Portal:Fatimid Caliphate
Portal maintenance status: (January 2019)
|
Introduction
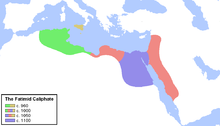
The Fatimid Caliphate (/ˈfætɪmɪd/; Arabic: ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْفَاطِمِيَّة, romanized: al-Khilāfa al-Fāṭimiyya), also known as the Fatimid Empire, was a caliphate extant from the tenth to the twelfth centuries CE under the rule of the Fatimids, an Isma'ili Shia dynasty. Spanning a large area of North Africa and West Asia, it ranged from the western Mediterranean in the west to the Red Sea in the east. The Fatimids trace their ancestry to the Islamic prophet Muhammad's daughter Fatima and her husband Ali, the first Shia imam. The Fatimids were acknowledged as the rightful imams by different Isma'ili communities as well as by denominations in many other Muslim lands and adjacent regions. Originating during the Abbasid Caliphate, the Fatimids initially conquered Ifriqiya (roughly-present Tunisia and north-eastern Algeria). They extended their rule across the Mediterranean coast and ultimately made Egypt the center of the caliphate. At its height, the caliphate included—in addition to Egypt—varying areas of the Maghreb, Sicily, the Levant, and the Hejaz.
Between 902 and 909, the foundation of the Fatimid state was realized under the leadership of da'i (missionary) Abu Abdallah, whose conquest of Aghlabid Ifriqiya with the help of Kutama forces paved the way for the establishment of the Caliphate. After the conquest, Abdallah al-Mahdi Billah was retrieved from Sijilmasa and then accepted as the Imam of the movement, becoming the first Caliph and founder of the dynasty in 909. In 921, the city of al-Mahdiyya was established as the capital. In 948, they shifted their capital to al-Mansuriyya, near Kairouan. In 969, during the reign of al-Mu'izz, they conquered Egypt, and in 973, the caliphate was moved to the newly founded Fatimid capital of Cairo. Egypt became the political, cultural, and religious centre of the empire and it developed a new and "indigenous Arabic culture". After its initial conquests, the caliphate often allowed a degree of religious tolerance towards non-Shia sects of Islam, as well as to Jews and Christians. However, its leaders made little headway in persuading the Egyptian population to adopt its religious beliefs. (Full article...)
Selected articles
-
Image 1Abū ʿAlī al-Ḥasan al-Aʿsam ibn Aḥmad ibn al-Ḥasan ibn Bahrām al-Jannābī (Arabic: أَبُو عَلِيّ ٱلحَسَن ٱلأَعْصَم بْنُ أَحْمَد بْنِ ٱلحَسَن بْنِ بَهْرَام الجَنَّابِيّ; al-Ahsa Oasis, 891 – Ramla, 977), was a Qarmatian leader, chiefly known as the military commander of the Qarmatian invasions of Syria (especially around Damascus and Palestine) in 968–977. Already in 968, he led attacks on the Ikhshidids, capturing Damascus and Ramla and extracting pledges of tribute. Following the Fatimid conquest of Egypt and the overthrow of the Ikhshidids, in 971–974 al-A'sam led attacks against the Fatimid Caliphate, who began to expand into Syria. The Qarmatians repeatedly evicted the Fatimids from Syria and invaded Egypt itself twice, in 971 and 974, before being defeated at the gates of Cairo and driven back. Al-A'sam continued fighting against the Fatimids, now alongside the Turkish general Alptakin, until his death in March 977. In the next year, the Fatimids managed to overcome the allies, and concluded a treaty with the Qarmatians that signalled the end of their invasions of Syria. (Full article...)
-
Image 2Jawdhar (Arabic: جوذر, before 909 – March 973), surnamed al-Ustadh (Arabic: الأستاذ, lit. 'the Master'), was a eunuch slave who served the Fatimid caliphs al-Qa'im, al-Mansur, and al-Mu'izz as chamberlain and de facto chief minister until his death. He was an extremely powerful figure in the Fatimid court, and was ranked immediately after the caliph and his designated heir. The accession of al-Mansur was probably due to Jawdhar's machinations, and he was placed in charge of keeping the new caliph's relatives under house arrest. He enjoyed close relations with the Kalbid emirs of Sicily, which enabled him to engage in profitable commerce with the island. Jawdhar accompanied al-Mu'izz during the migration of the court from Ifriqiya to Egypt, but died on the way at Barqa. His collected documents and letters were published after his death by his secretary as the Sirat al-Ustadh Jawdhar, and form one of the main historical sources for the governance of the Fatimid state in the period. (Full article...)
