Pseudoforest

In graph theory, a pseudoforest is an undirected graph[1] in which every connected component has at most one cycle. That is, it is a system of vertices and edges connecting pairs of vertices, such that no two cycles of consecutive edges share any vertex with each other, nor can any two cycles be connected to each other by a path of consecutive edges. A pseudotree is a connected pseudoforest.
The names are justified by analogy to the more commonly studied trees and forests. (A tree is a connected graph with no cycles; a forest is a disjoint union of trees.) Gabow and Tarjan[2] attribute the study of pseudoforests to Dantzig's 1963 book on linear programming, in which pseudoforests arise in the solution of certain network flow problems.[3] Pseudoforests also form graph-theoretic models of functions and occur in several algorithmic problems. Pseudoforests are sparse graphs – their number of edges is linearly bounded in terms of their number of vertices (in fact, they have at most as many edges as they have vertices) – and their matroid structure allows several other families of sparse graphs to be decomposed as unions of forests and pseudoforests. The name "pseudoforest" comes from Picard & Queyranne (1982).
Definitions and structure
We define an undirected graph to be a set of vertices and edges such that each edge has two vertices (which may coincide) as endpoints. That is, we allow multiple edges (edges with the same pair of endpoints) and loops (edges whose two endpoints are the same vertex).[1] A subgraph of a graph is the graph formed by any subsets of its vertices and edges such that each edge in the edge subset has both endpoints in the vertex subset. A connected component of an undirected graph is the subgraph consisting of the vertices and edges that can be reached by following edges from a single given starting vertex. A graph is connected if every vertex or edge is reachable from every other vertex or edge. A cycle in an undirected graph is a connected subgraph in which each vertex is incident to exactly two edges, or is a loop.[4]

A pseudoforest is an undirected graph in which each connected component contains at most one cycle.[5] Equivalently, it is an undirected graph in which each connected component has no more edges than vertices.[6] The components that have no cycles are just trees, while the components that have a single cycle within them are called 1-trees or unicyclic graphs. That is, a 1-tree is a connected graph containing exactly one cycle. A pseudoforest with a single connected component (usually called a pseudotree, although some authors define a pseudotree to be a 1-tree) is either a tree or a 1-tree; in general a pseudoforest may have multiple connected components as long as all of them are trees or 1-trees.
If one removes from a 1-tree one of the edges in its cycle, the result is a tree. Reversing this process, if one augments a tree by connecting any two of its vertices by a new edge, the result is a 1-tree; the path in the tree connecting the two endpoints of the added edge, together with the added edge itself, form the 1-tree's unique cycle. If one augments a 1-tree by adding an edge that connects one of its vertices to a newly added vertex, the result is again a 1-tree, with one more vertex; an alternative method for constructing 1-trees is to start with a single cycle and then repeat this augmentation operation any number of times. The edges of any 1-tree can be partitioned in a unique way into two subgraphs, one of which is a cycle and the other of which is a forest, such that each tree of the forest contains exactly one vertex of the cycle.[7]
Certain more specific types of pseudoforests have also been studied.
- A 1-forest, sometimes called a maximal pseudoforest, is a pseudoforest to which no more edges can be added without causing some component of the graph to contain multiple cycles. If a pseudoforest contains a tree as one of its components, it cannot be a 1-forest, for one can add either an edge connecting two vertices within that tree, forming a single cycle, or an edge connecting that tree to some other component. Thus, the 1-forests are exactly the pseudoforests in which every component is a 1-tree.
- The spanning pseudoforests of an undirected graph G are the pseudoforest subgraphs of G that have all the vertices of G. Such a pseudoforest need not have any edges, since for example the subgraph that has all the vertices of G and no edges is a pseudoforest (whose components are trees consisting of a single vertex).
- The maximal pseudoforests of G are the pseudoforest subgraphs of G that are not contained within any larger pseudoforest of G. A maximal pseudoforest of G is always a spanning pseudoforest, but not conversely. If G has no connected components that are trees, then its maximal pseudoforests are 1-forests, but if G does have a tree component, its maximal pseudoforests are not 1-forests. Stated precisely, in any graph G its maximal pseudoforests consist of every tree component of G, together with one or more disjoint 1-trees covering the remaining vertices of G.
Directed pseudoforests
Versions of these definitions are also used for directed graphs. Like an undirected graph, a directed graph consists of vertices and edges, but each edge is directed from one of its endpoints to the other endpoint. A directed pseudoforest is a directed graph in which each vertex has at most one outgoing edge; that is, it has outdegree at most one. A directed 1-forest – most commonly called a functional graph (see below), sometimes maximal directed pseudoforest – is a directed graph in which each vertex has outdegree exactly one.[8] If D is a directed pseudoforest, the undirected graph formed by removing the direction from each edge of D is an undirected pseudoforest.
