, the Caucasus Cavalry Brigade and several German infantry units which moved to the northern Jordan Valley had reinforced the Fourth Army under Jemal Pasha. These infantry units were based mainly on the west bank near Mafid Jozele where a pontoon bridge had been built. The Ottoman 24th Infantry Division, less one regiment and artillery, was also in the area and detachments patrolled the east bank to the south to maintain touch with Fourth Army patrols from Es Salt.[31][42][55] Also part of their force was a Circassian Cavalry Regiment of Arab and Circassian tribesmen.[52]
After the attack began Liman von Sanders requested reinforcements from the commander at Damascus who was to send all available troops by rail to Daraa. Two German infantry companies moving westward by rail from Daraa were ordered to de-train and join the Ottoman 24th Infantry Division. At Shunet Nimrin the VIII Corps held their ground while troops moved against the left flank of the Desert Mounted Corps.[50][56]
The Ottoman Seventh Army formed a new provisional combat detachment designed to counter-attack into the British flank.[57][Note 4] On 1 May the Ottoman troops which pushed in the 4th Light Horse Brigade's flank guard near Jisr ed Damieh, were the Ottoman 3rd Cavalry Division and part of an infantry division (probably the VIII Corps' 48th Division) part of whom continued on up the road to attack Es Salt.[58]
Attacking force
[edit]While the remainder of the Egyptian Expeditionary Force held the front line from the Mediterranean Sea to the Dead Sea and garrisoned the captured territories, Chauvel the commander of Desert Mounted Corps, replaced Chetwode, who was the commander of the XX Corps, as commander of the Jordan Valley. Chauvel took command of the Jordan Valley, as well as responsibility for second Transjordan operations.[19][59]
Chauvel's force was one mounted division stronger than the one that attacked Amman the month before, consisting of –
- the 60th (London) Division, an infantry division, commanded by Major General John Shea (less the 181st Brigade in reserve in the Judean Hills on the XX Corps front)
- the 20th Indian Brigade commanded by Brigadier General E. R. B. Murray, formed mostly by infantry from the Indian princely states,
- the Anzac Mounted Division commanded by Chaytor
- the Australian Mounted Division commanded by Major General H. W. Hodgson.[46][60]
The following units were attached to the Australian Mounted Division for their attack on Es Salt: the 1st Light Horse Brigade from the Anzac Mounted Division, the Mysore and Hyderabad lancers, from the Imperial Service Cavalry Brigade, the Dorset and Middlesex Yeomanry from the 6th, the 8th Mounted Brigades, the Hong Kong and Singapore Mountain Artillery Battery and the 12th Light Armoured Motor Battery.[46][60][Note 5]
In addition to this attacking force, stationed on the west bank of the Jordan River to guard the left flank were the Imperial Camel Corps Brigade with the 22nd Mounted Brigade.[46][60][Note 6] The XIX Brigade RHA comprising the 1/1st Nottinghamshire Royal Horse Artillery and "1/A" and "1/B" Batteries, Honourable Artillery Company,[61] were attached to the 4th Light Horse Brigade to support its defence of the northern flank in the Jordan Valley.[62][Note 7]

After their return from the first Transjordan raid, the Anzac Mounted Division remained in the Jordan Valley; camped near Jericho and were involved in the demonstration against Shunet Nimrin on 18 April. The Australian Mounted Division, which had been in rest camp near Deir el Belah from 1 January to April, moved via Gaza and Mejdel to Deiran 3 miles (4.8 km) from Jaffa in preparation to take part in the attacks northwards towards Tulkarem, known by the Ottomans as the action of Berukin from 9 to 11 April, however the engagement did not develop to a point where the mounted division could be deployed. [Note 8] During this time the Australian Mounted Division remained close to the front line, able to hear heavy bombardments from time to time both day and night and see increased aircraft operations.[63][64] After training and refitting at Deiran, on 23 April the division marched via Jerusalem and the next day down 1,500 feet (460 m) to the Jordan Valley to join the Anzac Mounted Division near Jericho.[65]
Then into Jerusalem by the Jaffa gate and right through the centre of the old city, with ancient buildings close on either side. Out through another old gate in the city wall, past the garden of Gethsemane with its fir trees, and the Mount of Olives ... Our ride through the Holy City was a tremendous thrill. The whole Division took about three hours to file slowly through the narrow streets, two horsemen abreast. It was an impressive and memorable occasion – over 6,000 mounted troops with their Machine Gun Sections, Engineers, Ambulances, supplies and transport, complete in every detail. Tough, efficient, splendidly equipped, battle-hardened, well led and well trained soldiers, a magnificent body of men and horses.
— Patrick M. Hamilton, 4th Light Horse Field Ambulance[66]


The Australian Mounted Division crossed the Jordan River at Ghoraniyeh on a pontoon bridge just wide enough for one vehicle or two horses abreast.[67][68] Then, led by the 4th Light Horse Brigade (Brigadier General William Grant) the division advanced rapidly northwards to Jisr ed Damieh; the 3rd Light Horse Brigade (Brigadier General Lachlan Wilson) continuing on to ride hard from Jisr ed Damieh to capture Es Salt. Meanwhile, the 4th Light Horse Brigade supported by at least two Royal Horse Artillery batteries took up their position of flank guard astride the Jisr ed Damieh to Es Salt road facing north-west opposite a strong German and Ottoman position holding the bridge over the Jordan River.[Note 9] The 5th Mounted Brigade (Brigadier General Philip Kelly) followed by the 2nd Light Horse Brigade (Brigadier General Granville Ryrie) moved towards Es Salt along the Umm esh Shert track.[67] They were followed later by the 1st Light Horse Brigade (Brigadier General Charles Cox) which remained across the track as guard for a time.[69][Note 10]
The force attacking Shunet Nimrin from the west was made up of the 179th and 180th Brigades (commanded by Brigadiers General FitzJ. M. Edwards and C. F. Watson) of the 60th (London) Division with their 301st and 302nd Brigades Royal Field Artillery, the IX Mountain Artillery Brigade (less one battery with the Australian Mounted Division) and the 91st Heavy Battery with the Canterbury Mounted Rifle Regiment, New Zealand Mounted Rifles Brigade, covering the right flank.[53][70][71][Note 11] The Anzac Mounted Division had one regiment from the New Zealand Mounted Rifles Brigade covering the right flank of the 60th (London) Division, and the 7th Light Horse Regiment, from the 2nd Light Horse Brigade, attached to the 60th Division. Their 1st Light Horse Brigade was attached to the Australian Mounted Division, and the remainder formed a reserve.[72]
Air support
[edit]Bombing raids on the German and Ottoman rear were carried out by No. 142 Squadron RAF (Martinsyde G.100s and Royal Aircraft Factory B.E.12a's) while roaming destroyer patrols over the whole front were carried out by No. 111 Squadron RAF (Royal Aircraft Factory S.E.5s). Aerial reconnaissance patrol aircraft flew as far as 60 miles (97 km) behind enemy lines locating several suspected Ottoman headquarters, new aerodromes, important railway centres, new railway and road works, dumps, parks of transport and troop camps. Strategic reconnaissance missions which had been carried out before the first Transjordan attack, were repeated by No. 1 Squadron, Australian Flying Corps; during 20 photography patrols over the eastern Jordan, 609 photographs were taken. The new information about all local roads, tracks and caravan routes in the Amman and Es Salt district was incorporated into revised maps.[73]
To stop the possibility of repetitions of attacks by German and Ottoman aircraft during the concentration of Chauvel's force, as had occurred prior to the first Transjordan operations, patrols were increased over the area during daylight hours.[74] These appear to have been completely successful as despite the size of the force, Liman von Sanders claims, "so secretly and ably had their [British Empire] preparations been carried out that even the most important were hidden from our aviators and from ground observation".[75]
Battle
[edit]30 April
[edit]Infantry in the Jordan Valley attack Shunet Nimrin
[edit]From the Ghoraniyeh crossing, a metaled road extended 6 miles (9.7 km) across the Jordan Valley to the Shunet Nimrin defile at the foot of the hills of Moab.[76][77] Here at Shunet Nimrin opposite the Ghoraniyeh bridgehead and crossing, the Ottoman Fourth Army's VIII Corps was strongly entrenched in positions, which controlled the main sealed road from Jericho to Es Salt and Amman and the Wadi Arseniyat (Abu Turra) track.[78][79][Note 12] The Ottoman Corps' main entrenchments ran north and south just to the west of Shunet Nimrin with the deep gorge of the Wadi Kerfrein forming their left flank while their right was thrown back in a half circle across the Wadi Arseniyat track to El Haud. Both flanks were protected by cavalry and the garrison was ordered to hold the strongly entrenched position of Shunet Nimrin at all costs. Their lines of communication to Amman ran through Es Salt and along the Wady Es Sir via the village of Ain es Sir.[50][74][78]
Chauvel's plan was to envelop and capture the Shunet Nimrin garrison and cut their lines of communication; firstly by the capture of Es Salt by light horse who would block the main road to Amman and secondly by the Beni Sakhr who were to capture Ain es Sir and block that track. With Shunet Nimrin isolated there was every reason to believe a frontal attack by British infantry from the Jordan Valley, with the New Zealand Mounted Rifles Brigade covering their right flank, would succeed.[78][80][Note 13]
The infantry attack was launched in bright moonlight at the same time as the Australian light horse galloped north along the eastern bank of the Jordan River towards Jisr ed Damieh.[81] By 02:15 leading infantry battalions were deployed opposite their first objectives which were 500–700 yards (460–640 m) away.[67] The infantry captured the advanced German and Ottoman outposts line in the first rush but the second line of solid entrenched works were strongly defended and by mid morning cross-fire from concealed machine guns had brought the advance to a standstill.[53][81] As soon as the 179th Brigade on the left emerged from cover to attack El Haud they were seen in the moonlight and fired on by these machine guns. Some slight progress was made by the 2/14th Battalion, London Regiment, 179th Brigade which captured 118 prisoners but progress became impossible due to heavy and accurate machine gun fire. Before dawn the 180th Brigade on the right made three attempts to gain two narrow paths but was fired on by machine guns and failed to reach their objective; the 2/20th Battalion, London Regiment managed to decisively defeat a reserve company killing 40 German or Ottoman soldiers and capturing 100 prisoners.[82]
Without the advantage of good observation the protracted artillery fire-fight which developed was lost by the British gunners who had problems getting ammunition forward over the fire-swept lower ground and at critical moments the infantry lacked much needed fire support owing to great difficulties in communicating with the artillery. It was eventually decided to stop the attack and to resume it the next morning.[81] After sunset the New Zealand Mounted Rifles Brigade withdrew into reserve by the Ghoraniyeh bridge leaving the Wellington Mounted Rifle Regiment with the 180th Brigade.[70]
The first infantry casualties arrived from Shunet Nimrin at the divisional receiving station three hours after the fighting began: two hours later they were at the corps main dressing station and later that day they reached the casualty clearing station at Jerusalem. By evening 409 cases had been admitted to the Anzac Mounted Division receiving station and evacuation was going on smoothly. To keep the station clear of casualties, on the following day the motor lorries, general service wagons and some of the light motor ambulances that had been brought inside the bridgehead were used to supplement the heavy cars taking the wounded back for treatment.[83]
Light horse advance up Jordan River's east bank
[edit]The Australian Mounted Division with the 1st Light Horse Brigade, the Hong Kong and Singapore Mountain Artillery Battery and the 12th Light Armoured Motor Battery (LAMB) attached, crossed the Ghoraniyeh bridge at 04:00 on the morning of 30 April.[72] The 4th Light Horse Brigade with the Australian Mounted Division's "A" and "B" Batteries HAC and the Nottinghamshire Battery RHA attached led the 3rd Light Horse Brigade 16 miles (26 km) north from the Ghoraniyeh bridgehead up the flat eastern bank of the Jordan towards Jisr ed Damieh.[39][84][85]

The 4th Light Horse Brigade was to act as the northern flank guard to prevent German and Ottoman forces moving from the east to the west bank of the Jordan River, while the 3rd Light Horse Brigade with six guns of the Hong Kong and Singapore Mountain Artillery Battery advanced up the road from Jisr ed Damieh to capture Es Salt.[85][86] If the 4th Light Horse Brigade were unable to capture the crossing they were to be deployed in such a way as cover and block this important route from Nablus and Beisan to Es Salt.[78][85][87][Note 14] At the same time as the two light horse brigades moved north on the eastern bank of the Jordan River, the Imperial Camel Corps Brigade was to move up the western bank to cover the Umm esh Shert crossing south of Jisr ed Damieh. The 1st Light Horse and 5th Mounted Brigades, the Australian Mounted Division headquarters and two mountain batteries were to ride up the Umm esh Shert track to Es Salt.[72][88]
The safety of galloping horses in open formation under shell-fire was never more strikingly demonstrated. In the long gallop only six men were killed and 17 wounded.
