Aldie Mill Historic District
Aldie Mill Historic District | |
 Aldie Mill and its millwheels | |
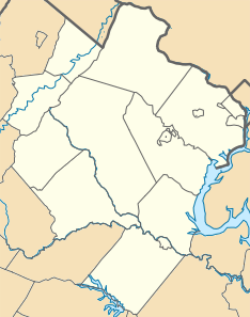
| Location | Both sides of U.S. 50 from E of Rte. 612 to W of Rte. 732, Aldie, Virginia |
|---|---|
| Area | 60 acres (24 ha) |
| Built | 1803 |
| NRHP reference No. | 70000806[1] |
| VLR No. | 053-0114 |
| Significant dates | |
| Added to NRHP | September 15, 1970 |
| Designated VLR | June 2, 1970[2] |
Aldie Mill is a water mill in Aldie, Virginia. Built shortly after 1804 to grind grain using the waters of the Little River, it retains much of its original machinery and is one of the best-preserved mills in Virginia.
History
[edit]Charles F. Mercer, a lawyer, Virginia legislator and military officer, obtained the right to dam the Little River and to build a mill in 1804. He built a house for himself across the Little River Turnpike, calling the complex "Aldie Manor," after Mercer's supposed ancestors' Aldie Castle in Scotland. The village that grew around the complex was named Aldie in 1810.[3] Mercer's father, James Mercer, had operated a tub mill at the location from about 1764. The new mill was built between 1807 and 1809 by William Cooke, who worked for Mercer under an indenture contract. Cooke built the mill, granary miller's house and store, as well as the now-disappeared distillery, blacksmith shop, sawmill, cooperage and wheelwright's shops, in return for a half-share in the mill operation.[4] The original mill machinery was a system patented and manufactured by Oliver Evans. Much of the machinery, along with the original wood water wheels, was replaced at the beginning of the twentieth century.[5] Mercer bought Cooke's share in the operation for $11,250 in 1816, leasing the mill to tenant operators.[6] Mercer sold the mill in 1835 to John Moore, whose descendants operated the mill until 1971, through six generations.[7]
Description
[edit]
The main portion of the brick mill building is two stories, with two loft levels under the roof. It is flanked by a one-story section on the east and a two-story portion to the west.
The milling machinery inside is powered by two overshot water wheels, arranged one after the other.
The historic district surrounding the mill includes two houses, the Mercer House and the Miller's House. The Mercer House overlooks the mill. It is a two-story Federal style house, covered in stucco and altered over time. The Miller's House, a two-story brick structure, is behind the mill between the Little River and the millrace. The Miller's House has been expanded to the rear.[3] Other buildings in the complex include a granary dating to the period 1809–1816 and a smaller "county mill" structure,[7] used to make plaster.[4]
The village of Aldie grew up around the mill after its construction.[3]
Park
[edit]The complex is part of the Aldie Mill Historic Park, operated by the Northern Virginia Regional Park Authority, and is open to the public. The metal millwheels have been restored and operate the mill's machinery.[8] It was placed on the National Register of Historic Places on September 15, 1970.[1]
References
[edit]- ^ a b "National Register Information System". National Register of Historic Places. National Park Service. July 9, 2010.
- ^ "Virginia Landmarks Register". Virginia Department of Historic Resources. Archived from the original on September 21, 2013. Retrieved June 5, 2013.
- ^ a b c Virginia Historic Landmarks Commission (March 4, 1970). "National Register of Historic Places Inventory - Nomination Form: Aldie Mill Historic District" (PDF). National Park Service. Archived from the original (PDF) on June 12, 2012. Retrieved September 15, 2011.
- ^ a b "The Mercers". Aldie Mill Historic Park. Northern Virginia Regional Parks Administration. Archived from the original on March 31, 2012. Retrieved September 15, 2011.
- ^ "The Machinery of Oliver Evans". Aldie Mill Historic Park. Northern Virginia Regional Parks Authority. Archived from the original on March 31, 2012. Retrieved September 15, 2011.
- ^ "Early Management of Mill Operations". Aldie Mill Historic Park. Northern Virginia Regional Park Authority. Archived from the original on March 31, 2012. Retrieved September 15, 2011.
- ^ a b "History". Aldie Mill Historic Park. Northern Virginia Regional Park Authority. Archived from the original on October 7, 2011. Retrieved September 15, 2011.
- ^ "Aldie Mill Historic Park". Northern Virginia Regional Park Authority. Archived from the original on October 5, 2011. Retrieved September 15, 2011.
External links
[edit]- Aldie Mill Historic Park Archived October 5, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- Aldie Mill Historic District at the Journey Through Hallowed Ground
- Grinding mills on the National Register of Historic Places in Virginia
- National Register of Historic Places in Loudoun County, Virginia
- Historic districts in Loudoun County, Virginia
- Journey Through Hallowed Ground National Heritage Area
- Mill museums in Virginia
- Museums in Loudoun County, Virginia
- Parks in Loudoun County, Virginia
- Watermills in the United States
- Historic districts on the National Register of Historic Places in Virginia
- Brick buildings and structures in Virginia