Ceutí
You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in Spanish. (December 2014) Click [show] for important translation instructions.
|
Ceutí | |
|---|---|
 | |
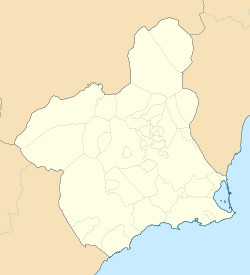
 Location in Murcia | |
| Coordinates: 38°4′44″N 1°16′20″W / 38.07889°N 1.27222°W | |
| Country | |
| Autonomous community | |
| Province | |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Juan Felipe Cano Martínez |
| Area | |
• Total | 10.34 km2 (3.99 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 62 m (203 ft) |
| Population (2018)[1] | |
• Total | 11,565 |
| • Density | 1,100/km2 (2,900/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Website | Official website |
Ceutí is a municipality in the autonomous region of Murcia in southeastern Spain[2] and is located in the south-east of the northeasternquarter of the Region.[3] As of 2021, there are 12,199 inhabitants.[4]
Geography
[edit]Climate
[edit]According to the Köppen climate classification, the municipality of Ceutí has a semi-arid climate (BSk), like its bordering municipalities. Winters are very mild and summers are hot and dry. There is limited precipitation, less than 300 mm annually, with maximum rainfall in the spring and fall and minimum rainfall in the summer. Temperatures below freezing are rare in the winter, as are temperatures higher than 104°F in the summer.[5]
Symbols
[edit]Flag
[edit]The Municipal Flag of Ceutí is described as follows: a surface with 2 by 3 dimensions, green, in whose center and occupying half the height is a golden yellow tower with a red door and window, guarded by a brown dog.
Culture
[edit]Ceutí offers a wide range of cultural experiences, highlighting the following museums:[6]
- Museo Antonio Campillo, dedicated to the work of Murcian sculptor Antonio Campillo Párraga.
- La Conservera, a museum of national and international contemporary art.
- Museo al aire libre de Ceutí, with a series of sculptural work from contemporary artists displayed in streets, parks, and gardens within the municipality. Includes work by José Planes, Manolo Belzunce, Antonio Campillo, Manolo Valdés, and Rafael Canogar.[7]
- Museo 7 chimeneas (also known as Museo de la Conserva Vegetal y las Costumbres), located in an old canning factory, which collects marks of the history of Ceutí, such as customs, ways of life, and popular festivals and other entertainment, especially with respect to the past economic boom in the canning industry.
The town also has a cultural center that serves as a municipal auditorium.
Heritage
[edit]Within the municipality of Ceutí are a series of buildings identified as the town's architectural heritage. A large majority of these buildings are made up of buildings of religious origins.
Church of Saint Mary Magdalene
[edit]The Church of Ceutí is dedicated to Saint Mary Magdalene (Spanish: Santa María Magdalena). The construction of the current building dates from the middle of the 20th century, when it was decided to build a new building in the same place that the previous one had occupied. The building is constructed in classical Roman style.
The building is approximately 115 feet long by 54 feet wide in the central nave and 62 feet in the transept. The height of the central nave is 39 feet, reaching 78 feet in the transept up to the dome. The bell tower rises to a height of 105 feet above the ground
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Municipal Register of Spain 2018. National Statistics Institute.
- ^ "Municipio de Ceutí". Retrieved 27 May 2015.
- ^ "Municipios en cifras - CREM". Portal Estadístico de la Región de Murcia - CREM (in Spanish). Archived from the original on 2017-02-11. Retrieved 2021-03-29.
- ^ "Murcia: Población por municipios y sexo. (2883)". INE (in Spanish). Retrieved 2022-11-10.
- ^ "Clima Ceutí: Temperatura, Climograma y Tabla climática para Ceutí - Climate-Data.org". es.climate-data.org. Retrieved 2022-11-10.
- ^ "Museos de Ceutí - Región de Murcia Digital". www.regmurcia.com. Retrieved 2022-11-10.
- ^ "Museo al Aire Libre - Región de Murcia Digital". www.regmurcia.com. Retrieved 2022-11-10.