Cephaeline
Appearance
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
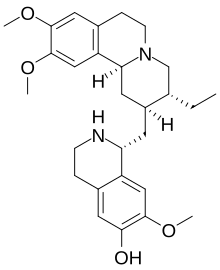
7′,10,11-Trimethoxyemetan-6′-ol
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(1R)-1-{[(2S,3R,11bS)-3-Ethyl-9,10-dimethoxy-1,3,4,6,7,11b-hexahydro-2H-pyrido[2,1-a]isoquinolin-2-yl]methyl}-7-methoxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolin-6-ol | |
| Other names
Cepheline; Desmethylemetine; Dihydropsychotrine
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.902 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C28H38N2O4 | |
| Molar mass | 466.622 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White silky crystals |
| Solubility in ethanol | Soluble[vague] |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Emetic / poisonous |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Cephaeline is an alkaloid that is found in Cephaelis ipecacuanha and other plant species including Psychotria acuminata.[1] Cephaeline induces vomiting by stimulating the stomach lining and is found in commercial products such as syrup of ipecac.[2] Chemically, it is closely related to emetine.
Poison treatment
[edit]Cephaeline in the form of syrup of ipecac was once commonly recommended as an emergency treatment for accidental poisoning, but its use has been phased out due to its ineffectiveness.[3]
References
[edit]- ^ Lara, Alfonso; Valverde, Roberto; Gomez, Luis; Hidalgo, Nancy (July 1, 2003). "Micropropagacion de la planta medicinal psychotria acuminata". Agronomía Costarricense. Retrieved 26 December 2009.
- ^ "Pharma Japan: Approval of 4 drugs including Seroquel recommended: CPAC panel". Chemical Business Newsbase. November 14, 2000. Retrieved 26 December 2009.
- ^ American Academy Of Pediatrics Committee On Injury, Violence (November 2003). "Policy statement: Poison treatment in the home". Pediatrics. 112 (5): 1182–1185. doi:10.1542/peds.112.5.1182. PMID 14595067.