Number of edges
Every pseudoforest on a set of n vertices has at most n edges, and every maximal pseudoforest on a set of n vertices has exactly n edges. Conversely, if a graph G has the property that, for every subset S of its vertices, the number of edges in the induced subgraph of S is at most the number of vertices in S, then G is a pseudoforest. 1-trees can be defined as connected graphs with equally many vertices and edges.[2]
Moving from individual graphs to graph families, if a family of graphs has the property that every subgraph of a graph in the family is also in the family, and every graph in the family has at most as many edges as vertices, then the family contains only pseudoforests. For instance, every subgraph of a thrackle (a graph drawn so that every pair of edges has one point of intersection) is also a thrackle, so Conway's conjecture that every thrackle has at most as many edges as vertices can be restated as saying that every thrackle is a pseudoforest. A more precise characterization is that, if the conjecture is true, then the thrackles are exactly the pseudoforests with no four-vertex cycle and at most one odd cycle.[9]
Streinu and Theran[10] generalize the sparsity conditions defining pseudoforests: they define a graph as being (k,l)-sparse if every nonempty subgraph with n vertices has at most kn − l edges, and (k,l)-tight if it is (k,l)-sparse and has exactly kn − l edges. Thus, the pseudoforests are the (1,0)-sparse graphs, and the maximal pseudoforests are the (1,0)-tight graphs. Several other important families of graphs may be defined from other values of k and l, and when l ≤ k the (k,l)-sparse graphs may be characterized as the graphs formed as the edge-disjoint union of l forests and k − l pseudoforests.[11]
Almost every sufficiently sparse random graph is pseudoforest.[12] That is, if c is a constant with 0 < c < 1/2, and Pc(n) is the probability that choosing uniformly at random among the n-vertex graphs with cn edges results in a pseudoforest, then Pc(n) tends to one in the limit for large n. However, for c > 1/2, almost every random graph with cn edges has a large component that is not unicyclic.
Enumeration
A graph is simple if it has no self-loops and no multiple edges with the same endpoints. The number of simple 1-trees with n labelled vertices is[13]
The values for n up to 300 can be found in sequence OEIS: A057500 of the On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences.
The number of maximal directed pseudoforests on n vertices, allowing self-loops, is nn, because for each vertex there are n possible endpoints for the outgoing edge. André Joyal used this fact to provide a bijective proof of Cayley's formula, that the number of undirected trees on n nodes is nn − 2, by finding a bijection between maximal directed pseudoforests and undirected trees with two distinguished nodes.[14] If self-loops are not allowed, the number of maximal directed pseudoforests is instead (n − 1)n.
Graphs of functions

Directed pseudoforests and endofunctions are in some sense mathematically equivalent. Any function ƒ from a set X to itself (that is, an endomorphism of X) can be interpreted as defining a directed pseudoforest which has an edge from x to y whenever ƒ(x) = y. The resulting directed pseudoforest is maximal, and may include self-loops whenever some value x has ƒ(x) = x. Alternatively, omitting the self-loops produces a non-maximal pseudoforest. In the other direction, any maximal directed pseudoforest determines a function ƒ such that ƒ(x) is the target of the edge that goes out from x, and any non-maximal directed pseudoforest can be made maximal by adding self-loops and then converted into a function in the same way. For this reason, maximal directed pseudoforests are sometimes called functional graphs.[2] Viewing a function as a functional graph provides a convenient language for describing properties that are not as easily described from the function-theoretic point of view; this technique is especially applicable to problems involving iterated functions, which correspond to paths in functional graphs.
Cycle detection, the problem of following a path in a functional graph to find a cycle in it, has applications in cryptography and computational number theory, as part of Pollard's rho algorithm for integer factorization and as a method for finding collisions in cryptographic hash functions. In these applications, ƒ is expected to behave randomly; Flajolet and Odlyzko[15] study the graph-theoretic properties of the functional graphs arising from randomly chosen mappings. In particular, a form of the birthday paradox implies that, in a random functional graph with n vertices, the path starting from a randomly selected vertex will typically loop back on itself to form a cycle within O(√n) steps. Konyagin et al. have made analytical and computational progress on graph statistics.[16]
Martin, Odlyzko, and Wolfram[17] investigate pseudoforests that model the dynamics of cellular automata. These functional graphs, which they call state transition diagrams, have one vertex for each possible configuration that the ensemble of cells of the automaton can be in, and an edge connecting each configuration to the configuration that follows it according to the automaton's rule. One can infer properties of the automaton from the structure of these diagrams, such as the number of components, length of limiting cycles, depth of the trees connecting non-limiting states to these cycles, or symmetries of the diagram. For instance, any vertex with no incoming edge corresponds to a Garden of Eden pattern and a vertex with a self-loop corresponds to a still life pattern.
