HD 54475
| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Puppis[2][note 1] |
| Right ascension | 07h 07m 07s[3] |
| Declination | −40° 53′ 35.77″[3] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 5.783±0.009[3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Evolutionary stage | B-type main-sequence star[3] |
| Spectral type | B3V[3] |
| Variable type | Pulsating variable[3] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | 6±3.2[3] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −10.554±0.069 mas/yr[3] Dec.: 11.163±0.0689 mas/yr[3] |
| Parallax (π) | 4.2 ± 0.2 mas[4] |
| Distance | 776.19 ly (238.1 pc)[4] |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | -0.95[5] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 6.2±0.1[6] M☉ |
| Radius | 3.544[7][a] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 689.67[8] L☉ |
| Temperature | 15,723[8] K |
| Age | 15.8±0.3[6] Myr |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
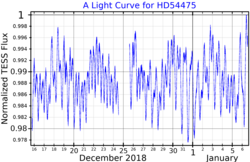
D Puppis, also known as HD 54475, is a B-type star and a pulsating variable in the constellation of Puppis.[3][5] It has an apparent magnitude of 5.783,[3] which is enough to be visible to the unaided eye.[b] The distance to D Puppis, based on a parallax of 4.2±0.2 mas from the Hipparcos satellite, is 776 light-years.[4][c]
Characteristics
[edit]This is a B-type main-sequence star with a spectral type of B3V.[3] It has 6.2 times the mass of the Sun[6] and 3.54 times the Sun's radius.[7] It radiates 690 times the solar luminosity from its outer atmosphere at a temperature of 15,723 K.[8] Its age is estimated to be of about 15 million years.[6]
The distance to D Puppis is about 776 light-years, based on a parallax of 4.2±0.2 mas from the Hipparcos satellite.[4]
It is mentioned to be a pulsating variable star on SIMBAD,[3] but the American Association of Variable Star Observers does not mention any variable-star type for the star.[2]
Notes
[edit]- ^ Calculated using an angular diameter of 0.1422608 mas and an adopted distance of 231.7 parsecs (756 ly).
- ^ According to the Bortle scale
- ^ The distance in parsecs is equivalent to .
References
[edit]- ^ "MAST: Barbara A. Mikulski Archive for Space Telescopes". Space Telescope Science Institute. Retrieved 27 December 2024.
- ^ a b "VSX : Detail for NSV 17352". www.aavso.org. Retrieved 2024-04-19.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m "HD 54475". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg.
- ^ a b c d van Leeuwen, F. (2007-11-01). "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 474 (2): 653–664. arXiv:0708.1752. Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357. ISSN 0004-6361.
- ^ a b Ford, Dominic. "D-Pup (Star)". In-The-Sky.org. Retrieved 2024-04-15.
- ^ a b c d Tetzlaff, N.; Neuhäuser, R.; Hohle, M. M. (2011-01-01). "A catalogue of young runaway Hipparcos stars within 3 kpc from the Sun". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 410 (1): 190–200. arXiv:1007.4883. Bibcode:2011MNRAS.410..190T. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.17434.x. ISSN 0035-8711.
- ^ a b Cruzalèbes, P.; Petrov, R. G.; Robbe-Dubois, S.; Varga, J.; Burtscher, L.; Allouche, F.; Berio, P.; Hofmann, K. -H.; Hron, J.; Jaffe, W.; Lagarde, S.; Lopez, B.; Matter, A.; Meilland, A.; Meisenheimer, K. (2019-12-01). "A catalogue of stellar diameters and fluxes for mid-infrared interferometry". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 490 (3): 3158–3176. arXiv:1910.00542. Bibcode:2019MNRAS.490.3158C. doi:10.1093/mnras/stz2803. ISSN 0035-8711.
- ^ a b c McDonald, I.; Zijlstra, A. A.; Boyer, M. L. (2012-11-01). "Fundamental parameters and infrared excesses of Hipparcos stars". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 427 (1): 343–357. arXiv:1208.2037. Bibcode:2012MNRAS.427..343M. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2012.21873.x. ISSN 0035-8711.
Sources
[edit]- Stift, Martin (19 April 1979). "Light Variations of HD 54475". Information Bulletin on Variable Stars. 1586 (1586). Konkoly Observatory, Budapest: Commission 27 of the IAU: 1. Bibcode:1979IBVS.1586....1S.