Wikipedia:Wikipedia Signpost/Single/2012-04-16
Inside the Arbitration Committee Mailing List
As part of the continuing Signpost series on analyzing the work of the Arbitration Committee, The Signpost takes a closer look this week at the internal messaging system committee members use for discussions and other internal business. The mailing list, of which all arbitrators and Jimbo Wales are members, is the main way the committee coordinates its actions, assesses the appeals of banned editors, and sometimes discusses its motions.
While the mailing list is no secret, it has long been the source of misgivings concerning the committee's transparency. In an effort to open up the process, The Signpost spoke to several arbitrators about how things specifically work on the server, and the way it has affected committee business.
Organizational use
The main purpose of the private mailing list is for arbitrators to organize technical issues in a faster, more efficient manner. For example, the selection of decision drafters – the one or two arbitrators that will post a proposed decision in a case – is effected exclusively through the mailing list. "Selection is basically a volunteer round-robin. Arbitrators volunteer for specific cases as they have time and interest", said arbitrator Jclemens. Fellow arbitrator Elen of the Roads elaborated on the self-selection process: "People nominate themselves dependent on availability and how long it is since they [last drafted a decision]". Long-time mediator (and arbitrator) PhilKnight explained the sometimes hesitant nature of deciding to draft a case, explaining even if it was "considerably more time consuming" he didn't think drafting was "any more difficult than handling an arbitration enforcement request or mediation case".
Along with technical organizational issues, Jclemens noted the private nature of some ArbCom business. He listed issues of "real-life harassment and threats against Wikipedia editors" along with the occasional "allegation of WP:CHILD violations". PhilKnight told The Signpost that some business is private because it is specifically sent to the committee under that assumption: "I think a large proportion of the mailing list can't be brought on-wiki as discussion concerns emails sent to the committee, which are considered confidential".
Intense workload
One thing the mailing list is known for is the high volume of mail all arbitrators receive on a daily basis. About 40–50 messages a day is not an abnormal amount, nor is 100 in a day of rapid on-wiki incidents. Jclemens noted that a great deal of the mail relates to ban appeals, while others deal with the private issues the committee must deal with separately.
Mailing list discussions
| “ | The community has done an excellent job of selecting principled and articulate candidates who have justice, fairness, and Wikipedia's long-term health in mind. | ” |
—Jclemens | ||
When a case is accepted by the committee, and a drafter has been chosen, the case undergoes a process of evidence review, workshop discussions, and sometimes even mailing list debates. Jclemens provided an example, saying "When there's substantial disagreement, you will see that in the proposed decisions themselves, such as in Betacommand 3, and the email discussion reflected deliberations of a divided committee. Others will have extensive off-wiki discussion because of the nature of the evidence, like the TimidGuy Ban Appeal." He also explained that the committee uses 'auxiliary mailing lists' "which are re-purposed as needed to handle matters in which specific arbitrators are recused."
In terms of the tone of the occasional mailing list debate, PhilKnight described it as "certainly more frank and open, [yet] generally speaking calm." Even when there have been heated disagreements, PhilKnight noted "that generally isn't a problem." Jclemens agreed with that perspective of mailing list discussions: "That is, we talk about the real issues, rather than personalities, for the most part, and there's no one egging on drama for drama's sake."
However, Jclemens mentioned a single, isolated incident where there was a threat to resign that was not acted on "and wasn't related to the committee's own internal workings anyways."
Looking forward
Whatever your opinion about transparency and the committee's mailing list is, it still remains a fact of their organization and procedure. Understanding how the committee operates reaches its highest point when we evaluate how they behave in a private setting. Each arbitrator is still a person, with beliefs, opinions, and emotions. Despite this, the mailing list has become a great, albeit sometimes inefficient, tool for internal discussions. Arbitrator Jclemens re-affirmed that in that environment, he felt that the committee still functions admirably: "ArbCom is a very high quality group of people, both in terms of their real-life skills, experience, logic, and dedication. The community has done an excellent job of selecting principled and articulate candidates who have justice, fairness, and Wikipedia's long-term health in mind."
The Signpost thanks all arbitrators who answered interview questions related to this article. If any reader has a suggestion for a future 'Arbitration analysis' article, let us know in the comments, or feel free to drop a note on the writer's talk page.
Reader comments
Does Wikipedia Pay? The Facilitator: Silver seren
- Does Wikipedia Pay? is an ongoing Signpost series seeking to illuminate paid editing and paid advocacy, for-profit Wikipedia consultants, editing public relations professionals, Conflict of Interest guidelines in practice, and the Wikipedians who work on these issues—by speaking openly with the people involved.
The Conflict of Interest Request for Comment is in full swing, various scandals are just settling in the news (including Portland Communications and Bell Pottinger, whose editing problems came under scrutiny as early as December last year), and the topic of paid editing raises its head regularly on Jimbo Wales' talk page. The idea of someone editing Wikipedia for financial gain remains highly controversial. As with any major conflict, it can be easy for participants to become entrenched in their views, to see things in extremes, and to substitute vague impressions for real people and their experiences. The goal of this series is to put a face to paid editing and to bring the discussion forward, without assumptions or hyperbole: to look at what is actually going on and illuminate one of the dark corners of Wikipedia.
The story so far
The history of paid editing traces back to MyWikiBiz, a commercial enterprise run by editor Thekohser, who was blocked and ultimately banned after selling his services as an article writer (in addition to sockpuppetry and violating his unblock conditions). Paid editing is part of the broader issue of conflict of interest (COI) editing, a topic which has roots in Wikipedia's 2004 guideline on vanity pages. In 2006, after US congressional staffers were revealed to be editing articles on behalf of their congressmen, the vanity guideline was quickly merged into WP:Conflict of Interest. Since then the guideline has evolved; fairly consistently, however, its stance has been that editing by COI editors is "strongly discouraged" and that using Wikipedia to promote one's interests (or those of one's employer or organization) is expressly forbidden.
In 2007 a computer science graduate student named Virgil Griffith unveiled WikiScanner, a tool which linked editor IP addresses with a database of corporate information. The result was a torrent of embarrassment, as everyone from the FBI to the Vatican was caught editing articles related to themselves. Recent scandals in the news have had the same "gotcha" quality, although there are also the beginnings of a change in tone. After years of being viewed as enemies, the public relations industry is starting to pursue a more collaborative relationship with Wikipedia and to argue that it has a rightful place and beneficial role to play in the encyclopedia. Both the Public Relations Society of America (PRSA) and the Chartered Institute of Public Relations (CIPR), the US and UK's leading industry groups, are publishing guidance for their members about working on Wikipedia, and Corporate Representatives for Ethical Wikipedia Engagement (CREWE) and WikiProject Cooperation have brought PR editors and Wikipedia editors together to collaborate in this new direction. Where these efforts will lead, and whether they will result in changes to policy, perception, or practice is still in the ether—but it is surely interesting to watch either way.
Interview
To kick off the series, The Signpost interviewed Wikipedia editor Silver seren, creator of WikiProject Cooperation.
Tell us about your background as a Wikipedian. When did you get started? What were your first edits and first impressions? What got you hooked?
That's going pretty far back, all the way to high school in 2006. I'd often used Wikipedia for my own interests, or for a school project here and there, pretty much all the way back to 2003. I don't quite remember why it was that I first got involved on Wikipedia, but looking back, this was my first edit. It was a Flash game I had been playing at the time. Wikipedia was something I really took to, I think, not having much trouble with the wikicode, as I parsed how to do it from edits other editors made. Of course, my editing back then was rather erratic and infrequent, Wikipedia not being something I was rather devoted to yet.