For 15 miles (24 km) from the Wadi Nimrin to the Jisr ed Damieh the terrain on the eastern side of the Jordan river was favourable for rapid movement by the mounted force; the Jordan river valley from the Wady\i Nimrin across the Wadi Arseniyat (which flows into the Jordan) to Umm esh Shert the flats were about 5 miles (8.0 km) wide but further north narrowed between foot-hills on the east and mud-hills along the river. Beyond Umm esh Shert the height of Red Hill jutted out from beside the Jordan to dominate the valley with encroaching foot-hills to the east. Ottoman fire was expected from guns attacking the Imperial Camel Corps Brigade on the west side of the river but Grant (commander of 4th Light Horse Brigade) relied on speed to get past machine gun and rifle fire from the foothills on his right and on his left from Red Hill and the mud-hills.[90] Firing from Red Hill and the western side of the river sent shrapnel bursting over the scattered squadrons whose pace was increased to a gallop.[89]
Posts held by the Ottoman cavalry formed a defensive line extending across the valley from Umm esh Shert.[91] This defensive line formed a line of communications, linking the German and Ottoman forces in the Fourth Army west of the Jordan River with the VIII Corps defending Shunet Nimrin. These defensive posts were attacked by the 4th Light Horse Brigade mounted, and driven back towards Mafid Jozele 4.5 miles (7.2 km) north of Umm esh Shert.[51][91] While the 3rd and 4th Light Horse Brigades continued northwards the 1st Light Horse Regiment (1st Light Horse Brigade) was ordered to attack the German and Ottoman force on Red Hill about 6,000 yards (5,500 m) north-east of Umm esh Shert.[92]
As the light horse screens advanced the mud-hills became more prominent, the passages deeper than they were further south and the two brigades were soon confined to a few broad winding wadi passages studded with large bushes. Ottoman resistance quickly developed along their whole front and the light horsemen were checked and held while still 1.5 miles (2.4 km) from Jisr ed Damieh at 05:30 on 30 April.[93][94][Note 15]

A squadron of the 11th Light Horse Regiment was sent forward at 08:00 to capture the Jisr ed Damieh bridgehead, but could not get closer than 2,000 yards (1,800 m) and even though the squadron was reinforced, they were attacked across the Jisr ed Damieh bridge by German and Ottoman infantry supported by a squadron of cavalry which forced the Australians to withdraw about 1 mile (1.6 km) eastwards. German and Ottoman forces then secured the bridge and German and Ottoman reinforcements were able to cross over the Jordan River as the bridge was no longer under observation nor threat from British artillery. Later two squadrons of the 12th Light Horse Regiment attempted to push along the Es Salt track onto the Jisr ed Damieh bridge but were unsuccessful. Meanwhile, a light horse patrol pushed northwards and at 08:00 reached Nahr ez Zerka (Wady Yabbok) about 1.5 miles (2.4 km) north of Jisr ed Damieh.[94][95][96]
The 4th Light Horse Brigade initially took up a line 8 miles (13 km) long with both flanks exposed facing north-west about 2,000 yards (1,800 m) west of the foothills covering the Jisr el Damieh to Es Salt track. This line stretched from the Nahr el Zerka to a point about .5 miles (0.80 km) south of the Es Salt track. They were supported by the Australian Mounted Division's XIX Brigade RHA which were pushed forward to cover the bridge at Jisr ed Demieh and the track leading down from Nablus on the west side. These batteries were ineffective as the range was extreme, the targets indefinite and the defensive fire power of the light 13-pounder guns small.[61][89][94]
About midday, the 1st Light Horse Regiment captured Red Hill and took over the prominent position after some intense fighting while its former German and Ottoman garrison retired across the Jordan to where there were already greatly superior enemy reinforcements. An attempt to approach these forces between Red Hill and Mafid Jozele by the light horse was stopped by heavy machine gun fire from the large force. At 15:00, the 1st Light Horse Brigade was directed by Desert Mounted Corps to move up the Umm esh Shert track to Es Salt, leaving one squadron on Red Hill.[94][95][96]
There was a gap of 3–4 miles (4.8–6.4 km) between the 4th Light Horse Brigade's left, which was held by the 11th Light Horse Regiment, and the squadron of 1st Light Horse Regiment on Red Hill supported by two squadrons deployed at the base of the hill.[97][98] Two armoured cars of the 12th Light Armoured Motor Battery were ordered by Grant to watch the gap on the left flank between Red Hill and Jisr ed Damieh. One of those cars was fairly quickly put out of action by a direct hit from a German or Ottoman shell (or was abandoned after being stuck in a deep rut), but the other remained in action until the following day when it was forced to retire, owing to casualties and lack of ammunition.[99][100] Chauvel came to inspect the deployments about 16:00 in the afternoon, when Grant (commander of 4th Light Horse Brigade) explained his difficulties, and requested another regiment to reinforce Red Hill. Chauvel had already sanctioned the move by the 1st Light Horse Brigade to Es Salt, leaving the squadron on Red Hill with four machine guns under Grant's orders and had withdrawn the 2nd Light Horse Brigade from supporting infantry in the 60th (London) Division, ordering it to follow the 1st Light Horse to Es Salt. He therefore had no spare troops and directed Grant to withdraw from Nahr ez Zerka but to continue to hold the Nablus to Es Salt road where it entered the hills towards Es Salt.[97]
After Chauvel returned to his headquarters, Grant was warned by Brigadier General Richard Howard-Vyse the Brigadier General General Staff head of G Branch (BGGS) to deploy his artillery batteries so that if necessary, they could be certain of being able to safely withdraw.[101]

On their way to Jisr ed Damieh, the 3rd and 4th Light Horse Field Ambulances [LHFA] were heavily shelled while following in the rear of their brigades.[Note 16] An advanced dressing station was formed by the 4th Light Horse Field Ambulance about 3 miles (4.8 km) north of the Umm esh Shert track, to serve both 3rd and 4th Light Horse Brigades. After sending its wheeled transport back to Ghoraniyeh bridgehead, the 3rd Light Horse Field Ambulance with their camels and horses made the journey on foot through the hills up the Jisr ed Damieh to Es Salt road, which went along the edges of very steep and in parts very slippery cliffs. At 20:00 they halted for the night in a wadi 4 miles (6.4 km) east of Es Salt.[69]
Camels move up western bank
[edit]At the same time as the light horse began their advance up the eastern bank, on the western bank of the Jordan River the Imperial Camel Corps Brigade supported by Staffordshire Yeomanry, the 383rd Siege Battery and the XVIII Brigade RHA held the Auja bridgehead and was to be prepared to advance its right at 04:00 to cover the western approaches to the Umm esh Shert crossing 7 miles (11 km) north of the Ghoraniyeh bridgehead.[41][72] This force was to establish a post, from which it could dominate the fords south of Jisr ed Damieh, at a point where the Jordan bends sharply westward 2 miles (3.2 km) north-west of Umm esh Shert.[102][103][Note 17]
The Imperial Camel Corps Brigade was stopped 1 mile (1.6 km) north-west of Umm esh Shert when confronted by strong opposition west of the river which may have included the Cossack posts dislodged by the light horse advance which had fallen back to Mafid Jozele 4.5 miles (7.2 km) north of Umm esh Shert and the garrison from Red Hill (about halfway between Umm esh Shert and Mafid Jozele) which had been forced off by the 1st Light Horse Regiment (1st Light Horse Brigade).[39][91][92]
The existence of this pontoon bridge [at Mafid Jozele] was not known until later though the pontoons must have been close handy. They had never been seen by our aeroplanes and, so far as we knew, there was no available crossing short of the bridge at Damieh.
— Lieutenant General H. G. Chauvel, commanding Desert Mounted Corps[104]
During the evening of 30 April Chauvel received reports of a pontoon bridge at Mafid Jozele and ordered the Imperial Camel Corps Brigade to attack it in the morning and destroy it. The squadron of 1st Light Horse Regiment with their four machine guns on Red Hill was instructed to cooperate from their position east of the river. Grant also instructed the 11th Light Horse Regiment (4th Light Horse Brigade) at Jisr ed Damieh to dispatch another squadron to Red Hill to assist in the destruction of the Mafid Jozele bridge; it set off at 06:00 on 1 May, by which time considerable movement could be seen to the north and it was evident large numbers of Ottoman troops had crossed the Jordan River at Jisr ed Damieh.[105]
Capture of Es Salt
[edit]At 06:30 on 30 April, the commander of the 3rd Light Horse Brigade (Brigadier-General Wilson) had a brief conference with the commander of the 4th Light Horse Brigade (Brigadier-General Grant) before his brigade began the climb up the Jisr ed Damieh road to Es Salt. Each man carried 230 rounds of ammunition; for each Hotchkiss machine-gun there were 3,100 rounds and for each machine gun 5,000 rounds. The brigade's six guns of the Hong Kong and Singapore Mountain Battery were carried, together with their ammunition, on a train of 360 camels. A further 29 camels with cacolets, completing the column.[86][106] As the brigade moved along the road an observer noted the whole brigade took three hours to pass a designated point.[101][Note 18]
The 3rd Light Horse Brigade surprised an Ottoman cavalry outpost north-west of Es Salt on the Jebel Jil'ad but the supporting troop escaped to give the alarm to German and Ottoman units holding a number of sangars in some strength further along the road. The 9th Light Horse Regiment was sent against these German and Ottoman defenders' right flank situated on a detached hillock which was quickly seized and from there the light horse opened an enfilade fire on the main position. Then under covering fire from the Hong Kong and Singapore Mountain Battery, another dismounted bayonet attack was launched frontally by the 9th Light Horse Regiment and 10th Light Horse Regiment. After a determined assault the German and Ottoman defenders were driven from the position with a loss of 28 prisoners; casualties are unknown. The Victorians in the 8th Light Horse Regiment which had been in reserve, immediately mounted and galloped into Es Salt despite fire from isolated groups of German or Ottoman soldiers in the hills. The town was full of German and Ottoman troops who were surprised by this sudden charge and the hustling tactics of the Australians broke up all attempts to organise a cohesive defence. A German officer who was attempting to rally soldiers, was forced to surrender to the leader of the first troop to enter the town at 18:30; Lieutenant C.D. Foulkes–Taylor threatened the officer with his sword and service revolver.[106][107][108]

Captures included prisoners who were equal to at least twice the fighting strength of the dismounted light horse regiment (without swords and carrying their rifles on their backs, light horse had no weapon to fight mounted)[dubious – discuss] as well as 30 machine guns and large quantities of other war material.[109] The 9th and 10th Light Horse Regiments remounted quickly and followed the 8th Regiment into the town where a total of 400 prisoners were captured by 19:00 together with a large number of machine guns and all the papers and documents of the Ottoman Fourth Army headquarters.[106][107][108]
The commander of 3rd Light Horse Brigade had orders to seize the junction of the road from Amman to Es Salt via Suweile with the Madaba to Es Salt roads at Ain Hummar on the opposite side of the town. At 20:00 one or possibly two squadrons from the 8th Light Horse Regiment pursued escaping German and Ottoman soldiers some distance down the Amman road until machine gun fire from a strong rearguard position stopped their advance 1 mile (1.6 km) from the junction with the Madaba road. The enemy position was situated astride the road at Ain Hummar, just west of the junction; here the light horsemen set up pickets and remained facing the German and Ottoman position until daylight.[108][110]
Meanwhile, climbed the escarpment on the central Umm esh Shert track (halfway between the Jisr ed Damieh and the Ghorianyeh roads) towards Es Salt were the 1st and 2nd Light Horse and the 5th Mounted Brigades with the Australian Mounted Division's headquarters and two batteries of mountain guns. This track was so steep and narrow that all were forced to lead their horses in single file; making only very slow progress.[39][88]
Places were so steep that personally I could only get up by holding on to my horse's tail and most of the way we had to struggle up on foot from the valley, no mean performance for the men carrying their rifles and over a hundred rounds of ammunition in full marching order. [The brigade was] strung out over a distance of possibly 2 miles (3.2 km) or more.
