1994 United States gubernatorial elections
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
38 governorships 36 states; 2 territories | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
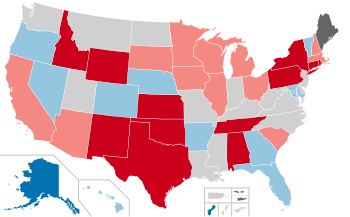 Results of the elections: Democratic gain Republican gain Democratic hold Republican hold Independent gain No election | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
On November 8, 1994, gubernatorial elections were held in 36 states and two territories across the United States. Many seats held by Democratic governors switched to the Republicans during the time known as the Republican Revolution. Notably, this marked the first time since 1969 that Republicans secured the majority of governorships in an election cycle.
Before the elections, 21 seats were held by Democrats, 14 held by Republicans, and one seat was held by an independent. After the elections, 11 seats would be held by Democrats, 24 by Republicans, and one seat by an independent.
These elections occurred concurrently with the midterm elections for the Senate and the House of Representatives. To date, it remains the last time that Democrats have won gubernatorial elections in Florida and Nebraska. Conversely, this election cycle began an ongoing pattern in which Rust Belt states Michigan, Pennsylvania, and Wisconsin would vote for gubernatorial candidates of the same party, with the sole exception of 2014.[2] As of 2024 this is the last time 10 seats switched parties.
Election results
[edit]States
[edit]| State | Incumbent | Party | First elected |
Result | Candidates |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alabama | Jim Folsom Jr. | Democratic | 1993[b] | Incumbent lost election to full term. New governor elected. Republican gain. |
|
| Alaska | Wally Hickel | Republican | 1966[c] 1969 (resigned) 1990 |
Incumbent retired. New governor elected. Democratic gain. |
|
| Arizona | Fife Symington | Republican | 1990 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Arkansas | Jim Guy Tucker | Democratic | 1992[d] | Incumbent elected to full term. |
|
| California | Pete Wilson | Republican | 1990 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Colorado | Roy Romer | Democratic | 1986 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Connecticut | Lowell Weicker | A Connecticut Party | 1990 | Incumbent retired. New governor elected. Republican gain. |
|
| Florida | Lawton Chiles | Democratic | 1990 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Georgia | Zell Miller | Democratic | 1990 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Hawaii | John D. Waihe'e III | Democratic | 1986 | Incumbent term-limited. New governor elected. Democratic hold. |
|
| Idaho | Cecil D. Andrus | Democratic | 1970 1977 (resigned) 1986 |
Incumbent retired. New governor elected. Republican gain. |
|
| Illinois | Jim Edgar | Republican | 1990 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Iowa | Terry Branstad | Republican | 1982 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Kansas | Joan Finney | Democratic | 1990 | Incumbent retired. New governor elected. Republican gain. |
|
| Maine | John R. McKernan Jr. | Republican | 1986 | Incumbent term-limited. New governor elected. Independent gain. |
|
| Maryland | William D. Schaefer | Democratic | 1986 | Incumbent term-limited. New governor elected. Democratic hold. |
|
| Massachusetts | Bill Weld | Republican | 1990 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Michigan | John Engler | Republican | 1990 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Minnesota | Arne Carlson | Republican | 1990 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Nebraska | Ben Nelson | Democratic | 1990 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Nevada | Bob Miller | Democratic | 1989[e] | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| New Hampshire | Steve Merrill | Republican | 1992 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| New Mexico | Bruce King | Democratic | 1970 1974 (term-limited) 1978 1982 (term-limited) 1990 |