What got me truly involved was likely a combination of both my love for science and everything related to it and the rapport I established with my early friends on-wiki, such as my once upon a time adopter Chrishy man. But, as I became more engaged in adding content and making new articles, I became dedicated to the people I knew and the articles I had made, like my early efforts with Biosocial theory and Albert Oppel.
You've garnered a reputation as a bit of a muckraker. Where do think that instinct to root out and sometime stir up controversy comes from?
Let's just say that I've long been the type of person who both tries to find the truth about subjects and who tries to make the world a better place, whether that be through spreading information or by more direct forms of help. I have a deep-felt opposition to secrecy that leads to people being harmed in any way, so I also have a natural desire to expose such secrets. It's this, I guess, that leads to what would be called "stirring up controversy". I see it as pushing for the answers they don't want you to know.
You're one of the minority of Wikipedians whose real name is known. Has it had positive or negative ramifications in your on-Wikipedia work? How about your off-Wikipedia life?
It hasn't really affected my on-Wiki work or my off-Wiki life at all, beyond the fact that I'm no longer bothering at all to try to hide the connection between my username and my real name. It works better that way regardless as I'm working through WikiProject Cooperation with people in a semi-official capacity.
What was your inspiration for starting WikiProject Cooperation?
My creation of WikiProject Cooperation came about after the proposal by Herostratus of WikiProject Paid Advocacy Watch in a discussion on Jimbo's talk page. I was (and am) personally opposed to the idea of automatic blocking of paid editors, and other methods of locking out companies from being a part of Wikipedia. I feel that this would only lead to more controversy and, as a whole, a worse encyclopedia. So I thought up WikiProject Cooperation as an alternative that would instead work together with such users for both their benefit and the benefit of Wikipedia from their knowledge.
| “ | I was (and am) personally opposed to the idea of automatic blocking of paid editors, and other methods of locking out companies from being a part of Wikipedia. I feel that this would only lead to more controversy and, as a whole, a worse encyclopedia. So I thought up WikiProject Cooperation as an alternative that would instead work together with such users for both their benefit and the benefit of Wikipedia from their knowledge. | ” |
How does WikiProject Cooperation deal with conflicts of interest?
WikiProject Cooperation has a specific process called Paid Editor Help that has those users in a conflict of interest related to paid editing list what additions they wish to be made to an article, with reliable sources linked if it's a content addition. This also includes the proposal of new articles. Then, one or two (or more) members of the WikiProject go through the request, checking it for neutrality, and then enact it if they feel it is proper and within policy to do so.
We've already had more than twenty requests and a fair amount of proposed new articles from a variety of different people and organizations. For the most part, other than some necessary changes, the requests have all been for things that are within policy and on notable topics.
There's a long list of scandals dating back to MyWikiBiz through WikiScanner and Bell Pottinger, in which COI editors have been exposed, blocked, or embarrassed. Do you see that trend improving or getting worse? Are we facing more of those controversies, or are we just more informed about them?
I would say the trend is rather constant. Sure, the amount has increased, but that is probably a combination of Wikipedia's growth over the years and the increasing focus in the media world on such incidents. I think the frequency of such incidents has stayed pretty relative to Wikipedia's own growth. Of course, I also don't see such scandals going away any time soon. There's always going to be those that try to get in the easy way or don't want to bother with doing something ethically. We can pre-emptively dissuade some of this activity by working more directly with corporations and giving them more clear avenues of access so they can request and discuss the changes they would like, but there will still always be the few bad apples. And we'll just have to live with them and remain vigilant in our protection of the encyclopedia.
What do you think of recent efforts to improve relations between the PR industry/paid editors, and Wikipedia? I'm thinking of CREWE and WikiProject Cooperation in particular.
I'm glad that, in terms of CREWE, PR people have finally stepped forward in order to try and work out ways to be collaborative with Wikipedia, rather than antagonistic as in the past. I truly think that the best way to improve Wikipedia is to work together with others. And it's a two-way street. We have to work toward helping others, such as paid editors, but they also have to put in the effort to work with us, by following the system we've set up here for building an encyclopedia. Our job is just to make that system as simple and open as possible, a goal that the Wikimedia Foundation has had since day one. WikiProject Cooperation is one such step toward having more options and openness for the PR community.
| “ | I truly think that the best way to improve Wikipedia is to work together with others. And it's a two-way street. We have to work toward helping others, such as paid editors, but they also have to put in the effort to work with us, by following the system we've set up here for building an encyclopedia. Our job is just to make that system as simple and open as possible. | ” |
Jimmy Wales has taken strong stance against direct editing of articles by COI editors. Do you think editors should ever edit articles directly if they are paid for their work?
I fully understand Jimbo's stance, considering his (and Wikipedia's) past interactions with paid editors, from the now widely known Bell Pottinger scandal to a number of other incidents in the past listed in Conflict of interest editing on Wikipedia. However, as can be seen from WikiProject Cooperation's success and from the groups that want to work with Wikipedia, like CREWE, there are a vast number of paid editors who want to work properly with Wikipedia to improve its coverage of corporation related topics and to fix inaccuracies.
The question on whether such editors should be directly editing isn't as clear cut as that. To splice it into two parts, I do not believe paid editors or those editors with a strong COI like them should be making major content additions or content changes to articles. However, I believe grammatical changes, the addition of references and images, and updates to financial information are all proper activities for paid editors to do in articlespace, as outlined in the COI guideline.
Which do you think is a bigger problem; paid editing, or unpaid advocacy? Do you think it's unfair that paid editors have a target painted on them while unpaid advocates can civilly push their point of view without consequence?
Unpaid advocacy, clearly. Advocacy, by definition, means the additions will be of a POV nature. Paid editing does not necessarily mean this at all. Often, paid editing merely means the update of financial information or more info on the history of the subject.
Yes, I do, but I also understand why such a target exists, as do practically all paid editors. The actions of unethical paid editors in the past has caused an atmosphere of inherent mistrust for the entire subject. Which is why I'm glad that Public Relations professionals and other paid editors are now stepping forward to do things properly, to show that paid editing can be done within Wikipedia's rules.
Do you think WP:COI needs to be updated, promoted to policy, or demoted to essay status? Should policy prohibit direct editing by paid editors?
I think WP:COI is perfectly fine as the guideline it is. Though I do think its wording needs to be updated, to be more clear and to also more properly explain what kind of editing is and is not proper within the COI rules.
No, it should not. As I stated elsewhere, there are a number of kinds of edits that paid editors can do comfortably, whether it is fixing grammar and sentence structure or adding references or uploading images. All of these things, and the rest outlined here are perfectly fine for paid editors to do. As long as the editors themselves are upfront about their COI and make sure to have support from other editors for any major changes, I don't see any issues with letting paid editors do the edits I just pointed out.
Should COI disclosures be required for paid editors?
Yes, of course. Just like anyone else who has a sufficiently large COI, whether they be the subject of an article, related to the subject, having been involved directly (sometimes even indirectly) in the creation of the subject, or whether they have been paid to improve the article. All of these should have a statement on the talk page, via {{Connected contributor}}, that they are involved.
Is the encyclopedia failing in some way? By not cracking down on paid editors more harshly, or by leaving gaps and inaccuracies about living people and corporations that paid editors have an interest in fixing?