The leading yeomanry brigade encountered some resistance from small parties of German or Ottoman machine gunners which had to be outflanked and the force did not reach the plateau until twilight where they bivouacked for the night unaware the 3rd Light Horse Brigade had captured Es Salt.[110]
The first troops of this column reached Es Salt early in the morning on 1 May. The 2nd Light Horse Brigade advanced through the town and along the Amman road to Ain Hummar where they drove off the German and Ottoman rearguard and occupied the road junction. The 3rd Light Horse Brigade held an outpost line north-west and north of Es Salt and the 1st Light Horse Brigade held a similar line to the west, astride the Umm esh Shert track. The three brigades thus formed a cordon round the town on the east, north, and west.[88][Note 19]
The 5th Mounted Field Ambulance followed its brigade up the Umm esh Shert track leaving both vehicles and camels at the foot of the hills 2 miles (3.2 km) east of the divisional collecting station. The 1st and 2nd Light Horse Field Ambulances accompanied their brigades; the 2nd Light Horse Field Ambulance with nine of its cacolet camels, reached Es Salt while the 1st Light Horse Field Ambulance without any transport animals, remained with its brigade 3.5 miles (5.6 km) down the Umm esh Shert to Es Salt track. The four brigades around Es Salt had 29 cacolet camels, a captured German motor ambulance wagon and driver and a number of captured motor cars and wagons. All these were employed to transport the wounded from the 2nd and 3rd Light Horse Field Ambulances back to the Jordan Valley.[83]
Preparations for a counter-attack
[edit]About 08:30 Liman von Sanders, the commander of Ottoman forces in Palestine, was at his headquarters in Nazareth when he was informed about the second Transjordan incursion. He phoned the Seventh Ottoman Army headquarters at Nablus 21 miles (34 km) north west of Jisr ed Damieh, ordering the concentration of the 24th Infantry Division and the 3rd Cavalry Division. They were to be sent towards either the Jisr ed Damieh or Mafid Jozele with a view to crossing the river and counter-attacking Chauvel's northern flank and lines of communication to Es Salt.[35][50][111][Note 20]
The Ottoman Seventh Army had formed a new provisional combat detachment designed to launch counter-attacks into the British Empire flank. This detachment was developed by infantry in the Ottoman 24th Division's assault company. This special unit was under the command of the German Lieutenant Colonel Erich Böhme,[citation needed] and had been expanded in late April into an assault battalion made up of the Ottoman 143rd Infantry Regiment, the 24th Assault Battalion of the infantry's 24th Division, the 6th Cavalry Regiment supported by the 3rd Horse Artillery Battery (3rd Cavalry Division) and the German 1st Battalion, 146th Infantry Regiment (German Asia Korps).[112]
Early in the afternoon of 30 April, columns of German and Ottoman troops were observed marching down to the west bank of the Jordan River and were fired on by the three Australian Mounted Division batteries. They appeared to dispersed, disappearing among the broken ground on the far side of the river but they were moving towards the pontoon bridge at Mafid Jozele between Red Hill and Jisr ed Damieh.[113]
During the night the Ottoman 3rd Cavalry Division and infantry in the 24th Division (less 2nd Regiment), crossed the Jordan River at Jisr ed Damieh and concealed themselves in the foothills to the north-west of the 4th Light Horse Brigade while the 2nd Regiment (24th Division) crossed the Jordan at the lower bridge [Mafid Jozele] but the Ottoman Seventh Army ordered it back to the Jisr ed Damieh crossing. Had the attack of the 2nd Regiment continued the withdrawal may have ended with the capture of the light horse brigade.[114][115]
1 May
[edit]Infantry continue attack on Shunet Nimrin
[edit]After a 75 minutes-long bombardment at 05:30 the infantry launched fresh attacks on the same objectives as the previous day. By 10:00 Chauvel was urging the 60th (London) Division to press its attack with additional forces; infantry from the 20th Indian Brigade was sent forward and the Canterbury Mounted Rifles Regiment (New Zealand Mounted Rifles Brigade) were sent to reinforce infantry in the 179th Brigade.[70][116] These attacks were halted 20 minutes later after gaining ground which would form a favourable base from which to launch further offensives.[117] A company of the 2/18th Battalion London Regiment captured two sangars and a few prisoners on tel Buleibil; this being the only success of the day.[118]
The 60th (London) Division fought hard to capture the position at Shunet Nimrin but without success; every attack ran into heavy enfiladed machine gun fire from positions which were so successfully concealed that they could not be found by the infantry's supporting artillery.[119] The fire from the German and Ottoman machine guns was so effectively directed and concentrated on the edge of scrub, which gave cover for the British infantry approach but did not extend to the foot of the hills, that these machine guns defeated all infantry efforts to cross the open ground.[118]
The Beni Sakhr had been asked to cut the road through Ain es Sir from Amman, which had been upgraded to allow a smooth flow of troops and supplies. The Beni Sakhr had failed to cut the road and towards evening German and Ottoman reinforcements from Amman which had moved along this road, began to reinforce Shunet Nimrin.[120][121] Having seen the difficulties suffered by infantry from the 60th (London) Division the Beni Sakhr had already dispersed; playing no part in the fighting.[122][123]
German and Ottoman attack in the Jordan Valley
[edit]After the first Transjordan attack on Amman, the Ottoman 4th Army east of the Jordan River had been reinforced by the 3rd Cavalry Division, the Caucasus Cavalry Brigade, a Circassian Cavalry Regiment and the German 146th Regiment which was stationed in the northern Jordan Valley, with the 24th Division also in the area.[42][124]

Two hours after the 60th (London) Division renewed its attack on Shunet Nimrin, at about 07:30 the northern flank guard provided by the 4th Light Horse Brigade (commanded by Brigadier General William Grant) was suddenly threatened by the Ottoman 24th Infantry Division less the 2nd Regiment and the German 146th Infantry Regiment which had crossed the Jordan River unseen during the night.[99][125][126][Note 21] This strong Ottoman force advanced from the broken ground east of the Jordan, in open order with their right flank directed on the gap between the left of the 4th Light Horse Brigade and Red Hill.[99] They advanced in two waves; the first, estimated by the commander of the 4th Light Horse Brigade at 4,000 Ottoman soldiers and the second, at 1,500 soldiers.[127] These figures have been disputed; "independent Turkish and German accounts" claim 1,750 formed the first wave (the Ottoman 143rd Infantry Regiment, a storm battalion with one German company in reserve or two German companies and a German machine gun company), while the second wave was made up of three or four regiments (two regiments from the Ottoman 3rd Cavalry Division with one or two regiments from the Caucasus Cavalry Brigade).[128]
The Ottoman attacking force emerged from cover, from the direction of Jisr ed Damieh and moved quickly against the light horse on a 1,000 yards (910 m) wide front. At the same time the Ottoman 3rd Cavalry Division appeared further north and moved into the foothills towards the light horse's right.[Note 22] While the attackers moved over open ground the three batteries of XIX Brigade RHA, Australian Mounted Division opened a rapid and accurate fire on the advancing soldiers. These guns continued firing on the strong attacking force while at the same time being heavily shelled by German, Austrian and Ottoman batteries from the west bank of the Jordan.[99][125][126]
The attack proceeded very rapidly; soon enemy forces on the right overlapped the light horse's left in the valley and forces on their left quickly turned the light horse's northern flank in the foothills requiring a hasty withdrawal.[125] The 4th Light Horse Brigade was being attacked from three directions; from the Nahr ez Zerka on the light horse's right and from Jisr ed Damieh in the centre.[129] A third group, the 2nd Regiment had crossed the Jordan at the lower bridge at Mafid Jozele north of Red Hill but the Ottoman Seventh Army ordered it back to the Jisr ed Damieh crossing.[114][Note 23]
I am carrying on some operations, E. of Jordan; and today there has been some busy fighting, in which I have lost some guns. I don't mind losing them, but it is an advertisement for the Turk, which he will not fail to exploit. I was down in the Jordan valley, today. The weather was perfect, fresh and bright, after rain, and mild without heat.
The main attack was towards that part of the line held by the 4th and 12th Light Horse Regiments which was forced back until they were facing due west, with their backs to the tangled maze of, for cavalry and guns, impassable rocky hills.[131][132] The 4th Light Horse Regiment supported by ‘A’ Battery HAC on the right or northern flank, had held their position until the attackers closed to within 200 yards (180 m) when they began their slow withdrawal into the hills. The Nottinghamshire Battery RHA was positioned near the centre of the brigade but each time an attack broke and melted away before the light horse fire from rifles and the guns, the German and Ottoman dead lay a little closer to the guns of these two batteries. Each time a short retirement was made, the heavy pressure of the attackers pushed the guns further into the hills and each time there were fewer men and horses to move the guns. They were forced into a position from which there was no escape fighting till all their ammunition was exhausted and the German and Ottoman attackers were within 200–300 yards (180–270 m) on three sides. Then the teams of horses were killed by machine gun fire and the nine 13–pounder guns were abandoned while the remaining men and horses scrambled up the hills to the east and succeeded in reaching the Wadi el Retem just to the north of the Umm esh Shert track.[122][131] While the dismounted light horse could retire east into the hills if necessary, the three batteries of artillery now had no apparent way out to the east or south.[98][132]
The 4th Light Horse Brigade's guns had been pushed back into gullies, from where they had to move almost due west before they could turn south down the valley; "B" Battery on the left or southern side managed to get away with the loss of one gun. However, "A" Battery HAC and the Nottinghamshire Battery, RHA could not be moved as their teams of horses had been shot. After firing these guns to the last moment, they were abandoned.[121][125] The gunners removed the breech-blocks and sights and did as much damage as was possible in a few minutes while the brigade withdrew slowly firing as it went, up the slopes of the range to a position to which the horses had already been taken. It may have been possible to concentrate on the hills above the guns and keep the attackers away from the guns for some hours but it could have cost the whole brigade.[133] Meanwhile, the 11th Light Horse Regiment on the left of the line, managed to withdraw down the valley with "B" Battery, two light horse regiments were forced eastward deep into the foothills to make a difficult withdrawal through rocky gullies and over craggy spurs.[121][125]
Red Hill attacked and captured
[edit]After the 4th Light Horse Brigade was pushed off the Jisr ed Damieh to Es Salt track and forced to retire, a large number of German and Ottoman soldiers which had evidently worked south along the Jordan, suddenly appeared at 10:00 in the open to attack the two squadrons of the 1st and 11th Light Horse Regiments defending the height of Red Hill.[Note 24] The squadrons were quickly forced to withdraw to the broken ground south and south-east of the hill.[134][135][Note 25] Only a narrow gap now remained for the 4th Light Horse Brigade to retreat southwards.[135]
Red Hill was a dirty show, over looking the plains that unfolded to a Jordan bridge held by the Turks. Nightly patrols were a nightmare, as the Turkish artillery had the hills ranged with stone cairns, and in shelling was both active and accurate. Next day B Troop, held the ridge, and Jim, on observation, noticed much Turkish activity. Cavalry, transport, infantry, were gathering from the Jordan bridge, towards a concentration point a few miles to the North of Red Hill ... Only a few minutes were necessary to convince the Major that unless an immediate withdrawal was made, the position would be surrounded, and he ordered the squadron to contact at once the led horses, then safely hidden behind a high ridge in the rear. B. Troop did the rearguard, and ere they left the ridge bullets were spitting up the dirt, and H.E. [High Explosive Shells] was bursting dangerously near. Just how B. troop, B Squadron got out was a miracle.
— J. T. S. Scrymgeour 2nd Light Horse Regiment[136]
Retreat from Jisr ed Damieh
[edit]Immediately after the loss of Red Hill an attack along the whole line was made by Ottoman units rushing forward and shouting ‘Allah! Allah! Allah!’ The 4th Light Horse Brigade was outnumbered by five to one and was gradually being forced back to the east against the hills, fighting desperately every step of the way. The right flank was driven back across the Jisr ed Damieh to Es Salt track and German and Ottoman units entered the foothills north of the track and began to work round to the light horse brigade's rear. At the same time enemy units began to push southwards, between the left flank of the light horse brigade and the remnants of the Red Hill garrison.[134]
Two troops were sent to try and check this movement long enough to allow the right flank of the brigade to be withdrawn; brigade headquarters and every man of ‘B’ Battery H.A.C. that could be spared joined this fight.[134] The 4th and 12th Light Horse Regiments formed into many little columns of led horses and began moving in single file along the side of the steep hills. Their movement soon turned into something of a race as the German and Ottoman attackers marched on the plain and the light horsemen lead their horses through the hills. These light horsemen arrived in time to reinforce the squadron of 11th Light Horse Regiment which had been driven to a position in the foothills almost due east of Red Hill, with their left extended towards the river. There a strong firing line was rapidly built up and the German and Ottoman advance checked.[133]
The casualties during the attack were one officer and one other rank killed, seven officers and 44 other ranks wounded and 48 other ranks missing. These were mainly wounded and personnel from the 4th Light Horse Field Ambulance who remained with them.[137] Some bearers of the 4th Light Horse Field Ambulance managed to escape the trap in the ravine by galloping down the ravine towards the advancing line of German and Ottoman soldiers a few hundred yards away and then swinging left and south across the advancing enemy front. Their escape was judged to have been due to luck and the speed of their horses. "It is remarkable how one can come through a veritable rain of bullets without getting hit."[138] Nine guns, two wagons, 16 limbers, four ambulance wagons, a general service wagon and a number of water-carts and motor-cycles were also captured.[104][137][139] [Note 26]
Chaytor's group reinforce left flank
[edit]After hearing of the German and Ottoman attack on the flank guard in the Jordan Valley, Chauvel urged the 60th (London) Division to press their attack, but at 10:00 ordered the withdrawal from Shunet Nimrin of the New Zealand Mounted Brigade (less two regiments), some machine guns and some guns all of which had been supporting the 60th (London) Division's attack. These units, together with the Middlesex Yeomanry (8th Mounted Brigade) which had been in Corps reserve, were ordered to move north on the east bank of the Jordan River to reinforce the 4th Light Horse Brigade.[19][70][125] The 4th Light Horse Brigade, one regiment of the 6th Mounted Brigade and one regiment of the New Zealand Mounted Rifles Brigade was reinforced by the 1/1st Dorset Yeomanry (6th Mounted Brigade) which was to move at a rate of 4 miles (6.4 km) per hour from Musallabeh to report at the exit from the bridgehead on the track towards Wadi Arseniyat (Wadi Abu Turra).[79][140] The 17th Machine Gun Squadron and the Berkshire Battery of horse artillery were also sent along with the Auckland Mounted Rifle Regiment and two armoured cars to reinforce the northern flank guard in the Jordan Valley.[70][140][141]
To command these units, Chauvel placed the commander of the Anzac Mounted Division Major General Edward Chaytor, in command of the defence against the German and Ottoman attack in the Jordan Valley.[19][70][125] Chaytor initially went forward in a car to assess the situation, eventually riding a horse to find Grant holding the line on a wadi due east of Red Hill (the Wady Ishkarara) with the 11th Light Horse Regiment while the 4th and 12th Light Horse Regiments could be seen moving southwards leading their horses along the lower slopes of the hills.[79] Chaytor decided the position was unfavourable and moved the line to just north of the Umm esh Shert track; this withdrawal was achieved without incident.[79][Note 27]
Establishment of new line covering Umm esh Shert
[edit]
When his right flank was turned Grant ordered a retirement and the 4th Light Horse Brigade was pushed slowly south. A new shorter defensive line protecting the northern flank of the attacking forces about Es Salt was established covering the Umm esh Shert track.[121][123][142] The German and Ottoman advance was stopped about 1 mile (1.6 km) north of Um esh Shert and covering the only track still open from the Jordan Valley to the light horse and mounted brigades on the mountains at Es Salt. The line which extended eastwards towards Es Salt from the Jordan River along the Wadi el Retem and into the foothills, was held by two New Zealand regiments, two Yeomanry regiments and the 4th Light Horse Brigade.[70][120][135][143]
At about 14:00 the Middlesex Yeomanry came up on the left and took up a line north of the Umm esh Shert track in the plain which was continued by the Auckland Mounted Rifles Regiment to the bank of the Jordan River. The line was covered by the Berkshire Battery and the 17th Machine Gun Squadron when they arrived. At 14:45 the Canterbury Mounted Rifles Regiment and the 11th Light Armoured Motor Battery [LAMB], were withdrawn from the 60th (London) Division's infantry still fighting the Ottoman garrison at Shunet Nimrin, to reinforce Chaytor's force.[70][141]
The Ottoman 24th Infantry Division launched three unsuccessful attacks against the line which was quickly established by Chaytor's force. This line was anchored on high ground at Table Top and Black Hill and although Table Top was lost the new line was held and the vital Umm esh Shert track to Es Salt remained open. The 1st Light Horse Brigade, which had been holding a line astride the Umm esh Shert track close to Es Salt, was ordered to help protect the Umm esh Shert track from all directions and moved down to find touch in the hills with the 4th Light Horse Brigade late in the afternoon touch.[125][140][144][Note 28]
The Australian Mounted Division's 2nd and 3rd Light Horse and 5th Mounted Brigades at Es Salt now had one track back to the Jordan Valley.[clarification needed][145] The Umm esh Shert track was very rough and precipitous but this vital path was firmly held by the New Zealand Mounted Rifles and 4th Light Horse Brigades and a regiment of the 6th Mounted Brigade along the line of the Wady er Ratem from the Jordan Valley into the hills and by the 1st Light Horse Brigade in the hills. Its loss could have led to the capture of two brigades of the Australian Mounted Division and one brigade of the Anzac Mounted Division; the equivalent of an entire mounted division.[145]
Air support
[edit]Australian airmen of No. 1 Squadron monitored the advance on Es Salt had reported the enemy threat from the north-west of Jisr ed Damieh and a raid by No. 142 Squadron of Bristol fighter aircraft dropped bombs on Jisr ed Damieh and fired 700 rounds into the scattering cavalry. Guns were seen coming into action at Jisr ed Damieh against the light horse beyond the river and in the evening at least 800 cavalry and 400 infantry were reported on the road to Es Salt south-east of Jisr ed Damieh. Two aircraft sent to drop leaflets on the Beni Sakhr were destroyed in strong winds over the Amman area and their pilots captured.[146]
Medical support
[edit]On 1 May the Australian Mounted Division collecting station was withdrawn to the Wady Abu Muhair at the junction with the main road, under the orders of the A.D.M.S., Anzac Mounted Division. During the day the Anzac Mounted Division receiving station admitted 372 more cases, all of whom were evacuated by evening.[147]
German and Ottoman advance on Es Salt
[edit]The 3rd Light Horse Brigade was covering Es Salt from the east about half a mile from the town while the 2nd Light Horse Brigade which had just arrived moved on the Ain Hummar crossroads to support two squadrons of the 10th Light Horse Regiment, two guns of the Hong Kong Battery followed and the enemy position withdrew as a result. The light horse withdrew during the night; a detachment from 3rd Light Horse Brigade returning to its brigade to defend the town while the 2nd Light Horse moved to get in touch with the 5th Mounted Brigade and assist in the attack on the rear of the Shunet Nimrin El Haud position at Huweij Bridge.[148]
During the day the Ottoman 3rd Cavalry Division and infantry in the 2nd Regiment (24th Division) marched along the Jisr ed Damieh track towards Es Salt from the north-west.[58][125] And in the evening at least 800 cavalry and 400 infantry were reported by reconnaissance aircraft on the road to Es Salt south-east of Jisr ed Damieh.[146]
It was not until 16:40 that Major General Sir Henry W. Hodgson (commander of Australian Mounted Division) at his headquarters in Es Salt learned of the loss of the Jisr ed Damieh road and that an enemy force was moving along that road towards Es Salt.[119][148][149] He rushed two troops, the only reserves at Es Salt to the north-western side of the town to face this threat.[148]
German and Ottoman forces amply supported by field artillery and machine guns were moving to converge on Es Salt; reinforcements travelled quickly from the north and south of the Ottoman Empire on the Hejaz railway to Amman (as they had done during the first Transjordan attack in March).[41][150] Here they left their troop trains to march on Es Salt from the east while reinforcements from Nablus and Beisan marched across the Jisr ed Damieh bridge.[41]
The 2nd and 3rd Light Horse and the 5th Mounted Brigades in the vicinity of Es Salt together with the Australian Mounted Division's headquarters were completely reliant on a single line of communication from the Ghoraniyeh bridgehead in the Jordan Valley; all their communications and supplies had to travel the Umm esh Shert track.[122] Ammunition and food were running short, and as no vehicles could get up the track, fresh supplies had to be sent up to Es Salt during the night of 1/2 May on about 200 donkeys. They were collected at Ghoraniyeh bridgehead in the evening, loaded with ammunition and stores and sent off in charge of a subaltern of the gunners. They reached Es Salt in the morning, delivered their supplies to Es Salt on the plateau and returned safely to Ghoraniyeh; a distance of 40 miles (64 km) through appallingly rugged and precipitous country.[151]
Allenby reporting the day's operations
[edit]This morning operations east of Jordan were continued; LXth Division [60th Infantry Division] resumed the attack on El Haud making some progress. Australian Mounted Division entered Es Salt at 4 a.m. capturing 350 prisoners, including 33 Germans; two brigades we left to hold Es Salt, while two brigades moved south-west to attack Shunet Nimrin position from east and north-east. Enemy, estimated at 4,000 infantry, succeeded during the night of 30 April–1 May in crossing Jordan from west to east at Jisr ed Damieh and attacked brigade protecting left flank; this brigade was forced back ... During the retirement three batteries of horse artillery supporting this brigade became entangled in broken foothills of the mountains, only three guns were able to retire: the remaining nine had to be abandoned, but detachments and most horses were brought back. Reinforcements have been sent up and this line is now held by six regiments supported by two additional batteries of artillery. Operations are proceeding in accordance with plan.
