Clavecin électrique
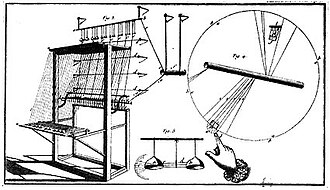
The clavecin électrique (or clavessin électrique) was a musical instrument invented in 1759 by Jean-Baptiste Thillaie Delaborde, a French Jesuit priest. It is the earliest known electric-powered musical instrument, antedated only by the Denis d'or, which is only known from written accounts.
The world's first electronic instrument was created in 1753 by the Czech musician and clergyman Prokop Divish (1698 - 1765). His distinctive feature was to show experiments in physics lessons. Among other things, Divish became famous for his original musical instrument, called "denidor". The very first writing about this instrument dates back to February 27, 1753 and is contained in a letter from the evangelical theologian Etinger Divish. It is a response to an unknown letter from Divish to the priest from the Württemberg city of Weinsberg. Therefore, work on the instrument was completed in early 1753.[1]
Later, Delaborde described the instrument in his 1761 publication, Le clavessin électrique.[2] The mechanism was based on a contemporary warning-bell device, and the instrument was essentially an electric carillon. A number of bells, two for each pitch, hang from iron bars along with their clappers (one for each pair). A globe generator charged the prime conductor and the iron bars. The musician pressed a key and one of the bells of the corresponding pair was grounded, cut off from the charge source. The clapper then oscillated between the grounded and the charged bells, producing the desired tone.
The somewhat inappropriate choice of the instrument's name was defended by Delaborde, who claimed that it was far superior to a carillon. He also mentioned that during a performance in a dark room, the listener's "eyes are agreeably surprised by the brilliant sparks" that were produced by the instrument. The press and the public admired the innovative machine, but it was not developed further. The model Delaborde himself built survives, and is kept at the Bibliothèque nationale de France in Paris.
References
[edit]- ^ портал, Школа для электрика-электротехнический. "Первые электромузыкальные инструменты: денидор Прокопа Дивиша, электрический клавесин де Лаборда, мелодром Поленова". Школа для электрика - электротехнический портал (in Russian). Retrieved 2024-09-10.
- ^ Delaborde, Jean-Baptiste (1761). Le clavessin électrique. Paris: H. L. Guérin & L. F. Delatour. Retrieved 28 June 2008.
Further reading
[edit]- Schiffer, Michael; Hollenback, Kasy; and Bell, Carrie. 2003. Draw the Lightning Down: Benjamin Franklin and Electrical Technology In the Age of Enlightenment. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-23802-2
External links
[edit]- Audio demo and photographs of a contemporary reconstruction of the clavecin électrique
- Clavecin électrique at '120 Years of Electronic Music'
- Clavecin électique and Benjamin Franklin
- Electric Harpsichord sound
- Introduction to 1970 electronic music
- Clavecin Electric
- Clavecin electric history of electric instruments
