TIRAP
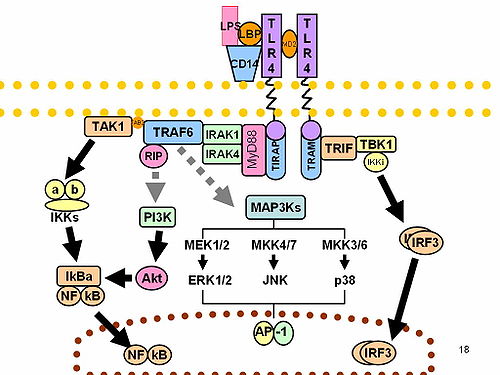
TIRAP (TIR domain containing adaptor protein) is an adapter molecule associated with toll-like receptors. The innate immune system recognizes microbial pathogens through Toll-like receptors (TLRs), which identify pathogen-associated molecular patterns. Different TLRs recognize different pathogen-associated molecular patterns and all TLRs have a Toll-interleukin 1 receptor (TIR) domain, which is responsible for signal transduction. The protein encoded by this gene is a TIR adaptor protein involved in the TLR4 signaling pathway of the immune system. It activates NF-kappa-B, MAPK1, MAPK3 and JNK, which then results in cytokine secretion and the inflammatory response. Alternative splicing of this gene results in several transcript variants; however, not all variants have been fully described.
See also
[edit]External links
[edit]- TIRAP+protein,+human at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000150455 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000032041 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.