No and no. We already have the processes in place to deal with unethical paid editors and dealing with them "more harshly" would likely only result in collateral damage, whether that be to articles or to the blocking of innocent editors. Neither of those are things any of us want to do and I think that we already have the situation of unethical paid editing already well in hand. There's some that sneaks through, sure, but I don't think it's possible to catch every last person doing something wrong on Wikipedia, just like it isn't possible to immediately root out all subtle vandalism. These are both things that, through our already established methods, will sort themselves out over time.
| “ | Articles aren't perfect when they're first made or ever and inaccuracies can enter in over time, whether that be from other editors or just from things changing in the world for that subject. All we should focus on is doing our best to fix the problems that we're presented with now and do our best to lessen the amount of such inaccuracies. But I don't think its possible to stop them from ever occurring. If we wanted to do that, then the best method would be to not let anyone edit ever again. | ” |
As for the second, just by the fact that we are now working with such editors to fix those inaccuracies shows that we're taking steps to mitigate it. Articles aren't perfect when they're first made or ever and inaccuracies can enter in over time, whether that be from other editors or just from things changing in the world for that subject. All we should focus on is doing our best to fix the problems that we're presented with now and do our best to lessen the amount of such inaccuracies. But I don't think its possible to stop them from ever occurring. If we wanted to do that, then the best method would be to not let anyone edit ever again.
What has surprised you about working with COI or paid editors? What is the most common misunderstanding they hold about Wikipedia?
The misunderstandings tend to fall on one of two polarized viewpoints. The first belief is that they are never allowed to touch any article ever, which is clearly not true, per our own COI guideline. And believe me, none of us want to be bogged down with Request Edit tags for some sort of minor correction.
The other extreme is the belief that, since they are trying to improve the article, it's okay that they just go ahead and jump right in and start doing stuff. While I can completely understand this viewpoint, as we allow COIs of various degrees to edit articles in the first place without anyone saying it's wrong (which inevitably leads to some sort of ARBCOM sanction for the entire topic area). For the most part, what they are trying to add is perfectly fine. The issues come in with the fact that such users are often new users and don't know how to use the interface properly, nor do they know how to write in the language we generally couch our articles in.
What has surprised me the most is probably just how vast the number of paid editors are that want to edit Wikipedia properly and by following our rules, but the rules are either not clearly defined or they don't know how to edit properly. Paid editing is definitely an area that we can get a lot of worthwhile content out of, but it's also an area where we run across common problems, problems that things like the WYSIWYG editor (What You See Is What You Get) will hopefully fix, and misunderstandings on how to properly go about editing within Wikipedia's rules. If we can make things more simple and straightforward, along with providing methods of assisting such editors, we'll all benefit in the end.
You do yeoman's work at WikiProject Cooperation's Paid Editor Help board. Do you ever feel like you're doing other people's work for them, that they're being compensated for and you're not?
Of course not. Being able to help other editors and improve Wikipedia is the exact point of all of this. If it really comes down to something like getting "credit" for my actions, I could say that increased edit count is one such benefit. Also, for new articles proposed by paid editors, I try my best to get them submitted to DYK if they meet the requirements therein, so I also get the compensation of a DYK nom. But as long as the process helps improves articles, that's all that really matters in the end.
Are you 'pro' paid editing? How would you respond to the potential charge that you are enabling, condoning, or inviting more paid and COI editing by helping facilitate it? Do you think helping some paid editors follow the project's policies could mask deeper problems with those who do not, or who provide cover to them—a gloss of reassurance where we would otherwise be more vigilant or less tolerant?
It depends on what you mean by "pro". I think it would be better if paid editing didn't exist, so we wouldn't have to deal with all of the complicated situations that arise from it, but I equally know that the world isn't like that and there's nothing we can do to change it. So, if you're asking about whether I support its existence, then the answer would be no, but if you're asking whether I support our working with it for our benefit and their benefit, then the answer is yes.
| “ | I think it would be better if paid editing didn't exist, so we wouldn't have to deal with all of the complicated situations that arise from it, but I equally know that the world isn't like that and there's nothing we can do to change it. So, if you're asking about whether I support its existence, then the answer would be no, but if you're asking whether I support our working with it for our benefit and their benefit, then the answer is yes. | ” |
I don't believe the existence of WikiProject Cooperation is affecting the amount of paid editing at all. I would like to believe that it is making some of those who would otherwise be editing unethically instead are choosing to work through the WikiProject and our other processes. I see it like this: paid editing is always going to exist no matter what we do. So long as we're covering subjects, such as corporations and living people, whose livelihood depends at least partially on their image, we're going to end up getting either the subjects editing here or paid editors editing here. If we try to just shut it out by, say, blocking any subject or paid editor we come across, they're just going to be ever more subtle about it to the extent that no one would know it's happening. And that doesn't benefit us at all.
Instead, if we work together with such groups and people, by setting up easy and simple processes that they can use to get the proper changes made to articles, then everyone wins in the end. It's really the better option all around.
As for it masking the unethical paid editors, I suppose that depends on us, the main content editors and patrollers. Just because we are working toward getting these mutually beneficial systems in place, that doesn't mean that vigilance should be slackened. We still have vandals to deal with and the unethical paid editors will still be out there. We still have to do our best to protect the integrity of the project as we always have.
Have you ever been accused of having a COI? If so, how did you deal with it?
A few times. Most of them were just for my involvement in an article, where an editor I'm in a dispute with accused me of having such and such involvement in the subject, when it wasn't true. Those sorts of accusations I just shrugged off and explained how they weren't true and how they couldn't be true. As far as I can remember, the one time where I was accused of having a COI and it was at least partly relevant was my editing of the Encyclopedia Dramatica article. In response to my editing the article, a negative ED page was made on me. After that, I was accused of having a COI whenever I got into a dispute with an ED-related account on the article. In those cases I explained that my opinion and, more or less, lack of COI was the same as before the ED article has been made on me. It didn't change anything in my mind or my actions on the article and I followed talk page consensus regardless. I also explained that if something like that was going to fly, then they would just make articles on anyone working against them in the article, a loophole in COI that we really couldn't let fly. But I digress, a complicated situation without an easy explanation. Regardless, in all cases, I just stated my opinion in regards to the articles and otherwise followed any consensus that arose about the articles.
What article or project are you most proud of on Wikipedia? What article or project was most controversial or unsuccessful? What did you learn from it?
For an article I worked on individually, I'm most proud of my Good article Life at the Bottom: The Worldview That Makes the Underclass. I'm not really the type to have an eye for the details needed to finish writing a Good or Featured article, most of the time, so I am rather proud for having made that one.
Another article that I'm proud of and that is likely to be and has been decently controversial is Cracker Barrel Old Country Store, which is currently undergoing a Featured Article Candidacy. It's an article that was written largely by WWB Too, who was paid in the past to work on it, and myself. WWB made sure to stay out of any conversations regarding the controversies section, because of his COI, and I fielded most of that. By working together with other editors, we were able to reach a compromise about the state of the article and its coverage of various things.
I learned that the best way to deal with a dispute is to make a reasonable compromise that takes both sides into account and satisfies both of them. That's not to say doing as such is easy. But it can immediately fix the issue if you do it right, so it's worth it to try.
Finally, what's your favorite quote or piece of advice about Wikipedia?
Remember that we're building an encyclopedia.
Too many editors get bogged down in the details or get caught up in the perpetual dramas that occur on Wikipedia and lose sight of why we're all here in the first place. We're here because we want to make the best encyclopedia in the world, the most comprehensive, the most accurate. Anything not working toward that is largely irrelevant. If all of the people caught up in drama on ANI, AN, and elsewhere focused on building content for just one day, just think of how much would be accomplished in those 24 hours. Each of us has our own skill sets, sure, but we should all remember that, in the end, we want to be making edits that improve the encyclopedia, not anything else.
