Ganglion cell
| Ganglion cell | |
|---|---|
 Various forms of nerve cells.
| |
| Details | |
| Location | Varies by type |
| Shape | Varies |
| Function | Varies but often excitatory projection |
| Neurotransmitter | Varies but often glutamate |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
Introduction
[edit]In neurophysiology, a ganglion cell is a cell found in a ganglion (a cluster of neurons in the peripheral nervous system). Examples of ganglion cells include:
- Retinal ganglion cell (RGC) found in the ganglion cell layer of the retina[1]
- Cells that reside in the adrenal medulla, where they are involved in the sympathetic nervous system's release of epinephrine and norepinephrine into the blood stream
- Cells of the sympathetic ganglia
- Cells of the parasympathetic ganglia
- Cells of the spiral ganglia[2]
General Morphology
[edit]During the late 1800s, early 1900s, Spanish Neuroscientist and Pathologist Santiago Ramón y Cajal proposed Neuron theory which basically introduced the idea that the Nervous system contained cells called the Neuron. The process he used was called Golgi staining of the vertebrae retina. Cajal was able to differentiate between different types of Ganglion cell based on dendritic morphology, cell body and dendritic tree size, and number of sub layers in which they arborize/stratification layers. Through this study, he discovered that the ganglion cell distribution amongst vertebrates were pretty similar minus the Rods and cones in the retinas.[3]
In the 1940s, American Neurologist Stephen Polyak[4] produced description of the Golgi-impregnated Cells that helped further classify types of Ganglion Cells. This data helped scientists get a better understanding of the ganglion cells present in the retinas of Mammals and Primates[3]
In 1974, Boycott and Wassle created a scheme for the classification of Ganglion Cells that was found to be in the cat retina. These cells, alpha, beta, delta and gamma are seen to be linked with the X,Y and W types of physiology. Boycott and Wassle confirmed the idea of Cajal's Ox and Dog retina idea by naming the alpha and beta.
In 1978, the idea of the alpha and beta ganglion cells could be divided into different subgroups, sublamina a and sublamina b. Sublamina a contains dendrite cells containing OFF-center receptive fields while the Sublamina b contains On-center receptive fields.[3][5]
Disorders Relating to Ganglion Cells
[edit]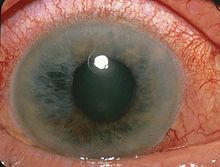
Glaucoma: Glaucoma is a collection of diseases that damages the nerve in the eye / retina. The damage in the nerve has the possibility to cause blindness. You may not know you have a Glaucoma without an in-depth eye exam normally using the dilation method. There is no cure for a Glaucoma, but it may be treated if found early. It is unknown the cause of a Glaucoma, but those who may be at risk include:
- Individuals over the age of 60 (most commonly those who are Hispanic or Latino)
- African Americans over the age of 40 years old Individuals with a family history of Glaucoma's.[7]
Hereditary optic neuroretinopathy: There are two different types of Hereditary Optic Neuroretinopathy, those including Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy and Autosomal Dominant Optic Atrophy. The Leber's Neuropathy is caused by a mutation in the Mitochondrial DNA (the DNA located inside the chromosome) This is only obtainable through the mother. Some individuals are carriers and experience no symptoms. Symptoms of individuals who are affected by Leber's Neuropathy include:
- Beginning with: loss of vision or clouding in the one eye, normally takes a few weeks before traveling to the other eye. most times not painful
Autosomal Dominant Optic Atrophy is a mutated gene in the autosomes (not sex-linked genes in humans chromosome pairs 1-22). This trait is present in anyone with the mutation in the autosome. The individual only needs one mutated gene to be affected. Symptoms of this condition include:
- Vision loss - in both eyes at the same time. The time it takes to occur varies per person, but normally progresses slowly.
These diseases can be examined by tests such as Eye exams, Image testing and a look through family history.[8]
Parkinson's disease: Parkinson's Disease is a condition that originates in the Nervous System and affects parts controlled by the nervous system. This disease is progressive, meaning it progressively gets worse overtime. A slow loss of Retinal Ganglion Cells may be observed overtime. List of symptoms include:
- Loss or lack of control in motor functions (i.e. Tremors)
- Change in cognitive function(i.e. Behavior,thoughts, and mood)
- Psychosis (losing contact with reality)
- and more.
Those who are at risk include genes (through family members), toxins from the environment, and the presence of Lewy bodies.[9][10]
References
[edit]- ^ Sernagor, Evelyne; Eglen, Stephen J; Wong, Rachel O.L (March 2001). "Development of Retinal Ganglion Cell Structure and Function". Progress in Retinal and Eye Research. 20 (2): 139–174. doi:10.1016/S1350-9462(00)00024-0.
- ^ Dhanasingh, Anandhan; Jolly, Claude N.; Rajan, Gunesh; van de Heyning, Paul (April 2020). "Literature Review on the Distribution of Spiral Ganglion Cell Bodies inside the Human Cochlear Central Modiolar Trunk". The Journal of International Advanced Otology. 16 (1): 104–110. doi:10.5152/iao.2020.7510. ISSN 1308-7649. PMC 7224428. PMID 32209520.
- ^ a b c Kolb, Helga (1995), Kolb, Helga; Fernandez, Eduardo; Nelson, Ralph (eds.), "Morphology and Circuitry of Ganglion Cells", Webvision: The Organization of the Retina and Visual System, Salt Lake City (UT): University of Utah Health Sciences Center, PMID 21413393, retrieved 2024-04-22
- ^ Arey, L. B. (1942-08-25). "The Retina, S. L. Polyak. 4to. Pp. X and 607, plus 100 plates on 56 leaves. The University of Chicago Press, Chicago, 1941. Price $10.00". The Anatomical Record. 83 (4): 597–601. doi:10.1002/ar.1090830412. ISSN 0003-276X.
- ^ Nelson, R.; Famiglietti, E. V.; Kolb, H. (1978-03-01). "Intracellular staining reveals different levels of stratification for on- and off-center ganglion cells in cat retina". Journal of Neurophysiology. 41 (2): 472–483. doi:10.1152/jn.1978.41.2.472. ISSN 0022-3077. PMID 650277.
- ^ "File:Acute Angle Closure-glaucoma.jpg - Wikipedia". commons.wikimedia.org. 2011-08-15. Retrieved 2024-04-22.
- ^ "Glaucoma | National Eye Institute". nei.nih.gov. Retrieved 2024-04-22.
- ^ "Hereditary Optic Neuropathies". Barrow Neurological Institute. Retrieved 2024-04-22.
- ^ "Parkinson's disease - Symptoms and causes". Mayo Clinic. Retrieved 2024-04-22.
- ^ "Understanding Psychosis - National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH)". nimh.nih.gov. Retrieved 2024-04-22.