Another early application of functional graphs is in the trains used to study Steiner triple systems.[18] The train of a triple system is a functional graph having a vertex for each possible triple of symbols; each triple pqr is mapped by ƒ to stu, where pqs, prt, and qru are the triples that belong to the triple system and contain the pairs pq, pr, and qr respectively. Trains have been shown to be a powerful invariant of triple systems although somewhat cumbersome to compute.
Bicircular matroid
A matroid is a mathematical structure in which certain sets of elements are defined to be independent, in such a way that the independent sets satisfy properties modeled after the properties of linear independence in a vector space. One of the standard examples of a matroid is the graphic matroid in which the independent sets are the sets of edges in forests of a graph; the matroid structure of forests is important in algorithms for computing the minimum spanning tree of the graph. Analogously, we may define matroids from pseudoforests.
For any graph G = (V,E), we may define a matroid on the edges of G, in which a set of edges is independent if and only if it forms a pseudoforest; this matroid is known as the bicircular matroid (or bicycle matroid) of G.[19][20] The smallest dependent sets for this matroid are the minimal connected subgraphs of G that have more than one cycle, and these subgraphs are sometimes called bicycles. There are three possible types of bicycle: a theta graph has two vertices that are connected by three internally disjoint paths, a figure 8 graph consists of two cycles sharing a single vertex, and a handcuff graph is formed by two disjoint cycles connected by a path.[21] A graph is a pseudoforest if and only if it does not contain a bicycle as a subgraph. [10]
Forbidden minors
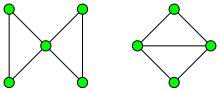
Forming a minor of a pseudoforest by contracting some of its edges and deleting others produces another pseudoforest. Therefore, the family of pseudoforests is closed under minors, and the Robertson–Seymour theorem implies that pseudoforests can be characterized in terms of a finite set of forbidden minors, analogously to Wagner's theorem characterizing the planar graphs as the graphs having neither the complete graph K5 nor the complete bipartite graph K3,3 as minors. As discussed above, any non-pseudoforest graph contains as a subgraph a handcuff, figure 8, or theta graph; any handcuff or figure 8 graph may be contracted to form a butterfly graph (five-vertex figure 8), and any theta graph may be contracted to form a diamond graph (four-vertex theta graph),[22] so any non-pseudoforest contains either a butterfly or a diamond as a minor, and these are the only minor-minimal non-pseudoforest graphs. Thus, a graph is a pseudoforest if and only if it does not have the butterfly or the diamond as a minor. If one forbids only the diamond but not the butterfly, the resulting larger graph family consists of the cactus graphs and disjoint unions of multiple cactus graphs.[23]
More simply, if multigraphs with self-loops are considered, there is only one forbidden minor, a vertex with two loops.
