Schloss Pirmasens
49°12′01″N 7°36′20″E / 49.200249°N 7.605497°E

The Palace of Pirmasens (German: Schloss Pirmasens or German: Pirmasenser Schloss) is a former palace in Pirmasens, Germany. Constructed in the first half of the 18th century as a hunting lodge for Johann Reinhard III (1665-1736), the last count of Hanau-Lichtenberg, the palace became later the main residence of Louis IX, Landgrave of Hesse-Darmstadt (1719-1790). During the French Revolution, the palace was destroyed and later demolished. Today, nothing reminds anymore of the Pirmasenser Schloss.
History
[edit]Reinhard III of Hanau-Lichtenberg
[edit]

The palace in Pirmasens traces its origins to a hunting lodge built either in 1712 or 1720 for Count Johan Reinhard III of Hanau-Lichtenberg.[1][2] Architect was Leonhard Jennewein (1682-1754), a stone mason from Tirol.[2] Construction was completed in 1725.[1] The location was chosen due to rich forests around Pirmasens, ideal for hunting. The lodge became the center for so-called Par force hunts.
‘Par force’ hunts were grand theatrical events, meticulously planned to demonstrate power and greatness. Count Reinhard III and his guests participated in the hunt, or positioned themselves centrally in the forest while they waited to be summoned. Meanwhile, the mounted hunters and their hounds pursued the day's quarry. From their waiting place, the count and his guests could watch the hunters, horses and hounds as they persecuted the frantic stag at great speed. When the exhausted stag was no longer able to run, the dogs held it fast by biting its throat, ears, legs and muzzle. Thus, the stag was “fixed” and the count was summoned with a special horn signal. He carried out his duty as the master of the hunt by killing the stag with a stab wound to the heart.
Following Johan Reinhard III’s death in 1736 without a male heir, Pirmasens and the Hanau lands passed to his grandson Louis, who later became Landgrave Louis IX of Hesse-Darmstadt in 1768.[1]
Louis IX of Hesse-Darmstadt
[edit]