— Allenby's report to the War Office at 20:00 on 1 May 1918[152]
Yeomanry advance towards El Howeij bridge and rear of Shunet Nimrin
[edit]
While the 1st, 2nd and 3rd Light Horse Brigades were deployed in defensive positions around Es Salt and protecting the line of communication to the Jordan Valley, Hodgson ordered the 5th Mounted Brigade (commanded by Brigadier General P. J. V. Kelly) to move through Es Salt and down the main road to Jericho, towards Shunet Nimrin. The mounted brigade was to attack the rear of this strong position held by the Ottoman VIII Corps, while the 60th (London) Division continued their frontal attack from below in the Jordan Valley.[88][153] The 1st Light Horse Brigade had taken up a position at the junction of the Umm esh Shert and the Abu Turra tracks, the latter of which was covered by the Ottoman forces defending the rear of Shunet Nimrin.[154] Shortly afterwards the 1st Light Horse Brigade was sent to attack Shunet Nimrin from the rear, but a little further to the north down the Abu Turra track, while the 3rd Light Horse Brigade remained covering the town of Es Salt.[88][153]
At 08:40 the Royal Gloucestershire Hussars reported they were within .5 miles (0.80 km) of the El Howeij bridge but that further progress was impossible. The remainder of the 5th Mounted Brigade arrived to support the Royal Gloucestershire Hussars about 3 miles (4.8 km) south of Es Salt where it encountered a unit of Ottoman soldiers entrenched on a cliff. The brigade commander considered the position too strong to attack but he was confident the Ottoman defenders would attempt to recover some guns he had captured. In order to be ready for an attack, he took up a defensive position astride the road even though he was aware that infantry from the 60th (London) Division, attacking Shunet Nimrin from the Jordan Valley, was having some success. At 11:00 Kelly was ordered by Hodgson to attack vigorously down the road towards Shunet Nimrin and the rear of the Ottoman position.[119][143] At 15:00 Kelly rode back to meet with Hodgson; when he described the strength of the Ottoman position defending El Howeij bridge, Hodgson decided to postpone the attack until dawn the following day when the 2nd Light Horse Brigade would join the attack.[154]
2 May
[edit]
Chauvel's force fought desperately for success; an attempt by 1st Light Horse very nearly succeeded in turning the Shunet Nimrin flank, but the VIIIth Corps was too strong, continuing to hold off the infantry attacks from the Jordan Valley, while the yeomanry mounted brigade held its position in the hills between Shunet Nimrin and Es Salt. The position of the light horse brigades at Es Salt was being seriously threatened on the east by reinforcements from Amman and from the north and northwest from Jisr ed Damieh.[155] The German and Ottoman reinforcements which had advanced from Beisan and Nablus over the Jordan River at Jisr ed Damieh began strongly attacking the 3rd Light Horse Brigade at Es Salt from the north and northwest. Later in the day Es Salt was also attacked from the east by another German and Ottoman force which had advanced from Amman forcing two regiments of the 2nd Light Horse Brigade to be withdrawn from the 5th Mounted Brigade's attack on the rear of Shunet Nimrin.[147]
By 17:30 the general situation of Hodgson's force in the hills was as follows:
- the 5th Mounted Brigade was 3,000 yards (2,700 m) north of Huweij Bridge
- the 2nd Light Horse Brigade was engaged east of Es Salt against 400 infantry, 200 cavalry and four heavy guns advancing from Suweile
- the 3rd Light Horse Brigade was northwest of Es Salt with a regiment covering the Jisr ed Damieh track as it approached Es Salt
- the 1st Light Horse Brigade (less the 1st Light Horse Regiment which was moving to reinforce the 2nd Light Horse Brigade) had its right 2 miles (3.2 km) west of Es Salt and its left in touch with the troops commanded by Chaytor protecting the line of communication; the Umm esh Shert track to the Jordan Valley.[156]
By the evening the attack by the mounted troops on the rear of Shunet Nimrin had definitely failed and Es Salt was being attacked from the southeast, from the north and from the northwest.[147] While the attack on Es Salt from Amman was held, the force approaching Es Salt from the Jisr ed Damieh was pushing strongly and vigorously against the light horse defenders; one attack at 20:00 got to within 20 yards (18 m) of the right of the 3rd Light Horse Brigade – fighting continued intermittently throughout the night.[156]
It was a five-day stunt and rations were issued accordingly for both horse and man at the beginning. That meant that by the fourth day everyone was as 'miskeen' as any Bedouin praying for baksheesh ...
— George Berrie, Driver 2nd Light Horse Field Ambulance[157]
A convoy of ammunition and medical supplies, marching through the night, succeeded in reaching Es Salt in the morning, but the corridor of supply and retreat to the Jordan Valley was very narrow; being kept open only by hard fighting.[155] The three days' rations, which each man had carried with him when the attack began, had now run out, but there was no shortage of water and good grazing for the horses as well as grain, and for the men raisins and fresh meat were requisitioned in Es Salt.[156]
Chaytor's force defends Umm esh Shert track
[edit]Chaytor's force, which was defending the left flank and the Umm esh Shert line of communication with Es Salt, was being attacked by increasingly strong Ottoman forces.[156] Two troops of the 11th Light Horse Regiment and one troop of the 4th Light Light Horse Regiment held an advanced position on a small flat-topped hill known as "Table Top" on the right, in front of Chaytor's main line of defence. This outpost was attacked from both flanks at 15:45 by German and Ottoman soldiers of the Assault Battalion of the 24th Division and Companies (these may have been the 146th Regiment, 3/32nd, 1/58th, 1/150th Battalions).[dubious – discuss] After repulsing the attackers twice with the bayonet the light horsemen were forced to withdraw losing access to a good spring but the loss of Table Top did not compromise the integrity the Umm esh Shert line.[158]
Light horse join yeomanry in attack on El Howeij bridge
[edit]The 2nd Light Horse Brigade had joined the 5th Mounted Brigade at the rear of the German and Ottoman positions at El Haud and Shunet Nimrin, but both commanders considered they had little or no hope of reaching their objectives before dark.[159] However, by 07:00 the attack on Es Salt from the east had become so threatening that Hodgson telephoned Chauvel asking if the 5th Mounted and the 2nd Light Horse Brigades could be moved to defend Es Salt.[160] At 11:30 Hodgson informed the 2nd Light Horse and 5th Mounted Brigades of the seriousness of the attacks on Es Salt and ordered one regiment of the 2nd Light Horse Brigade to be sent to reinforce the town.[159] In the early afternoon, after a telephone conversation with Hodgson, Chauvel ordered the attempt to reach the rear of the Shunet Nimrin position to be continued. Success here would resolve all difficulties and Chauvel insisted that the attack by the 2nd Light Horse and 5th Mounted Brigades on the rear of Shunet Nimrin must be continued.[119][147][149] At the time Chauvel had refused Hodgson's request for the two brigades attacking the rear of Shunet Nimrin to reinforce Es Salt, he agreed that a second regiment of 2nd Light Horse Brigade be withdrawn to defend Es Salt against growing German and Ottoman attacks.[159] Despite having redeployed two regiments of the 2nd Light Horse Brigade to defend Es Salt, Hodgson had also not lost sign of the importance of winning the attack on the rear of the Shunet Nimrin position and planned to move the regiments back to assist the 5th Mounted Brigade next morning.[119][147][149]
The 5th Mounted Brigade was left with three regiments to carry out an operation which its commander had thought impossible with five.[159] Nevertheless, two regiments, the Worcester Yeomanry and Sherwood Rangers Yeomanry, moved in single file down the wadi east of but parallel to the Es Salt road, finding progress impossible they withdrew slightly and climbed up on the east bank south of the Abu Turra.[Note 29] Here they came under heavy artillery fire and the commander of the Worcester Yeomanry decided to break off the attack on his own initiative as he considered the German and Ottoman position too strong.[161]
Further at 16:30 the commander of yeomanry in the 5th Mounted Brigade, reported Ottoman cavalry at El Fuheis south of Es Salt threatening his left flank and rear. Hodgson had no troops to spare for defence on the south side and ordered him to protect his flank and rear with two squadrons of the 6th Light Horse Regiment (2nd Light Horse Brigade) and to put in his reserve regiment in one last attack on El Howeij.[160] The mounted yeomanry tried very hard to force their way towards Shunet Nimrin, but the configuration of the ground continually forced them into defiles swept by machine gun fire and across open ridges where well placed artillery exacted its toll. Their advance was finally halted well short of its objective.[119]
The commander of the 2nd Light Horse Brigade had agreed with Kelly "that to attack down the Es Salt road was doomed to failure" and on Kelly's request reported "the ground is impossible and the position impregnable" but Hodgson refused to cancel his order.[162] This attack represented the only chance of driving in the German and Ottoman flank at El Howeij and El Haud from the east while the attack on El Haud and Shunet Nimrin by infantry in the 60th (London) Division continued from the west. Worn out by three days and nights of continuous marching and fighting, reduced by casualties, and with no support to give their attack depth, they could not reach the rear of the enemy position and the attack failed. The brigade re-formed, and took up a position on the north side of the wadi, facing the German and Ottoman force.[160]
We were on low ground. The enemy had an Artillery OP on the top of the high ground overlooking us and the Huweij Bridge. No movement on our part was possible without heavy shelling from an invisible How. Battery. We had already experienced the accuracy and deadly effect of this fire in various reconnaissance which had taken place. The attack was carried out by elements of 2 regiments [Gloucester and Notts Sherwood Ranger Yeomanry] and a very weak 3rd regiment held in reserve. The only covering fire was that of a mountain pack artillery battery which had accompanied me. M.G.s [machine guns] and Hotchkiss had to be quite early in the advance left behind, as the ground was found to be impassable to any form of pack. The attacking regiments had no opportunity of ever firing a shot, nor did we ever see any of the enemy. ... The advance, over a distance of about 1 miles from the point of assembly to the hill domineering and commanding the Huweij Bridge, took between 6 & 7 hours – during most of this time the advancing troops were under continuous and heavy How. fire from shrapnel and H.E. I remember that 5 very good officers were literally blown to bits. ... There was no question of breaking off the attack, it simply spent itself, and elements of the Bde really straggled back, some wounded, others helping wounded.