Reader comments
French language outreach, WikiTravel debate, and HighBeam reloaded
French language outreach

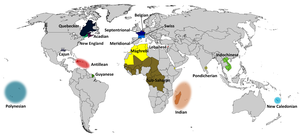
Language has never been the subject of public policy in Anglophone countries, so it might come as a surprise to English-speakers to learn that in some countries there is a tradition of state support and intervention on language issues. This is particularly so in France, where the tradition stretches back for more than three centuries: there, it has been seen as an important part of building the nation state and, during the 20th century, of binding together French-speakers worldwide. Among notable policies have been several laws to resist the contamination of French with English words, and controversial moves to suppress the teaching in schools of minority languages in France – reverted by a 2008 law providing greater acceptance of multilingualism and support for such teaching.
Adrienne Alix, the director of programs at Wikimedia France, has posted a report on a collaboration between the chapter and DGLFLF, a unit in the French Ministry for Culture and Communications that is dedicated to furthering government language policy. Adrienne told The Signpost that aside from French itself, more than 50 languages fall into the ambit of the Ministry: "some of them are regional languages like Provençal and Corsican [minority languages spoken in France itself]; others are from the overseas territories – an astonishing 27 languages just in new-Caledonia, and more than 20 creole and Indian languages in French Guyana, a small country in South America".
Adrienne says, "last May, the DGLFLF asked the chapter to write a report about French on Wikimedia projects. The report was well received, and as part of a larger report on the French language was distributed among all deputies in the national parliament. The Ministry frequently cites the document to show the importance of the internet in sustaining languages."
Chapter representatives then attended by invitation a major conference in French Guyana last December to explain the significance of WMF projects to both French and the minority languages. "The DGLFLF was very interested in the philosophy and work of the Wikimedia movement, and discussions after the conference resulted in an ongoing collaboration to publish a Wikibook on the event (in French, in progress). The Wikibook publications are designed to promote language issues and contain many links to WMF projects such as Wikipedia and Commons. She points out that "content about French overseas territories and native languages is not so good and this combined effort by government and chapter is really promoting better contributions." A bonus is that a year ago, the DGLFLF decided to release content under a licence similar to CC-BY.
Some 10 employees of the Ministry are involved in contributing to the Wikibook project and making Wikipedia edits. The Signpost asked whether such close involvement by the state employees might lead to the political slanting of content, against the independence and neutrality so keenly guarded by the Wikimedia movement. Adrienne says the chapter has been "very careful to train the people from the Ministry to be real contributors in terms of neutrality and sourcing; they're identified by a userbox on their userpage and have no special rights. We don't have any problem at this time."
Significantly, the collaboration is likely to lead to further joint work: "We're thinking about other projects for francophone areas that have poor internet access, with the DGLFLF and with some other institutions including the World Organization of Francophonie." Adrienne will present a paper to Wikimania 2012 in Washington DC (July 12–14) entitled What place for the "small languages" on Wikimedia projects?. There, she will discuss the chapter's experience in the light of key questions for the movement as a whole – among them, the best way to create a Wikipedia or a Wiktionary in a language that has no fixed writing system and the best way to work with a local administration regarding questions of language.
WikiTravel debate

A debate on whether to integrate WikiTravel, or parts of it, into the Wikimedia universe unfolded over the last week on Meta and the Wikimedia-l (I, II, III). The project aims to create a free collaborative travel guide, and its main language version, English, provides around 25,000 articles. Another possibly affected project could be Wikivoyage, a longstanding WikiTravel fork run by the German community.
The proposal is backed by significant parts of the WikiTravel-community, including the project founders Evan Prodromou and Michele Ann Jenkins, as well as Stefan Fussan, the chairman of the board of the Wikivoyage association. It also commands some support in parts of the Wikimedia-community, led by Doc James. Proponents of the idea argue that taking WikiTravel on board would be mutually beneficial, since Wikimedia would broaden its scope of educational material on the one hand and the possible new member of the family would benefit from improved software (the project currently runs on an older version of MediaWiki), as well as new funding environment.
However, to date there has been no official statement addressing the points raised in the discussion from Internet Brands, the entity which owns the trademarks to and runs WikiTravel. Additionally, several commenters on wikimedia-l raised concerns in regard to the neutrality of the content, and questioned the purported educational nature of travel guides in principle. Another aspect discussed was possible new forms of conflicts of interest (WP:COI) that might come from adopting such a project format.
A roadmap of the process of evaluating the workability and technical aspects of merging between now and June is outlined on Meta. The case is being discussed as the new Sister Projects Committee (see Brief notes) gets off the ground with discussing procedures affecting the possible merger.
Brief notes
- Article Feedback Tool, Version 5 update: A discussion has now been opened addressing the Article Feedback Tool, Version 5 and how Edit Filters would best be applied to feedback received using the tool. The community has been encouraged to participate in the discussion, which will influence the design of the new version of the tool when it comes into use later in the year. Interested editors can sign up for the here. (See the proposed AFT-v5 at Article Feedback Version 5 @ Mediawiki)
- HighBeam 2.0: The first round of handing out free HighBeam accounts to the community for one year (Signpost coverage) ended on April 9. The partnership-project handed out several hundred of the originally agreed 1000 accounts so far. Accordingly, a second round of applications will open on Monday, April 16, with the same requirements – a one-year-old account with 1000 edits – as the first round. Editors interested in scientific sources may also be interested in a project hoping to facilitate access to JSTOR, which the Foundation is working on together with Raul654.
- Terms of Use update: The efforts to update Wikimedia's Terms of Use (Signpost coverage) will reach a new phase on April 20 as the newly updated version will be legally announced. The new terms will not come into effect until the notice period has finished. The accompanying statement can be read on the Foundation wiki.
- Sister Projects Committee: The creation of a new Sister Projects Committee, aimed at improving the regulation of the new project process and located on Meta, was announced on April 10.
- WMF March report: The Wikimedia Foundation's activity report for March 2012, highlighting Mobile, Arabic outreach and MediaWiki development, has been published on Meta.
- IRC office hour: The log of the first IRC office hour held by the WMF's chief of finance and administration, Garfield Byrd (on April 12), which tackled issues such as donations in different currencies and the preparations for the new Funds Dissemination Committee (FDC), has been published on Meta.
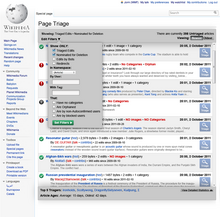
A mockup of the "list" interface for Page Triage showing the "filters" dialog - New Page Triage update: New Page Triage (NPT) is working on NPT list view which they hope to deploy in the next couple of weeks. This deployment will be of a prototypical nature only, and will occur on the English-language Wikipedia, as promised by the Community Liaison, Product Development in his engagement strategy. It will run in parallel to the existing Special:NewPages so people can improve and get used to the system, but will not yet replace the current system. Currently, 96 editors have signed up to receive the NPT newsletter. Users with any other ideas for engagement are still able to suggest them on Wikipedia talk:New Page Triage. (See the project proposal at New Page Triage @ Mediawiki). The log for the latest office hour on 2012-03-22 for NPT is posted on meta here.
- New administrators: The Signpost welcomes our newest administrator, ItsZippy (an editor who focuses on philosophy- and theology-related articles) at the second attempt. According to one co-nominator, Steven Zhang, "the key skill he brings to the table is experience in dispute resolution". Although the successful result means that two admins have been promoted within a fortnight – only the second time that has occurred this year – ItsZippy's promotion does little to stop the continuing drought engulfing RfA, which could see as few as fifty editors promoted in this calendar year.
