Politics of Novi Sad


Novi Sad is the capital of the Serbian province of Vojvodina, and second largest city in Serbia.
Political history
[edit]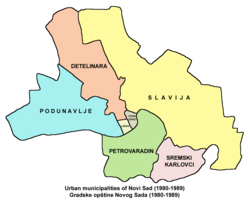
The city was founded in 1694 and its first names were Ratzen Stadt (Serbian: Racka Varoš) and Peterwardein Schantz (Serbian: Petrovaradinski Šanac). Since 1702, it was part of the Habsburg Military Frontier. In 1746–1748, when one part of Military Frontier was abolished, city was placed under civil administration and obtained royal free city status. The edict of empress Maria Theresa of Austria that made Novi Sad a royal free city was proclaimed on February 1, 1748. That is also a time when current name of the city was introduced. In various languages it was written as: Neoplantae (Latin), Neusatz (German), Újvidék (Hungarian), and Novi Sad (Serbian).
During the 1880s, Hungarians took over local city administration from Serbs and their representatives dominated in city government until 1918. After 1918, the city government was again dominated by Serbs. Although it was a cultural and political center of Vojvodinian Serbs (and Serbs in general) in the 19th century, Novi Sad was not administrative center of any larger administrative unit during most of the period of Habsburg administration. Briefly, it was a district center in the Voivodeship of Serbia and Banat of Temeschwar province that existed from 1849 to 1860. Administrative significance of the city highly increased in 1918, when it became part of the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes. In 1918–1919, Novi Sad was capital of Banat, Bačka and Baranja region, and also administrative center of Novi Sad County (from 1918 to 1922). From 1922 to 1929 it was administrative center of Bačka Oblast, and from 1929 to 1941 administrative center of Danube Banovina.
From 1941 to 1944, city was under Axis occupation and occupational authorities degraded status of Novi Sad to administratively unimportant town located on the border between Horthy's Hungary and Pavelić's Independent State of Croatia. After the war, administrative significance of Novi Sad increased again and it became the capital of the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina within People's Republic of Serbia and new socialist Yugoslavia.
From 1980 to 1989, city was divided into seven urban municipalities: Stari Grad, Podunavlje, Liman, Slavija, Petrovaradin, Detelinara and Sremski Karlovci. In 1989, six of those municipalities were merged into single Municipality of Novi Sad, while municipality of Sremski Karlovci was transformed into separate administrative unit, which is completely independent from Novi Sad. In 2000–2002, the Municipality of Novi Sad was changed to City of Novi Sad and two urban municipalities (Novi Sad and Petrovaradin) were formed within the city. Since 2002, when the new statute of Novi Sad came into effect, City of Novi Sad is divided into 46 local communities. City has its parliament, governing mayor and a city council.
Administration bodies
[edit]Mayor
[edit]
The executive branch is headed by the Mayor of Novi Sad City, who is elected by direct popular vote. The mayor serves a term of four years and is limited to two terms in office. Until 2004, all mayors and municipality presidents in Serbia were elected by the city's and municipality parliaments. After changes in the law, in 2004 elections, all mayors and municipality presidents (except for urban municipalities) were elected by direct popular vote.
The City's second mayor elected by direct popular vote in September 2004 was Maja Gojković, who is also the only female yet to be the major political figure of Novi Sad.[2] Afterwards the electoral system was reversed, so city currently has no mayor in classical meaning of the word, but President of the Executive council of the assembly, which is currently Milan Đurić from Serbian Progressive Party.[3]
City Assembly
[edit]| Party | Seats |
|---|---|
| SNS Coalition | 45 |
| United for a Free Novi Sad | 21 |
| I'm Novi Sad Too–Go-Change | 8 |
| Heroes | 3 |
| Alliance of Vojvodina Hungarians | 1 |
The Assembly of the City of Novi Sad is the lawmaking body of the City. It comprises 78 members from 46 local communities throughout the two municipalities. The Assembly monitors performance of city agencies and makes land use decisions as well as legislating on a variety of other issues. The Assembly also has sole responsibility for approving the city budget. The Council has seventeen committees with oversight of various functions of the city government. City has also committee for improving and protection of the city's national minorities.
Assembly members are elected every four years. In 2024 local elections, SNS Coalition won most seats in the City parliament, and formed a coalition with Socialist Party of Serbia, Party of United Pensioners, Farmers, and Proletarians of Serbia – Solidarity and Justice, Serbian Radical Party, Movement of Socialists, Serbian People's Party, Serbian Party Oathkeepers, Independent Serbian Party and the Alliance of Vojvodina Hungarians. Current president of the city assembly is Jelena Marinković Radomirović.