-
Image 3El-Mansuriya or Mansuriya (Arabic: المنصورية), also known as Sabra or Sabra al-Mansuriyya, near Kairouan, Tunisia, was the capital of the Fatimid Caliphate during the rule of the Ismaili Imams al-Mansur bi-Nasr Allah (r. 946–953) and al-Mu'izz li-Din Allah (r. 953–975).
Built between 946 and 972, el-Mansuriya was a walled city holding elaborate palaces surrounded by gardens, artificial pools and water channels. It was briefly the centre of a powerful state that encompassed most of North Africa and Sicily. It continued to serve as provincial capital of the Zirids until 1057, when it was destroyed by the invading Banu Hilal tribes. Any useful objects or relics were scavenged during the centuries that followed. Today, only faint traces remain. (Full article...) -
Image 4Abu Ali al-Mansur (Arabic: أبو علي المنصور, romanized: Abū ʿAlī al-Manṣūr; 13 August 985 – 13 February 1021), better known by his regnal name al-Hakim bi-Amr Allah (Arabic: الحاكم بأمر الله, romanized: al-Ḥākim bi-Amr Allāh, lit. 'The Ruler by the Order of God'), was the sixth Fatimid caliph and 16th Ismaili imam (996–1021). Al-Hakim is an important figure in a number of Shia Ismaili sects, such as the world's 15 million Nizaris and 1–2 million Musta'lis, in addition to 2 million Druze.
Histories of al-Hakim can prove controversial, as diverse views of his life and legacy exist. Historian Paul Walker writes "Ultimately, both views of him, the mad and despotic tyrant (like Germanic and Roman despots) irrationally given to killing those around him on a whim, and the ideal supreme ruler, divinely ordained and chosen, whose every action was just and righteous, were to persist, the one among his enemies and those who rebelled against him, and the other in the hearts of true believers, who, while perhaps perplexed by events, nonetheless remained avidly loyal to him to the end." Appraisals of the more controversial accounts of al-Hakim's life and rule have earned him such monikers as "the Nero of Egypt", and "the Mad Caliph". (Full article...) -
Image 5Egypt was repeatedly invaded from 1163 to 1169 by King Amalric of Jerusalem, who wished to strengthen its position in the Levant by taking advantage of the weakness of the Fatimid Caliphate.
The invasions began as part of a succession crisis in the caliphate, which began to crumble under the pressure of Muslim Syria ruled by the Zengids and the Christian Crusader states. While one side called for help from the emir of Syria, Nur ad-Din Zengi, the other called for Crusader assistance. As the war progressed, however, it became a war of conquest. A number of Syrian campaigns into Egypt were stopped short of total victory by the aggressive campaigning of King Amalric. Even so, the Crusaders generally speaking did not have things go their way, despite several sackings. A combined Byzantine–Crusader siege of Damietta failed in 1169, the same year that Saladin took power in Egypt as vizier. In 1171, Saladin became sultan of Egypt and the crusaders thereafter turned their attention to the defence of their kingdom, which, despite being surrounded by Syria and Egypt, held for another 16 years. Later crusades tried to support the Kingdom of Jerusalem by targeting the danger that was Egypt, but to no avail. (Full article...) -
Image 6Abū Muḥammad ʿAbd Allāh ibn al-Ḥusayn (Arabic: أبو محمد عبد الله بن الحسين; 31 July 874 – 4 March 934), better known by his regnal name al-Mahdī biʾllāh (Arabic: المهدي بالله, "The Rightly Guided by God"), was the founder of the Isma'ili Fatimid Caliphate, the only major Shi'a caliphate in Islamic history, and the eleventh Imam of the Isma'ili branch of Shi'ism.
