Bristol Babe
| Babe | |
|---|---|

| |
| Replica of the Babe I | |
| Role | sports biplane |
| National origin | United Kingdom |
| Manufacturer | British & Colonial Aeroplane Co. Ltd. |
| Designer | Frank Barnwell |
| First flight | 28 November 1919 |
| Number built | 3 |
This article needs additional citations for verification. (September 2022) |
The Bristol Babe was a British-built light single-seat biplane, intended for the private flyer and produced immediately after the First World War. Only two flew.
Development
[edit]The Bristol Babe[1][2] was the creation of Frank Barnwell, a flying enthusiast as well as Bristol's chief designer. It was aimed at the private owner flyer and was a small single-engined single-seat biplane with unswept staggered single-bay wings of unequal span. Full-span ailerons were fitted on the top wing only. The fuselage was plywood-skinned, with fabric covering it for protection.[3] The cockpit was below the upper wing trailing edge with rounded decking aft to the tail. The fin and rudder were generous and rounded, the undercarriage a conventional single-axle plus tailskid arrangement.

Finding a suitable small engine proved difficult. The original intention was to use the 60 hp (50 kW) ABC Gadfly radial, but in April 1919 ABC pulled out of aero-engine manufacture. A possible alternative was the 40 hp (30 kW) flat-twin Siddeley Ounce currently being developed, so a third Babe was begun as a testbed. In the meantime, Barnwell resurrected a 1911 Viale 35 hp five-cylinder radial engine of 45 hp (34 kW) that had been installed in an Avro Type F and which had been put into storage following a crash. This engine ran satisfactorily for up to half an hour, after which it tended to overheat. This was installed in the second Babe which made its first flight on 28 November 1919. The pilot, Cyril Uwins reported that it was an easy aircraft for an experienced pilot but rather unstable for a novice. Though it was useful for testing, the old Viale was not reliable enough for sale, so following discussions at the Paris Aero Show in November 1919, two seven-cylinder 60 hp (50 kW) Le Rhône Type 7B2 rotary engines were ordered for the first two Babes. The third Babe appeared at this show with an incomplete Ounce engine.[1]
The second Babe built was referred to as the Babe I when it had the Viale engine and then as the Babe III with the Le Rhône engine. The Le Rhône-powered first machine was the other Babe III. The Ounce-powered third machine, designated Babe II, never flew, but the two Babe IIIs did and were registered over the winter of 1919-20.[1]
The first Babe underwent a drastic modification in May 1920 when it received a thick cantilever monoplane wing. Safety concerns prevented its testing and by February 1921 both aircraft were off the Civil Register. The Viale engine is now in the Science Museum, London. In the retrospective allocation of Bristol type numbers made in 1923, the Babe I was labelled Type 30, the Babe IIs as Type 46 and the unflown Babe III the Type 46A.[1]

Specifications (Babe III)
[edit]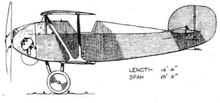
Data from Barnes 1964, p. 150
General characteristics
- Crew: one
- Length: 14 ft 11 in (4.55 m)
- Wingspan: 19 ft 8 in (6.00 m)
- Height: 5 ft 9 in (1.75 m)
- Wing area: 108 sq ft (10.0 m2)
- Empty weight: 460 lb (209 kg)
- Gross weight: 840 lb (381 kg)
- Powerplant: 1 × Le Rhône Type 7B2 , 60 hp (45 kW)
Performance
- Maximum speed: 107 mph (172 km/h, 93 kn)
- Service ceiling: 15,000 ft (4,570 m)
References
[edit]Citations
[edit]- ^ a b c d Barnes 1964, pp. 148–50
- ^ Flight 1919
- ^ Flight 1920
Bibliography
[edit]- Barnes, C. H. (1964), Bristol Aircraft since 1910, London: Putnam Publishing, ISBN 0-370-00015-3
- Flight (1919), "Bristol Babe", Flight (18 December 1919): 1612–3
- Flight (1920), "Bristol Babe at Paris Salon 1919", Flight (1 January 1920): 15
