37th Air Division
| 37th Air Division | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Active | 1951–1952; 1955–1959; 1966–1970 |
| Country | |
| Branch | |
| Role | Command of strategic strike forces, then of air defense forces |
| Insignia | |
| 37th Air Division emblem (Approved 6 September 1953)[2] |  |
The 37th Air Division (37th AD) is an inactive United States Air Force organization. Its last assignment was with Air Defense Command at Goose Air Force Base, Labrador, Canada It was inactivated on 30 June 1970.
History
[edit]Strategic Air Command
[edit]Established under Strategic Air Command in 1952[2] as an intermediate-level command and control organization at Lockbourne Air Force Base, Ohio. Was responsible for strategic reconnaissance operations at Lockbourne and at Lake Charles Air Force Base, Louisiana. Assigned wings operated Boeing RB-29 Superfortress very long range reconnaissance aircraft. Both wings deployed operational aircraft to Far East Air Forces in early 1952 for use in Korean War. Wings re-equipped with new Boeing RB-47 Stratojets. Inactivated in May 1952.[2]
Air Defense Command
[edit]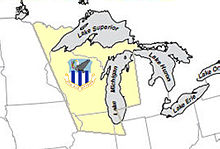
Reactivated on 8 September 1955 by Air Defense Command (ADC) at Truax Field, Wisconsin under Eastern Air Defense Force.[2] Was responsible for the construction and development of several Semi Automatic Ground Environment (SAGE) Data Centers. SAGE centers developed were at Truax Field, Wisconsin (DC-07) and Combat Center (CC-02); Direction Center (DC-10) at Duluth Municipal Airport, Minnesota; and Direction Center (DC-14) at K.I. Sawyer Air Force Base, Michigan. Its defense area included parts of Wisconsin, Michigan, Minnesota, Illinois, Indiana, Missouri, Iowa and southern parts of Ontario, Canada as part of the Pinetree Line.
On 8 March 1957, the Chicago Air Defense Sector, along with DC-07 and was assigned to the Division. On 8 October, the Duluth Air Defense Sector, along with DC-10 was assigned.[2] On 8 November, the Sault Sainte Marie Air Defense Sector was also activated along with DC-14. Inactivated on 1 April 1959[2] as part of an ADC reorganization, most assets reassigned to the senior ADC 30th Air Division (SAGE).
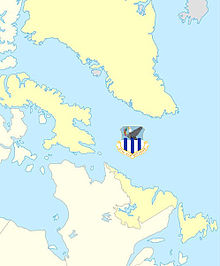
Reactivated by ADC a second time in April 1966,[2] assuming the assets of inactivating Goose Air Defense Sector at Goose Air Force Base, Labrador, Canada, including the Manual Control Center (MCC) at Goose. Assumed designation of 37th NORAD Region for stations and allied Canadian Forces assigned to NORAD air defense duties in Canada.
Was responsible for atmospheric defenses (interceptor and radar) for northeastern North America, including Greenland and Air Forces Iceland which was transferred from Military Air Transport Service.
Inactivated June 1970[2] by ADCOM as part of draw-down of USAF air defense forces in Canada and budget reductions, remaining assets in Canada transferred to Canadian Forces.
Lineage
[edit]- Established as the 37 Air Division and organized on 10 October 1951
- Discontinued on 28 May 1952
- Redesignated 37 Air Division (Defense) on 3 May 1955
- Activated on 8 September 1955
- Inactivated on 1 April 1959
- Redesignated 37th Air Division and activated on 20 January 1966 (not organized)
- Organized on 1 April 1966
- Inactivated on 30 June 1970[2]
Assignments
[edit]- Second Air Force, 10 October 1951 – 28 May 1952
- Eastern Air Defense Force, 8 September 1955 – 1 April 1959
- Air Defense Command, 20 January 1966 (not organized)
- First Air Force, 1 April 1966
- Aerospace Defense Command, 1 December 1969 – 30 June 1970[2]
Stations
[edit]- Lockbourne Air Force Base, Ohio, 10 October 1951 – 28 May 1952
- Truax Field, Wisconsin, 8 September 1955 – 1 April 1959
- Goose Air Force Base, Labrador, Canada, 1 April 1966 – 30 June 1970[2]
Components
[edit]Strategic Air Command
[edit]- 68th Strategic Reconnaissance Wing: 10 October 1951 – 28 May 1952
- Detached for service in Japan (Korean War): 10 October 1951-c. 15 May 1952
- Lake Charles Air Force Base, Louisiana
- 91st Strategic Reconnaissance Wing: 10 October 1951 – 28 May 1952
- Detached for service in Japan (Korean War): 10 October 1951 – 17 March 1952[2]
- Lockbourne Air Force Base, Ohio
Air Defense Command
[edit]Air Force
[edit]- Keflavik Airport, Iceland, 1 April 1966 – 31 December 1969
Sectors
[edit]- Truax Field, Wisconsin, 8 March 1957 – 1 April 1959
- Duluth Airport, Minnesota, 1 October-20 December 1957; 1 January-1 April 1959
- K.I. Sawyer Air Force Base, Michigan, 8 November 1958 – 1 April 1959[2]
Wings
[edit]- O'Hare International Airport, Illinois, 1 March-1 July 1956
- O'Hare International Airport, Illinois, 1 March-8 July 1956[2]
Groups
[edit]
|
|
Interceptor squadron
[edit]- Goose Air Force Base, Labrador, Canada, 1 April 1966 – 2 January 1967
Radar squadrons
[edit]
|
|
See also
[edit]- List of United States Air Force air divisions
- List of United States Air Force Aerospace Defense Command Interceptor Squadrons
- United States general surveillance radar stations
References
[edit]Notes
[edit]Bibliography
[edit]![]() This article incorporates public domain material from the Air Force Historical Research Agency
This article incorporates public domain material from the Air Force Historical Research Agency
- Cornett, Lloyd H; Johnson, Mildred W (1980). A Handbook of Aerospace Defense Organization, 1946–1980 (PDF). Peterson AFB, CO: Office of History, Aerospace Defense Center. Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 February 2016. Retrieved 23 March 2012.
- Winkler, David F.; Webster, Julie L (1997). Searching the skies: The legacy of the United States Cold War Defense Radar Program. Champaign, IL: US Army Construction Engineering Research Laboratories. LCCN 97020912.[dead link]
- "ADCOM's Fighter Interceptor Squadrons". The Interceptor. 21 (1). Aerospace Defense Command: 5–11, 26–31, 40–45, 54–59. January 1979.