City Council
[edit]Council is a body that coordinates between City's parliament and Mayor and manage the City. It has 11 members who are elected by the mayor and confirmed by the parliament. Chairman of the council is the mayor. Council has also a responsibility for conferred City's budget and helps the mayor with governing.
Administrative subdivisions
[edit]Municipalities
[edit]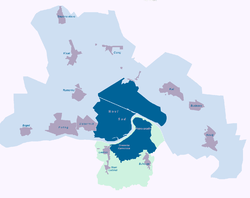

In 2000–2002, the municipality of Novi Sad was divided into two urban municipalities, Novi Sad and Petrovaradin; making the way on the changes of the law in Serbian parliament which says that the city status in Serbia is only possible if the city is divided into two or more urban municipalities. Since then, the law was changed, and the city need not to be divided into urban municipalities.[4]
Municipality of Novi Sad includes: Novi Sad proper, Futog, Veternik, Begeč, Budisava, Kać, Kovilj, Kisač, Rumenka, Stepanovićevo, and Čenej. Municipality of Petrovaradin includes: Petrovaradin town, Sremska Kamenica, Bukovac, Ledinci, and Stari Ledinci. Geographically, the municipality of Novi Sad is located in Bačka, while municipality of Petrovaradin is located in Syrmia.
By city statute from 2002, Novi Sad's municipalities do not have any "real" power of decision making and do not have bodies which municipalities normally have in Serbia. Like other cities in Serbia, Novi Sad doesn't have direct elections for municipality parliaments. Members of parliament in the Novi Sad's two urban municipalities comprise City's parliament members who are elected in territory of the municipality.
Municipalities of Novi Sad were established because of the sole reason that Novi Sad can get city status within Serbia. Future of this municipalities is questionable, keeping in mind that under new Constitution of Serbia (from November 2006), cities do not have to be divided into municipalities to get city status. There are, however, proposals that city should be further divided into more municipalities. According to the proposal of the Serbian Renewal Movement party, there should be six more municipalities besides Novi Sad and Petrovaradin. New proposed municipalities are Futog, Veternik, Rumenka, Kać, Klisa, and Sremska Kamenica.[5]
Local communities
[edit]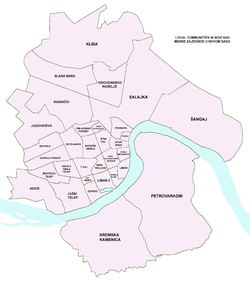
Both municipalities, Petrovaradin and Novi Sad, are divided into local communities (Serbian: Mesne zajednice / Месне заједнице). There are 47 local communities in the city.
Every local community has its own council, which comprises one or two MPs in the city's parliament and community president. The president is elected by majority of residents on local meetings. Local community has meetings (couple of times in one month). At local meetings are present members of the council as well as local residents. Meetings are good for discussing local maters, like constructions of new buildings, new roads, complaints of the local residents, and to address their local city's MPs, who can pass their complaints on to the city's officials.
City holidays
[edit]| February 1 | On this day, in 1748, Novi Sad gained "free royal city" status. |
| October 23 | The partisan forces from Srem and Bačka entered and liberated the city from occupation on this day, in 1944. |
| November 9 | Troops of the Kingdom of Serbia entered the city on this day, in 1918, led by commandant Petar Bojović. |
| November 25 | In 1918, the Assembly of Serbs, Bunjevci, and other Slavs of Vojvodina (Banat, Bačka and Baranja) in Novi Sad proclaimed the unification of Vojvodina region with the Kingdom of Serbia. |
City also commemorates the year 1694, when it was established.
Street names
[edit]This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (July 2010) |
Twin towns – sister cities
[edit] Alexandria, Egypt (2021)[7][8]
Alexandria, Egypt (2021)[7][8] Budva, Montenegro (1996)[9]
Budva, Montenegro (1996)[9] Changchun, China (1981)[10]
Changchun, China (1981)[10] Cleveland, Ohio, United States (2023)[11]
Cleveland, Ohio, United States (2023)[11] Dortmund, Germany (1982)[12]
Dortmund, Germany (1982)[12] Gomel, Belarus (2013)[13]
Gomel, Belarus (2013)[13] Ilioupoli, Greece (1994)[14]
Ilioupoli, Greece (1994)[14] Istočno Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina (2021)[15]
Istočno Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina (2021)[15] Kumanovo, North Macedonia (2019)[16]
Kumanovo, North Macedonia (2019)[16] Modena, Italy (1964)[17]
Modena, Italy (1964)[17] Nizhny Novgorod, Russia (2006)[18]
Nizhny Novgorod, Russia (2006)[18] Norwich, England, United Kingdom (1989)[19]
Norwich, England, United Kingdom (1989)[19] Pécs, Hungary (2009)[20]
Pécs, Hungary (2009)[20] Taverny, France (2020)[21][22]
Taverny, France (2020)[21][22] Timișoara, Romania (2005)[23]
Timișoara, Romania (2005)[23] Tivat, Montenegro (2023)[24][25]
Tivat, Montenegro (2023)[24][25] Toluca, Mexico (2015)[26]
Toluca, Mexico (2015)[26]
Cooperation agreements
[edit]Novi Sad cooperates with:[6]
 Banja Luka, Bosnia and Herzegovina (2006)
Banja Luka, Bosnia and Herzegovina (2006) Corfu, Greece (2017)[27]
Corfu, Greece (2017)[27] Enghien-les-Bains, France (2020)[21]
Enghien-les-Bains, France (2020)[21] Frunzensky District, Russia (2003)[28]
Frunzensky District, Russia (2003)[28] Gothenburg, Sweden (2002)
Gothenburg, Sweden (2002) Kranj, Slovenia (2004)
Kranj, Slovenia (2004) Krasnodar, Russia
Krasnodar, Russia Lviv, Ukraine (1999)
Lviv, Ukraine (1999) Nant, France (2002)
Nant, France (2002) Osijek, Croatia (2002)
Osijek, Croatia (2002) Oryol, Russia (2017)[29]
Oryol, Russia (2017)[29] Saint-Leu-la-Forêt, France (2020)[21]
Saint-Leu-la-Forêt, France (2020)[21] Shiraz, Iran (2023)[30]
Shiraz, Iran (2023)[30] Szeged, Hungary (2001)
Szeged, Hungary (2001) Tivat, Montenegro (2023)[31]
Tivat, Montenegro (2023)[31] Tuzla, Bosnia and Herzegovina (2002)
Tuzla, Bosnia and Herzegovina (2002) Ulm, Germany (2000)[32]
Ulm, Germany (2000)[32]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Skupština grada Novog Sada". mojnovisad.com (in Serbian). Retrieved 11 July 2024.
- ^ Election results by Cesid Archived 2007-09-27 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Milan Đurić novi gradonačelnik Novog Sada". Radio Television of Serbia (in Serbian). 2022-10-26. Retrieved 2022-10-26.
- ^ "Zakon o lokalnoj samoupravi". www.novibechej.com. Archived from the original on 2008-08-28.
- ^ "SPO: Novi Sad u osam opština | www.dnevnik.rs". Archived from the original on 2011-02-03. Retrieved 2011-07-15.
- ^ a b "Međunarodna saradnja". skupstina.novisad.rs (in Serbian). Novi Sad. Retrieved 2020-06-06.
- ^ "Gradovi pobratimi: Potpisan sporazum o saradnji između Novog Sada i Aleksandrije". 021.rs (in Serbian). 021.rs. 21 September 2021. Retrieved 5 November 2023.
- ^ "УПОЗНАЈМО ГРАДОВЕ ПОБРАТИМЕ НОВОГ САДА – АЛЕКСАНДРИЈА" (in Serbian). gradskeinfo.rs. 28 July 2022. Retrieved 5 November 2023.
- ^ "УПОЗНАЈМО ГРАДОВЕ ПОБРАТИМЕ НОВОГ САДА − БУДВА" (in Serbian). gradskeinfo.rs. 22 January 2022. Retrieved 5 November 2023.
- ^ "УПОЗНАЈМО ГРАДОВЕ ПОБРАТИМЕ НОВОГ САДА – ЧАНГЧУН, НР КИНА" (in Serbian). gradskeinfo.rs. 15 November 2021. Retrieved 5 November 2023.
- ^ "Srpska Atina nastavlja da nižе pobratimstva i to sa tri kontinеnta! REKORDERI U JAČANjU SARADNjE: Grad Novi Sad ima čak 24 grada pobratima, poslеdnji u nizu Klivlеnd koji ima jaku srpsku dijasporu". dnevnik.rs (in Serbian). 3 November 2023. Retrieved 5 November 2023.