- Milestones: The following Wikipedia projects reached milestones this week:
- The Lithuanian Wikipedia has reached 150,000 articles.
- The Cheyenne Wikipedia has reached 200 articles.
- The Vietnamese Wikipedia has reached 400,000 articles.
- New England Wikimedia General Meeting: On April 22, Wikimedians in New England will be holding a meetup at the Boston Public Library which will be an opportunity to plan for the future of the local community, raise awareness about real-world outreach and discuss the possibility of forming a new Wikimedia chapter in the area. All are encouraged to come.
Reader comments
The future of pending changes
Pending changes, often condensed to "PC", is a tool that underwent a two-month trial on the English Wikipedia in 2010. At the end of the trial, a straw poll was held, and closed in September 2010 with 407 in favor of implementation, 217 opposed and 44 other responses. A Request for Comment (RfC), opened in February 2011, saw more than three months of community deliberation, with the outcome that closing administrator Newyorkbrad found consensus in favor of full removal of pending changes from the English Wikipedia. However, the closure was made without prejudice against future reinstatement in some form, given consensus and discussion; this open-ended closure has ultimately led to the ongoing 2012 RfC on pending changes.
| Unregistered or newly registered | Confirmed or autoconfirmed | Extended confirmed | Template editor | Admin | Interface admin | Appropriate for (See also: Wikipedia:Protection policy) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No protection | Normal editing | The vast majority of pages. This is the default protection level. | |||||
| All users can edit Edits by unregistered or new editors (and any subsequent edits by anyone) are hidden from readers who are not logged in, until reviewed by a pending changes reviewer or admin. Logged-in editors see all edits, whether accepted or not. |
Infrequently edited pages with high levels of vandalism, BLP violations, edit-warring, or other disruption from unregistered and new users. | ||||||
| Cannot edit | Normal editing | Pages that have been persistently vandalized by anonymous and registered users. Some highly visible templates and modules. | |||||
| Cannot edit | Normal editing* | Specific topic areas authorized by ArbCom, pages where semi-protection has failed, or high-risk templates where template protection would be too restrictive. | |||||
| Cannot edit | Normal editing | High-risk or very-frequently used templates and modules. Some high-risk pages outside of template space. | |||||
| Cannot edit | Normal editing | Pages with persistent disruption from extended confirmed accounts. Critical templates and modules. | |||||
| Cannot edit | Normal editing | Scripts, stylesheets, and similar objects central to operation of the site or that are in other editors' user spaces. | |||||
| * In order to edit through extended confirmed protection, a template editor must also be extended confirmed, but in practice this is almost always the case. Other modes of protection: | |||||||
Polling
Provided with three options, discussion participants can endorse one of three standpoints presented. The three positions propose outright abandonment of the tool; use under a draft policy; or use once another policy has secured consensus:
- "The negative aspects of pending changes outweigh the positive. Therefore the tool should not be used at all on the English Wikipedia."
- "Despite the flaws of the trial period pending changes has proven to be a useful tool for combating vandalism and other types of problematic edits. The tool should be used in accordance with the following draft policy. This policy is intended to reflect the community input in discussions. It is not set in stone and after use of the tool is resumed there may be unanticipated problems which can be corrected through normal consensus gathering processes."
- "Pending changes should be kept in the long term, but the draft policy is insufficient and/or out of step with what the community wants from the tool. Pending changes should not be rejected entirely but should remain unused until such time as there is a more complete policy in place that has been explicitly approved by the community."
At the time of writing, there were 77 in support of option 1, 202 in support of option 2 and 9 in support of option 3. There has been no set deadline for the closure of this discussion but based on the assumption that the polling period will be at least 30 days in length, the earliest closure date would be April 23.
Discussion
According to Beeblebrox, initiator of the current discussion, pending changes is active on the German Wikipedia where they "[use] the more restrictive 'flagged revisions' tool." Pending changes on the English Wikipedia is, per Beeblebrox, "a specialized version of that tool developed specifically to meet the requests of this project."
As pending changes should be distinct from any other protection medium on the English Wikipedia, concerns have been raised about the differences between pending changes and semi-protection, and why there is a need for what appears to be replica copy of semi-protection. For example, Sven Manguard broached the issue that pending changes level 1 and semi-protection have no distinct set boundaries as to when either is to be used. In another example, Zaminamina suggested that semi-protection be replaced by pending changes. Because pending changes should be like any other protection medium and not warrant any special treatment, there are further concerns as to why a separate policy is needed or why the project needs a new protection request system separate from Requests for Page Protection (RfPP).
In support of Option 1, SoWhy argued: "While I do understand the benefits of PC and why people support it, I still believe that any PC/FR-style protection is against the fundamental principles of the project, in that there should [be] no difference between editors (except such differences that are unavoidable) and that everyone should be able to edit equally (while semi-protection for example blocks IPs, those users can easily get the status that allows them to edit regardless – PC on the other hand would restrict editing in those cases to a small group of users). I also think that the PC trial showed that this is a kind of "power" that a number of admins do not grasp correctly and I fear that PC will lead to further problems with incorrect usage and problems with anon / new users being scared away by overzealous "reviewers" who use their new-found "powers" to reject valid edits they don't agree with. [In my humble opinion] the problems of any tool that allows one group of users to decide which edits of other users are valid without discussion by far outweigh the benefits."
On the other hand, in support of Option 2, Dcheagle contended that: "PC worked good during and after the trial and it would be a shame to let a useful thing dry up and blow away in the wind. Simply put PC is perfect in allowing good faith edits while combating bad faith edits."
And finally, in support of Option 3, Xavexgoem opined that: "I like the idea, but think it should only be used exceptionally. I'm worried about a huge backlog, and the drama that could ensue when a reviewer decides that an otherwise good-faith edit is rejected. It'll happen, and I fear it'll be hard to tell whether a reviewer was acting maliciously. Furthermore, new editors may perceive a chilling effect when they make a good-faith edit that's at odds with a reviewer's idea of a good-faith edit. I'm not sure if the ensuing drama from this technology will be less than the drama it solves. All in all, I just think there needs to be a whole lot more documentation on what's expected from a reviewer, and what's expected from an admin who has the option of choosing between [protection] and pending changes."
What the future holds
As this may be the final Request for Comment on pending changes, the community is strongly encouraged to participate and weigh in with their views. This discussion may kill pending changes for good or may establish it as a permanent feature of the encyclopaedia's defense mechanisms.
Any further developments will be covered in next week's Discussion Report. For a more partisan discussion of the topic, see also this opinion piece by Beeblebrox, written in August 2011.
Reader comments
The Butterflies and Moths of WikiProject Lepidoptera






This week, we spread our wings with WikiProject Lepidoptera. Started in May 2006, the project has grown to include over 45,000 pages about butterflies and moths. The project maintains a list of tasks, various helpful resources, and a taxonomic checklist showing where work still needs to be done. We interviewed project founder AshLin and members IvanTortuga, Grmanners (GRM), Ruigeroeland, and Shyamal.
What motivated you to join WikiProject Lepidoptera? Does your educational background or professional experience involve working with Lepidoptera or other insects?
