Roosevelt Campobello International Park
| Roosevelt Campobello International Park | |
|---|---|
IUCN category V (protected landscape/seascape) | |
 The Roosevelt cottage at Campobello (2011) | |
| Location | Campobello Island, New Brunswick, Canada |
| Nearest city | Saint John, New Brunswick |
| Coordinates | 44°52′33″N 66°57′33″W / 44.8758°N 66.9592°W |
| Area | 11.01 km2 (4.25 sq mi) |
| Established | July 7, 1964 |
| Governing body | Roosevelt Campobello International Park Commission |
| Website | Roosevelt Campobello International Park |
Roosevelt Campobello International Park preserves the house and surrounding landscape of the summer retreat of Franklin D. Roosevelt, Eleanor Roosevelt and their family. It is located on the southern tip of Campobello Island in the Canadian province of New Brunswick, and is connected to the mainland by the Franklin Delano Roosevelt Memorial Bridge, at Lubec, Maine in the United States.
The cottage, built in the Shingle Style and completed in 1897, was designed by Willard T. Sears. It was given as a wedding present to Franklin and Eleanor in 1908, by Franklin's mother Sara Roosevelt. In August 1921, 39-year-old Roosevelt, who would go on to become the 32nd President of the United States, was stricken by a severe paralytic illness, believed to be polio at the time, leaving him permanently paralyzed from the waist down.[1]: 236 FDR was no longer able to stay at the "beloved island",[2] but he sailed there in 1933 and visited briefly in 1936 and 1939.[3] Eleanor Roosevelt loved the cool summer weather and visited many times with her children and friends. Armand Hammer acquired the cottage in 1952. After Eleanor's death in 1962, Hammer deeded the property to the governments of the U.S. and Canada. In 1964, they created the 2,800-acre (11 km2) International Park.[4]
Description
[edit]In addition to the 19th century vacation cottage, related outbuildings, gardens, and hiking trails, Roosevelt Campobello International Park has a visitor centre with a gift shop and a small bilingual display on the open Canada–United States border.[5]
Administrative history
[edit]The park, a US Government Agency and a Canadian Government Corporation, is owned by the governments of Canada and the United States, and is administered by the Roosevelt Campobello International Park Commission. The Commission was created by international treaty signed by Governor General Georges Vanier, Prime Minister Lester B. Pearson, and President Lyndon B. Johnson on January 22, 1964. The park was established on July 7, 1964. Both countries provide equal financial support to the park. It is an affiliated area of Parks Canada and of the U.S. National Park Service.
According to the treaty, Canada and US share equally "in the costs of development, operation, and maintenance"; the Park is jointly managed and staffed.[6]
The Roosevelt Campobello International Park Commission consists of charter members and alternates: a chairperson and three board members from each country, as well as three Alternate Commissioners from both the US and Canada.[7] The US President appoints the US members of the Commission, while the Canadian Governor in Council appoints the Canadian members. In September 2020, the Canadian government was seeking applicants for two vacant RCIP positions on the Commission.[8] The positions are unpaid, but the Canadian government states that "members may be paid reasonable per diem and travel expenses by the Commission".[9]
See also
[edit]- Sunrise at Campobello, 1958 play
- Sunrise at Campobello, 1960 film
- Franklin D. Roosevelt's paralytic illness
- List of residences of presidents of the United States
- List of buildings and monuments honoring presidents of the United States in other countries
Gallery
[edit]-
The Roosevelt cottage, a wedding gift from Sara Delano Roosevelt
-
Main room
-
Interior
-
Dining room
-
Franklin Roosevelt climbing rocks with friends (1902)
-
Franklin Roosevelt with friends (1902)
-
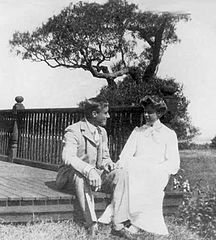
Franklin and Eleanor Roosevelt (1904)
-
FDR playing golf (1904)
-
FDR on the Half Moon (1906)
-
Franklin and Eleanor Roosevelt (1910)
-
The Roosevelt family (1920)
-
FDR sailing to Campobello (1933)
References
[edit]- ^ Ward, Geoffrey C.; Burns, Ken (2014). The Roosevelts: An Intimate History. New York: Alfred A. Knopf. ISBN 9780307700230.
- ^ Roosevelt, Eleanor (August 10, 1962). "My Day". The Eleanor Roosevelt Papers Project. Department of History, The George Washington University. Retrieved 2015-09-26.
- ^ "The Roosevelts on Campobello". Roosevelt Campobello International Park. Retrieved 2020-12-03.
- ^ Stephen O. Muskie, Campobello: Roosevelt’s Beloved Island (1982)
- ^ "Chapter 1: Eastern Maine". United Divide: A Linear Portrait of the USA/Canada Border. The Center for Land Use Interpretation. Winter 2015. Archived from the original on 2018-12-10. Retrieved 2017-11-14.
- ^ About the Park
- ^ The Commission
- ^ NOTICE OF OPPORTUNITY: RCIP COMMISSIONERS, CANADIAN
- ^ Organization Profile - Roosevelt Campobello International Park Commission
- The National Parks: Index 2001-2003. Washington: U.S. Department of the Interior.
External links
[edit]- IUCN Category V
- Monuments and memorials to Franklin D. Roosevelt
- Parks in New Brunswick
- Peace parks
- Geography of Charlotte County, New Brunswick
- Protected areas established in 1964
- Cummings and Sears buildings
- Museums in New Brunswick
- Historic house museums in Canada
- Buildings and structures in Charlotte County, New Brunswick
- Tourist attractions in Charlotte County, New Brunswick
- Eleanor Roosevelt
- 1964 establishments in New Brunswick
- Roosevelt family residences