Draft:LiMeS-Wetting
| Submission declined on 6 February 2025 by Pygos (talk). This submission is not adequately supported by reliable sources. Reliable sources are required so that information can be verified. If you need help with referencing, please see Referencing for beginners and Citing sources. This draft's references do not show that the subject qualifies for a Wikipedia article. In summary, the draft needs multiple published sources that are:
Where to get help
How to improve a draft
You can also browse Wikipedia:Featured articles and Wikipedia:Good articles to find examples of Wikipedia's best writing on topics similar to your proposed article. Improving your odds of a speedy review To improve your odds of a faster review, tag your draft with relevant WikiProject tags using the button below. This will let reviewers know a new draft has been submitted in their area of interest. For instance, if you wrote about a female astronomer, you would want to add the Biography, Astronomy, and Women scientists tags. Editor resources
|  |
 Comment: Please add more sources (WP:SECONDARY) to show that the content is notable, as currently, there's only one source for the main body of the article. Pygos (talk) 00:59, 6 February 2025 (UTC)
Comment: Please add more sources (WP:SECONDARY) to show that the content is notable, as currently, there's only one source for the main body of the article. Pygos (talk) 00:59, 6 February 2025 (UTC)
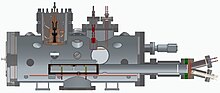
LiMeS-Wetting is a device at the Differ – Dutch Institute For Fundamental Energy Research ("DIFFER".) research institute in Eindhoven. The LiMeS lab within Differ, which is the acronym for Liquid-Metal Shield, focuses on creating and verifying materials for future nuclear fusion reactors, in which the liquid metal is held by capillary action.
The device is used to perform both wetting studies for tin on tungsten and filling 3d printed capillary porous tungsten structures for use in a larger test-setup. The process for this is first plasma cleaning the sample material, followed by injecting tin droplets to fill the sample.
For the cleaning there are a Cascaded Arc Plasma Source,[1] as well as a radical source and glow discharge cleaning. The injector provides tin droplets and the process is verified by the diagnostics: double Langmuir probe, radical probe, shadowgraph and an optical emission spectrometer.
See also
[edit]- Chemical vapor deposition
- Pulsed laser deposition
- Gas discharge plasmas and their applications.[2]
- Semiconductor manufacturing; Plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition
- National Spherical Torus Experiment in nuclear fusion
- DIFFER
References
[edit]- ^ Kroesen, G.M.W.; Schram, D.C. & de Haas, J.C.M. (1990). "Description of cascade arc plasma" (PDF). Plasma Chemistry and Plasma Processing. 10 (4): 531–551. doi:10.1007/BF01447263 – via alexandria.tue.nl (free article repository).
- ^ Bogaerts, A.; Neyts, E.; Gijbels, R.; van der Mullen, J. (2002). "Gas discharge plasmas and their applications" (PDF). Spectrochimica Acta. Part B. 57 (4): 609–658. doi:10.1016/S0584-8547(01)00406-2. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2004-09-27.
Further reading
[edit]- Tanke, Victor; Alonso van der Westen, Santi; van der Meiden, Hennie j. (27 September 2023). "LiMeS-Lab: An Integrated Laboratory for the Development of Liquid–Metal Shield Technologies for Fusion Reactors". Journal of Fusion Energy. 42 (44). doi:10.1007/s10894-023-00379-3.
- Wang, Shih-Chi; van der Horst, R. M. (2022). "Application of a dual-thermopile radical probe to expanding hydrogen plasmas" (PDF). Plasma Sources Science and Technology. 31 (8). doi:10.1088/1361-6595/ac71c3.
- Hermann, A.; Krebaum, P.; Berra, S. (November 2024). "Enhanced Catalytic Probe Design for Mapping Radical Density in the Plasma Afterglow". Journal of Physical Chemistry A. 128 (46): 10080–10086. doi:10.1021/acs.jpca.4c06195. PMC 11586897. PMID 39527051.
- Tschersich, K. G.; Fielschauer, J. P.; Schuler, H. (5 August 2008). "Design and characterization of a thermal hydrogen atom source". Journal of Applied Physics. 104 (3). doi:10.1063/1.2963956.
