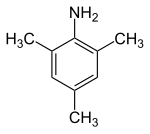
2,4,6-Trimethylaniline
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,4,6-Trimethylaniline | |||
| Other names
Aminomesitylene; 2,4,6-Trimethylbenzenamine; Mesitylamine; Mesidine
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.632 | ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C9H13N | |||
| Molar mass | 135.21 g/mol | ||
| Density | 0.963 g/mL | ||
| Melting point | −4.9 °C (23.2 °F; 268.2 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 233 °C (451 °F; 506 K) | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
2,4,6-Trimethylaniline is an organic compound with formula (CH3)3C6H2NH2. It is an aromatic amine that is of commercial interest as a precursor to dyes. It is prepared by selective nitration of mesitylene, avoiding oxidation of the methyl groups, followed by reduction of the resulting nitro group to the aniline.[1]
Coordination chemistry
[edit]Trimethylaniline is a building block to a variety of bulky ligands. Condensation with glyoxal gives the 1,2-diimine ligands. An example is glyoxal-bis(mesitylimine), a yellow solid that is synthesized by condensation of 2,4,6-trimethylaniline and glyoxal. The diimine is a useful precursor to popular NHC ligands including IMes.[2] N-heterocyclic carbenes, as found in 2nd generation Grubbs' catalyst, are also prepared from this compound.[3]
References
[edit]- ^ Gerald Booth (2007). "Nitro Compounds, Aromatic". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a17_411. ISBN 9783527303854.
- ^ Elon A. Ison, Ana Ison "Synthesis of Well-Defined Copper N-Heterocyclic Carbene Complexes and Their Use as Catalysts for a “Click Reaction”: A Multistep Experiment That Emphasizes the Role of Catalysis in Green Chemistry" J. Chem. Educ., 2012, volume 89, pp 1575–1577. doi:10.1021/ed300243s
- ^ Scholl, M.; Ding, S.; Lee, C. W.; Grubbs, R. H. (1999). "Synthesis and Activity of a New Generation of Ruthenium-Based Olefin Metathesis Catalysts Coordinated with 1,3-Dimesityl-4,5-dihydroimidazol-2-ylidene Ligands". Organic Letters. 1 (6): 953–956. doi:10.1021/ol990909q. PMID 10823227.