- AshLin: When I joined up I found that there was no WikiProject for these creatures. Then IronChris came up with WikiProject Arthropods and I was intrigued. At that time, Shyamal, VirenVaz and I had an informal task force on Indian butterflies which we immediately affiliated to the WikiProject. Over time, I found the courage to set up WikiProject Lepidoptera. IronChris, Kylu, Kugamazog and Shyamal helped me at first. Soon people began to join in and we had a small bunch of enthusiastic editors going about this humungous task. Being an electrical engineer, I had no formal training except for a lifelong passion for the creatures.
- IvanTortuga: I joined the project because of my love for all invertebrates and thought my photographic abilities could help the project. Both my educational and professional backgrounds have lead me to work within the field of entomology. I've worked with the Encyclopedia of Life, iNature and a few other random sites here and there and once worked as an Aquatic Entomologist at Northern Michigan University where I finished a minor in Biology (focusing on entomology).
- GRM: When I returned to the UK in 2003 after 14 years in the tropics, I restarted an "old" hobby of butterfly watching. In the intervening time, I also became seriously interested in conservation. I am an avid reader when it comes to my hobbies and a professional editor and writer. I then "found" Wikipedia and worked on Heath Fritillary as I was doing the same for Butterfly Conservation local branch. One of my fellow Wikipedians then persuaded me to take on a more active role for British butterflies in general.
Writing articles on the taxonomy and anatomy of living creatures can become fairly technical. What can the average editor contribute to Lepidoptera articles, even if they don't have specialized knowledge in the field?
- IvanTortuga: The project always needs help. Even if you don't have knowledge in the field you can still help with general grammar, clean up and vandalism protection.
- Ruigeroeland: I am not an expert at all, but I have learned quite a bit about taxonomy down the road. In my experience, there are two crucial things (with regards to taxonomy) to keep in mind when writing an article on a living thing: 1. always include the original combination (i.e.: the genus the species was first placed in + the name of the species) as a synonym. 2. Add all synonyms you can find. This is the only way to ensure a single species will not be added to wikipedia under various names.
- AshLin: Among the things I felt deprived as a child were good books informing us about butterfly physiology, behaviour, migration etc. I had an urge to help create just such a resource as I had coveted. Sadly, I found there were no experts willing to spare any time. So I decided that this was just the kind of challenge so many Wikipedians have faced and will face again and that it was doable. A simple framework was created and by adding fact after referenced fact and images, slowly but surely an article began to develop on the external morphology of Lepidoptera. Many other editors cooperated in ways big and small and after many months we had a very large article with almost a hundred images developed which we took to Good Article level. This proved to me that amateurs could make substantial contributions. Formal training in biology was less important here than an affinity for biology and scientific temperament in general. So yes, it was proved that an average editor like me could contribute substantially to science despite not possessing formal degrees.
- GRM: Yes, if they have access to relevant taxonomic works.
Which tend to be better covered by Wikipedia: butterflies or moths? In general, how does Wikipedia's coverage of Lepidoptera compare to coverage of other living things? What can be done to improve this coverage?
- IvanTortuga: In my personal experience butterflies tend to get a lot more coverage unless the species of moth is of economic importance (invasives, silk worms, etc.). Though in general the project covers their bases pretty darn well compared to other projects in zoology.
- Shyamal: The situation of Lepidopteran taxonomy is a bit confused and there is as yet no single global project that has reached the maturity level of say the world's birds. Even at the family level, there have been major shakeups in recent times. There are a few expert projects that have attempted to create a systematic index but this is as yet incomplete and that ambiguity spills over as a problem for Wikipedia.
- Ruigeroeland: The number of moth articles is far greater, but this is mainly due to the fact that there are a lot more moth species (I think it was 20,000 butterflies vs. 130,000 moths). I am mainly working on moths and add about 10 new articles to Wikipedia each day. We even have "complete coverage" for some of the moth families. For those interested, you can see the progress here: [1]. In my experience, coverage on Wikipedia is mostly influenced by distribution of the species and not if they are a butterfly or a moth. Information on Neotropical, African and especially south-east Asian species is often hard to find, while there is a lot of info available for European species.
- GRM: I'd guess butterflies. Can we advertise for contributors within Wikipedia itself? Make it clear that the input of the most inexperienced writers who are keen is better than having a stub or no entry at all!
How difficult is it to obtain images of Lepidoptera? Are there specific butterflies and moths the project could use some help photographing?
- IvanTortuga: Its not all that hard to find images of Lepidoptera, I am one of the photographers and I am always on the look out for images that can help the project grow. There is a rather sizable list of Leps that need photos though, anything from the deep jungles and tundras.
- Shyamal: Many of the old works on Lepidoptera have gone into the public domain and the Biodiversity Heritage Library has done a marvellous job of making these available for harvesting (e.g. commons:Category:Lepidoptera Indica).
- Ruigeroeland: We have a lot of pictures of western European and Australian species and quite some for North American species. In my experience it is a lot harder to find images for species from other parts of the world though. I had some success convincing someone from Taiwan to release over a 1,000 images of moths to wikimedia. I would love to see other people try the same.
- GRM: Yes and no. Maybe the Project page should have specific requests. Maybe someone should tell me to get on and upload my images of African Lepidoptera!
Does WikiProject Lepidoptera collaborate with any other projects?
- AshLin: As such we have not had any notable collaboration that I can think off. We are not averse to the idea but no opportunity seems to have come about.
What are the project's short-term and long-term goals? How do you envision the project changing and growing over the next few years?
- IvanTortuga: I would personally like to see the project take on the large scale research of deep jungle Leps. This would take a lot of work but it would be a hugely useful tool for students, teachers and for environmental conservation.
- AshLin: Besides the taxon-related articles, we have a great need for well-developed Lepidoptera biology and conservation related articles. We don't have a complete framework in place on these topics, much less developed articles.
What are the project's most urgent needs? How can a new member help today?
- Ruigeroeland: There are tons of articles on species to be made. At this point, only a handful of people are active in the project and all help would be greatly appreciated.
- AshLin: I concur with Ruigeroeland, lack of eyeballs and minds is a serious constraint to us. Lack of up-to-date taxonomic resources is another challenge we face. For example, our work on Indian butterflies came to a halt when we realised that we were creating more dubious species than valid ones. No dependable taxonomic work on Indian butterflies has emerged since last fifty years. We are now waiting for Krushnamegh Kunte's Indian butterfly checklist which has been under making for a number of years. This will help us decide which articles to delete/merge/rename etc. Lack of access to resources cloistered behind paywalls has also hampered us but Wikipedia:Resource request has been able to help us in many cases.
Next week, we'll find out if the truth is really out there. Until then, trust no one in the archive.
Reader comments
A few good sports: association football, rugby league, and the Olympics vie for medals

Featured content





Two featured articles were promoted this week:
- HMS Vanguard (23) (nom) by Sturmvogel 66. HMS Vanguard, the only ship in her class, was the last battleship ever launched in the world. Ordered in 1941 by the UK government for combat against joint Japanese and German forces, the Vanguard was not completed until after the war was over. The ship was used to transport King George VI and his family on the first Royal Tour of South Africa, then as the country's flagship in the Mediterranean sea. After several years of participating in training exercises, she was broken down for scrap in 1960.
- Chrisye (nom) by Crisco 1492. Chrismansyah Rahadi (1949–2007), better known by his stage name of Chrisye, was an Indonesian progressive-pop singer and song writer. In his 40-year career he won many awards and accolades, and several of his albums were certified silver or gold. Five albums to which he contributed were included in the Rolling Stone Indonesia list of the 150 Best Indonesian Albums of All Time. The following year, the magazine listed five of his songs (and a sixth to which he contributed) as some of the best Indonesian songs.