He was born as Saʿīd ibn al-Ḥusayn (سعيد بن الحسين) in Askar Mukram to a family that led the secret Isma'ili missionary network (da'wa), propagating on behalf of the hidden imam, Muhammad ibn Isma'il, who would return as the prophesied Islamic messiah (mahdi). Orphaned at a young age, he moved to Salamiya, the family's base of operations, where he was adopted by his uncle. In the mid-890s Sa'id succeeded to the leadership of the expanding da'wa, which had expanded and gained adherents across the then Muslim world. However, his claims of not merely being a trustee of the hidden imam, but of him and his ancestors holding the imamate itself, led in 899 to a schism in the Isma'ili movement: those who did not recognize his claims split off to become the Qarmatians. The schism was followed by uprisings of pro-Isma'ili Bedouin in Syria in 902–903, launched without his consent by over-eager supporters, who aimed to force him to come forward as the mahdi. The Bedouin uprising was suppressed by the Abbasids, but drew the attention of the Abbasid Caliphate's authorities to him, forcing him to abandon Salamiya, and flee first to Ramla, then Fustat in Egypt, and finally Sijilmasa in what is now Morocco. There he remained, living as a merchant, until one of his missionaries, Abu Abdallah al-Shi'i, at the head of the Kutama Berbers overthrew the Aghlabid dynasty of Ifriqiya in 909. (Full article...) -
Image 7Manjutakin (Arabic: منجوتكين) was a military slave (ghulam) of the Fatimid Caliph al-Aziz (r. 975–996). Of Turkic origin, he became one of the leading Fatimid generals under al-Aziz, fighting against the Hamdanids and the Byzantines in Syria. He rebelled against the Berber-dominated regime of the early years of al-Hakim (r. 996–1021), but was defeated and died in captivity. (Full article...)
-
Image 8Abū Muḥammad ʿAbd Allāh ibn Yūsuf ibn al-Ḥāfiẓ (Arabic: أبو محمد عبد الله بن يوسف بن الحافظ; 1151–1171), better known by his regnal name al-ʿĀḍid li-Dīn Allāh (Arabic: العاضد لدين الله, lit. 'Strengthener of God's Faith'), was the fourteenth and last caliph of the Fatimid dynasty, and the twenty-fourth imam of the Hafizi Isma'ili branch of Shi'a Islam, reigning from 1160 to 1171.
Like his two immediate predecessors, al-Adid came to the throne as a child, and spent his reign as a puppet of various strongmen who occupied the vizierate. He was a mostly helpless bystander to the slow collapse of the Fatimid Caliphate. Tala'i ibn Ruzzik, the vizier who had raised al-Adid to the throne, fell victim to a palace plot in 1161, and was replaced by his son, Ruzzik ibn Tala'i. Ruzzik was in turn overthrown by Shawar in 1163, but the latter lasted only a few months in office before being overthrown by Dirgham. The constant power struggles in Cairo enfeebled the Fatimid state, allowing both the Crusader Kingdom of Jerusalem and the Sunni ruler of Syria, Nur al-Din, to advance their own designs on the country. The Crusaders repeatedly invaded Egypt, extracting tribute and ultimately aiming to conquer it; in turn, Nur al-Din supported Shawar's bid to retake the vizierate from Dirgham, and sent his general Shirkuh to counter the Crusaders. For a while, Shawar played the Crusaders and Syrians against one another, but in January 1169, Shirkuh overthrew Shawar, occupied Cairo and became vizier. When Shirkuh died shortly after, he was succeeded by his nephew, Saladin. (Full article...) -
Image 9The House of Knowledge (Arabic: دار العلم, romanized: Dār al-ʿIlm) was an ancient university built by the Fatimid Caliphate in Cairo in 1004 CE. Originally a library, the House of Knowledge was converted to a state university by the Fatimid Imam-Caliph al-Hakim bi-Amr Allah in the same year.
In keeping with the Islamic tradition of knowledge, the Fatimids collected books on a variety of subjects and their libraries attracted the attention of scholars from around the world. al-Hakim was a great patron of learning and provided paper, pens, ink and inkstands without charge to all those who wished to study there. (Full article...) -
Image 10Abū al-Qāsim Aḥmad ibn al-Mustanṣir (Arabic: أبو القاسم أحمد بن المستنصر; 15/16 September 1074 – 11/12 December 1101), better known by his regnal name al-Mustaʿlī biʾllāh (المستعلي بالله, lit. 'The One Raised Up by God'), was the ninth Fatimid caliph and the 19th imam of Musta'li Ismailism.