— Brigadier General P. J. V. Kelly, commander of the 5th Mounted Brigade recalled in 1928[163]
Kelly had failed to follow the orders of his two superior officers, making the point that neither Hodgson nor Chauvel or any of their staff had inspected the ground over which his men were ordered to advance and push in his reserves "to the last man." Kelly believed that "it would have been nothing short of criminal to have pushed in a very weak reserve where twice their numbers had failed" and that "the attack had inflicted no casualties whatsoever on the enemy."[164][Note 30]
Meanwhile, Chauvel refused to abandon the attack on the rear of the Shunet Nimrin position.[159] An attack by his light horse was almost successful; by moving along an unexpected route the 1st Light Horse Regiment very nearly made contact with the infantry left of the 60th (London) Division, which again attacked strongly during the night. But the Ottoman VIII Corps continued to present a strong front while their Austrian gunners, having fired away all their ammunition took their rifles and joined the detachment protecting the rear of El Haud and Shunet Nimrin.[165]
Infantry attacks on El Haud and Shunet Nimrin continue
[edit]Infantry from the 60th (London) Division continued to pressure the German and Ottoman position at Shunet Nimrin from the west while reinforcements were continuing to reach the enemy force at Shunet Nimrin via the Ain es Sir road.[147]
Shea the commander of the 60th (London) Division concluded that there was little chance of progress until El Haud was captured and planned to launch a night attack by the 179th Brigade; the 2/13th and 2/16th Battalions, London Regiment, protecting its right and two companies of the Patiala infantry on the left. The 2/18th Battalion, London Regiment (180th Brigade) was to send strong patrols along the Tell Buleibil spur towards El Haud and instead of support from 5th Mounted Brigade, the 1st Light Horse Brigade was to send a detachment from its junction with the Umm esh Shert track, down the Wadi Abu Turra track to attack El Haud from the north. At the same time the remainder of Tooth's Detachment was to work up the Wadi Abu Turra to find touch with the 1st Light Horse Brigade's detachment moving down from the north east.[166]
A necessary prerequisite for this attack towards El Haud was the capture of Ma'qqer ed Derbasi. This proved impossible during the day and plans were made for a night attack; at 02:00 one and a half companies of the 2/17th Battalion, London Regiment simultaneously assaulted Ma'qqer ed Derbasi from both the north and the south. Although the northern detachment had some success it was strongly counter-attacked and compelled to withdraw while the southern group was held up and then attacked on the flank losing 20 men captured during the retirement. Although these preliminary attacks were unsuccessful and compromised the main attack, the main attack still went ahead. Tooth's Detachment consisting of one squadron 6th Light Horse Regiment, two companies Patiala Infantry and the 16th Mountain Battery, had early successes in their advance up the Wadi Abu Turra to attack El Haud. But the advances by the 2/15th and the 2/18th Battalions, London Regiment were soon stopped by German and Ottoman defenders at Ma'qqer ed Derbasi, although there were considerable successes on the left of infantry in the 17th Brigade. At 02:00 the 2/13th Battalion, London Regiment made an advance of nearly 1,000 yards (910 m) to establish its flank well to the north of El Haud while the Patiala infantry advanced from the Wadi Abu Turra to reach a hill 1,000 yards (910 m) north west of El Haud, very nearly succeeding in turning the German and Ottoman position. Heavy machine gun fire on exposed infantry ended the attempt.[167] Daylight caught the 2/13th Battalion, London Regiment in an exposed position; forced to lie flat on the summit under heavy machine gun fire during the day, they withdrew that night.[166] Meanwhile, a squadron of 1st Light Horse Brigade moved down the Abu Turra track to a point about 1,000 yards (910 m) north of El Haud at 06:00 but was compelled to retire soon after.[168]
The frontal and rear attacks on El Haud and Shunet Nimrin had only narrowly failed, but during the day while the battle continued, the German and Ottoman force had been greatly reinforced and it became clear that the operations could not succeed.[169]
German and Ottoman attacks on Es Salt
[edit]Early in the morning of 2 May the 3rd Cavalry Division and Ottoman infantry in the 2nd Regiment (24th Division) formed a column which advanced up the road from Jisr ed Damieh, after the 4th Light Horse Brigade was forced to withdraw on 1 May. This Ottoman force made a strong attack on the positions held by the 3rd Light Horse Brigade and became heavily engaged on a line north-west and north of Es Salt. At this time Hodgson ordered two troops to move around to the north-western side of the town to stop these attackers.[119][170] At 11:00 a regiment from the 1st Light Horse Brigade was dispatched to reinforce the 3rd Light Horse Brigade and 30 minutes later a second regiment was withdrawn from the 1st Light Horse Brigade for the same purpose. At this critical time, the donkey convoy carrying 100,000 rounds of small arms ammunition and about 300 rounds for the mountain batteries arrived.[171]
During the early morning pressure from Arabs, Circassians and Ottoman reinforcements from Amman also developed on the eastern side of Es Salt.[119][Note 31]
Two regiments of the 2nd Light Horse Brigade and one of the 1st Light Horse Brigade moved to defend Es Salt on the north-east and east against German and Ottoman forces attacking from the direction of Amman. One regiment of the 2nd Light Horse Brigade which had been attacking the rear of Shunet Nimrin was ordered to move back to support the defence of Es Salt and shortly after a second regiment was withdrawn for the same purpose. By 14:30 the battle for Es Salt had become so serious on the eastern side of the town that the 1st Light Horse Brigade was ordered to send another regiment at once to join the two regiments of the 2nd Light Horse Brigade at Es Salt.[172][Note 32] Although Hodgson was forced to recall the 1st Light Horse Brigade, he ordered it to leave the 1st Light Horse Regiment to continue working south towards the rear of Shunet Nimrin.[119]
No. 1 Squadron AFC flew a series of reconnaissance missions over the Es Salt area. At 06:00 a German two-seater was sighted at about 9,000 feet (2,700 m) between Jericho and Jisr ed Damieh and was successfully attacked by an Australian Bristol Fighter aircraft. At 06:30 a large enemy cavalry forces about Ain es Sir southeast of Es Salt was sighted. By 12:00 enemy reinforcements and ammunition were seen being transported from Nablus to Mejdel Beni Fadl, and the lower Wady Fara road from Nablus to Jisr ed Damieh was full of transport, cavalry and guns, while on the Jisr ed Damieh to Es Salt section of the same road enemy cavalry was seen advancing towards Es Salt.[173]
[By 2 May] the ambulances in Es Salt were becoming short of dressings, anti-tetanic serum, chloroform, sutures and medical comforts. A stock of these was sent out on a donkey ammunition convoy and by very fine handling it made the ascent of the Umm esh Shert pass in the dark and arrived at Es Salt next morning. A duplicate supply was sent by aeroplane ... these supplies could only be dropped from the aeroplane and as Es Salt was in a basin, the drop would be about 1,000 feet. No experiment had previously been made in Palestine to determine in what manner they could be packed so as to avoid breakage when dropped. It was thought that they would be best wrapped in motor tubes but none could he obtained quickly enough. Accordingly the method adopted was that which had been employed in the siege of Kut-el-Amara. The materials were placed in a loosely filled sandbag, bottles being well packed in cotton wool in addition; this was enclosed in a second sandbag. Forty pounds of dressings were prepared at Jerusalem whence the aeroplane started. All were received intact at Es Salt with the exception of phials and bottles, the whole of which were broken.
— Colonel R. Downes commanding Australian Medical Corps and official medical historian[174]
3 May
[edit]During the night the third infantry brigade of the 60th (London) Division; the 181st Brigade, which had been in reserve on the XX Corps front, was ordered to move to the Jordan Valley from Ram Allah. The infantry brigade had arrived at Bethany at midnight, travelling in motor lorries from Jerusalem to the Jordan Valley; they arrived during the morning and concentrated in the Wadi Nimrin east of Ghoraniyeh but they were too late to affect the outcome of the battle.[174][175][176][Note 33]
Chauvel was inclined to renew the attacks on El Haud and Shunet Nimrin as he thought the Abu Turra track would be required for the retirement from Es Salt but Hodgson had decided to rely entirely on the Umm esh Shert track and infantry in the 60th (London) Division was ordered to keep the German and Ottoman force occupied during the afternoon by sudden bursts of artillery fire and feint attacks. During the day the R. A. F. dropped 600 pounds (270 kg) of bombs on Amman reporting a direct hit on the railway station.[176]
Chaytor's force continues defence of Umm esh Shert track
[edit]At 04:00 a German and Ottoman bombing assault [possibly stick bombs thrown by hand] on Black Hill on the right of the line held by Chaytor's force got to within 20 yards (18 m) of the 4th Light Horse Brigade's position. They were eventually forced to withdraw, leaving a machine gun; a second attack at dusk also failed. The defenders on Black Hill knew Hodgson's force at Es Salt depended on the Umm esh Shert track and were prepared to fight to the last man.[177]
By the evening of 3 May the German and Ottoman forces in the Jordan Valley, which had been unable to break Chaytor's force holding the Umm esh Shert track, began to withdraw to the north to reinforce the attacks on Es Salt.[178]
Meanwhile, the Queen's Own Dorset Yeomanry moved to the east bank of the Jordan River and became the reserve of the 6th Mounted Brigade.[177]
Medical support
[edit]Wounded kept arriving at 4th Light Horse Field Ambulance during a very hot Friday 3 May; their wounds were dressed in the open before sending the men straight on. The ambulance was up nearly all night evacuating patients; four ambulance loads were sent off in 5th Mounted Brigade ambulances.[179]
Decision to withdraw
[edit]
The British garrison at Es Salt was being attacked virtually from all sides when Allenby and Chauvel met on the afternoon of 3 May. At 15:00 Allenby flew to meet with Chauvel at his battle HQ 1 mile (1.6 km) west of the Ghoraniyeh bridgehead. He knew the state of battle; he had seen for himself from his aircraft the strength of the German and Ottoman troops being held by Chaytor's force.[177][180][181]
The strong attack on the light horse at Jisr ed Damieh could have been managed if Shunet Nimrin had fallen. Instead the frontage of the attack had been considerably widened and the initiative had passed firmly into German and Ottoman hands. The brigades in the hills were living off the land but running short of ammunition, and reconnaissance aircraft sighted a large concentration of German and Ottoman reinforcements at Amman.[104][122][181] On top of the threat to his lines of communication, Hodgson, the commander of the Australian Mounted Division at Es Salt, was now being seriously pressed by attacks on the town.[122]
The two great threats to the lines of communication along the Umm esh Shert track and to Es Salt, eventually compelled the abandonment of the operations when the main objective of the second Transjordan operations, to surround and capture the garrison at Shunet Nimrin, could not succeed.[123] Further the threat of encirclement and capture of Hodgson's force meant there was little to be gained and a great deal to lose from further fighting. Allenby could only acknowledge the facts; therefore he told Chauvel to issue orders for a general withdrawal. The orders went out at 16:00.[177][181][182]
German and Ottoman attacks on Es Salt held
[edit]During these operations east of the Jordan, some useful co-operation with Colonel Lawrence and the more biddable of his warlike Arabs was being achieved by the Australian Light Horse and there is no doubt that the Arabs ... diverted limited Turkish attention and forces from our front."
