Lomatia silaifolia
| Lomatia silaifolia | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Order: | Proteales |
| Family: | Proteaceae |
| Genus: | Lomatia |
| Species: | L. silaifolia
|
| Binomial name | |
| Lomatia silaifolia | |
| |
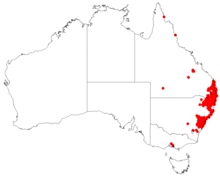
| Collections data from AVH | |
Lomatia silaifolia, commonly known as crinkle bush or parsley fern, is a plant of the family, Proteaceae native to eastern Australia. Naturally found in open forest, it grows as a small shrub 1–2 m high with highly pinnate leaves reminiscent of parsley. The white inflorescences appear in summer.
Description
[edit]Lomatia silaifolia is a small upright shrub which grows 1–2 metres (3.3–6.6 ft) high with glaucous smooth stems. It has highly pinnate leaves which can vary in appearance and are reminiscent of parsley. They are up to 35 to 50 centimetres (14 to 20 in) long. The white inflorescences appear in summer and are up to 45 centimetres (18 in) high.[1][2]

Taxonomy
[edit]English botanist James Edward Smith first described this species as Embothrium silaifolium in 1793.[3] At the time, Embothrium was a wastebasket taxon to which many proteaceae were assigned.[4] It was given its current binomial name by Robert Brown in his 1810 On the natural order of plants called Proteaceae.[5][6] An alternative name, Tricondylus silaifolius, published by Joseph Knight in his 1809 On the cultivation of the plants belonging to the natural order of Proteeae, was rejected,[7] after Brown's 1810 description of the genus Lomatia was officially conserved against Salisbury's 1809 Tricondylus. The species name is derived from resemblance of the leaves to the parsley genus Silaum.[4]
An early common name applied in England was sulphur-wort-leaved lomatia.[8] Other common names include crinkle bush, parsley fern, wild parsley, and fern-leaved lomatia.[4]
Hybrids with L. fraseri and L. myricoides have been recorded.[1] Analysis of chloroplast DNA showed that there is extensive hybridization between the five species (L. arborescens, L. fraseri, L. ilicifolia, L. myricoides and L. silaifolia) of mainland southeastern Australia, though each is distinct enough to warrant species status.[9]
Distribution and habitat
[edit]Lomatia silaifolia is found across much of eastern Australia east of the Great Dividing Range, on the Blackdown Tableland in central Queensland, then from Gympie in the south-east of the state to the New England area of north-eastern New South Wales, and then also from the Hunter Region to Jervis Bay in central New South Wales.[1] It grows as an understory shrub in open forest on sandstone soils, associated with such trees as red bloodwood (Corymbia gummifera), turpentine (Syncarpia glomulifera), blackbutt (Eucalyptus pilularis), Sydney peppermint (E. piperita), narrow-leaved peppermint (E. radiata), blue-leaved stringybark (E. agglomerata), red stringybark (E. macrorhyncha), grey gum (E. punctata), scribbly gum (E. sclerophylla), smooth-barked apple (Angophora costata) or rose sheoak (Allocasuarina torulosa).[10]
Ecology
[edit]Plants are thought to live for over 60 years and regenerate after bushfire by resprouting from the base. The leaves are eaten by swamp wallabies (Wallabia bicolor).[10] Calves are thought to have died after eating it, and cut flowers kept indoors have been reported to attract and kill flies. Positive cyanide reactions have been recorded for the anthers, styles and stigmas.[4]
Use in horticulture
[edit]Lomatia silaifolia was trialled in cultivation in England in 1808, though noted to flower rarely and require a greenhouse.[8] The unusual leaves and fruits of the species make it a suitable garden feature. It can be easily propagated from seed, is hardy in most soils and aspects.[11]
Gallery
[edit]-
Lomatia silaifolia in the Boonoo Boonoo National Park
-
L. silaifolia leaves and flowers
-
L. silaifolia fruit in Cathedral Rock National Park
-
Leaves, Cranbourne Botanic Gardens
References
[edit]- ^ a b c "Lomatia silaifolia (Sm.) R.Br". Flora of Australia Online. Department of the Environment and Heritage, Australian Government.
- ^ Harden, Gwen J. "Lomatia silaifolia ". PlantNET - New South Wales Flora Online. Royal Botanic Gardens & Domain Trust, Sydney Australia. Retrieved 20 September 2011.
- ^ "Embothrium silaifolium Sm". Australian Plant Name Index (APNI), IBIS database. Centre for Plant Biodiversity Research, Australian Government.
- ^ a b c d Wrigley, John; Fagg, Murray (1991). Banksias, Waratahs and Grevilleas. Sydney: Angus & Robertson. pp. 447, 451–52. ISBN 978-0-207-17277-9.
- ^ Brown, Robert (1810). "On the Proteaceae of Jussieu". Transactions of the Linnean Society of London. 10 (1): 15–226 [199]. doi:10.1111/j.1096-3642.1810.tb00013.x.
- ^ "Lomatia silaifolia (Sm.) R.Br". Australian Plant Name Index (APNI), IBIS database. Centre for Plant Biodiversity Research, Australian Government.
- ^ "Tricondylus silaifolius (Sm.) Knight". Australian Plant Name Index (APNI), IBIS database. Centre for Plant Biodiversity Research, Australian Government.
- ^ a b Sims, John (1810). Curtis's botanical magazine. Vol. XXXI. London: Sherwood, Neely & Jones. pp. 1271–72.
- ^ Milner, Melita; Rossetto, Maurizio; Crisp, Michael D.; Weston, Peter H. (2012). "The impact of multiple biogeographic barriers and hybridization on species-level differentiation". American Journal of Botany. 99 (12): 2045–57. doi:10.3732/ajb.1200327. PMID 23221499.
- ^ a b Benson, Doug; McDougall, Lyn (2000). "Ecology of Sydney plant species". Cunninghamia. 6 (4): 1017–1202. Retrieved 5 January 2018.
- ^ Wrigley, John W.; Fagg, Murray (1983). Australian native plants : a manual for their propagation, cultivation and use in landscaping (2nd ed.). Sydney: Collins. pp. 258–259. ISBN 978-0002165754.