Although not the eldest (and most likely the youngest) of the sons of Caliph al-Mustansir Billah, al-Musta'li became caliph through the machinations of his brother-in-law, the vizier al-Afdal Shahanshah. In response, his oldest brother and most likely candidate for their father's succession, Nizar, rose in revolt in Alexandria but was defeated and executed. This caused a major split in the Isma'ili movement. Many communities, especially in Persia and Iraq, split off from the officially sponsored Isma'ili hierarchy and formed their own Nizari movement, holding Nizar and his descendants as the rightful imams. (Full article...) -
Image 11Abu'l-Najm Badr ibn Abdallah al-Jamali al-Mustansiri, better known as Badr al-Jamali (Arabic: بدر الجمالى) or by his eventual title as Amir al-Juyush (أمير الجيوش, lit. 'Commander of the Armies'), was a military commander and statesman for the Fatimid Caliphate under Caliph al-Mustansir. Of Armenian origin but a convert to Islam, Badr had been brought up as a military slave (mamluk) by the ruler of Tripoli, Jamal al-Dawla ibn Ammar. In the 1060s, he was appointed twice as governor of Damascus in Syria, at a time when Fatimid authority there was disintegrating, and the central government in Egypt was on the verge of collapse as a result of the Mustansirite Hardship. Badr was unable to prevent the loss of most of Syria to local potentates and Turkoman warlords, but managed to hold on to the coastal cities, making Acre his base.
As the sole major military commander outside Egypt, he was called upon by al-Mustansir to help rescue the dynasty. Badr landed in Egypt in late 1073, rapidly eliminated his rivals, and was appointed vizier with plenipotentiary powers, making him a quasi-sultan or military dictator, with the caliph relegated to his religious duties as Isma'ili imam. Control over the state was solidified with the marriage of one of his daughters to al-Mustansir, and the appointment of his own son, al-Afdal Shahanshah, as his successor in 1085. Badr managed to restore order in Egypt and initiated major administrative reforms, defeated Turkoman attempts to invade Egypt, and recovered control over Palestine and the Hejaz. He initiated a series of new constructions, including the Juyushi Mosque and the new city wall of Cairo, some of whose gates stand to this day. Badr's tenure saved the Fatimid regime, but also began a period where the vizierate was dominated by military strongmen who held power on their own, rather than through caliphal appointment, and who increasingly sidelined the caliphs to puppet rulers. Badr also initiated a wave of Armenian migration into Egypt, and was the first of a series of viziers of Armenian origin, who played a major role in the fortunes of the Fatimid Caliphate over the subsequent century. (Full article...) -
Image 12Abūʾl-Qāsim ʿĪsā ibn al-Ẓāfir (Arabic: أبو القاسم عيسى بن الظافر; 1149–1160), better known by his regnal name al-Fāʾiz bi-Naṣr Allāh (الفائز بنصر الله), was the thirteenth and penultimate Fatimid caliph, reigning in Egypt from 1154 to 1160, and the 23rd imam of the Hafizi Ismaili branch of Shi'a Islam. Al-Fa'iz was raised to the throne at the age of five after the murder of his father by the vizier Abbas ibn Abi al-Futuh, and spent his entire life as a puppet of Abbas' successor, Tala'i ibn Ruzzik. Experiencing epileptic seizures, al-Fa'iz died from an episode at the age of eleven, and his nephew, al-Adid, the final Fatimid caliph, succeeded him. (Full article...)
-
Image 13Abu Ali Salih ibn Mirdas (Arabic: ابو علي صالح بن مرداس, romanized: Abū ʿAlī Ṣāliḥ ibn Mirdās), also known by his laqab (honorific epithet) Asad al-Dawla ('Lion of the State'), was the founder of the Mirdasid dynasty and emir of Aleppo from 1025 until his death in May 1029. At its peak, his emirate (principality) encompassed much of the western Jazira (Upper Mesopotamia), northern Syria and several central Syrian towns. With occasional interruption, Salih's descendants ruled Aleppo for the next five decades.
Salih launched his career in 1008, when he seized the Euphrates river fortress of al-Rahba. In 1012, he was imprisoned and tortured by the emir of Aleppo, Mansur ibn Lu'lu'. Two years later he escaped, capturing Mansur in battle and releasing him for numerous concessions, including half of Aleppo's revenues. This cemented Salih as the paramount emir of his tribe, the Banu Kilab, many of whose chieftains had died in Mansur's dungeons. With his Bedouin warriors, Salih captured a string of fortresses along the Euphrates, including Manbij and Raqqa, by 1022. He later formed an alliance with the Banu Kalb and Banu Tayy tribes and supported their struggle against the Fatimids of Egypt. During this tribal rebellion, Salih annexed the central Syrian towns of Homs, Baalbek and Sidon, before conquering Fatimid-held Aleppo in 1025, bringing "to success the plan which guided his [Banu Kilab] forebears for a century", according to historian Thierry Bianquis. (Full article...) -
Image 14Abu'l-Hasan Ali ibn Muhammad al-Iyadi al-Tunisi (Arabic: علي بن محمد الإيادي, romanized: ʿAlī ibn Muḥammad al-Iyādī; died 976) was a 10th-century Maghrebi Arabic poet in the service of the Fatimid caliphs al-Qa'im, al-Mansur, and al-Mu'izz.