All day long the German and Ottoman attackers closed in on Es Salt from the east, north and north-west.[169] Australian aircraft on reconnaissance just after dawn on 3 May found that enemy camps at Wady Fara and Jisr ed Damieh had increased overnight, and units were seen crossing at Jisr ed Damieh by a punt.[184]
A fresh column of German and Ottoman reinforcements consisting of the 2nd Regiment (24th Division under the command of 3rd Cavalry Division), which had crossed the Jordan River at Mafid Jozele on the night of 30 April but had been sent back to recross at Jisr ed Damieh, worked up to within 50 yards (46 m) of the 10th Light Horse Regiment (3rd Light Horse Brigade) at Kefr Huda. Although the 2nd Regiment successfully attacked this post covering the road from Jisr ed Damieh, this post was not of great tactical importance as the road was covered by other posts. Although the 10th Light Horse Regiment was strongly attacked, the enemy were unable to continue their advance after gaining Kefr Huda.[169][177] During the day the 5th Mounted Brigade was ordered to send a regiment into reserve south east of the town.[176]
At dawn on the Amman side of Es Salt the 2nd Light Horse Brigade on the outskirts of town covering the road from Amman came to close quarters with German and Ottoman attackers. They had closed in on the position held by two squadrons of the 8th Light Horse Regiment (3rd Light Horse Brigade temporarily attached to the 2nd Light Horse Brigade) which had been sent to support the 2nd Light Horse Brigade near where the Amman road turns sharply southwards into the town.[169][176]
The situation was cleared by Major Shannon, commanding the 8th Light Horse Regiment, when he dispatched a troop of 25 men to work round the German and Ottoman right flank, if possible unseen by the enemy, and charge them from the rear. They made a desperate bayonet charge, crashing into the enemy just as they were massing for an assault, killing more than a hundred. The sudden and unexpected attack from behind so disconcerted the Germans and Ottomans that they became disorganised, while at the same time the remainder of the 8th Light Horse Regiment made a frontal attack which resulted in the enemy soldiers being driven back more than .5 miles (0.80 km).[169][176] On the right of the 8th Light Horse Regiment, the firing line had been commanded in enfilade by the 5th Light Horse Regiment (2nd Light Horse Brigade). This desperate expedient successfully broke up the attacks from the east and relieved pressure on the north side of Es Salt; 319 Ottoman soldiers were captured.[169][185]
Soon after midday a regiment of the 2nd Light Horse Brigade, still far below strength (some troops had only 20 men), took over part of the line where the full force of the enemy attack had been directed that morning. The post overlooked a deep gorge which in places was sheer, running almost to the road. Beyond the gorge another light horse regiment was holding the flank; the troop got in touch with the post on their right before dark and it was estimated that they were responsible for roughly 300 yards (270 m) of the outpost line, with orders not to withdraw until definite word from headquarters. The 20 men were split into six listening posts with instructions to retire to a little knob overlooking the road in case of a serious attack.[157]
From the post at the edge of the gorge a narrow track led down to a broad ledge with a deep drop below where the rearguard stumbled on another group who had been left behind. "At about 22:00 whispering could be heard coming from the ledge, so a stone was bowled over. They were Australians who got a shock when they found that their squadron had retired nearly an hour before and quickly left." From 21:00 the left flank was completely unprotected after the regiment posted there pulled out. Had the enemy known, they could have walked quietly round and down the road to the horses. After several more quiet hours, at 02:00 orders came to fall back on the horses and with scarcely a halt rode steadily back to the Jordan Valley.[186]
Evacuation of the wounded
[edit]By the afternoon of 3 May only 42 minor casualties had been evacuated on horseback from the Greek church in Es Salt, where an advanced dressing station had been established. Only 29 camels and the riderless horses remained for the wounded. By 18:00 2nd Light Horse Field Ambulance had left with all the wounded their camels could carry, leaving the seriously wounded and the medical personnel caring for them to await capture. After a great deal of equipment was abandoned, all but two mortally wounded men were finally mounted on to the camel cacolets of the 3rd Light Horse Field Ambulance and under heavy but wild rifle fire from the townspeople of Es Salt, left at 19:30 on a perilous 20-mile (32 km) descent of the Umm esh Shert track. Some of the wounded had been waiting for three days to leave Es Salt. Every man who could possibly cling to or tie himself on to a horse's saddle, did so in preference to trusting himself to the dreadful camel cacolets. What the wounded men in the cacolets must have suffered during this terrible journey can scarcely be imagined.[187][188]
Egyptian Camel Transport Corps not required by the fighting troops accompanied the evacuation of the wounded down the Umm Esh Shert track, preparatory to the withdrawal of the whole force. Camels, slow and sometimes obstinate beasts, made barely .5 miles (0.80 km) an hour moving in single file down the precipitous goat path of Umm esh Shert. Their feet, more suited to sand, were cut and bruised by the sharp stones and slippery rocks of the path. Groaning and protesting, the unwieldy beasts lurched perilously down the track. Every now and then one of them would stop short, blocking the way for those behind it and refuse obstinately to move on. It was past mid-day before the last camel had cleared Es Salt [178]
They travelled through the bitterly cold night, closely followed by the personnel of the advanced dressing station. One camel fell over a cliff and was killed, but its two patients were rescued. The camels loaded with the wounded in cacolets were led over places which would have been thought impassable but towards morning they showed signs of exhaustion and it was only with the greatest difficulty that they were encouraged forward. The convoy arrived at the Australian Mounted Division collecting station on the Wady Abu Muhair where the wounded were fed before being taken by ambulance wagons to the Anzac Mounted Division receiving station at Ghoraniyeh.[178][187]
The Australian Mounted Division's divisional collecting station was situated 2 miles (3.2 km) east of the Jordan on the Umm esh Shert to Es Salt track. Motor ambulance wagons of the 1st Mounted (later 4th Cavalry) Division (which was not ready to take the field) were used to transport wounded 6 miles (9.7 km) to the main dressing-station after being processed through the divisional receiving station near Ghorniyeh. Two hours after leaving Ghoraniyeh, casualties reached the main dressing station, in motor ambulance wagons supplied by the 1st (British) Mounted Division and the XX Corps. Here, three operating teams performed surgery, including 78 major operations, before the wounded were sent on to the casualty clearing station at Jerusalem. The trip from the Corps' main dressing station to Jerusalem took seven hours in 28 heavy and 10 Ford motor ambulance wagons. Army Service Corps motor lorries returning to Jerusalem were also employed.[189]
Wounded were still coming in steadily to the 4th Light Horse Field Ambulance on Saturday 4 May, when German and Ottoman guns shelled the area round a cliff where the Field Ambulance had set up a dressing station. Two men on horses were caught by the shelling; their wounds were dressed and the dressing station shifted further up the gully. At dusk word came for all troops to retreat. Some wounded were still out in the field on slow moving cacolet camels and 4th Light Horse Field Ambulance personnel went out about .5 miles (0.80 km) to meet them, and found six wounded being loaded onto transport wagons, as no ambulances were available.[179][Note 34]
Retreat on 4–5 May
[edit]Withdrawal from Es Salt
[edit]In preparation for the retreat, two sections of the 519th Field Company Royal Engineers from the infantry division; the 60th (London) Division, were sent the night before to improve the Umm esh Shert track.[190] Then during the night of 3/4 May, Hodgson's force withdrew from Es Salt down the Umm esh Shert track and by the evening of 4 May the whole force had passed through the bridgehead at Ghoraniyeh, recrossed the Jordan and returned to their lines west of the river.[155][182][Note 35]

Once the order to withdraw was given, the first priority was to hold the large bridgehead from Makhadet Hajlah to the line now held by infantry from the 60th (London) Division in front of Shunet Nimrin, and on to the Umm esh Shert until the withdrawal from Es Salt was completed.[191] At 17:15 Hodgson ordered the withdrawal of his force. The 2nd Light Horse Brigade covered the first stage of the withdrawal to a rearguard position south-west of Es Salt, while the 1st Light Horse Brigade took up a position across the Umm esh Shert track south-west of Es Salt, and facing east piqueting the heights covering the Umm esh Shert track all the way down from the rearguard position to the Jordan Valley.[178][192] Two hours after the last wounded and camels left, a force of 3,000 German and Ottoman infantry attacked the 3rd Light Horse Brigade at Es Salt. As the wounded were now well on their way down to the valley, Chauvel, the commander of Desert Mounted Corps, ordered Hodgson to withdraw to a position south-west of Es Salt covering the Umm esh Shert track.[178]
As they fell back, the 2nd and 3rd Light Horse Brigades left small groups on the tracks north and east of Es Salt to keep up intermittent firing until dawn.[192] After dark, the remainder of the force withdrew through this line regiment by regiment and marched down the track during the night. The evacuation of Es Salt was completed by 02:30, but as they could only move in single file, the regiments and brigades were strung out for many miles along the track. In the dark, movement down the mountainous Umm esh Shert track was exhausting for the long column of fighting men, wounded and refugees. The column was still making its way down to the Jordan Valley at daybreak.[178][193] The 5th Mounted Brigade, in particular, had great difficulty moving by a terrible path; their retirement had begun at 20:30 but they did not reach Jebel Umm 'Awiya until 03:45, when the brigade came under the command of Brigadier General Cox (1st Light Horse Brigade).[193]
Rearguards
[edit]After the evacuation of Es Salt was complete the 2nd Light Horse Brigade was ordered to withdraw all but the fighting troops of one regiment from its rearguard position. Australian Mounted Divisional headquarters moved to the junction of the Umm esh Shert and Abu Turra tracks where Hodgson reported at 06:10 that all camels, pack animals and prisoners had passed down the track. A column of donkeys with ammunition and biscuits which had recently arrived, joined the retreat, dumping their biscuits at the roadside for the troops to help themselves before turning back to join the withdrawal.[192]
At daylight German and Ottoman forces pushed through Es Salt to attack and press the 1st Light Horse Brigade rearguard until it was 3 miles (4.8 km) from Es Salt. At the same time enemy guns heavily shelled the light horse rearguard and several German and Ottoman aircraft caused a number of casualties when they bombed the retiring columns as they moved down the narrow, steep-sided gorge.[178] The light horse rearguard was about halfway between Es Salt and Umm esh Shert at dawn, when all the British Empire reconnaissance aircraft were sent off carrying four 20-lb. bombs.[184]
Defence of bridgeheads
[edit]By 10:30 on 4 May the mounted brigades were all clear of the hills and moving in extended order down the Jordan Valley towards the Ghoraniyeh crossing, covered by Chaytor's force of the 4th Light Horse Brigade, two regiments from the 6th and one from the 8th Mounted Brigades and part of the New Zealand Mounted Rifles Brigade with the 17th Machine Gun Squadron and the Berkshire Battery and two armoured cars. This force had been in action almost continuously, since they had taken up their position covering the Umm esh Shert track on 1 May, repelling all attacks.[140][147][178]
The rearguard of Hodgson's column was closely followed by German and Ottoman units firing on the rear of the retreating column. When they reached the Jordan Valley, the right rear of Chaytor's force was threatened by enemy units which pressed in strongly on the piquets in the hills which were soon driven in, while German aircraft continued to machine gun the column.[188][190] Five Taubes came over and for half an hour bombed the large formations and about midday German and Ottoman forces closed in on the right as our troops withdrew under heavy fire. The 4th Light Horse Brigade was being strongly pushed as it fell back following orders to retire.[179] During this crucial part of the retirement, the 4th Light Horse Brigade's right had become uncovered but when the formations got to the lower slopes of the hills the dismounted Canterbury Mounted Rifles Regiment reinforced the 4th Light Horse Brigade's right. A squadron of Queen's Own Dorset Yeomanry (6th Mounted Brigade) with the Berkshire, Leicester Batteries and the remaining three guns of "B" Battery H. A. C. came into action against this German and Ottoman force advancing down the Umm esh Shert track.[190][194] These squadrons and artillery came into action and checked the strong enemy attack with the support of the 8th Light Horse Regiment (3rd Light Horse Brigade) which had also been sent back to support the rearguard. The 1st and 3rd Light Horse Brigades and the 10th Mountain Battery formed a reserve while the 2nd Light Horse and 5th Mounted Brigades proceeded straight on through to the bridgehead.[188][195]
Attacks continued trying to work round the right flank of Chaytor's force in the Jordan Valley throughout the day, but were firmly held while Grant, beginning at 18:45, withdrew his troops by units from the left in good order.[195] The New Zealand Mounted Rifles Brigade withdrew across the Jordan River, reaching their bivouac by 04:00 on 5 May; they had left the Wellington and Auckland Mounted Rifles Regiments temporarily at the bridgehead.[194]
Infantry retirement
[edit]Shortly the 60th (London) Division broke off its fight at Shunet Nimrin and withdrew across the Jordan River leaving one infantry brigade in the bridgehead at Ghoraniyeh.[188] As they were withdrawing, two Ottoman or German aircraft attacked the 60th (London) Division west of Shunet Nimrin; they were both shot down by the infantry.[184] The dead infantrymen from the 60th (London) Division were removed in wagons for burial; it is not known what happened to the bodies of Australian light horsemen, British mounted yeomanry and New Zealand riflemen who died while fighting around Es Salt and in the Jordan Valley.[196] The 179th and 180th Brigades were moved west of the Jordan River while the 181st Brigade held the Ghoraniyeh bridgehead. Allenby decided to maintain the original bridgehead at Ghoraniyeh and to create a second one at El Auja where a bridge was to be thrown across. Chaytor sent a regiment for the defence of the El Auja crossing under the orders of Brigadier General Smith commanding the Imperial Camel Corps Brigade while engineers began work on the defences at El Auja. All troops not required to hold these bridgeheads were withdrawn west of the river.[195]
Each lifeless body was lifted into the wagons; ten, twenty, thirty and more, the very best of fellows; men with whom we had lived, with whom we had laughed, men with who we had discussed the past and planned the future, now all covered with blood and dust, tattered and disfigured – dead. It was a horrible sight. As each corpse was lifted up, we half expected to hear the old familiar laugh or the same cheerful voice. There had been no last look, no parting words. Not a sound broke the grim silence save the dull thud as each limp form found its place at the bottom of the wagon.
