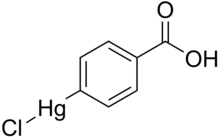
4-Chloromercuribenzoic acid
Appearance
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(4-Carboxyphenyl)chloromercury
| |
| Other names
p-Chloromercurybenzoic acid; p-Chloromercuribenzoate; 4-Chloromercuribenzoate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| Abbreviations | PCMB |
| 3662892 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.402 |
| EC Number |
|
| 261316 | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H5ClHgO2 | |
| Molar mass | 357.16 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 287 °C (549 °F; 560 K) (dec.) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  
| |
| Danger | |
| H300, H310, H330, H373, H410 | |
| P260, P262, P264, P270, P271, P273, P280, P284, P301+P310, P302+P350, P304+P340, P310, P314, P320, P321, P322, P330, P361, P363, P391, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
4-Chloromercuribenzoic acid (p-chloromercuribenzoic acid, PCMB) is an organomercury compound that is used as a protease inhibitor, especially in molecular biology applications.
PCMB reacts with thiol groups in proteins and is therefore an inhibitor of enzymes that are dependent on thiol reactivity, including cysteine proteases such as papain and acetylcholinesterase. Because of this reactivity with thiols, PCMB is also used in titrimetric quantification of thiol groups in proteins.
Preparation
[edit]4-Chloromercuribenzoic acid can be prepared by oxidation of 4-chloromercuritoluene using potassium permanganate.[2] 4-chloromercuritoluene is in turn obtained by the chloromercuration of sodium toluene sulfinite:[3]
- CH3C6H4SO2Na + HgCl2 → CH3C6H4HgCl + SO2 + NaCl
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ 4-Chloromercuribenzoic acid at Sigma-Aldrich
- ^ Whitmore, Frank C.; Hamilton, Frances H.; Thurman, N. (1927). "P-Chloromercuribenzoic ACID". Organic Syntheses. 7: 18. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.007.0018.
- ^ Whitmore, Frank C.; Woodward, Gladys E. (1923). "p-Tolyl Chloride CHLORIDE". Organic Syntheses. 3: 99. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.003.0099.