Algorithms
An early algorithmic use of pseudoforests involves the network simplex algorithm and its application to generalized flow problems modeling the conversion between commodities of different types.[3][24] In these problems, one is given as input a flow network in which the vertices model each commodity and the edges model allowable conversions between one commodity and another. Each edge is marked with a capacity (how much of a commodity can be converted per unit time), a flow multiplier (the conversion rate between commodities), and a cost (how much loss or, if negative, profit is incurred per unit of conversion). The task is to determine how much of each commodity to convert via each edge of the flow network, in order to minimize cost or maximize profit, while obeying the capacity constraints and not allowing commodities of any type to accumulate unused. This type of problem can be formulated as a linear program, and solved using the simplex algorithm. The intermediate solutions arising from this algorithm, as well as the eventual optimal solution, have a special structure: each edge in the input network is either unused or used to its full capacity, except for a subset of the edges, forming a spanning pseudoforest of the input network, for which the flow amounts may lie between zero and the full capacity. In this application, unicyclic graphs are also sometimes called augmented trees and maximal pseudoforests are also sometimes called augmented forests.[24]
The minimum spanning pseudoforest problem involves finding a spanning pseudoforest of minimum weight in a larger edge-weighted graph G. Due to the matroid structure of pseudoforests, minimum-weight maximal pseudoforests may be found by greedy algorithms similar to those for the minimum spanning tree problem. However, Gabow and Tarjan found a more efficient linear-time approach in this case.[2]
The pseudoarboricity of a graph G is defined by analogy to the arboricity as the minimum number of pseudoforests into which its edges can be partitioned; equivalently, it is the minimum k such that G is (k,0)-sparse, or the minimum k such that the edges of G can be oriented to form a directed graph with outdegree at most k. Due to the matroid structure of pseudoforests, the pseudoarboricity may be computed in polynomial time.[25]
A random bipartite graph with n vertices on each side of its bipartition, and with cn edges chosen independently at random from each of the n2 possible pairs of vertices, is a pseudoforest with high probability whenever c is a constant strictly less than one. This fact plays a key role in the analysis of cuckoo hashing, a data structure for looking up key-value pairs by looking in one of two hash tables at locations determined from the key: one can form a graph, the "cuckoo graph", whose vertices correspond to hash table locations and whose edges link the two locations at which one of the keys might be found, and the cuckoo hashing algorithm succeeds in finding locations for all of its keys if and only if the cuckoo graph is a pseudoforest.[26]
Pseudoforests also play a key role in parallel algorithms for graph coloring and related problems.[27]
Notes
- ^ a b The kind of undirected graph considered here is often called a multigraph or pseudograph, to distinguish it from a simple graph.
- ^ a b c d Gabow & Tarjan (1988).
- ^ a b Dantzig (1963).
- ^ See the linked articles and the references therein for these definitions.
- ^ This is the definition used, e.g., by Gabow & Westermann (1992).
- ^ This is the definition in Gabow & Tarjan (1988).
- ^ See, e.g., the proof of Lemma 4 in Àlvarez, Blesa & Serna (2002).
- ^ Kruskal, Rudolph & Snir (1990) instead use the opposite definition, in which each vertex has indegree one; the resulting graphs, which they call unicycular, are the transposes of the graphs considered here.
- ^ Woodall (1969); Lovász, Pach & Szegedy (1997).
- ^ a b Streinu & Theran (2009).
- ^ Whiteley (1988).
- ^ Bollobás (1985). See especially Corollary 24, p.120, for a bound on the number of vertices belonging to unicyclic components in a random graph, and Corollary 19, p.113, for a bound on the number of distinct labeled unicyclic graphs.
- ^ Riddell (1951); see OEIS: A057500 in the On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences.
- ^ Aigner & Ziegler (1998).
- ^ Flajolet & Odlyzko (1990).
- ^ Konyagin et al. (2010).
- ^ Martin, Odlyzko & Wolfram (1984).
- ^ White (1913); Colbourn, Colbourn & Rosenbaum (1982); Stinson (1983).
- ^ Simoes-Pereira (1972).
- ^ Matthews (1977).
- ^ Glossary of Signed and Gain Graphs and Allied Areas
- ^ For this terminology, see the list of small graphs from the Information System on Graph Class Inclusions. However, butterfly graph may also refer to a different family of graphs related to hypercubes, and the five-vertex figure 8 is sometimes instead called a bowtie graph.
- ^ El-Mallah & Colbourn (1988).
- ^ a b Ahuja, Magnanti & Orlin (1993).
- ^ Gabow & Westermann (1992). See also the faster approximation schemes of Kowalik (2006).
- ^ Kutzelnigg (2006).
- ^ Goldberg, Plotkin & Shannon (1988); Kruskal, Rudolph & Snir (1990).
References
- Ahuja, Ravindra K.; Magnanti, Thomas L.; Orlin, James B. (1993), Network Flows: Theory, Algorithms and Applications, Prentice Hall, ISBN 0-13-617549-X.
- Aigner, Martin; Ziegler, Günter M. (1998), Proofs from THE BOOK, Springer-Verlag, pp. 141–146.
- Àlvarez, Carme; Blesa, Maria; Serna, Maria (2002), "Universal stability of undirected graphs in the adversarial queueing model", Proc. 14th ACM Symposium on Parallel Algorithms and Architectures, pp. 183–197, doi:10.1145/564870.564903, hdl:2117/97553, S2CID 14384161.
- Bollobás, Béla (1985), Random Graphs, Academic Press.
- Colbourn, Marlene J.; Colbourn, Charles J.; Rosenbaum, Wilf L. (1982), "Trains: an invariant for Steiner triple systems", Ars Combinatoria, 13: 149–162, MR 0666934.
- Dantzig, G. B. (1963), Linear Programming and Extensions, Princeton University Press.