His exact origin is unknown. The nisba "al-Tunisi" has led to suggestions that he was born in Tunis, but his other nisba of "al-Iyadi" suggests ties to the Iyad, a clan of the Arab Banu Hilal tribe settled near Msila. Pro-Shi'ite, he was court poet of the Isma'ili Shi'a caliphs al-Qa'im, al-Mansur, and al-Mu'izz. His reputation during his lifetime was considerable, and he was highly regarded by later critics. However, possibly due to his pro-Shi'a partisanship, which may have led to an attempted damnatio memoriae after the Zirid dynasty turned to Sunni Islam, or due to shifting literary tastes, none of his works survives in complete form. His work survives mostly in fragments that were appreciated and gathered together by later anthologists for their vivid and evocative language, such as descriptions of the Fatimid navy, a galloping horse, or the so-called Lake Palace in the palace city of Mansuriya. The only evidently pro-Shi'a works surviving are a eulogy for al-Mansur, and a moving description of the end of the famous anti-Fatimid rebel Abu Yazid. Al-Iyadi died in 976, probably in Cairo, where he had followed the Fatimid court following the Fatimid conquest of Egypt in 969. (Full article...) -
Image 15Abu’l-Qāsim ʿAlī ibn Aḥmad al-Jarjarāʾī was a Fatimid official of Iraqi origin, who served as the Fatimid vizier from 1027 until his death on 27 March 1045.
As his nisba shows, he came from the locality of Jarjaraya, south of Baghdad. He came to Egypt along with his brother Abu'l-Barakat al-Husayn al-Jarjara'i, and held a succession of offices in the Fatimid bureaucracy. He entered the service of Sitt al-Mulk, before becoming secretary to the police chief of Cairo. He was convicted of disloyalty when he opened letters of the secret services in 1013, as a result of which his hands were cut off. However the Caliph al-Hakim soon regretted this harsh punishment, and took him back into the palace and promoted him to high office. (Full article...) -
Image 16
Banu Kanz (Arabic: بنو كنز), also known as Awlad Kanz, was a semi-nomadic Muslim dynasty of Arab descent that ruled the border region between Upper Egypt and Nubia between the 10th and 15th centuries. They were descended from the sons of sheikhs of the Arab Banu Hanifa tribe who intermarried with the princesses of the Beja Hadariba tribe. They gained official control over the region of Aswan, Wadi Allaqi and the frontier zone in the early 11th century when their chief, Abu al-Makarim Hibatallah, captured a major rebel on behalf of the Fatimid authorities. Abu al-Makarim was accorded the title Kanz al-Dawla (Treasure of the State) by Caliph al-Hakim and his successors inherited the title. The Banu Kanz entered into conflict with the Ayyubids in 1174, during which they were defeated and forced to migrate southward into northern Nubia, where they helped accelerate the expansion of Islam in the mostly Christian region. They eventually assumed control of the Nubian Kingdom of Makuria in the early 14th century, but by the early the 15th century, they were supplanted by the Hawwara tribesmen dispatched by the Mamluks to combat the Banu Kanz. Their modern-day descendants are a Sudanese tribe known as the "Kunuz", who live in the far north of the country. (Full article...)Banu Kanz بنو كنزParent family Banu Hanifa Country Upper Egypt and Nubia Place of origin Najd, Arabia Founded 943 Founder Ishaq ibn Bishr Historic seat Aswan Titles Kanz al-Dawla Dissolution 1365 -
Image 17Abu Abdallah al-Husayn ibn Ahmad ibn Muhammad ibn Zakariyya, better known as Abu Abdallah al-Shi'i (Arabic: ابو عبد الله الشيعي, romanized: Abū ʿAbd Allāh ash-Shīʿī), was an Isma'ili missionary (dāʿī) active in Yemen and North Africa. He was successful in converting and unifying a large part of the Kutama Berber tribe, leading them on the conquest of Ifriqiya from 902 to 909 and the overthrowing of the Aghlabid dynasty. This ultimately led to the establishment of the Fatimid Caliphate in Ifriqiya under the Imam–caliph Abdullah al-Mahdi Billah. However, Abdullah al-Mahdi Billah quickly fell out with Abu Abdallah and had Abu Abdallah executed on 18 February 911. (Full article...)
-
Image 18The Fatimid architecture that developed in the Fatimid Caliphate (909–1167 CE) of North Africa combined elements of eastern and western architecture, drawing on Abbasid architecture, Byzantine, Ancient Egyptian, Coptic architecture and North African traditions; it bridged early Islamic styles and the medieval architecture of the Mamluks of Egypt, introducing many innovations.
The wealth of Fatimid architecture was found in the main cities of Mahdia (921–948), Al-Mansuriya (948–973) and Cairo (973–1169). The heartland of architectural activity and expression during Fatimid rule was at al-Qahira (Cairo), on the eastern side of the Nile, where many of the palaces, mosques and other buildings were built. Large-scale constructions were undertaken during the reigns of al-Mui'zz (r. 953–975) Al-Aziz Billah (r. 975–996) and al-Hakim (r. 996–1021). (Full article...) -
Image 19Sayf al-Dawla Khalaf ibn Mulāʿib al-Ashhabī al-Kilābī (Arabic: سيف الدولة خلف بن ملاعب الأشهبي الكلابي; died 3 February 1106) was the emir of Homs and Apamea between 1082 and 1090. He later seized Apamea again in 490 A.H./1096 from Ridwan and held the city, under the suzerainty of the Fatimid Caliphate, until his assassination by the Assassins. (Full article...)
-
Image 20The second Fatimid invasion of Egypt occurred in 919–921, following the failure of the first attempt in 914–915. The expedition was again commanded by the Fatimid Caliphate's heir-apparent, al-Qa'im bi-Amr Allah. As during the previous attempt, the Fatimids captured Alexandria with ease. However, while the Abbasid garrison in Fustat was weaker and mutinous due to lack of pay, al-Qa'im did not exploit it for an immediate attack on the city, such as the one that had failed in 914. Instead, in March 920, the Fatimid navy was destroyed by the Abbasid fleet under Thamal al-Dulafi, and Abbasid reinforcements under Mu'nis al-Muzaffar arrived at Fustat. Nevertheless, in the summer of 920, al-Qa'im was able to capture the Fayyum Oasis, and in the spring of 921, extend his control over much of Upper Egypt as well, while Mu'nis avoided an open confrontation and remained at Fustat. During that time, both sides were engaged in a diplomatic and propaganda battle, with the Fatimids' in particular trying to sway the Muslim populace to their side, without success. The Fatimid expedition was condemned to failure when Thamal's fleet took Alexandria in May/June 921; when the Abbasid forces moved on Fayyum, al-Qa'im was forced to abandon it and flee west over the desert. (Full article...)
-
Image 21Abū Manṣūr Ismāʿīl ibn al-Ḥāfiẓ (Arabic: أبو منصور إسماعيل بن الحافظ, February 1133 – April 1154), better known by his regnal name al-Ẓāfir bi-Aʿdāʾ Allāh (الظافر بأعداء الله, lit. 'Victor over God's Enemies') or al-Ẓāfir bi-Amr Allāh (الظافر بأمر الله, lit. 'Victorious by the Command of God'), was the twelfth Fatimid caliph, reigning in Egypt from 1149 to 1154, and the 22nd imam of the Hafizi Ismaili sect. (Full article...)
-
Image 22Hafizi Isma'ilism (Arabic: الحافظية, romanized: al-Ḥāfiẓiyya), also known as Majidi Isma'ilism (Arabic: المجيدية, romanized: al-Majīdiyya), was a branch of Musta'li Isma'ilism that emerged as a result of a split in 1132. The Hafizis accepted the Fatimid caliph Abd al-Majid al-Hafiz li-Din Allah (r. 1132–1149) and his successors as imams, while the rival Tayyibi branch rejected them as usurpers, favouring the succession of the imamate along the line of al-Hafiz's nephew, al-Tayyib.
