Portal:Politics
| Main | Topics and categories | Tasks and projects |
The Politics portal
Politics (from Ancient Greek πολιτικά (politiká) 'affairs of the cities') is the set of activities that are associated with making decisions in groups, or other forms of power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of status or resources. The branch of social science that studies politics and government is referred to as political science.
Politics may be used positively in the context of a "political solution" which is compromising and non-violent, or descriptively as "the art or science of government", but the word often also carries a negative connotation. The concept has been defined in various ways, and different approaches have fundamentally differing views on whether it should be used extensively or in a limited way, empirically or normatively, and on whether conflict or co-operation is more essential to it.
A variety of methods are deployed in politics, which include promoting one's own political views among people, negotiation with other political subjects, making laws, and exercising internal and external force, including warfare against adversaries. Politics is exercised on a wide range of social levels, from clans and tribes of traditional societies, through modern local governments, companies and institutions up to sovereign states, to the international level.
In modern nation states, people often form political parties to represent their ideas. Members of a party often agree to take the same position on many issues and agree to support the same changes to law and the same leaders. An election is usually a competition between different parties.
A political system is a framework which defines acceptable political methods within a society. The history of political thought can be traced back to early antiquity, with seminal works such as Plato's Republic, Aristotle's Politics, Confucius's political manuscripts and Chanakya's Arthashastra. (Full article...)
Selected article
The College Republican National Committee is a national organization for college and university students who support the Republican Party of the United States. The organization is known as an active recruiting tool for the Republican Party and has produced many prominent Republican and conservative activists and introduced more party members to the Republican party than any other organization in the nation. The College Republicans were founded as the American Republican College League on May 17, 1892, at the University of Michigan. The organization was spear-headed by law student James Francis Burke, who would later serve as a Congressman from Pennsylvania. The inaugural meeting was attended by over 1,000 students from across the county, from Stanford University in the west to Harvard University in the east. Contemporary politicians also attended the meeting, including Judge John M. Thurston, Senator Russell A. Alger, Congressman J. Sloat Fassett, Congressman W. E. Mason, John M. Langston, and Abraham Lincoln's successor in the Illinois State Legislature, A. J. Lester. Then-Governor of Ohio William McKinley gave a rousing keynote speech.
Featured picture

Andrew Gregg Curtin (1817–1894) was a U.S. lawyer and politician. He served as the 15th Governor of Pennsylvania during the American Civil War. During the Civil War, Curtin organized the Pennsylvania reserves into combat units, and oversaw the construction of the first Union military camp for training militia. After the Battle of Gettysburg, Governor Curtin was the principal force behind the establishment of the National Cemetery there. After serving two terms as governor, Curtin was appointed ambassador to Russia by Ulysses S. Grant, and he later served in the House of Representatives from 1881 until 1887.
In Missouri, the county level of government comes between those of the city and the state. Its primary responsibilities include maintaining roads, providing security, prosecuting criminals, and collecting taxes. Elected officials at this level include a sheriff, prosecuting attorney, and assessor. (Full article...)

The Minister of Transport (Norwegian: Samferdelsministeren) is a Councillor of State and Chief of the Norwegian Ministry of Transport. The post has been held by Jon-Ivar Nygård of the Labour Party since 2021. The ministry is responsible for policy and public operations within postal services, telecommunications, civil aviation, public roads, rail transport and public transport, including ferry services that are part of national roads and coastal transport infrastructure. The ministry has seven agencies and four limited companies, including the airport operator Avinor, railway operator Vy, the Norwegian National Rail Administration, the Norwegian Public Roads Administration and Norway Post. There are also inspectorates and authorities related to accident investigation, civil aviation, and railways.
The position was created with the ministry on 22 February 1946, when Nils Langhelle (Labour) was appointed. The ministry and minister position were split out from the Ministry of Labour. Twenty-eight people have held the position, representing six parties. Sixteen people have represented the Labour Party, five the Centre Party, two each the Christian Democratic Party, the Conservative Party and the Liberal Party and one for the Progress Party. The longest-sitting minister is Kjell Opseth (Labour) who sat a week short of six years. Lars Leiro (Centre) sat for only four weeks, giving him the shortest tenure. He both succeeded and preceded Trygve Bratteli, the only person to have held the position twice and the only officeholder to later become Prime Minister. (Full article...)
Within Rhode Island, Washington County is colloquially referred to as South County. (Full article...)
The governor of Alabama is the head of government of the U.S. state of Alabama. The governor is the head of the executive branch of Alabama's state government and is charged with enforcing state laws.
There have officially been 54 governors of the state of Alabama; this official numbering skips acting and military governors. The first governor, William Wyatt Bibb, served as the only governor of the Alabama Territory. Five people have served as acting governor, bringing the total number of people serving as governor to 59, spread over 63 distinct terms. Four governors have served multiple non-consecutive terms: Bibb Graves, Jim Folsom, and Fob James each served two, and George Wallace served three non-consecutive periods. Officially, these non-consecutive terms are numbered only with the number of their first term. William D. Jelks also served non-consecutive terms, but his first term was in an acting capacity. (Full article...)

British Columbia is the third-most populous province in Canada, with 5,000,879 residents as of 2021, and is the second-largest in land area, at 920,687 km2 (355,479 sq mi). British Columbia's 161 municipalities cover only 11 percent of the province's land mass yet are home to 89 percent of its population. A municipality is a local government incorporated by the province allowing a community to govern itself and to provide and regulate local services. These services typically include, but are not limited to, the provision of drinking water, sewers, roads, fire protection, street lights, garbage/recycling collection, land use planning, building inspection, and parks.
Within their limited jurisdictions, municipalities are autonomous, responsible and accountable to their citizens and to the province. Their powers and responsibilities are regulated through the Local Government Act, the Community Charter, and, in the case of Vancouver, the Vancouver Charter. They have the power of a natural person, the power to expropriate, and the power to establish and enforce bylaws. They are able to raise funds through property taxes and user fees, and borrow a limited amount through the Municipal Finance Authority of British Columbia to pay for capital costs. (Full article...)

The prime minister of the United Kingdom is the principal minister of the crown of His Majesty's Government, and the head of the British Cabinet.
There is no specific date for when the office of prime minister first appeared, as the role was not created but rather evolved over time through a merger of duties. The term was regularly, if informally, used by Robert Walpole by the 1730s. It was used in the House of Commons as early as 1805, and it was certainly in parliamentary use by the 1880s, although did not become the official title until 1905, when Arthur Balfour was prime minister. (Full article...)
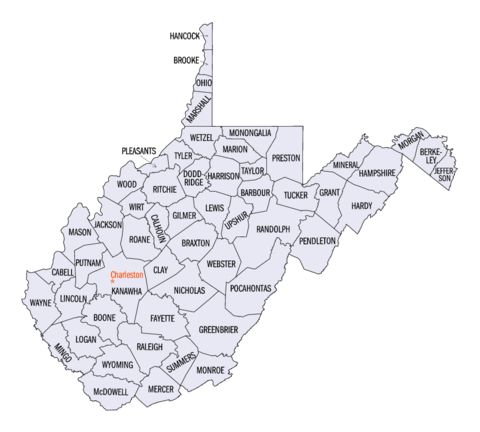
The U.S. state of West Virginia has 55 counties. Fifty of them existed at the time of the Wheeling Convention in 1861, during the American Civil War, when those counties seceded from the Commonwealth of Virginia to form the new state of West Virginia. West Virginia was admitted as a separate state of the United States on June 20, 1863. Five additional counties (Grant, Mineral, Lincoln, Summers, and Mingo) were formed from the original counties in the decades following admission.
After the Civil War, Berkeley County and Jefferson County, the two easternmost counties of West Virginia, refused to recognize their inclusion in the state, and the Virginia General Assembly passed legislation attempting to reclaim them. In March 1866, the United States Congress passed a joint mandate assenting to their inclusion in the new state, and the Supreme Court of the United States confirmed this outcome in the case of Virginia v. West Virginia (1871). (Full article...)
The governor of Ohio is the head of government of Ohio and the commander-in-chief of the U.S. state's military forces. The officeholder has a duty to enforce state laws, the power to either approve or veto bills passed by the Ohio General Assembly, the power to convene the legislature and the power to grant pardons, except in cases of treason and impeachment.
There have been 64 governors of Ohio, serving 70 distinct terms. The longest term was held by Jim Rhodes, who was elected four times and served just under sixteen years in two non-consecutive periods of two terms each (1963–1971 and 1975–1983). The shortest terms were held by John William Brown and Nancy Hollister, who each served for only 11 days after the governors preceding them resigned in order to begin the terms to which they had been elected in the United States Senate; the shortest-serving elected governor was John M. Pattison, who died in office five months into his term. (Full article...)

The 23rd and current prime minister is Justin Trudeau, who assumed office on 4 November 2015. There are currently five living former prime ministers. The most recent former prime minister to die was Brian Mulroney, on 29 February 2024. (Full article...)
The list includes all those initially elected to the Storting. Between 19 October 2005 and 30 September 2009, the Parliament of Norway consisted of 169 members from 7 parties and 19 constituencies, elected during the 2005 Norwegian parliamentary election on 11 and 12 September. The Red-Green Coalition, consisting of the Labour Party (61 members), the Socialist Left Party (15 members) and the Centre Party (11 members) gained a majority and created Stoltenberg's Second Cabinet. The majority cabinet lasted the entire session and was reelected in the 2009 election. The opposition consisted of four parties: the Progress Party (38 members), the Conservative Party (23 members), the Christian Democratic Party (11 members) and the Liberal Party (10 members).
Members of the Parliament of Norway are elected based on party-list proportional representation in plural member constituencies. This means that representatives from different political parties are elected from 19 constituencies, which are identical to the 19 counties. The electorate does not vote for individuals but rather for party lists, with a ranked list of candidates nominated by the party. This means that the person on top of the list will get the seat unless the voter alters the ballot. Parties may nominate candidates from outside their own constituency, and even Norwegian citizens currently living abroad. (Full article...)
This article lists the heads of state of the Central African Republic. There have been seven heads of state of the Central African Republic and the Central African Empire since independence was obtained from France on 13 August 1960. This list includes not only those persons who were sworn into office as President of the Central African Republic but also those who served as de facto heads of state.
Jean-Bédel Bokassa served as a de facto head of state (and also reigned as emperor from 1976 to 1979), while David Dacko (who served as de facto head of state from 1979 to 1981), André Kolingba, Ange-Félix Patassé, and François Bozizé were elected into office at some point during their tenure. To date, Kolingba is the only former head of state of the Central African Republic to voluntarily step down from the office through a democratic process, following the 1993 general election. (Full article...)
Selected quote
Selected biography
Edmund Burke PC (12 January [NS] 1729– 9 July 1797) was an Irish statesman, author, orator, political theorist and philosopher who, after moving to England, served for many years in the House of Commons of Great Britain as a member of the Whig party. He is mainly remembered for his support of the cause of the American Revolutionaries, and for his later opposition to the French Revolution. The latter led to his becoming the leading figure within the conservative faction of the Whig party, which he dubbed the "Old Whigs", in opposition to the pro–French Revolution "New Whigs", led by Charles James Fox. Burke was praised by both conservatives and liberals in the 19th century. Since the 20th century, he has generally been viewed as the philosophical founder of modern Conservatism, as well as a representative of classical liberalism.
Did you know (auto-generated) -

- ... that the ideas of Albert Schädler became the founding ideas of the Progressive Citizens' Party, though he himself was opposed to the formation of political parties?
- ... that Crossing a Line compares Palestinian political expression on either side of the Green Line between Israel and the occupied Palestinian territories?
- ... that although Uzun-Hajji and Najmuddin of Gotzo were originally political allies, they later fought on opposing sides of the Russian Civil War?
- ... that Dave Barrow quit municipal politics to work at his family's insurance brokerage before becoming mayor of Richmond Hill?
- ... that Checheyigen's political acumen ensured that her family became one of the most powerful in the Mongol Empire?
- ... that Patricia Grace did not intend for her novel Potiki, about the impact of land development on an indigenous community, to be seen as political?
More did you know...
- ...that the Voting Rights Act of 1965 banned literacy tests as a voting qualification in the U.S.?
- ...that four member states of the European Union have de jure opt-outs and do not participate fully in all common policies?
- ...that Cornelius, Oregon is named after pioneer Thomas R. Cornelius, who served in both the Territorial and State legislatures?
- ...that the Society of the Friends of Peasants had significant influence on the Danish Constitution of 1849?
- ...that depending on a time and place, the same social movement may be revolutionary or not?
- ...that Roman embassies to China are reported in Chinese historical accounts from as early as 166?
In this month
- January 1, 1912 – The Republic of China was proclaimed.
- January 4, 2011 – Tunisian street vendor Mohamed Bouazizi dies after setting himself on fire a month earlier, sparking anti-government protests in Tunisia and later other Arab nations. These protests become known collectively as the Arab Spring.
- January 5, 1912 – Vladimir Lenin and the Bolshevik Party break away from the rest of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party.
- January 12, 1729 – Edmund Burke was born, considered to be the philosophical founder of modern conservatism.
- January 25, 2006 – Hamas wins a victory in the Palestinian legislative election, taking 76 of the 132 seats.
News and Current events
- August 11: 4 local government areas in New South Wales, Australia locked down after COVID-19 case
- August 11: Australia: AstraZeneca vaccine access expanded by Victorian government
- August 1: Australia: Victorian lockdown lifted
- July 29: Tunisia's president dismisses prime minister, suspends parliament
- July 25: Australia: Wikinews interviews Reg Kidd, mayor of the City of Orange, about COVID-19 lockdown and local government
- July 23: South Australia enters week-long lockdown to contain COVID-19 Delta variant spread
- July 21: Technological University Dublin senior lecturer Dr Lorcan Sirr speaks to Wikinews on housing market in Ireland
- July 21: Three rural councils in New South Wales, Australia enter 7-day lockdown
- July 21: Australia: Victoria lockdown extended by a week with 85 active cases recorded
- July 15: California governor signs new state budget, eligible Californians to get stimulus payments
Topics and categories
General images
Related portals
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus