Yueban
Yueban | |
|---|---|
| 160–490 | |
 | |
| Historical era | 1st millennium |
• Established | 160 |
• Disestablished | 490 |
| Today part of | Kazakhstan |
Yueban (Chinese: 悅般) (Middle Chinese: */jiuᴇt̚-pˠan/ < Late Han Chinese: */jyat-pɑn/[1]), colloquially: "Weak Xiongnu", was the name used by Chinese historians for remnants of the Northern Xiongnu[2] in Zhetysu, now part of modern-day Kazakhstan. In Chinese literature they are commonly called Yueban. The Yuebans gained their own visibility after disintegration of the Northern Xiongnu state, because unlike the main body of the Northern Xiongnu, who escaped from the Chinese sphere of knowledge, the Yueban tribes remained closer to China.
The Yueban emerged after the disintegration of the Xiongnu confederation. About 480s, the Yueban split into four Chuy tribes:[3] Chuyue (處月), Chumi (處密), Chumukun (處木昆), and Chuban (處半).
One Yueban branch, Chuyue, later intermixing with Göktürks, formed the Shatuo of the Western Göktürk Khaganate.[4] The Yueban-descended Shatuo played an important role in Chinese dynastic history. In the 10th century the remaining Shatuo branch of the Chuy tribe possibly joined Mongolic-speaking Tatar confederation in the territory of the modern Mongolia, and became known as Ongud or White Tatars[5][6] branch of the Tatars.
Another Yueban-descended tribe, Chumukun, might be associated with the Kimek confederation.
Identity and location
[edit]Yury Zuev reconstructed 悅般 Yueban's underlying form as *Örpen ~ Ürpen, identifiable with the toponym Örpün mentioned in Bilge Khagan inscription.[7][8] Zuev also compared *Örpen ~ Ürpen to the prefecture 咽麫 Yànmiàn (supposedly from MC < *iet-mien < *ermen ~ örmen?) at the Irtysh headwaters in the 7th century. Meanwhile, Vladimir Tishin compared 咽麫 Yànmiàn (< LMC *ʔjianˊ-mjianˋ < EMC *ʔɛnH-mjianH < *Emän) to the names of the Chumukun's "town of Yan" (咽城) and the Emel River.[9]
Gumilyov further identified Yueban with the Altï Čub Soğdak "Six Prefectures' Sogdians".[10] Meanwhile, Sergey Klyashtorny identified the Altï Čub Soğdak with the Sogdian-populated "Six Barbarian Prefectures" (六胡州 Liùhúzhōu)[11] of Lu 魯, Li 麗, Han 含 (or She 舍), Sai 塞, Yi 依, and Qi 契, established by Tang Chinese in 679[12] from "surrendered Turks" (降突厥),[13] "originally a Sogdian people who had submitted collectively to the Eastern Turks"[14] Later on, Altï Čub Soğdak were mentioned in Kul Tegin inscription as enemies of the Second Turkic Khaganate,[15] and they were conquered by Bilge Khagan in 701. The Six Prefectures also revolted against Tang, until Tang army dispersed them in 722.[16]
Language and customs
[edit]According to the Book of Wei, the Yuebans' language and customs were the same as the Gaoche, who were Turkic speakers. Yuebans cut their hair and trimmed their ghee-smeared, sun-dried, glossy eyebrows evenly, and washed before meals three times every day.[17][18]
History
[edit]
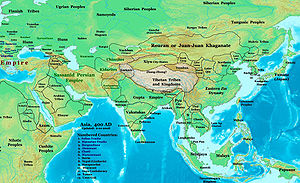
Between 155 and 166, the Xianbei (*Särpi) (Ch. 鮮卑, Wade–Giles Hsien-pi, Hsien-pei), a former vassal tribe of the Xiongnu, united under Tanshihuai conducted a series of campaigns against Northern Xiongnu, eventually defeating them and forcing them to flee west, which started a series of Xiongnu migrations (93 CE - circa 380 CE) westward to southern Siberia and Central Asia.[19][20]
The defeat ended the prominence of the Xiongnu as a major power in inner Asia. Tanshihuai expelled the Xiongnu from Dzungaria to beyond the Tarbagatai Mountains, and pushed the Dingling beyond the Sayan Mountains. The defeat had cost the Xiongnu their revenue from the Silk Road in the agricultural dependencies in the Tarim Basin ("Western Territories", Xiyu or Xinjian of the Chinese annals), forcing them to find new dependencies, and the Xiongnu split again.
Tribes known as the "Weak Xiongnu"[21] or Yueban took advantage of the vulnerability of the neighboring Uar (a people possibly linked to the Hephthalites and/or the "Avars" who later invaded Eastern Europe) and conquered Zhetysu, where they established the principality of Yueban. Later, some Uar returned to Zhetysu, and in cooperation with the Mukrins, a Xianbei tribe, occupied the Tianshan slopes in the 2nd century, retaining their independence for some time as the Western Xianbei Horde.[22]
Zhetysu was also populated by the Azi (who lived between Suyab and Uzkent) and the Tuhsi. The Azi and Tuhsi are sometimes linked to Asii[a][23][24] and Tukharas;[25] Indo-European peoples who had conquered Bactria six centuries earlier, and formed the Kushan Empire. According to Persian historian Gardizi, Azi and Tuhsi were remnants of Türgesh,[26][27] along with Khalaj.[28] Karakhanid linguist Mahmud Kashgari described Tuhsi as a dynastic tribe of Turkic-speaking monoglots.[29] This may suggest that Indo-European peoples underwent language replacement, in the form of "Turkification", had occurred. The Azi were also alternatively proposed to be Yeniseian-speaking, as Vasily Bartold noted the similarities between Old Turkic 𐰔 Az and the ethnonym Assan of a people who spoke an extinct Yeniseic Kott dialect.[30]
In 448 the Emperor Taiwu of Northern Wei received an envoy from the Yueban to negotiate a war with the Rouran. If the Yueban would pressure them from the west, the Rouran would lose any freedom to maneuver. Though no direct records exist about the war in Dzungaria, by the course of the events, there was no peace, and the nomadic empire of Rouran began to decline.[22]
In the late 5th century the Yueban were attacked by the Tiele, who had split from the Rouran in 487. The Yueban principality ceased to existed during the 480s and split into four tribes, known as the Chuyue, Chumi, Chumuhun, and Chuban.[31] The dominance of Yueban's Tiele enemies was short-lived: first, the Hephthalites conquered the Tiele (495-496), followed by the Rouran in 530s[32] and finally in 551, the Turks, as Rouran's vassals, again quelled Tiele's rebellion.[33]
Nevertheless, the four splinter tribes still became major players in the First Turkic Khaganate.[22] After the First Khaganate's disintegration, Chumukun were in the Duolu wing, whereas Chuban were in both Duolu and Nushibi wings of the Western Turkic Khaganate On Oq (Ten Arrows) elites.[34][35] Much later, Chuyue branch, intermixing with Göktürk remnants, formed the Shatuo tribe in Southern Dzungaria, west of Lake Barkol.[3]
An 8th-century Tibetan geographer mentioned Chumuhuns in Altai and south of it as the Ibilkur, and associated them with Külüg-Külchur. They were the only Chuy tribe that in the middle of the 8th century preserved their independence, in spite of being sandwiched between Karluks and Turgesh. Their possessions were on the west side of the Tarbagatai range.[36] Chinese chroniclers listed Chumukun (處木昆), led by a *Külüg čor ([屈]律啜 [Qu]lü chuo), as the first of five Duolu tribes in the On-Ok union.[37][38][39][40]
Based on a reconstruction of Yueban history, Lev Gumilev argued against a then-widespread view that the Rouran were synonymous with the "Avars" or "Pseudo-Avars" (who attacked the Sabirs before invading Eastern Europe), because the Rouran would have had to pass through the Yueban state to attack the Sabirs.[41]
Theism, spirits, and magic
[edit]No records address the Yueban religion, though Chinese annals depict some manifestations of religious rites and magic. A narration about the Yuebans tells about sorcerers, able to cause frost and rainstorm. During a war with the Rouran, Chuban sorcerers incited a snowstorm against them, making the Rouran so frostbitten they had to stop their campaign and retreat. A similar legend is later told about the Eurasian Avars sorcerers in their war with the Franks, and Naiman sorcerers against Chingis-Khan.[42]
The Manichaean Chuyue tribe's descendants, Shatuo, later founded the Chinese state Hou Tang (923-936) in Northern China, and adopted a Chinese surname Li (李). The Shatuo had a predominant Dragon cult. Later Tang's founder Li Keyong also came from the Dragon tribe. The annals even noted that the Shatuo were praying "old services following the custom of the North" at the Thunder-mountain, at the Gates of Dragon.[43] Within China, Chuy Shatuo became active adherents and protectors of Buddhism and Taoism, and initiated construction of many Buddhist temples. Subsequent to Shatuo, most of these temples were demolished.[44]
Legacy
[edit]The Chuyue (處月) were often identified with the Čigil,[45][46][47] a Middle Turkic-speaking tribe "opposing Rūm" mentioned by 10th century Karakhanid scholar Mahmud al-Kashgari;[48] still, Atwood (2010) doubts this Chuyue-Chigil identification and notes that Chuyue is phonetically closer to the Chunghyl "bones" of the Yugurs.[49]
The Chumi (處密) tribe may be identified with the Čömül, another tribe opposing Rūm and spoke both Middle Turkic and their own "gibberish" (Ar. رَطَانَة raṭāna).[48][50]
The Chumukun (處木昆) were identified by Gumilyov with the Kimek (which existed in the period of 743-1050 AD).[51][52] Abu Said Gardizi (d. 1061) listed the Kimek khaganate's seven constituents as Imi, Yemeks, Tatars, Bayandur, Kipchaks, Lanikaz, and Ajlad. Much later, both Chumukun and Kipchaks would possibly contribute to the ethnogenesis of the Polovtsy.[53]
See also
[edit]Notes
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Schuessler, Axel. 2007. An Etymological Dictionary of Old Chinese. University of Hawaii Press. p. 586, 155
- ^ Book of Wei. Vol. 102. "悅般國,在烏孫西北,去代一萬九百三十里。其先,匈奴北單于之部落也。" Tr. "Yueban State is to the northwest of Wusun, at a distant of 10,930 lĭ from Dai. It formerly [was] the Northern Xiongnu chanyu's tribe."
- ^ a b Gumilev L.N., "Ancient Türks", Moscow, 'Science', 1967, Ch.20 http://gumilevica.kulichki.net/OT/ot20.htm (In Russian)
- ^ C. P. Atwood, Encyclopedia of Mongolia and the Mongol Empire, p.424
- ^ Ozkan Izgi, "The ancient cultures of Central Asia and the relations with the Chinese civilization"//The Turks, Ankara, 2002, p. 98, ISBN 975-6782-56-0
- ^ Paulillo, Mauricio. "White Tatars: The Problem of the Öngũt conversion to Jingjiao and the Uighur Connection" in From the Oxus River to the Chinese Shores: Studies on East Syriac Christianity in China and Central Asia (orientalia - patristica - oecumenica) Ed. Tang, Winkler. (2013) pp. 237-252
- ^ Bilge Khagan isncription at Türik Bitig
- ^ Zuev, Yu. A., Rannie tyurki: ocherki istorii i ideologii, Dajk-Press, Almaty, 2004, p. 27, 68-70 (in Russian)
- ^ Tishin, V.V (2018). ["Kimäk and Chù-mù-kūn (处木昆): Notes on an Identification" https://doi.org/10.17746/1563-0110.2018.46.3.107-113]. p. 108-109
- ^ Gumilyov, L. Millenium around the Caspian Sea Ch. 49. Litres, 2014. in Russian
- ^ Klyashtorny S. G. Ancient Turkic runic monuments as a source on the history of Central Asia Moscow, 1964. p. 78-80, 93-94
- ^ Pulleyblank, E.G. "A Sogdian Colony in Inner Mongolia" T'oung Pao, 2nd Series, Vol. 41, Livr. 4/5 (1952), p. 326-327
- ^ New Book of Tang. Vol. 37
- ^ Moribe, Y. "The Sogdian Turks and Shatuo in Daibei during the Late Tang and Five Dynasties Periods" 東洋史研究 Vol. 62, Issue 4. (2004). Pages 660-693
- ^ Kül Tegin Inscription at Türik Bitig
- ^ Namba Walter, M. "The Sogdians and Buddhism". Sino-Platonic Paper 174 (2006). p. 16
- ^ *Kyzlasov, L. R. (1 January 1996). "Northern Nomads". In Litvinsky, B. A. (ed.). History of Civilizations of Central Asia: The crossroads of civilizations, A.D. 250 to 750. UNESCO. pp. 310–320. ISBN 9231032119.
- ^ Weishu, Vol. 102 "其風俗言語與高車同,而其人清潔於胡。俗剪髮齊眉,以醍醐塗之,昱昱然光澤,日三澡漱,然後飲食。"
- ^ Yablonsky, L. T. (1999). "Stock-Breeders of the Ancient Khorezm". Bulletin of Russian Humanities Foundation. 1–2. Russian Academy of Sciences Institute of Archaeology: 198.
- ^ E.A.Tsvetsinskaya "Integrated assessment of landscape evolution in the Amudarya Prisarykamysh delta, 2001
- ^ Book of Wei, vol. 102 "為漢車騎將軍竇憲所逐,北單于度金微山,西走康居,其羸弱不能去者住龜茲北。" Tr. "Chased by Han General-of-Chariot-and-Cavalry Dou Xian, the Northern Chanyu crossed the Jinwei Mountains and fled west to Kangju. Those [who were] gaunt, weak, and unable to run settled north of Qiuci."
- ^ a b c Gumilev L.N., "Hunnu in China", Moscow, 'Science', 1974, Ch. 9, http://gumilevica.kulichki.com/HIC/hic09.htm (In Russian)
- ^ Golden, Peter B. An Introduction to the History of Turkic Peoples (1992). p. 53, 142
- ^ Kubarev, G.V. "A Runic Inscription at Kalbak-Tash II, Central Altai, with Reference to the Location of the Az Tribe" in Archaeology, Ethnology and Anthropology of Eurasia 44/4 (2016). p. 97-98 of 92–101
- ^ Prakash, B. Political and social movements in Ancient Punjab (1964) p. 96.
- ^ Gumilyov, L. "The Shattered Silence (961–1100)". Searches for an Imaginary Kingdom: The trefoil of the Bird's Eye View.
- ^ Zuev, Yu.A. (2002) Early Turks: Sketches of history and ideology Daik Press, Almaty. p. 153 (in Russian)
- ^ Pylypchuk, Ya. "Turks and Muslims: From Confrontation to Conversion to Islam (End of VII century - Beginning of XI Century)" in UDK 94 (4): 95 (4). In Ukrainian
- ^ Zuev, Yu. (2002). Early Türks: Sketches of history and ideology. Almaty: Daik-Press. pp. 152–153. (in Russian)
- ^ Barthold, Wilhelm (1935). Zwölf Vorlesungen über die Geschichte der Türken Mittelasiens [Twelve Lectures on the History of the Turks of Central Asia]. Deutsche Gesellschaft für Islamkunde. Berlin: Arthur Collignon. p. 37. OCLC 2221089.
- ^ Gumilev L.N., "History of Hun People", Moscow, 'Science', Ch.16, http://gumilevica.kulichki.net/HPH/hph16.htm (In Russian)
- ^ Golden, Peter B. (1992). An Introduction to the History of the Turkic People. Otto Harrassowitz, Wiesbaden. p. 79
- ^ Duan, "Dingling, Gaoju and Tiele", p. 346–347
- ^ Old Book of Tang. Vol. 194
- ^ Tongdian vol. 199
- ^ Bacot J. "Reconnaissance en Haute Asie Seplentrionale par cinq envoyes ouigours au VIII siecle" // JA, Vol. 254, No 2,. 1956, p.147, in Gumilev L.N., "Ancient Türks", Moscow, 'Science', 1967, Ch.27 http://gumilevica.kulichki.net/OT/ot27.htm (In Russian)
- ^ Tongdian, Vol. 199
- ^ Old Book of Tang, Vol. 194
- ^ Dobrovits, Mihály (2014–2015). "On the Titulature of Western Turkic Chieftains". Archivum Eurasiae Archivi Aevii. 21. Wiesbaden: Otto-Harassowitz Verlag.
- ^ Tishin, V.V. (2018). "Kimäk and Chù-mù-kūn (处木昆): Notes on an Identification"
- ^ Gumilev L.N., "Hunnu in China", Moscow, 'Science', 1974, Ch. 9 Note 26, http://gumilevica.kulichki.com/HIC/hic09.htm (In Russian)
- ^ Gumilev L.N., "Ancient Türks", Moscow, 'Science', 1967, Ch.7 http://gumilevica.kulichki.com/OT/ot07.htm (In Russian)
- ^ Yu. Zuev, "Early Türks: Sketches of history and ideology", Almaty, Daik-Press, 2002, p. 145, ISBN 9985-4-4152-9
- ^ Ozkan Izgi, "The ancient cultures of Central Asia and the relations with the Chinese civilization"//The Turks, Ankara, 2002, p. 100
- ^ Golden, P.B. (1992) An Introduction to the History of the Turkic Peoples in Turcologica (9). p. 199
- ^ Zuev, "Early Turks: Essays of history and ideology", Almaty, Daik-Press, 2002, p. 145, 250
- ^ Lee, J.Y. (2018) "Some remarks on the Turkicisation of the Mongols in post-Mongol Central Asia and the Qipchaq Steppe" in Acta Orientalia 71(2). p. 129 of 121-144
- ^ a b Maħmūd al-Kaśğari. "Dīwān Luğāt al-Turk". Edited & translated by Robert Dankoff in collaboration with James Kelly. In Sources of Oriental Languages and Literature. Part I. (1982). p. 82-83
- ^ Atwood, Christopher P. (2010). "The Notion of Tribe in Medieval China: Ouyang Xiu and the Shatup Dynastic Myth". Miscellanea Asiatica: p. 602, n. 27 of 593–621.
- ^ Bailey, H. W. "Turks in Khotanese Texts", in The Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain and Ireland, No. 1 (Jan., 1939), pp. 87
- ^ Gumilev L.N. Ancient Turks, Moscow, 'Science', 1967, Ch. 27 (in Russian)
- ^ Tishin, V.V (2018). "Kimäk and Chù-mù-kūn (处木昆): Notes on an Identification"
- ^ Gumilyov, L. (2009) Searches for an Imaginary Kingdom: The Legend of the Kingdom of Prester John ch. 14 (in English; translated by R.E.F. Smith)