The Hafizi sect lost state backing and gradually disappeared after the abolition of the Fatimid Caliphate in 1171 and the conquest of the Fatimid-aligned dynasties of Yemen by the Ayyubid dynasty shortly after. The last remnants of the Hafizi branch are attested in the 14th century in Egypt and Syria, but had died out by the 15th century. (Full article...) -
Image 23Ridwan ibn Walakhshi (Arabic: رضوان بن ولخشي) was the vizier of the Fatimid Caliphate in 1137–1139, under Caliph al-Hafiz li-Din Allah. He was a Sunni military commander, who rose to high offices under caliphs al-Amir bi-Ahkam Allah and al-Hafiz. He participated in the coup of Kutayfat, which in 1130–1131 briefly overthrew the Fatimid dynasty, serving as gaoler of the future caliph al-Hafiz. Under al-Hafiz he rose to the powerful position of chamberlain, and emerged as the leader of the Muslim opposition during the vizierate of the Christian Bahram al-Armani in 1135–1137, when he served as governor of Ascalon and the western Nile Delta.
In February 1137, he rose in revolt against Bahram, drove him from Cairo, and was in turn appointed to the vizierate with the title of "Most Excellent King" (al-malik al-afdal) denoting his ambitions and status as a de facto monarch in his own right. His tenure lasted two years and five months, and was marked by a reorganization of the government and by a persecution of Christian officials, who were replaced by Muslims, as well as the introduction of restrictions on Christians and Jews. Ridwan also planned to depose al-Hafiz and the Fatimid dynasty in favour of a Sunni regime headed by himself, but the Caliph raised the army and the people of Cairo against him, forcing him to flee his post in June 1139. Ridwan rallied his followers and tried to capture Cairo, but was defeated and had to surrender. (Full article...) -
Image 24The Qarmatians (Arabic: قرامطة, romanized: Qarāmiṭa; Persian: قرمطیان, romanized: Qarmatiyān) were a militant Isma'ili Shia movement centred in Al-Ahsa in Eastern Arabia, where they established a religious—and, as some scholars have claimed, proto-socialist or utopian socialist—state in 899 CE. Its members were part of a movement that adhered to a syncretic branch of Sevener Ismaili Shia Islam, and were ruled by a dynasty founded by Abu Sa'id al-Jannabi, a Persian from Jannaba in coastal Fars. They rejected the claim of Fatimid Caliph Abdallah al-Mahdi Billah to imamate and clung to their belief in the coming of the Mahdi, and they revolted against the Fatimid and Abbasid Caliphates.
Mecca was sacked by a Qarmatian leader, Abu Tahir al-Jannabi, outraging the Muslim world, particularly with their theft of the Black Stone and desecration of the Zamzam Well with corpses during the Hajj season of 930 CE. (Full article...) -
Image 25Mufarrij ibn Daghfal ibn al-Jarrah al-Tayyi (fl. ca. 977–1013), in some sources erroneously called Daghfal ibn Mufarrij, was an emir of the Jarrahid family and leader of the Tayy tribe. Mufarrij was engaged in repeated rebellions against the Fatimid Caliphate, which controlled southern Syria at the time. Although he was several times defeated and forced into exile, by the 990s Mufarrij managed to establish himself and his tribe as the de facto autonomous masters of much of Palestine around Ramlah (the district of Jund Filastin) with Fatimid acquiescence. In 1011, another rebellion against Fatimid authority was more successful, and a short-lived Jarrahid-led Bedouin state was established in Palestine centred at Ramlah. The Bedouin even proclaimed a rival Caliph to the Fatimid al-Hakim, in the person of the Alid Abu'l-Futuh al-Hasan ibn Ja'far. Bedouin independence survived until 1013, when the Fatimids launched their counterattack. Their will to resist weakened by Fatimid bribes, the Bedouin were quickly defeated. At the same time Mufarrij died, possibly poisoned, and his sons quickly came to terms with the Fatimids. Among them, Hassan ibn Mufarrij al-Jarrah managed to succeed to his father's position, and became a major player in the politics of the region over the next decades. (Full article...)
Did you know...
- ... that Qadi al-Fadil began his career under the Fatimids, became Saladin's chief minister, and was renowned for the elegance of his epistolary writing?
- ... that the members of an abortive conspiracy to restore the Fatimid Caliphate were said to have asked the Order of Assassins for assistance in eliminating Saladin?
- ... that Abbas ibn Abi al-Futuh was a Zirid prince who became a vizier of the Fatimid Caliphate after assassinating his stepfather, and was overthrown after murdering caliph al-Zafir?
- ... that Da'ud, the heir apparent of the last Fatimid caliph, spent almost his entire life imprisoned by the succeeding Ayyubid dynasty?
Need help?
Do you have a question about the Fatimid Caliphate that you can't find the answer to?
Consider asking it at the Wikipedia reference desk or at the talk page of WikiProject Islam.