- El-Mallah, Ehab; Colbourn, Charles J. (1988), "The complexity of some edge deletion problems", IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems, 35 (3): 354–362, doi:10.1109/31.1748.
- Flajolet, P.; Odlyzko, A. (1990), "Random mapping statistics", Advances in Cryptology – EUROCRYPT '89: Workshop on the Theory and Application of Cryptographic Techniques, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 434, Springer-Verlag, pp. 329–354.
- Gabow, H. N.; Tarjan, R. E. (1988), "A linear-time algorithm for finding a minimum spanning pseudoforest", Information Processing Letters, 27 (5): 259–263, doi:10.1016/0020-0190(88)90089-0.
- Gabow, H. N.; Westermann, H. H. (1992), "Forests, frames, and games: Algorithms for matroid sums and applications", Algorithmica, 7 (1): 465–497, doi:10.1007/BF01758774, S2CID 40358357.
- Goldberg, A. V.; Plotkin, S. A.; Shannon, G. E. (1988), "Parallel symmetry-breaking in sparse graphs", SIAM Journal on Discrete Mathematics, 1 (4): 434–446, doi:10.1137/0401044.
- Konyagin, Sergei; Luca, Florian; Mans, Bernard; Mathieson, Luke; Shparlinski, Igor E. (2010), Functional Graphs of Polynomials over Finite Fields
- Kowalik, Ł. (2006), "Approximation Scheme for Lowest Outdegree Orientation and Graph Density Measures", in Asano, Tetsuo (ed.), Proceedings of the International Symposium on Algorithms and Computation, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 4288, Springer-Verlag, pp. 557–566, doi:10.1007/11940128, ISBN 978-3-540-49694-6.
- Kruskal, Clyde P.; Rudolph, Larry; Snir, Marc (1990), "Efficient parallel algorithms for graph problems", Algorithmica, 5 (1): 43–64, doi:10.1007/BF01840376, S2CID 753980.
- Picard, Jean-Claude; Queyranne, Maurice (1982), "A network flow solution to some nonlinear 0–1 programming problems, with applications to graph theory", Networks, 12 (2): 141–159, doi:10.1002/net.3230120206, MR 0670021.
- Kutzelnigg, Reinhard (2006), "Bipartite random graphs and cuckoo hashing", Fourth Colloquium on Mathematics and Computer Science, Discrete Mathematics and Theoretical Computer Science, vol. AG, pp. 403–406.
- Lovász, L.; Pach, J.; Szegedy, M. (1997), "On Conway's thrackle conjecture", Discrete and Computational Geometry, 18 (4): 369–376, doi:10.1007/PL00009322.
- Martin, O.; Odlyzko, A. M.; Wolfram, S. (1984), "Algebraic properties of cellular automata", Communications in Mathematical Physics, 93 (2): 219–258, Bibcode:1984CMaPh..93..219M, doi:10.1007/BF01223745, S2CID 6900060.
- Matthews, L. R. (1977), "Bicircular matroids", The Quarterly Journal of Mathematics, Second Series, 28 (110): 213–227, doi:10.1093/qmath/28.2.213, MR 0505702.
- Riddell, R. J. (1951), Contributions to the Theory of Condensation, Ph.D. thesis, Ann Arbor: University of Michigan, Bibcode:1951PhDT........20R.
- Simoes-Pereira, J. M. S. (1972), "On subgraphs as matroid cells", Mathematische Zeitschrift, 127 (4): 315–322, doi:10.1007/BF01111390.
- Stinson, D. R. (1983), "A comparison of two invariants for Steiner triple systems: fragments and trains", Ars Combinatoria, 16: 69–76, MR 0734047.
- Streinu, I.; Theran, L. (2009), "Sparsity-certifying Graph Decompositions", Graphs and Combinatorics, 25 (2): 219, arXiv:0704.0002, doi:10.1007/s00373-008-0834-4, S2CID 15877017.
- White, H. S. (1913), "Triple-systems as transformations, and their paths among triads", Transactions of the American Mathematical Society, 14 (1), American Mathematical Society: 6–13, doi:10.2307/1988765, JSTOR 1988765.
- Whiteley, W. (1988), "The union of matroids and the rigidity of frameworks", SIAM Journal on Discrete Mathematics, 1 (2): 237–255, doi:10.1137/0401025.
- Woodall, D. R. (1969), "Thrackles and deadlock", in Welsh, D. J. A. (ed.), Combinatorial Mathematics and Its Applications, Academic Press, pp. 335–348.
External links