— Bernard Blaser, Kilts across the Jordan: Being Experiences and Impressions with the Second Battalion London Scottish in Palestine (London: H. F. & G. Witherby, 1926) p. 241 quoted in [196]
Bridgeheads re-established
[edit]By the evening Chaytor's force had retired and the battle ceased. The whole of Chauvel's force had withdrawn behind infantry from the 181st Brigade of the 60th (London) Division which had been brought across the Jordan from the west bank to form an extended bridgehead at Ghoraniyeh. During the night the last of Hodgson's force recrossed the river, and all were safely on the west bank before the morning of 5 May.[197]
Chauvel's force withdrew west of the Jordan River, retaining bridgeheads on the eastern bank.[188] The original bridgeheads at Ghoraniyeh and at Makhadet Hajlah to the south were re-established and an additional bridgehead was established at the el Auja ford to the north of Ghoraniyeh.[123] The Australian Mounted Division took over the left sector of the Jordan Valley defences along the river el Auja, including the new bridge and bridgehead thrown across the Jordan at its junction with the el Auja, during the operations. The Anzac Mounted Division took over the right sector of the Jordan Valley defences, including the Ghoraniyeh bridgehead.[197]
Casualties
[edit]The Anzac and Australian Mounted Divisions and the 60th (London) Division brought with them nearly 1,000 German and Ottoman prisoners at a cost of 1,649 British Empire casualties.[198][199] Of these 1,649 casualties (including 137 missing) 1,116 were suffered by the 60th (London) Division and the attached Patiala Infantry Battalion.[200] The total evacuations during these operations was 1,784 of whom 1,076 were wounded and 708 were sick. Only 310 of these casualties were from the light horse and mounted brigades; the infantry attack at Shunet Nimrin had been extremely costly.[201]
The Ottoman VIII Corps lost 831 casualties and its claimed half of the force which attacked the 4th Light Horse Brigade were casualties; giving a total of more than 2,000, while 44 German, 389 Ottoman and 39 Bedouin were captured.[200]
Aftermath
[edit]In January 1918, Field Marshal Jan Smuts had conferred with Allenby, to determine the future direction of operations in Palestine. Between them, they had planned for the advance to Damascus and Aleppo to begin on 5 May. As part of the first phase of this advance Lawrence and Feisal's force was undertaking the siege of Ma'an, but due to the delay in the advance northwards German and Ottoman units from Amman were in a position to threaten Feisal's Hejaz Arabs from Aba el Lissan back to Aqaba, while Allenby was threatening German and Ottoman forces to the east of the Jordan River with the capture of Es Salt. Allenby offered technical equipment to strengthen the precarious position of Lawrence and Feisal's position on the plateau.[202] With the break up of the Imperial Camel Corps Brigade Allenby gave Feisal's force 2,200 riding-camels, and 1,300 transport camels.[203]
Chauvel held the opinion, that Allenby had already determined his plans for the Battle of Megiddo, before the Second Transjordan attack.[204] Instead of the general advance to Damascus, Allenby attempted a similar operation to the First Transjordan with a force that had been strengthened by a factor of one third; by the addition of one mounted division, yet British GHQ estimates of the strength of enemy forces east of the Jordan River were about double what they had been at the time of the First Transjordan attack.[4]
The Second Transjordan revealed, not only the determination of the defending forces to cover the vital railway junction at Deraa, but difficulties for mounted units imposed by the rough terrain.[204] Shea's force attacking Shunet Nimrin and Grant's and later Chaytor's force in the Jordan Valley as well as Hodgson's force in the hills around Es Salt all demonstrated strong cohesion and leadership in skilfully conducted operations against a determined enemy where less determination would have met with disaster.[205]
During the First Transjordan attack in April 1918, when Allenby employed infantry from the 60th (London) Division, the Anzac Mounted Division and the Imperial Camel Corps Brigade in an attack on Amman, the German, Austrian and Ottoman forces demonstrated they were still capable of winning battles. And during the five weeks between the first and second Transjordan operations they demonstrated a substantial measure of recovery at Tulkarem, offensive tendencies in the upper Jordan Valley, and had created a strong defensive position at Shunet Nimrin which withstood all attacks. This already formidable enemy force was further strengthened with reinforcements said to number twice that faced during the first Transjordan operations and had been put on the alert by the demonstration on 18 April.[4] It is therefore hard to understand how Allenby concluded that Chauvel's force was strong enough to carry out its mission. Allenby may have thought German and Ottoman reinforcements would not, or could not in the time, transfer troops across the Jordan River; he may have thought that the better weather would enable his troops to move more rapidly which was indeed true, but German and Ottoman forces also benefited and it seems Allenby placed too much reliance on the Beni Sakhr.[206]

The two Transjordan operations in 1918 have been widely referred to as 'raids' implying an eventual withdrawal. The first Transjordan operation to Amman was always referred to as a 'raid' but the second incursion to Es Salt had the term imposed on it. The intention of the second Transjordan had been to open up a large and ambitious new front and the operation was referred to by German General Liman von Sanders commanding the German and Ottoman armies as 'The Second Battle of the Jordan.'[3][Note 36]
Although the first and second Transjordan operations were a distinct tactical defeat, the losses were not too heavy; about 500 in the mounted divisions and 1,100 in the infantry and close on a 1,000 prisoners were captured. The strategic effect was nevertheless favourable due to the fact that from then on one third of the total German and Ottoman forces were stationed east of the Jordan.[207] These two operations had convinced the German and Ottoman high command that their left flank would be the main focus of British offensive activity and that Allenby would not advance on the coastal plain until he had secured his right flank by the capture of Amman. As a result, the whole of the Ottoman 4th Army was employed in monitoring and harassing the Occupation of the Jordan Valley (1918) by the Egyptian Expeditionary Force leaving the extreme right of their line comparatively weak and giving Allenby an opportunity to attack on the coast of the Mediterranean in mid-September 1918.[194][198]
For his gallant and successful leadership Lieutenant Colonel Erich Böhme was awarded the Pour le Mérite by Wilhelm II on 7 May 1918.[208] Little recalled today, the Es Salt operation was with the exception of the Gallipoli evacuation, perhaps the most 'close run thing' to occur to the Egyptian Expeditionary Force in the whole Sinai and Palestine campaign. The Ottoman attack on 1 May quickly overwhelmed the 4th Light Horse Brigade and that it managed to withdraw in as good an order as it did, in confused and dangerous circumstances, is testimony to the experience of the troops and the quality of the junior, squadron and regimental leadership. If the brigade had been lost at this time, virtually the entire Australian Imperial Force in the Middle East could have been captured. The Desert Mounted Corps followed these operations with a long, hot, dusty and disease-plagued summer in the Jordan Valley while Allenby's army's British troops were replaced by Indian Army troops before the Battle of Megiddo.[209]
Beni Sakr
[edit]The Beni Sakhr did not turn up at all. The envoys who offered support represented only a small sub-tribe, and when they got back from their conference, they found all their fighting men had gone south to join the Hejazis.[81]
Notes
[edit]- Footnotes
- ^ But during the first Transjordan two light horse regiments were attacked by just such a force coming from over the Jisr ed Damieh crossing of the Jordan River in the same mann as the force which attacked the 4th Light Horse Brigade on 1 May. [Keogh 1955 p. 212, Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 349]
- ^ Although the commander of the 60th (London) Division) is referred to as Barrow, it would have been J. Shea who according to Falls commanded the 60th (London) Division in October 1917 and September 1918. Barrows commanded the 4th Cavalry Division which did not take part. [Falls 1930 Vol. 2 Part II pp. 663 & 671, 667]
- ^ See Falls' Sketch Map 21 Defence of Jerusalem Situation at 6 pm 30 December 1917 in subsection 'Defence of Jerusalem' Battle of Jerusalem (1917)
- ^ This demonstrated the continuing ability of the Ottoman army to reorganise combat groups quickly to react to new combat conditions. [Erickson 2007, p. 134]
- ^ The Warwickshire Yeomanry, 5th Mounted Brigade Australian Mounted Division, was replaced by the Sherwood Rangers Yeomanry from the 7th Mounted Brigade which was attached to the Desert Mounted Corps at the time.[Falls 1930 Vol. 2 pp. 365, 662]
- ^ It has been asserted the Imperial Camel Corps Brigade was disbanded in April. [Hall 1967 p. 43]
- ^ A siege battery and a heavy battery from the Royal Garrison Artillery also formed part of the attacking force.[Downes 1938 p. 688]
- ^ This action of Berukin was similar to but on a much smaller scale than the initial attacks which began the Battle of Megiddo (1918) five months later; in this case the losses were heavy and the gains small; 1,500 British casualties and about 200 Ottoman dead on the battlefield with 27 Ottoman and German prisoners captured. [Falls 1930 Vol. 2 pp. 350–7]
- ^ Major General Hodgson's written orders did not tell him to seize the crossing, but to establish a force astride the track leading from it towards Es Salt. [Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 369]
- ^ When fighting dismounted, one quarter of the light horse, mounted rifle and yeomanry were holding the horses, a dismounted brigade in the firing line was equivalent in rifle strength to an infantry battalion. [Preston 1921 p.168]
- ^ The 181st Brigade was in reserve on the XX Corps front where demonstrations were carried out on 29 April. On the same day the 10th (Irish) Division occupied Mezra north-west of 'Arura. [Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 368]
- ^ The Wadi Arseniyat and Wadi Abu Turra tracks are the same track. [Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 330 note]
- ^ Chauvel had employed this tactic of envelopment successfully at the Battle of Magdhaba see "Map of Magdhaba, showing Ottoman redoubts in green and attacking forces in red" and at the Battle of Rafa see "Powles' map showing the attack on Rafa and El Magruntein,"[Cutlack 1941 pp. 49–51] was very nearly successfully at the First Battle of Gaza see Map "Position at about 1800" [Bruce 2002 p. 92, Cutlack 1941 p. 59]
- ^ During the first Transjordan attack on Amman a few weeks previously, the job of the 4th Light Horse Brigade had been done by two regiments of the 1st Light Horse Brigade.
- ^ Bruce claimed the 4th Light Horse Brigade arrived at Jisr ed Damieh at 17:30. [Bruce 2002 p. 200]
- ^ For a description of German and Ottoman artillery firing on the 4th Light Horse Field Ambulance see Hamilton 1996 p. 112.
- ^ Gullett's Maps 33 and 34 below show they were not able to get into a position to dominate the fords and were unable to advance during the day.
- ^ The routes used were the Na'ur track, the Ain es Sir track, the Wadi Abu Turra track (also known as the Wadi Arseniyat track "owing to a defective map") and the Umm esh Shert track. The main road from Ghoraniyeh had been blocked at Shunet Nimrin by Ottoman forces. [Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 330] The road from Nablus via Jisr ed Damieh to Es Salt was employed by both sides at different times during the course of the engagements.
- ^ The 6th Mounted Brigade was on the west bank of the Jordan protecting Musallabeh as Chauvel thought there was some risk of an Ottoman attack there. [Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 373] The New Zealand Mounted Rifles Brigade remained in the Jordan Valley covering the flanks of the infantry as they continued their attack on Shunet Nimrin.
- ^ See Sketch map 24
- ^ The northern flank guard during the First Transjordan attack on Amman (1918) from 24 to 31 March and until 2 April (when they formed part of the rearguard), had been the 1st and 2nd Light Horse Regiments (1st Light Horse Brigade) supported by artillery and a Light Armoured Motor Battery [L. A. M. B]. These two regiments had taken it in turn to defend the Umm esh Shert track from increasingly strong Ottoman forces which had crossed the river at Jisr ed Damieh. [1st Light Horse Brigade's War Diary March and April 1918 AWM 4-10-1-44, 45]
- ^ This attack demonstrated a high degree of effective planning and coordination between Liman von Sanders' Fourth Army (headquartered at Es Salt) and his Seventh Army (headquartered at Nablus). [Hughes 1999 pp. 73 & 86]
- ^ Wavell claims this third group advanced into the gap between Red Hill and the light horse's left after crossing the pontoon bridge at Mafid Jozele. [Wavell 1968 pp. 186–7] Hughes also claims the Nablus force crossed at Mafid Jozele. [Hughes 1999 p. 86] These claims are not supported by Keogh or Falls and Gullett's Map 33 indicates the whole attacking force used the bridge at Jisr ed Damieh.
- ^ Falls assumes these soldiers crossed by the Mafid Jozele pontoon bridge. [Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 376]
- ^ The squadrons are identified as part of 1st Light Horse Regiment. [Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 376]
- ^ For a first hand description of the attack see Hamilton 1996 pp. 113–17
- ^ See Gullett's Map 34.
- ^ For a first hand description of the fighting to stop the enemy advance by R. W. Gregson 4th Light Horse Regiment regimental no. 2663, see letter published in Holloway pp. 211–2. The "Mac" referred to was Signaller Sergeant McHugh 4th Light Horse Regiment regimental no. 2664. He was awarded a Distinguished Conduct Medal for maintaining "perfect communication" between his regimental headquarters and all three squadrons of his regiment throughout the period 30 April to 4 May 1918.
- ^ This was probably the Wadi Nimrin/Shaib; the Wadi Abu Turra was some considerable distance to the north of the Howeij position. [Gullett's Map 35 – Positions on 2 May]
- ^ Kelly was removed from his command by Allenby five months later because he failed to push his advantage and capture Nazareth.[Woodward 2006 p. 179]
- ^ Downes suggests this attack from the east on Es Salt only developed later in the day. [Downes 1938 p. 692]
- ^ Preston places the remaining regiment of the 1st Light Horse Brigade in divisional reserve in the town before being sent as reinforcement. [Preston 1921 pp.169–70]
- ^ When infantry from the 181st Brigade 60th (London) (2/6th London) Division moved from Jerusalem to the Jordan Valley during the night of 2 May, its field ambulance could not bring its transport, so the transport of the 6th Mounted Field Ambulance, which had not so far been engaged, was attached to it. [Downes 1938 p. 694]
- ^ Hamilton recalled: Then got word of another wounded man still out in the field. I went forward again a short way, lit a lamp and dressed a wound in his face. I gave him a hypodermic shot of morphia, got him on a camel and hurried back. He was Trooper Good of the 4th Light Horse Regiment. A sand cart from the 1st Light Horse Field Ambulance caught us up. I transferred Good from the slow-moving camel to the sand cart and finally got him to the Anzac Mounted Division Receiving Station near the bridgehead and watched him operated on. His left eye was taken out. [Hamilton 1996 pp.117–8]
- ^ Hughes dates the return to the Jordan Valley as 3 May. [Hughes 1999 p. 87]
- ^ It was well understood that "wherever there is a numerous and highly organised body of mounted troops on either side, and when the country, comprising the theatre of war, is favourable, raids or invasions of mounted troops into the country occupied by the enemy will be one of the most important duties of the mounted services." [Mounted Service Manual for Mounted Troops of the Australian Commonwealth (Government Printer Sydney 1902) p.339]
- Citations
- ^ a b Battles Nomenclature Committee 1922 p. 33
- ^ a b Erickson 2001 p. 195
- ^ a b Baly 2003 p. 202
- ^ a b c Keogh 1955 pp. 225–6
- ^ Falls 1930 Vol. 1 pp. 279–350, 378–9, Vol. 2 Part I pp. 78–291, 302–9, Vol. 2 Part II pp. 650–7
- ^ Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 662
- ^ "Imperial Camel Corps". Australian War Memorial. Retrieved 11 January 2012.
- ^ Falls 1930 Vol. 2 Part I pp. 328–49, Part II, pp. 654–7
- ^ Baker, Chris. "British Divisions of 1914–1918". The Long Long Trail. Archived from the original on 16 December 2011.