If you are interested in reading more about the Fatimid caliphate, some up-to-date summary books and encyclopedia articles are:
- Brett, Michael (2017). The Fatimid Empire. The Edinburgh History of the Islamic Empires. Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press. ISBN 978-0-7486-4076-8.
- Daftary, Farhad (1999). "Fatimids". In Yarshater, Ehsan (ed.). Encyclopædia Iranica. Vol. IX/4: Fārs II–Fauna III. London and New York: Routledge & Kegan Paul. pp. 423–426. ISBN 978-0-933273-32-0.
- Halm, Heinz (2014). "Fāṭimids". In Fleet, Kate; Krämer, Gudrun; Matringe, Denis; Nawas, John; Rowson, Everett (eds.). Encyclopaedia of Islam (3rd ed.). Brill Online. ISSN 1873-9830.
- Sanders, Paula (1998). "The Fāṭimid state, 969–1171". In Petry, Carl F. (ed.). The Cambridge History of Egypt, Volume 1: Islamic Egypt, 640–1517. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 151–174. ISBN 0-521-47137-0.
- Walker, Paul E. (1998). "The Ismā'īlī Da'wa and the Fātimid caliphate". In Petry, Carl F. (ed.). The Cambridge History of Egypt, Volume 1: Islamic Egypt, 640–1517. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 120–150. ISBN 0-521-47137-0.
- Walker, Paul E. (2018). "Fāṭimids". In Madelung, Wilferd; Daftary, Farhad (eds.). Encyclopaedia Islamica Online. Brill Online. ISSN 1875-9831.
Selected images
-
Image 1Men hunting, on ivory panel, 11th century (from Fatimid Caliphate)
-
Image 2Architectural fragment from a bathhouse in al-Fustat, 11th century CE (pre-1168 CE). Museum of Islamic Art, Cairo, 12880. (from Fatimid Caliphate)
-
Image 3Side chapel in the Hanging Church in Old Cairo, including frescoes (partly visible behind the screen here) dating from the late 12th or 13th century, before the church's later renovation (from Fatimid Caliphate)
-
Image 5Al-Juyushi Mosque, Cairo, overlooking the city from the Muqattam Hills (from Fatimid Caliphate)
-
Image 6Lustreware Plate with Bird Motif, 11th century. Archaeological digs have found many kilns and ceramic fragments in al-Fustat, and it was likely an important production location for Islamic ceramics during the Fatimid period. (from Fatimid Caliphate)
-
Image 7Fragments of mosaic pavement from the palace of al-Qa'im in al-Mahdiyya (Mahdia), on display at the Mahdia Museum (from Fatimid Caliphate)
-
Image 8Fatimid gold dinar minted during the reign of al-Mustansir Billah (1036–1094) (from Fatimid Caliphate)
-
Image 9Al-Salih Tala'i Mosque in Cairo, built by Tala'i ibn Ruzzik in 1160 and originally intended to house the head of Husayn (the head ended up being interred instead at the present-day al-Hussein Mosque) (from Fatimid Caliphate)
-
Image 10Image of two standing soldiers. 11th century, Fatimid period, from Fustat near Cairo. Museum of Islamic Art, Cairo, inv. no. 13703. Attribution to the Fatimid period is sometimes questioned. (from Fatimid Caliphate)
-
Image 11Al-Azhar Mosque in Cairo, built by the Fatimids between 970 and 972 (from Fatimid Caliphate)
-
Image 13The Al-Hakim Mosque in Cairo, commissioned by al-Aziz in 990 and completed by al-Hakim in 1013 (later renovated in the 1980s by the Dawoodi Bohra) (from Fatimid Caliphate)
-
Image 14Fatimid ewer, 10th century CE (from Fatimid Caliphate)
-
Image 15Cover page of the Leningrad Codex, a manuscript of the Hebrew Bible copied in Cairo/Fustat in the early 11th century (from Fatimid Caliphate)
-
Image 16Map of Abu Abdallah's campaigns and battles during the overthrow of the Aghlabids (from Fatimid Caliphate)
-
Image 17Fatimid Caliph al-Mahdi Billah receiving an envoy from Simeon I of Bulgaria, Madrid Skylitzes, 12th century. (from Fatimid Caliphate)
-
Image 18Bab al-Futuh, one of the gates of Cairo dating from Badr al-Jamali's reconstruction of the city walls (1987) (from Fatimid Caliphate)
Subcategories
Subtopics
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus