Catellani reaction
The Catellani reaction was discovered by Marta Catellani (Università degli Studi di Parma, Italy) and co-workers in 1997.[1][2] The reaction uses aryl iodides to perform bi- or tri-functionalization, including C-H functionalization of the unsubstituted ortho position(s), followed a terminating cross-coupling reaction at the ipso position. This cross-coupling cascade reaction depends on the ortho-directing transient mediator, norbornene.
Reaction mechanism
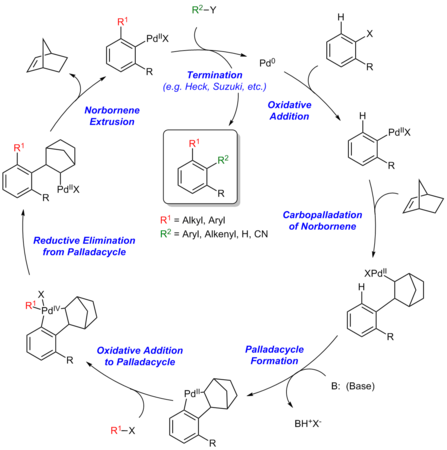
[edit]The Catellani reaction is catalyzed by palladium and norbornene, although in most cases superstoichiometric amounts of norbornene are used to allow the reaction to proceed at a reasonable rate.[4] The generally accepted reaction mechanism, as outlined below, is intricate and believed to proceed via a series of Pd(0), Pd(II), and Pd(IV) intermediates, although an alternative bimetallic mechanism that avoids the formation of Pd(IV) has also been suggested.[5]
Initially, Pd(0) oxidatively adds into the C–X bond of the aryl halide. Subsequently, the arylpalladium(II) species undergoes carbopalladation with the norbornene. The structure of the norbornylpalladium intermediate does not allow for β-hydride elimination at either of the β-positions due to Bredt's Rule for the bridgehead β-hydrogen and the trans-configuration between palladium and other β-hydrogen.[6] Thereafter, the Pd(II) species undergoes electrophilic cyclopalladation at the ortho position of the aryl group. Subsequently, the palladacyclic intermediate undergoes a second oxidation addition with the alkyl halide coupling partner to form a Pd(IV) intermediate, which undergoes reductive elimination to forge the first C–C bond of the product. After β-carbon elimination of norbornene, the resultant Pd(II) species then undergoes a second C–C bond forming step via a Heck reaction or cross coupling with an organoboron reagent to afford the final organic product and close the catalytic cycle.[7]
Steps of the Catellani reaction:
- Oxidative addition
- Carbopalladation of norbornene
- Palladacycle formation
- Oxidative addition to palladacycle
- Reductive elimination from palladacycle
- Norbornene extrusion
- Termination via Heck reaction, Suzuki reaction, etc.
Ortho and ipso cross-coupling partners
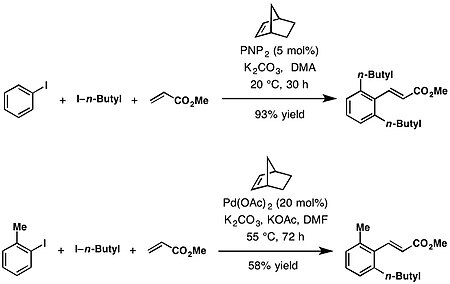
[edit]The Catellani reaction facilitates a variety of C—C and C—N bond-forming reactions at the ortho position. These include alkylation from alkyl halides,[1] arylation from aryl bromides,[8] amination from benzyloxyamines,[9][10][11][12] acylation from anhydrides.[13][14] Likewise in the case of terminating ipso coupling partners with Heck-type termination with olefins,[1] Suzuki-type reaction with boronic esters,[9] borylation with bis(pinacolato)diboron,[10][15] protonation with i-PrOH,[11] decarboxylative alkynylation with alkynyl carboxylic acids.[12]
Uses
[edit]With tethered cross-coupling partners, Lautens, Malacria, and Catellani used this reaction to construct a variety of fused ring systems since 2000.[7] The Catellani reaction has been used as a key step for the total synthesis (+)-linoxepin,[16] rhazinal,[17] aspidospermidine,[18] and (±)-goniomitine.[18]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c Catellani, Marta; Frignani, Franco; Rangoni, Armando (1997-02-03). "A Complex Catalytic Cycle Leading to a Regioselective Synthesis of o,o′-Disubstituted Vinylarenes". Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English. 36 (1–2): 119–122. doi:10.1002/anie.199701191. ISSN 1521-3773.
- ^ Catellani; et al. (1997). "Regioselektive Synthese o,o′-disubstituierter Vinylarene über einen komplexen Katalysecyclus". Angewandte Chemie. 109 (1–2): 142–145. doi:10.1002/ange.19971090146.
- ^ Martins; et al. (2010). "Synthesis in the Key of Catellani: Norbornene-Mediated ortho C–H Functionalization". C-H Activation. Topics in Current Chemistry. Vol. 292. pp. 1–33. doi:10.1007/128_2009_13. ISBN 978-3-642-12355-9. PMID 21500401.
