Mpumalanga Provincial Legislature
Mpumalanga Provincial Legislature Mpumalanga Provinsiale Wetgewer (Afrikaans) IsiShayamthetho Sifundazwe saseMpumalanga (Zulu) IsiBethamthetho Sesfunda sePumalanga (Southern Ndebele) | |
|---|---|
| 7th Legislature | |
 | |
| Type | |
| Type | |
| Leadership | |
Deputy Speaker | |
Premier | |
| Structure | |
| Seats | 51 |
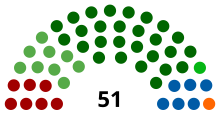 | |
Political groups | Government (27)
Official Opposition (9)
Other parties (15) |
| Elections | |
| Party-list proportional representation | |
Last election | 28 May 2024 |
| Website | |
| http://www.mpuleg.gov.za/ | |
The Mpumalanga Provincial Legislature (MPL), previously known as the Eastern Transvaal Legislature, is the primary legislative body of the South African province of Mpumalanga.[2]
The First Legislature was inaugurated in May 1994 as the Eastern Transvaal Legislature. It was renamed in 1995.
The Provincial Legislature, along with the other provincial legislatures of South Africa, exists by virtue of Chapter 6 of the Constitution of South Africa. It is unicameral, and consists of 30 members elected by a system of party-list proportional representation.
The 7th Provincial Legislature was elected on 29 May 2024 in South Africa's 2024 general elections. A majority of the members belong to the African National Congress.
At the commencement of the 7th provincial legislature on 14 June 2024, the number of seats allocated to the Mpumalanga Provincial Legislature increased from 30 to 51.[3]
Powers
[edit]The Mpumalanga Provincial Legislature elects the Premier of Mpumalanga. The legislature can force the Premier to resign by passing a motion of no confidence. Although the Executive Council is appointed by the Premier of Mpumalanga, the legislature may pass a motion of no confidence to compel the Premier to reorient the Council. The legislature also appoints Mpumalanga's delegates to the National Council of Provinces, allocating delegates to parties in proportion to the number of seats each party holds in the legislature.
The legislature has the power to pass legislation in various fields mentioned in the national constitution; in some fields the legislative power is shared with the national parliament, while in others it is reserved to Mpumalanga alone. The fields include such matters as health, education, agriculture, housing, environmental protection, and development planning.
The legislature oversees the administration of the provincial government, and the Premier and the members of the Executive Council are required to report to the legislature on the performance of their responsibilities. The legislature also manages the fiscal matters of the provincial government by way of the appropriation bills which determine the provincial budget.
Election
[edit]The Provincial Legislature consists of 30 members, who are elected through a system of party list proportional representation with closed lists. In other words, each voter casts a vote for one political party, and seats in the legislature are allocated to the parties in proportion to the number of votes received. The seats are then filled by members in accordance with lists submitted by the parties before the election.
The Legislature is elected for a term of five years unless it is dissolved early. This may occur if the legislature votes to dissolve and it is at least three years since the last election, or if the Premiership falls vacant and the legislature fails to elect a new Premier within ninety days. By convention, all nine provincial legislatures and the National Assembly are elected on the same day.
The most recent election was held on 28 May 2024. The following table reflects the results.
| Party | Votes | % | Seats | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| African National Congress | 584,609 | 51.31 | 27 | |
| uMkhonto weSizwe | 193,995 | 17.03 | 9 | |
| Economic Freedom Fighters | 158,511 | 13.91 | 7 | |
| Democratic Alliance | 137,408 | 12.06 | 6 | |
| Freedom Front Plus | 17,514 | 1.54 | 1 | |
| ActionSA | 5,727 | 0.50 | 1 | |
| United Africans Transformation | 5,512 | 0.48 | 0 | |
| African Christian Democratic Party | 5,401 | 0.47 | 0 | |
| Inkatha Freedom Party | 5,352 | 0.47 | 0 | |
| African Transformation Movement | 4,918 | 0.43 | 0 | |
| African Independent People's Organisation | 4,004 | 0.35 | 0 | |
| African People's Convention | 3,542 | 0.31 | 0 | |
| Patriotic Alliance | 1,911 | 0.17 | 0 | |
| Rise Mzansi | 2,189 | 0.19 | 0 | |
| Build One South Africa | 2,147 | 0.19 | 0 | |
| Pan Africanist Congress of Azania | 1,811 | 0.16 | 0 | |
| Bolsheviks Party of South Africa | 1,064 | 0.09 | 0 | |
| United Democratic Movement | 916 | 0.08 | 0 | |
| Sindawonye Progressive Party | 793 | 0.07 | 0 | |
| Good | 501 | 0.04 | 0 | |
| Economic Liberators Forum | 480 | 0.04 | 0 | |
| National Freedom Party | 443 | 0.04 | 0 | |
| Able Leadership | 258 | 0.02 | 0 | |
| Africa Restoration Alliance | 258 | 0.02 | 0 | |
| African Movement Congress | 163 | 0.01 | 0 | |
| Total | 1,139,427 | 100.00 | 51 | |
The following table shows the composition of the provincial parliament after past elections.
| Event | ActionSA | ANC | BRA | COPE | DP/DA | EFF | FF/FF+ | NP/NNP | UDM | MK |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1994 election | — | 25 | — | — | 0 | — | 2 | 3 | 0 | — |
| 1999 election | — | 26 | — | — | 1 | — | 1 | 1 | 1 | — |
| 2004 election | — | 27 | — | — | 2 | — | 1 | 0 | 0 | — |
| 2009 election | — | 27 | — | 1 | 2 | — | 0 | — | 0 | — |
| 2014 election | — | 24 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 0 | — | 0 | — |
| 2019 election | — | 22 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 4 | 1 | — | 0 | 1 |
| 2024 election | 1 | 27 | — | 0 | 6 | 7 | 1 | — | 0 | 9 |
Presiding Officers
[edit]Each of the nine provincial legislatures has Presiding Officers. The Presiding Officers can be the Speaker, Deputy Speaker, Chairperson of Committees and the Deputy Chairperson of Committees. The following people have served as the Speaker:
| Name | Entered / left office | Party |
|---|---|---|
| Elias Nicodemus “Mbalekelwa” Ginindza | 1994 – 1998 | ANC |
| Sipho William Lubisi | 1998 – 2004 | ANC |
| Yvonne Nkwenkwezi “Pinky” Phosa | 2004 – 2009 | ANC |
| Jackson Mphikwa Mthembu | 2009 | ANC |
| Sipho William Lubisi | 2009 – 2014 | ANC |
| Blessing Thandi Shongwe | 2014 – 2018 | ANC |
| Violet Sizani Siwela | 2018 – 2019 | ANC |
| Busi Shiba | 2019 – 2021 | ANC |
| Makhosazane Masilela | 2021 – 2024 | ANC |
| Lindi Masina | 2024 – Present | ANC |
Members
[edit]- List of members of the 2nd Mpumalanga Provincial Legislature (1999–2004)
- List of members of the 3rd Mpumalanga Provincial Legislature (2004–2009)
- List of members of the 4th Mpumalanga Provincial Legislature (2009–2014)
- List of members of the 5th Mpumalanga Provincial Legislature (2014–2019)
- List of members of the 6th Mpumalanga Provincial Legislature (2019–2024)
References
[edit]- ^ a b c "Mpumalanga's new premier promises stability in the province". 2024-06-14. Retrieved 2024-06-16.
- ^ Legislature
- ^ "Electoral Commission on determination of seats for provincial legislatures | South African Government". www.gov.za. Retrieved 2024-06-14.
