Thiophosphoric acid
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Monothiophosphoric acid
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| H3PO3S | |
| Molar mass | 114.061 |
| Appearance | colorless |
| Acidity (pKa) | 1.79, 5.42, 10.08[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
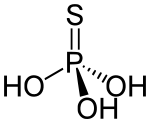
Thiophosphoric acid is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula H3PO3S. Structurally, it is the acid derived from phosphoric acid with one oxygen atom replaced by sulfur atom, although it cannot be prepared from phosphoric acid. It is a colorless compound that is rarely isolated in pure form, but rather as a solution. The structure of the compound has not been reported, but two tautomers are reasonable: S=P(−OH)3 and O=P(−OH)2(−SH).
Preparation
[edit]The compound has been prepared in a multistep process starting with the base hydrolysis of phosphorus pentasulfide to give dithiophosphate, which is isolated as its barium salt:[2]
- P2S5 + 6 NaOH → 2 Na3PO2S2 + H2S + 2 H2O
- 2 Na3PO2S2 + 3 BaCl2 → 2 Ba3(PO2S2)2 + 6 NaCl
In a second stage, the barium salt is decomposed with sulfuric acid, precipitating barium sulfate and liberating free dithiophosphoric acid:
- Ba3(PO2S2)2 + 3 H2SO4 → BaSO4 + 2 H3PO2S2
Under controlled conditions, dithiophosphoric acid hydrolyses to give the monothioderivative:
- H3PO2S2 + H2O → H3PO3S + H2S
References
[edit]- ^ Perrin, D. D., ed. (1982) [1969]. Ionisation Constants of Inorganic Acids and Bases in Aqueous Solution. IUPAC Chemical Data (2nd ed.). Oxford: Pergamon (published 1984). Entry 238. ISBN 0-08-029214-3. LCCN 82-16524.
- ^ R. Klement "Phosphorus" in Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry, 2nd Ed. Edited by G. Brauer, Academic Press, 1963, NY. Vol. 1. p. 570, 568.