Incumbent lost re-election. New governor elected. Republican gain. |
|
| New York | Mario Cuomo | Democratic | 1982 | Incumbent lost re-election. New governor elected. Republican gain. |
|
| Ohio | George Voinovich | Republican | 1990 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Oklahoma | David Walters | Democratic | 1990 | Incumbent retired. New governor elected. Republican gain. |
|
| Oregon | Barbara Roberts | Democratic | 1990 | Incumbent retired. New governor elected. Democratic hold. |
|
| Pennsylvania | Bob Casey Sr. | Democratic | 1986 | Incumbent term-limited. New governor elected. Republican gain. |
|
| Rhode Island | Bruce Sundlun | Democratic | 1990 | Incumbent lost renomination. New governor elected. Republican gain. |
|
| South Carolina | Carroll A. Campbell Jr. | Republican | 1986 | Incumbent term-limited. New governor elected. Republican hold. |
|
| South Dakota | Walter Dale Miller | Republican | 1993[f] | Incumbent lost nomination to full term. New governor elected. Republican hold. |
|
| Tennessee | Ned McWherter | Democratic | 1986 | Incumbent term-limited. New governor elected. Republican gain. |
|
| Texas | Ann Richards | Democratic | 1990 | Incumbent lost re-election. New governor elected. Republican gain. |
|
| Vermont | Howard Dean | Democratic | 1991[g] | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Wisconsin | Tommy Thompson | Republican | 1986 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Wyoming | Mike Sullivan | Democratic | 1986 | Incumbent term-limited. New governor elected. Republican gain. |
|
Territories and federal district
[edit]| Territory | Incumbent | Party | First elected |
Result | Candidates |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| District of Columbia | Sharon Pratt | Democratic | 1990 | Incumbent lost renomination. New mayor elected. Democratic hold. |
|
| Guam | Joseph Franklin Ada | Republican | 1986 | Incumbent retired. New governor elected.[3] Democratic gain. |
|
| U.S. Virgin Islands | Alexander Farrelly | Democratic | 1986 | Incumbent term-limited. New governor elected.[4] Independent gain. |
|
Closest races
[edit]States where the margin of victory was under 1%:
- Alaska, 0.2%
- Maryland, 0.4%
- Alabama, 0.9%
States where the margin of victory was under 5%:
- Florida, 1.5%
- Maine, 1.5%
- Georgia, 2.1%
- South Carolina, 2.5%
- New York, 3.3%
- Connecticut, 3.5%
- Rhode Island, 3.8%
States where the margin of victory was under 10%:
- Pennsylvania, 5.5%
- Hawaii, 5.9%
- Texas, 7.6%
- Arizona, 8.2%
- Idaho, 8.4%
- Oregon, 8.5%
- Tennessee, 9.6%
- Guam, 9.7%
- New Mexico, 9.9%
See also
[edit]Notes
[edit]- ^ Alaskan Governor Wally Hickel was elected on the Alaskan Independence Party line in 1990 but switched to the Republican Party in April 1994.[1]
- ^ Folsom took office after his predecessor (H. Guy Hunt) was removed from office.
- ^ Hickel was elected as a Republican in his first term in 1966. He was elected under the Alaskan Independence Party for his second term in 1990, before switching back to the Republican Party towards the end of his second term in April 1994.
- ^ Tucker took office after his predecessor (Bill Clinton) resigned.
- ^ Miller took office after his predecessor (Richard Bryan) resigned. He was subsequently elected in the 1990 Nevada gubernatorial election.
- ^ Miller took office after his predecessor (George S. Mickelson) died.
- ^ Dean took office after his predecessor (Richard Snelling) died. He was subsequently elected in the 1992 Vermont gubernatorial election.
References
[edit]- ^ "Alaska's Gov. Hickel Rejoins Gop Amid Speculation Over Another Term". The Seattle Times. Seattle. Associated Press. April 15, 1994. Retrieved September 28, 2008.
- ^ Brownstein, Ronald (September 16, 2024). "Why these three states are the most consistent tipping point in American politics". CNN. Retrieved September 16, 2024.
- ^ "Guam Governor Race - Nov 08, 1994". Our Campaigns. July 3, 2015.
- ^ "USVI Governor Race - Nov 08, 1994". Our Campaigns. January 19, 2006.