- ^ "УПОЗНАЈМО ГРАДОВЕ ПОБРАТИМЕ НОВОГ САДА − ДОРТМУНД" (in Serbian). gradskeinfo.rs. 30 November 2021. Retrieved 5 November 2023.
- ^ "УПОЗНАЈМО ГРАДОВЕ ПОБРАТИМЕ НОВОГ САДА – ГОМЕЉ" (in Serbian). gradskeinfo.rs. 30 April 2022. Retrieved 5 November 2023.
- ^ "УПОЗНАЈМО ГРАДОВЕ ПОБРАТИМЕ НОВОГ САДА − ИЛИУПОЛИ" (in Serbian). gradskeinfo.rs. 10 January 2022. Retrieved 5 November 2023.
- ^ "Upoznajemo gradove pobratime Novog Sada – Grad Istočno Sarajevo" (in Serbian). vojvodinauzivo.rs. 3 September 2022. Retrieved 5 November 2023.
- ^ "Kumanovo i Novi Sad postali gradovi pobratimi" (in Serbian). danas.rs. 10 November 2019. Retrieved 5 November 2023.
- ^ "УПОЗНАЈМО ГРАДОВЕ ПОБРАТИМЕ НОВОГ САДА – НИЖЊИ НОВГОРОД" (in Serbian). gradskeinfo.rs. 23 February 2022. Retrieved 5 November 2023.
- ^ "УПОЗНАЈМО ГРАДОВЕ ПОБРАТИМЕ НОВОГ САДА – МОДЕНА" (in Serbian). gradskeinfo.rs. 7 November 2021. Retrieved 5 November 2023.
- ^ "УПОЗНАЈМО ГРАДОВЕ ПОБРАТИМЕ НОВОГ САДА – НОРИЧ" (in Serbian). gradskeinfo.rs. 27 December 2021. Retrieved 5 November 2023.
- ^ "УПОЗНАЈМО ГРАДОВЕ ПОБРАТИМЕ ГРАДА НОВОГ САДА – ПЕЧУЈ" (in Serbian). gradskeinfo.rs. 24 March 2022. Retrieved 5 November 2023.
- ^ a b c "The Ambassador of France Visits Novi Sad". novisadinvest.rs. 25 May 2022. Retrieved 5 November 2023.
- ^ "Novi Sad – Serbie" (in French). Taverny. Retrieved 2023-05-12.
- ^ "УПОЗНАЈМО ГРАДОВЕ ПОБРАТИМЕ НОВОГ САДА – ТЕМИШВАР" (in Serbian). gradskeinfo.rs. 5 February 2022. Retrieved 5 November 2023.
- ^ Luković, Siniša (7 July 2023). "Pobratimili se gradovi Tivat i Novi Sad" (in Serbian). vijesti.me. Retrieved 5 November 2023.
- ^ "Upoznajmo gradove pobratime Novog Sada – Tivat" (in Serbian). nsuzivo.rs. 16 July 2023. Retrieved 5 November 2023.
- ^ "УПОЗНАЈМО ГРАДОВЕ ПОБРАТИМЕ НОВОГ САДА – ТОЛУКА" (in Serbian). gradskeinfo.rs. 12 April 2022. Retrieved 5 November 2023.
- ^ "Нови Сад и Крф побратими и пријатељи" (in Serbian). 21 May 2017. Retrieved 5 November 2023.
- ^ "Vučević: Saradnja Novog Sada i Sankt Peterburga" (in Serbian). rtv.rs. 3 June 2021. Retrieved 5 November 2023.
- ^ "Potpisan sporazum o saradnji sa Orelom" (in Serbian). kanal9tv.com. 1 February 2017. Retrieved 5 November 2023.
- ^ "Novi Sad uspostavlja saradnju sa iranskim gradom Širazom" (in Serbian). kanal9tv.com. 27 June 2023. Retrieved 5 November 2023.
- ^ Luković, Siniša (7 July 2023). "Pobratimili se gradovi Tivat i Novi Sad" (in Serbian). vijesti.me. Retrieved 5 November 2023.
- ^ Kadrić, Milana (1 February 2017). "Sporazum o saradnji Novog Sada i Ulma" (in Serbian). rtv.rs. Retrieved 5 November 2023.
External links
[edit]- Official site of city assembly (in Serbian)

