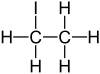
Ethyl iodide
 | |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Iodoethane[1] | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 505934 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.758 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C2H5I | |||
| Molar mass | 155.966 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colourless liquid | ||
| Density | 1.940 g mL−1 | ||
| Melting point | −111.10 °C; −167.98 °F; 162.05 K | ||
| Boiling point | 71.5 to 73.3 °C; 160.6 to 163.8 °F; 344.6 to 346.4 K | ||
| 4 g L−1 (at 20 °C) | |||
| Solubility in ethanol | Miscible | ||
| Solubility in diethyl ether | Miscible | ||
| log P | 2.119 | ||
| Vapor pressure | 17.7 kPa | ||
Henry's law
constant (kH) |
1.8 μmol Pa−1 kg−1 | ||
| -69.7·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.513–1.514 | ||
| Viscosity | 5.925 mPa s (at 20 °C) | ||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Heat capacity (C)
|
109.7 J K−1 mol−1 | ||
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−39.9–−38.3 kJ mol−1 | ||
Std enthalpy of
combustion (ΔcH⦵298) |
−1.4629–−1.4621 MJ mol−1 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
 
| |||
| Danger | |||
| H302, H315, H317, H319, H334, H335 | |||
| P261, P280, P305+P351+P338, P342+P311 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | 72 °C (162 °F; 345 K) | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose)
|
330 g m−3 (oral, rat) | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related iodoalkanes
|
|||
Related compounds
|
|||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Ethyl iodide (also iodoethane) is a colorless flammable chemical compound. It has the chemical formula C2H5I and is prepared by heating ethanol with iodine and phosphorus.[2] On contact with air, especially on the effect of light, it decomposes and turns yellow or reddish from dissolved iodine.
It may also be prepared by the reaction between hydroiodic acid and ethanol, typically by generating the hydroiodic acid in situ via an iodide salt (such as sodium iodide) and an acid (such as sulfuric acid), after which the ethyl iodide is distilled off. Ethyl iodide should be stored in the presence of copper powder to avoid rapid decomposition, though even with this method samples do not last more than 1 year.

Because iodide is a good leaving group, ethyl iodide is an excellent ethylating agent. It is also used as the hydrogen radical promoter.
Production
[edit]Ethyl iodide is prepared by using red phosphorus, absolute ethanol and iodine. The iodine dissolves in the ethanol, where it reacts with the solid phosphorus to form phosphorus triiodide.[3] During this process, the temperature is controlled.
- 3 C2H5OH + PI3 → 3 C2H5I + H3PO3
The crude product is purified by distillation.
References
[edit]- ^ "iodoethane - Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 26 March 2005. Identification and Related Records. Retrieved 29 February 2012.
- ^ Merck Index of Chemicals and Drugs, 9th ed., monograph 3753
- ^ Csámpai, A; Láng, E; Majer, Zs; Orosz, Gy; Rábai, J; Ruff, F; Schlosser, G; Szabó, D; Vass, E (2012). Szerves Kémiai Praktikum. Eötvös kiadó. p. 274. ISBN 978-963-312-129-0.