Delisted featured article
- Chennai (review) was delisted based on unresolved issues of synthesis in the education section, incomplete verification of text by sources, lack of proper coverage of some topics such as art and architecture and lack of information on poverty, slums, overpopulation and other areas needed to be comprehensive.
Featured lists
Six featured lists were promoted this week:
- List of Connecticut Huskies in the WNBA Draft (nom) by Grondemar. The University of Connecticut (UConn) women's basketball team, known as the Connecticut Huskies, has had 23 players selected in the Women's National Basketball Association (WNBA) draft. Twelve were selected in the first round of the draft; four players were picked first overall. A UConn women's basketball alumna has been selected in twelve of the last fourteen WNBA Drafts.
- List of Malmö FF managers (nom) by Reckless182. Since its establishment in 1910, the Swedish association football club Malmö Fotbollförening has had 28 managers. The longest serving was Antonio Durán, who managed the team from 1964 to 1971. Sven Nilsson, who was manager for seven months in 1950, has the highest win percentage, winning 78.3% of the 23 games he managed.
- Birmingham City F.C. league record by opponent (nom) by Struway2. The Birmingham City football club have played against 106 teams since their founding in 1875. The team have most often been in competition with Manchester City, playing them 134 times and being defeated 60, more than Birmingham have lost against any other club. They have a 100% win percentage against six teams, none of whom they have played more than four times.
- List of Tranmere Rovers F.C. players (nom) by U+003F. The English football club Tranmere Rovers have 155 players who have made more than 100 appearances for the team since it was established in 1884. The player with the most appearances is defender Ray Mathias, who played in 637 games over 22 years. The player with the most goals is Ian Muir, who scored 180 goals in 393 games.
- List of Olympic medalists in art competitions (nom) by Canadian Paul. In the early 20th century, the Olympic Games featured art competitions in architecture, literature, music, painting, and sculpturing; further subdivisions were included at some games. The art competitions made their first appearance in the 1912 games and their last in 1948. Several participants won multiple medals, though only two won medals in both arts and sports competitions.
- List of Hot 100 number-one singles of 2011 (U.S.) (nom) by 1111tomica. In 2011, fourteen singles topped the Hot 100 chart published by American music magazine Billboard; nine acts had their first number one single, either as lead artist or a featured guest. The best-performing was Adele's "Rolling in the Deep", which topped the Year-End Hot 100 chart. The single with the most staying power was Rihanna's "We Found Love", which held the top position for eight consecutive weeks in 2011 and two more in 2012.
Featured pictures
Eleven featured pictures were promoted this week:
- Female Australian Shelduck (nom; related article), by JJ Harrison. The Australian Shelduck is a large shelduck from southern Australia and Tasmania. This specimen was photographed in Perth, Western Australia.
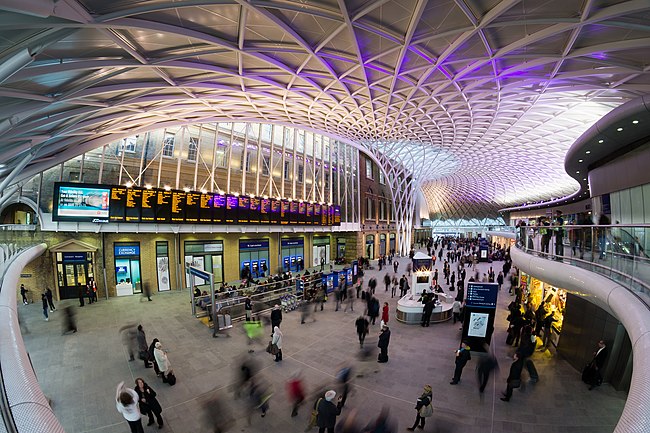
- King's Cross Western Concourse (nom; related article), by Colin. The new departures concourse at London King's Cross railway station, designed by John McAslan, opened in March 2012. According to the image's creator, there is a tribute to the Harry Potter series – present in the actual station – somewhere in the image.
- Cary Grant (Suspicion) (nom; related article), created by an unknown RKO publicity photographer, edited by Crisco 1492, and nominated by A Thousand Doors. This publicity still from the 1941 feature film Suspicion depicts English-American actor Cary Grant. Known for his debonair demeanor and "dashing good looks", Grant was a popular Hollywood leading man.
- Tewkesbury Abbey (nom; related article), created by Saffron Blaze and nominated by Tomer T. The Abbey of the Blessed Virgin Mary at Tewkesbury, better known as Tewkesbury Abbey, is located in the English county of Gloucestershire. The second largest parish church in the country, its location has been used for religious services since the 7th century.
- Emperor Dragonfly at Puerto de la Cruz (nom; related article) by Quartl. The Emperor Dragonfly (Anax imperator), a species of hawker dragonfly which averages 78 millimetres (3.1 in) in length, is one of the largest dragonflies in Europe; its range includes parts of Africa and Asia as well. This specimen was photographed in Spain.
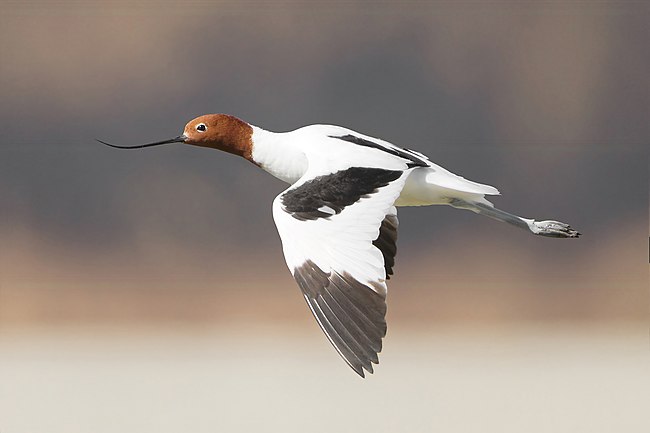
- Red-necked Avocet in flight at lake Joondalup (nom; related article) by JJ Harrison. The Red-necked Avocet (Recurvirostra novaehollandiae) is a waterbird endemic to Australia. This specimen was photographed in Western Australia.
- Perth Central Business District (CBD) from Mill Point (nom; related article) by JJ Harrison. The CBD of Perth, Western Australia, is bordered by the Swan River to the south and east, Kings Park on the west, and railway lines to the north. This skyline, taken several minutes after sunset, was described as "one of the best cityscapes I've seen in a long time" by reviewer Clegs.
- Charles III of Spain (nom; related article), created by Anton Raphael Mengs and nominated by Crisco 1492. This portrait of Charles III of Spain, painted in 1761, was described by reviewer Saffron Blaze as having odd composition but capturing the monarch's character "quite well". Charles led numerous reforms in Spain during his reign, but the country relapsed after his death.
- Line-out (rugby union) (nom; related article), created by PierreSelim and nominated by Mmxx. In rugby union, the line-out is the manner in which the ball is returned to play after leaving the field. Each team sends representatives to stand in parellel lines to intercept a thrown-in ball. This picture depicts Stade Toulousain (left) and Lyon OU.
- DeWitt Clinton (nom; related article), created by Rembrandt Peale and nominated by Crisco 1492. Clinton (1769–1828) was an American politician who served as senator and Governor of New York; he also ran for president in 1812. This portrait was painted c. 1823 and measures 28.625 by 23.175 inches (72.71 cm × 58.86 cm).