- ^ Catellani, Marta; Motti, Elena; Della Ca’, Nicola (2008-11-18). "Catalytic Sequential Reactions Involving Palladacycle-Directed Aryl Coupling Steps". Accounts of Chemical Research. 41 (11): 1512–1522. doi:10.1021/ar800040u. ISSN 0001-4842. PMID 18680317.
- ^ Cárdenas, Diego J.; Martín-Matute, Belén; Echavarren, Antonio M. (2006). "Aryl Transfer between Pd(II) Centers or Pd(IV) Intermediates in Pd-Catalyzed Domino Reactions". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 128 (15): 5033–5040. doi:10.1021/ja056661j. PMID 16608337.
- ^ Martins; et al. (2010). "Synthesis in the Key of Catellani: Norbornene-Mediated ortho C–H Functionalization". C-H Activation. Topics in Current Chemistry. Vol. 292. pp. 1–33. doi:10.1007/128_2009_13. ISBN 978-3-642-12355-9. PMID 21500401.
- ^ a b Ye, Juntao; Lautens, Mark (2015). "Palladium-catalysed norbornene-mediated C–H functionalization of arenes". Nature Chemistry. 7 (11): 863–870. Bibcode:2015NatCh...7..863Y. doi:10.1038/nchem.2372. PMID 26492005.
- ^ Faccini, Fiorenza; Motti, Elena; Catellani, Marta (2004-01-01). "A New Reaction Sequence Involving Palladium-Catalyzed Unsymmetrical Aryl Coupling". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 126 (1): 78–79. doi:10.1021/ja039043g. ISSN 0002-7863. PMID 14709068.
- ^ a b Ye, Changqing; Zhu, Hui; Chen, Zhiyuan (2014-09-19). "Synthesis of Biaryl Tertiary Amines through Pd/Norbornene Joint Catalysis in a Remote C–H Amination/Suzuki Coupling Reaction". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 79 (18): 8900–8905. doi:10.1021/jo501544h. ISSN 0022-3263. PMID 25171687.
- ^ a b Shi, Hang; Babinski, David J.; Ritter, Tobias (2015-03-25). "Modular C–H Functionalization Cascade of Aryl Iodides". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 137 (11): 3775–3778. doi:10.1021/jacs.5b01082. ISSN 0002-7863. PMID 25763682.
- ^ a b Dong, Zhe; Dong, Guangbin (2013-12-11). "Ortho vs Ipso: Site-Selective Pd and Norbornene-Catalyzed Arene C–H Amination Using Aryl Halides". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 135 (49): 18350–18353. doi:10.1021/ja410823e. ISSN 0002-7863. PMID 24256439.
- ^ a b Sun, Fenggang; Gu, Zhenhua (2015-05-01). "Decarboxylative Alkynyl Termination of Palladium-Catalyzed Catellani Reaction: A Facile Synthesis of α-Alkynyl Anilines via Ortho C–H Amination and Alkynylation". Organic Letters. 17 (9): 2222–2225. doi:10.1021/acs.orglett.5b00830. ISSN 1523-7060. PMID 25899570.
- ^ Huang, Yunze; Zhu, Rui; Zhao, Kun; Gu, Zhenhua (2015-10-19). "Palladium-Catalyzed Catellani ortho-Acylation Reaction: An Efficient and Regiospecific Synthesis of Diaryl Ketones". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 54 (43): 12669–12672. doi:10.1002/anie.201506446. ISSN 1521-3773. PMID 26331234.
- ^ Zhou, Ping-Xin; Ye, Yu-Ying; Liu, Ce; Zhao, Lian-Biao; Hou, Jian-Ye; Chen, Dao-Qian; Tang, Qian; Wang, An-Qi; Zhang, Jie-Yu (2015-08-07). "Palladium-Catalyzed Acylation/Alkenylation of Aryl Iodide: A Domino Approach Based on the Catellani–Lautens Reaction". ACS Catalysis. 5 (8): 4927–4931. doi:10.1021/acscatal.5b00516.
- ^ Sui, Xianwei; Grigolo, Thiago A.; O’Connor, Colin J.; Smith, Joel M. (2019-11-15). "Ortho/Ipso Alkylborylation of Aryl Iodides". Organic Letters. 21 (22): 9251–9255. doi:10.1021/acs.orglett.9b03674. ISSN 1523-7060. PMID 31696718. S2CID 207943611.
- ^ Weinstabl; et al. (16 Apr 2013). "Total Synthesis of (+)-Linoxepin by Utilizing the Catellani Reaction". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 52 (20): 5305–5308. doi:10.1002/anie.201302327. PMC 3715096. PMID 23592590.
- ^ Sui; et al. (June 2013). "Pd-Catalyzed Chemoselective Catellani Ortho-Arylation of Iodopyrroles: Rapid Total Synthesis of Rhazinal". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135 (25): 9318–9321. doi:10.1021/ja404494u. PMID 23758183.
- ^ a b Jiao, Lei; Herdtweck, Eberhardt; Bach, Thorsten (2012-09-05). "Pd(II)-Catalyzed Regioselective 2-Alkylation of Indoles via a Norbornene-Mediated C–H Activation: Mechanism and Applications". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 134 (35): 14563–14572. doi:10.1021/ja3058138. ISSN 0002-7863. PMID 22913367.