- ^ Cutlack 1941, pp. 92, 109
- ^ Woodward 2006, p. 163
- ^ Blenkinsop 1925, p. 224
- ^ Falls 1930 Vol. 2 Part I pp. 345–49
- ^ Woodward 2006 p. 176
- ^ Woodward 2006 pp. 169–70
- ^ Blenkinsop 1925, pp. 225–6
- ^ a b c d Bou 2009 p. 186
- ^ Allenby report to Henry Wilson Chief of the Imperial General Staff (CIGS) in Hughes 1999 p. 75
- ^ a b c d Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 365
- ^ Keogh 1955 pp. 214, 216
- ^ Powles 1922 pp. 218–9
- ^ Keogh 1955 pp. 217–18
- ^ Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 655
- ^ Hughes 2004 p. 144
- ^ Falls 1930 Vol. 2 pp. 361–2
- ^ Keogh 1955 p. 218
- ^ a b Hill 1978 pp. 144–5
- ^ Blenkinsop 1925 p. 225
- ^ a b c Powles 1922 p. 219
- ^ Berrie 1949 p. 197
- ^ a b c d e f g Keogh 1955 p. 219
- ^ a b c d e Hill 1978 p. 145
- ^ Keogh 1955 p. 212
- ^ Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 349
- ^ a b Cutlack 1941 p. 95
- ^ Falls Sketch Maps Nos. 12 and 30
- ^ a b Downes 1938 p. 689
- ^ a b Powles 1922 p. 220
- ^ a b c d e Keogh 1955 p. 220
- ^ Hughes 1999 p. 76
- ^ a b c d e f Hill 1978 p. 146
- ^ a b c d Kinloch 2007 p. 283
- ^ Hughes 2004 pp. 144–5
- ^ Keogh 1955 pp. 218–9
- ^ a b Wavell 1968 p. 184
- ^ a b c d Downes 1938 p. 688
- ^ Lawrence 1962 pp. 539–40
- ^ Cutlack 1941 p. 114
- ^ Hughes 1999 p. 73
- ^ a b c d Keogh 1955 pp. 220–1
- ^ a b Hill 1978 p. 148
- ^ a b c d Falls 1930 Vol. 2 Part II p. 657
- ^ a b c d Wavell 1968 p. 185
- ^ a b Woodward 2006 p. 177
- ^ Falls 1930 Vol. 2 Parts I & II pp. 393 & 657
- ^ Hill 1978 p. 149
- ^ Erickson 2007, p. 134
- ^ a b Preston 1921 pp. 165–6
- ^ Brief Record of the Advance of the EEF 1919 pp. 37–79
- ^ a b c Falls 1930 Vol. 2 pp. 365, 368
- ^ a b Powles 1922, p.333
- ^ Gullett 1941 p. 603
- ^ Falls 1930 Vol 2 pp. 350–7
- ^ Hamilton 1996 pp. 106–7
- ^ Hamilton 1996 pp. 107 & 110
- ^ Hamilton 1996 p. 107
- ^ a b c Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 369
- ^ Hamilton 1996 p.110
- ^ a b Downes 1938 p. 690
- ^ a b c d e f g h Powles 1922 p. 221
- ^ Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 367
- ^ a b c d Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 368
- ^ Cutlack 1941 pp. 95 & 113
- ^ a b Cutlack 1941 pp. 112–3
- ^ Bruce 2002 pp. 199–200
- ^ Downes 1938 p. 682
- ^ Wavell 1968 pp. 180–1
- ^ a b c d Preston 1921 pp. 156–7
- ^ a b c d Falls 1930 Vol. 2 pp. 377–8 note
- ^ Cutlack 1941 p. 112
- ^ a b c d Keogh 1955 p. 221
- ^ Falls 1930 Vol. 2 pp. 369–70
- ^ a b Downes 1938 p. 691
- ^ Falls 1930 Vol. 2 pp. 368–69
- ^ a b c Bruce 2002 p. 200
- ^ a b Gullett 1941 p. 605
- ^ Falls 1930 Vol 2 p. 369
- ^ a b c d e Preston 1921 pp. 159–60
- ^ a b c Gullett 1941 p. 604
- ^ Gullett 1941 pp. 603–4
- ^ a b c Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 371
- ^ a b Gullett 1941 p. 606
- ^ Gullett 1941 pp. 604–5
- ^ a b c d Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 372
- ^ a b Gullett 1941 p. 604-6
- ^ a b Preston 1921 pp. 157–8
- ^ a b Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 372–73
- ^ a b Baly 2003 pp. 204–5
- ^ a b c d Preston 1921 p. 160
- ^ Falls 1930 Vol 2. p. 376
- ^ a b Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 373
- ^ Falls 1930 Vol. 2 pp. 366–7
- ^ Keogh 1955 pp. 220 & 222
- ^ a b c Hughes 1999 p. 86
- ^ Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 375
- ^ a b c Falls 1930 Vol. 2 pp. 373–4
- ^ a b Bostock 1982 p. 147
- ^ a b c Preston 1921 p.159
- ^ Gullett 1919 p. 20
- ^ a b Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 374
- ^ Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 393
- ^ Erickson 2007 p. 134, Table 5.2 p. 135
- ^ Preston 1921 p.158
- ^ a b Keogh 1955 p. 222
- ^ Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 386
- ^ Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 377
- ^ Keogh 1955 pp. 222–3
- ^ a b Falls 1930 Vol. 2 pp. 374–5
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Keogh 1955 p. 224
- ^ a b Preston 1921 p. 164-5
- ^ a b c d Bruce 2002 p. 201
- ^ a b c d e Bou 2009 p. 187
- ^ a b c d Cutlack 1941 p. 115
- ^ Falls 1930 Vol. 2 Parts I and II, pp. 393 & 657
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Keogh 1955 p. 223
- ^ a b Hughes 1999 pp. 73 & 86
- ^ Falls 1930 Vol. 2 pp. 375–6 Note & p. 393
- ^ Falls 1930 Vol. 2 pp. 375–6 Note & p. 393
- ^ Wavell 1968 pp. 186–7
- ^ Hughes 2004 p. 146
- ^ a b Preston 1921 p.162
- ^ a b Gullett 1941 pp. 614–5
- ^ a b Gullett 1941 pp. 618–9
- ^ a b c Preston 1921 p. 161
- ^ a b c Wavell 1968 p. 187
- ^ Scrymgeour 1961 pp. 53–4
- ^ a b Gullett 1941 pp. 620–2
- ^ Warrant Officer Bill Inglis 4th Light Horse Field Ambulance in Hamilton p. 118
- ^ Downes 1938 pp. 691–2
- ^ a b c d Kinloch 2007 p. 285
- ^ a b Falls 1930 Vol. 2 pp. 378–9
- ^ Preston 1921 pp. 162, 164–5
- ^ a b Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 379
- ^ Preston 1921 pp. 164–5, 159–60
- ^ a b Downes 1938 pp. 692–3
- ^ a b Cutlack 1941 pp. 115–6
- ^ a b c d e f g Downes 1938 p. 692
- ^ a b c Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 380
- ^ a b c Woodward 2006 pp. 177–8
- ^ Falls 1930 Vol. 2 pp. 330–1
- ^ Preston 1921 p.166
- ^ Hughes 2004 pp. 146–7
- ^ a b Keogh 1955 pp. 223–4
- ^ a b Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 379-80
- ^ a b c Wavell 1968 pp. 187–8
- ^ a b c d Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 383
- ^ a b Berrie 1949 p. 198
- ^ Falls 1930 Vol. 2 pp. 383–4, 393
- ^ a b c d e Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 382
- ^ a b c Preston 1921 pp.168–70
- ^ Falls 1930 Vol. 2 pp. 382–3
- ^ Kelly's 1928 recollection in Woodward 2006 pp. 177–8
- ^ Woodward 2006 pp. 178–9
- ^ Kelly's 1928 recollection in Woodward 2006 p. 179
- ^ Keogh 1955 pp. 224–5
- ^ a b Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 384
- ^ Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 381
- ^ Falls 1930 Vol. 2 pp. 384–5
- ^ a b c d e f Preston 1921 pp. 170–2
- ^ Preston 1921 pp. 167, 169–70
- ^ Preston 1921 p.167
- ^ Preston 1921 pp.169–70
- ^ Cutlack 1941 pp. 116–7
- ^ a b Downes 1938 p. 693
- ^ Hill 1978 pp. 149–50
- ^ a b c d e Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 385
- ^ a b c d e Falls 1930 Vol 2 p. 386
- ^ a b c d e f g h Preston 1921 pp.173–5
- ^ a b c Hamilton 1996 p. 117
- ^ Bruce 2002 pp. 201–2
- ^ a b c Hill 1978 p. 150
- ^ a b Hughes 1999 p. 87
- ^ Kempe 1973 p.100
- ^ a b c Cutlack 1941 p. 119
- ^ Falls 1930 Vol. 2 pp. 385–6
- ^ Berrie 1949 p. 199
- ^ a b Downes 1938 pp. 694–5
- ^ a b c d e Keogh 1955 p. 225
- ^ Downes 1938 pp. 690–1, 695
- ^ a b c Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 388
- ^ Falls 1930 Vol. 2 pp. 386–7
- ^ a b c Falls 1930 Vol. 2, p. 387
- ^ a b Falls 1930 Vol. 2 pp. 387–88
- ^ a b c Powles 1922 p. 222
- ^ a b c Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 389
- ^ a b Woodward 2006 p. 179
- ^ a b Preston 1921 p.175
- ^ a b Bruce 2002 p. 202
- ^ Woodward 2006 p. 180
- ^ a b Falls 1930 Vol. 2 pp. 389, 394
- ^ Downes 1938 pp. 691, 695
- ^ Lawrence 1962 p. 540
- ^ Lawrence 1962 p. 541
- ^ a b Hill 1978 p. 161
- ^ Pugsley 2004 pp. 142–3
- ^ Keogh 1955 p. 226
- ^ Wavell 1968 p. 188
- ^ Reichsarchiv (1925). "Yildirim" Deutsche Streiter auf heiligem Boden. Schlachten des Weltkriegs Band 4. Oldenburg/Berlin: Druck und Verlag Gerhard Stalling. p. 166.
- ^ Bou 2009 p. 188
References
[edit]- "1st Light Horse Brigade War Diary". First World War Diaries AWM4, 10-1-44, 45. Canberra: Australian War Memorial. March–April 1918.
- The Official Names of the Battles and Other Engagements Fought by the Military Forces of the British Empire during the Great War, 1914–1919, and the Third Afghan War, 1919: Report of the Battles Nomenclature Committee as Approved by The Army Council Presented to Parliament by Command of His Majesty. London: Government Printer. 1922. OCLC 29078007.
- Allenby, E. H. H.; H. Pirie-Gordon; Army of Great Britain; Egyptian Expeditionary Force (1919). A Brief Record of the Advance of the Egyptian Expeditionary Force under the command of General Sir Edmund H.H. Allenby, GCB, GCMG July 1917 to October 1918 compiled from Official Sources (2nd ed.). London: H.M. Stationery Office. OCLC 17017063.
- Baly, Lindsay (2003). Horseman, Pass By: The Australian Light Horse in World War I. East Roseville, Sydney: Simon & Schuster. OCLC 223425266.
- Berrie, George (1949). Morale A Story of Australian Light Horsemen. Sydney: Holland & Stephenson. OCLC 6273740.
- Blenkinsop, Layton John; Rainey, John Wakefield, eds. (1925). History of the Great War Based on Official Documents Veterinary Services. London: H.M. Stationers. OCLC 460717714.
- Bou, Jean (2009). Light Horse: A History of Australia's Mounted Arm. Australian Army History. Port Melbourne: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-19708-3.
- Bruce, Anthony (2002). The Last Crusade: The Palestine Campaign in the First World War. London: John Murray. ISBN 978-0-7195-5432-2.
- Cutlack, Frederic Morley (1941). The Australian Flying Corps in the Western and Eastern Theatres of War, 1914–1918. Official History of Australia in the War of 1914–1918. Vol. VIII (11th ed.). Canberra: Australian War Memorial. OCLC 220900299.
- Downes, Rupert M. (1938). "The Campaign in Sinai and Palestine". In Butler, Arthur Graham (ed.). Gallipoli, Palestine and New Guinea. Official History of the Australian Army Medical Services, 1914–1918: Volume 1 Part II (2nd ed.). Canberra: Australian War Memorial. pp. 547–780. OCLC 220879097.
- Erickson, Edward J. (2001). Ordered to Die: A History of the Ottoman Army in the First World War: Forward by General Hüseyiln Kivrikoglu. No. 201 Contributions in Military Studies. Westport Connecticut: Greenwood Press. OCLC 43481698.
- Erickson, Edward J. (2007). John Gooch; Brian Holden Reid (eds.). Ottoman Army Effectiveness in World War I: A Comparative Study. No. 26 of Cass Series: Military History and Policy. Milton Park, Abingdon, Oxon: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-203-96456-9.
- Falls, Cyril; A. F. Beck (1930). Military Operations Egypt & Palestine from June 1917 to the End of the War. Official History of the Great War Based on Official Documents by Direction of the Historical Section of the Committee of Imperial Defence: Volume 2 Part 1. London: HM Stationery Office. OCLC 644354483.
- Gullett, Henry S.; Charles Barnet; David Baker, eds. (1919). Australia in Palestine. Sydney: Angus & Robertson. OCLC 224023558.
- Gullett, Henry S. (1941). The Australian Imperial Force in Sinai and Palestine, 1914–1918. Official History of Australia in the War of 1914–1918. Vol. VII (11th ed.). Canberra: Australian War Memorial. OCLC 220900153.
- Hamilton, Patrick M. (1996). Riders of Destiny: The 4th Australian Light Horse Field Ambulance 1917–18: An Autobiography and History. Gardenvale, Melbourne: Mostly Unsung Military History. ISBN 978-1-876179-01-4.
- Hill, Alec Jeffrey (1978). Chauvel of the Light Horse: A Biography of General Sir Harry Chauvel, GCMG, KCB. Melbourne: Melbourne University Press. ISBN 978-0-522-84146-6.
- Holloway, David (1990). Hooves, Wheels & Tracks: A History of the 4th/19th Prince of Wales' Light Horse Regiment and its predecessors. Fitzroy, Melbourne: Regimental Trustees. OCLC 24551943.
- Hughes, Matthew (1999). John Gooch; Brian Holden Reid (eds.). Allenby and British Strategy in the Middle East 1917–1919. Military History and Policy. Vol. 1. London: Frank Cass. OCLC 470338901.
- Hughes, Matthew, ed. (2004). Allenby in Palestine: The Middle East Correspondence of Field Marshal Viscount Allenby June 1917 – October 1919. Army Records Society. Vol. 22. Phoenix Mill, Thrupp, Stroud, Gloucestershire: Sutton Publishing. ISBN 978-0-7509-3841-9.
- Kempe, Humphrey (1973). Participation. Melbourne: Hawthorn Press. OCLC 1057436.
- Keogh, E. G.; Joan Graham (1955). Suez to Aleppo. Melbourne: Directorate of Military Training by Wilkie & Co. OCLC 220029983.
- Kinloch, Terry (2007). Devils on Horses in the Words of the Anzacs in the Middle East,1916–19. Auckland: Exisle Publishing. ISBN 978-0-908988-94-5.
- Lawrence, T. E. (1962). Seven Pillars of Wisdom: A Triumph. London: Penguin Jonathan Cape. OCLC 560954677.
- Powles, C. Guy; A. Wilkie (1922). The New Zealanders in Sinai and Palestine. Official History New Zealand's Effort in the Great War. Vol. III. Auckland: Whitcombe & Tombs. OCLC 2959465.
- Preston, R. M. P. (1921). The Desert Mounted Corps: An Account of the Cavalry Operations in Palestine and Syria 1917–1918. London: Constable & Co. OCLC 3900439.
- Pugsley, Christoper (2004). The Anzac Experience New Zealand, Australia and Empire in the First World War. Auckland: Reed Books. ISBN 978-0-7900-0941-4.
- Scrymgeour, J. T. S. (c. 1961). Blue Eyes: A True Romance of the Desert Column. Infracombe: Arthur H. Stockwell. OCLC 220903073.
- Wavell, Field Marshal Earl (1968) [1933]. "The Palestine Campaigns". In Sheppard, Eric William (ed.). A Short History of the British Army (4th ed.). London: Constable & Co. OCLC 35621223.
- Woodward, David R. (2006). Hell in the Holy Land: World War I in the Middle East. Lexington: The University Press of Kentucky. ISBN 978-0-8131-2383-7.
- Battles in 1918
- 1918 in British-administered Palestine
- Battles of World War I involving the Ottoman Empire
- Battles of World War I involving Germany
- Battles of World War I involving Australia
- Battles of World War I involving the United Kingdom
- Battles of World War I involving New Zealand
- Battles of World War I involving Indian Princely States
- Middle Eastern theatre of World War I
- April 1918 events
- May 1918 events