From 1741 onwards Louis IX began spending more time in Pirmasens and, in 1757, officially made the city his main residence.[1] Although Bouxwiller was the capital of the County of Hanau-Lichtenberg, Louis IX favored Pirmasens because this part of the county was free from French sovereignty, allowing him greater autonomy in managing his army and to have a garnison stationed there. He commissioned the expansion of the old hunting lodge to suit his preferences, once again enlisting his grandfather’s architect, Leonhard Jennewein, who involved both his brother Peter Jennewein and son-in-law, Philip Schiffer, in the project. [2]
Although Schloss Pirmasens was expanded, it remained a modest and unadorned palace. It did not suit the tastes of Louis IX’s wife, Landgravine Caroline, who, unlike her husband, was less focused on military affairs and more passionate about art and music. At a certain point, she began living separately from him in the Château de Bouxwiller, which she transformed into a "small Versailles" in Alsace, complete with beautiful gardens.
Ludwig succeeded his father as ruler of Hesse-Darmstadt in 1768. Together with his first minister, Friedrich Karl von Moser, he reformed the state based on the Prussian model. Most of the existing officials were dismissed, and the parforce hunt, which had nearly ruined agriculture in Hesse-Darmstadt, was abolished. The army was expanded, and barracks and garrisons were developed.
Ludwig's personality exhibited some irrational traits, such as his fear of ghosts, and he was mocked by some contemporaries for his "soldier games."[3] However, the Landgrave was deeply caring toward his soldiers and had a particular fondness for military drills and parades. Unlike many rulers of the time, including his relatives, the Landgraves of Hesse-Kassel, he did not engage in the common practice of trading soldiers. [4]
Louis IX also composed countless military marches,[5] which earned him the nickname Chief Drummer of the Empire.[6]
The End
[edit]
Louis IX did not live to witness the destruction of his palace, as he died and was buried in Pirmasens in 1790.[2] Only three years later, during the French Revolution, French troops occupied the city and completely destroyed the palace.[2] The ruins were auctioned off in 1805 and eventually demolished.[1] Several administrative and noble residences that had been part of the palace complex initially survived but were all destroyed during the Second World War.[2]
Architecture
[edit]
The palace stood on what is now the site of the Schlosstreppen (palace steps) and Schlossbrunnen (palace fountain), built on a hillside.[2] To the east runs Schlossstraße, across from which stands St. Pirmin Roman Catholic Church.[2] To the west lies Schlossplatz, where the old town hall is located.[2]
The palace’s rectangular main building, a plastered structure with nine window bays and a mansard roof, had four stories on its western side and two on the eastern side due to its sloping location.[2] Two ramps led to a grassy parterre on the west side, enclosed by a small guardhouse.[2] Two mansard-roofed outbuildings created an honorary courtyard on the eastern side.[2] To the south, parallel to one of the ramps, stood a long structure that housed stables and a barn.[2] In 1763, the side buildings were replaced by square pavilions, and the guardhouse was expanded into the main guard post.[2]
A large drill house was constructed opposite the palace in 1770, which was demolished in 1806.[1] St. Pirmin Church was later constructed on that site.
Schloss Pirmasens was comparable in style to Schloss Wilhelmsthal in Calden near Kassel, Schloss Neuwied, and Jagdschloss Windhof near Weilburg.
Today
[edit]Today, the only surviving remnants of the palace, such as paintings and furniture, are housed in the Pirmasens City Museum and the Darmstadt Palace Museum.[2] Additionally, a triangular gable from a former noble residence and officer’s casino, dating from 1780 and bearing Louis IX's emblem, can still be seen at Hauptstraße 102.[2] It was incorporated into a building constructed after 1945.[2]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d e f "Pirmasenser Chronik". www.historischer-verein-pirmasens.de (in German). Retrieved 30 September 2024.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q "Das landgräfliche Schloss zu Pirmasens". www.regionalgeschichte.net (in German). Retrieved 30 September 2024.
- ^ Jürgen Rainer Wolf (1987), "Ludwig IX.", Neue Deutsche Biographie (in German), vol. 15, Berlin: Duncker & Humblot, pp. 392–392; (full text online)
- ^ Wilhelm Oncken (1882), "Zehntes Buch der Lebensabend Friedrichs des Großen. Der Erbvergleich von 1770. Wilhelmsstein und Pirmasens", Das Zeitalter Friedrichs des Großen – Mit Porträts, Illustrationen und Karten, vol. Band 2, Berlin: Baumgärtel, p. 708, OCLC 463170868
- ^ Robert Eitner: Biographish-bibliographisches Quellen-Lexikon der Musiker und Musikgelehrten der christlichen Zeitrechnung bis zur Mitte des neunzehnten Jahrhunderts. Band 6, La—Milleville, Barnaba, Breitkopf & Haertel, Leipzig, 1902, S. 239.
- ^ Ludwig IX., des Reiches Erz-Tambour.
Literature
[edit]- Eckardt, Anton; Erich, Hans (1957). Die Kunstdenkmäler der Stadt und des Landkreises Pirmasens (=Die Kunstdenkmäler von Rheinland-Pfalz. Bd. 2) (in German). München.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Lehnung, Julius (1982). Geliebtes Pirmasens. Heimatgeschichtliche Erinnerungen. Band I. 740-1790 (in German). Pirmasens.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Wenz, Martin (2002). "Das ehemalige Residenzschloss in Pirmasens". Jahrbuch Historischer Verein Pirmasens (in German). Pirmasens: Historischer Verein Pirmasens. pp. 139–169.
- Bauer, Markus (2015). "Tiroler Bauhandwerker als Einwanderer in die Westpfalz". Pfälzisch-Rheinische Familienkunde 64 (in German). pp. 212–214.
See also: Other palaces owned by Reinhard III of Hanau-Lichtenberg
[edit]- Hanauer Hof - City palace in Strassbourg
- Château de Bouxwiller - The residence in the capital of Hanau-Lichtenberg
- Stadtschloss Hanau - The city palace of Hanau
- Schloss Philippsruhe - The baroque summer palace in Hanau
- Chateau de Brumath - Summer palace constructed for his daughther, the mother of Louis IX of Hesse-Darmstadt
External links
[edit]
Gallery: Development and views of Schloss Pirmasens in city plans and views of Pirmasens
[edit]The plans and city views are from the map collections of the Universitätsbibliothek in Darmstadt.
-
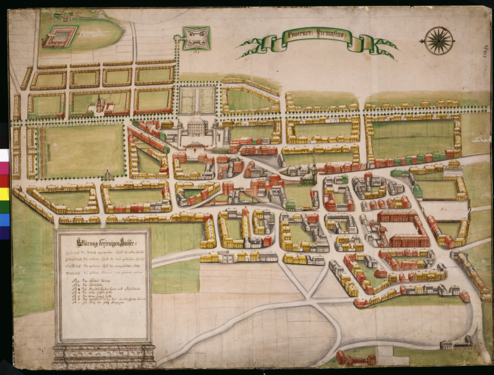
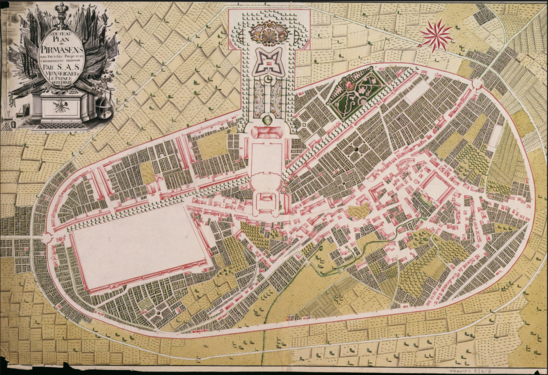
City plan of Pirmasens published in 1770, before the drill house was constructed. Schloss Pirmasens is in the center of the town
-
1762 city plan of Pirmasens. Schloss Pirmasens is in the middle. Above the palace is the drill house, and right above are Landgravinne Caroline's gardens with a pavillion in the middle
-
1788 City plan of Pirmasens with Schloss Pirmasens extended compared to the other city plans. Also note that the landscape style of the Landgravinne's garden changed from a French formal style to an English landscape style
-
1790 City view of Pirmasens from the North with the palace in the middle, left of the drill house with the large blue roof
-
1790 City view of Pirmasens from the West with the palace in the middle, the drill house in the back and the city town hall in the front
Gallery: Palaces similar to Schloss Pirmasens in Style
[edit]-
Schloss Wilhelmsthal in Calden near Kassel
-
Schloss Wilhelmsthal in Calden near Kassel
-
Schloss Neuwied in Neuwied
-
Schloss Neuwied in Neuwied
-
Jagdchloss Windhof near Weilburg
-
Jagdchloss Windhof near Weilburg