- Untitled painting by Francisco de Goya y Lucientes (known as Fight with Cudgels) (nom; related article), created by Francisco Goya and nominated by Crisco 1492. This is one of the series of Black Paintings that Goya painted directly onto the walls of his house sometime between 1820 and 1823 and depicts two men fighting one another with cudgels. It was selected as a newly featured picture because of the high quality of the image of this notable painting, its interesting composition, and the symbolism of the subject matter.

Reader comments
Evidence submissions begin in Rich Farmbrough case, proposed decision in R&I Review
The Arbitration Committee opened no cases this week, keeping the number of open cases at two.
Open cases
Rich Farmbrough (Week 2)
This case involves accusations of disruptive editing against Rich Farmbrough. Specifically, concerns have been raised about the editor and his observance of bot policy. Arbitrator Hersfold originally filed the case, which the committee chose to accept last week. Arbitrator Newyorkbrad is drafting a proposed decision, expected in about a month's time.
For the past week, editors on both sides have posted evidence concerning the accusations of disruptive editing. Rich Farmbrough posted a short response to the allegations, promising to go into more detail on the workshop page. Most evidence submissions have concerned potential violations of editing restrictions through the use of bots.
Evidence will be accepted until Wednesday, 18 April.
Race and intelligence review (Week 5)
A review of the Race and intelligence case was opened as a compromise between opening a new case and ruling by motion. The review is intended to be a simplified form of a full case, and has the stated scope of conduct issues that have purportedly arisen since the closure of the 2010 case.
A complete decision was proposed on 16 April by drafter Roger Davies. The proposed principles include clarifications of harassment policies and sockpuppet investigation procedures. After a long series of findings of fact, the proposed decision seeks to admonish one editor involved in disruptive actions and ban two others for no less than one year.
Other requests and committee action
- The Arbitration Committee has continued voting on a series of proposals to change the limits for evidence submissions in cases. At the time of publication, no motion had passed.
Reader comments
MediaWiki 1.20wmf1 hits first WMF wiki, understanding 20% time, and why this report cannot yet be a draft
Renewed interest in drafts feature
There was renewed interest among developers this week in the provision of automatic "Save as draft" functionality during editing, allowing users to either deliberately set aside part-finished changes to an article when interrupted, or to recover work lost if their workstation unexpectedly terminates their session (wikitech-l mailing list).
The feature was first discussed over three years ago, when a Drafts extension that provided the required functionality even made it as far as being enabled on a test wiki (see previous Signpost coverage from January 2009). Despite this, as regular editors will be aware, the feature never made it onto Wikimedia wikis and the extension languished until it was revived this week by developer Petr Bena. As of time of writing, the extension is deployed on a (different) test wiki, awaiting fixes both to bring elements of its design up to modern standards and to make it compatible with recent versions of the MediaWiki software that underpins Wikimedia wikis (not least visual changes to make it compatible with new default skin Vector, which had not yet been written back in January 2009).
Initial investigations show that the extension, which has been deployed on several external wikis, could well be salvageable, making it possible that it could theoretically be deployed on Wikimedia wikis soon if it were picked up by Foundation developers. Any work done on it, however, could yet be overtaken by the deployment of the new Visual Editor to its first WMF wiki (currently scheduled, very approximately, for later this year).
What is: 20% time?
Wikipedia:Wikipedia Signpost/Templates/What is The issues surrounding the volunteer–staff divide – and the probable impact upon it of the change in review paradigm that accompanied the Git switchover – were crystallised this week in a post by WMF Director of Platform Engineering Rob Lanphier on the wikitech-l mailing list. The subject of the email was 20% time, a WMF protocol that makes provision for one day a week when staff developers will work on tasks more closely associated with the wider volunteer developer community than their usual development workflow.
Given the recent questions about code review times, Lanphier used the email to describe the protocol (which he was personally responsible for managing until recently) more fully. Before the Git migration, he wrote, code review was the primary task allotted to staff developers to fill the 20% of time set aside from their main development projects. This was done because "the consequences of falling behind there were more severe than letting other things slide". The point of the post, however, was to stress the new, more diverse set of topics that would be covered during this "20% time" now that the Git switchover had reduced the impact of code review backlogs – the primary aim being that no volunteer developer felt that their preferred area of development is neglected.
The new list of possible tasks during 20% time, which is most commonly taken by staff developers on Fridays, includes "merging reviewed code into the release or deployment branch and deploying it", code review, and "Updating public wiki pages, documenting/sharing data, and otherwise contributing to making WMF engineering work transparent". In addition to the obvious benefits to the success of volunteer development work, the policy is also intended to help staff developers maintain a sense of the "bigger picture" and hence to increase the bus factor of large sections of MediaWiki code.
In brief
Not all fixes may have gone live to WMF sites at the time of writing; some may not be scheduled to go live for many weeks.
- First MediaWiki 1.20 deployment begins: As previewed in last week's "Technology report", the first deployments of MediaWiki 1.20 to Wikimedia wikis commenced this week, affecting MediaWiki.org and a test wiki (at time of publication, the deployment to Wikimedia Commons is underway, with the English Wikipedia scheduled to receive the update on 23 April). The most significant feature of MediaWiki 1.20wmf1 is its new set of diff colours; 1.20wmf2 will follow in approximately a fortnight, 1.20wmf3 approximately a fortnight after that, and so on until in a number of months MediaWiki 1.20 is officially released to external sites (Wikimedia blog, full roadmap).
- Google grants WMF nine slots: Further to previous Signpost coverage, it was confirmed this week on the wikitech-l mailing list that Google will fund nine placements in its 2012 Summer of Code programme for students wishing to work under the auspices of the Wikimedia Foundation. The number Google are making provision for this year – with sums of up to $5000 set aside for each – represents a slight increase on last year's eight student total. It is now up to WMF and MediaWiki developers to select up to nine students to take part in this year's summer placements scheme; as reported last week, some 41 serious applications were made for those places, making it the numerically toughest year on record.
- Two hires for WMF Engineering: Two new members of staff were announced this week by the Wikimedia Foundation's Engineering department. Greek contractor Faidon Liambotis joins the operations department to work on "enhancing and deploying more services on the new Wikimedia Labs platform" (wikitech-l mailing list), while Belgian developer Matthias Mullie joins as a features engineer. His initial remit will include "New Page Triage, the Article Creation Wizard, and the Article Feedback Tool" (also wikitech-l). The Foundation have traditionally had difficulty in hiring enough 'good people' fast enough to meet its rapidly-increasing workload, although there is evidence that (even without compromising the quality of new hiring) the problem has eased slightly in more recent months.
- DippyBird improvements: Mobile Software Engineer Arthur Richards announced this week a series of improvements to his Gerrit "bulk change" script DippyBird (wikitech-l mailing list). For those with sufficient permissions, the script (written in PHP and – somewhat ironically – not yet migrated to Git) allows the users to comment on, approve, or decline multiple patchsets submitted to new code review tool Gerrit using a single command; a work in progress, the script is designed to make reviewers' lives easier, particularly when attempting bulk administrative changes.
- Five bots approved: 5 BRfAs were recently approved:
- AnomieBOT's 62nd BRfA, adding {{old AfD multi}} to the talk pages of new articles that have previously appeared at WP:AFD
- Cyberbot I, maintaining the bad image list with {{badimage}}
- タチコマ robot's 12th BRfA, bypassing File: namespace redirects
- MadmanBot's 15th BRfA, e-mailing activation codes to contributors who signed up for free 1-year HighBeam Research accounts
- warddrBOT, an interwiki bot operated by a sysop from nl:
- At the time of this writing, 10 BRfAs are active. As always, community input is encouraged.
Reader comments