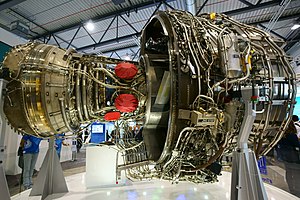
Rolls-Royce Trent XWB
| Trent XWB | |
|---|---|
| |
| Type | Turbofan |
| National origin | United Kingdom |
| Manufacturer | Rolls-Royce Holdings |
| First run | 14 June 2010[1] |
| Major applications | Airbus A350 |
| Developed from | Rolls-Royce Trent |
The Rolls-Royce Trent XWB is a high-bypass turbofan produced by Rolls-Royce Holdings. In July 2006, the Trent XWB was selected to exclusively power the Airbus A350.[2] The first engine was run on 14 June 2010,[3] it first flew on an A380 testbed on 18 February 2012,[4] was certified in early 2013,[5] and first flew on an A350 on 14 June 2013.[6] It had its first in-flight shutdown on 11 September 2018 as the fleet accumulated 2.2 million flight hours.[7] It keeps the characteristic three-shaft layout of the Rolls-Royce Trent, with a 3 m (120 in) fan, an IP and HP spool.[8] The 84,200–97,000 lbf (375–431 kN) engine has a 9.6:1 bypass ratio and a 50:1 pressure ratio.[9] It is the most powerful member of the Trent family.[10]
Development
[edit]By 2004 Airbus had been facing pressure from customers to develop a competitor to the Boeing 787 Dreamliner, so in October 2005 launched the A350, at the time an improved A330. Rolls-Royce initially offered a conventional bleed air engine variant of the Trent 1000 with a throttle-push to 75,000 lbf (330 kN) static thrust, the Trent 1700.[11] In 2006, after a review of the Airbus A350, Rolls-Royce reached an agreement to supply all versions of the aircraft with a brand-new Trent XWB variant with 75,000 to 95,000 lbf (330 to 420 kN) of thrust.[2]
Before the December 2008 design freeze, Airbus established that the A350's empty weight was 2.2 t (4,900 lb) greater than the 133.5 t (294,000 lb) target. Due to this, the MTOW was increased by 3 t (6,600 lb) in order to maintain the payload and range capability. As a further result, Rolls-Royce announced that the nominal engine thrusts were increased slightly, each variant receiving an additional 1,000 lbf (4 kN) thrust. A350 programme chief Didier Evrard was quoted as saying that the change had a "very marginal" impact on fuel consumption.[12] This was then revised again in 2011, and the engines for the largest A350 were uprated to 97,000 lbf (430 kN) to meet new performance requirements, and better compete with the Boeing 777-300ER.[13]
Testing
[edit]
The first engine test on a static test-bed was made on 14 June 2010.[3] On 18 February 2012, Airbus announced that the Trent XWB had successfully made its maiden flight aboard Airbus’ dedicated Airbus A380 flying test bed.[4] By October, the first engine was expected to enter service in 2014,[14] and certification for the early engine variants was achieved in early 2013.[5] The first flight of the Trent XWB powering the Airbus A350 XWB took place on 14 June 2013.[6]
On 15 May 2014 Rolls-Royce delivered the first production 84,000 lbf (370 kN) thrust Trent XWB engines intended for the first Airbus A350 XWB to enter service with Qatar Airways[15] - final assembly of these production engines had started in February 2014.[16] On 15 July 2014 Rolls-Royce announced the first run of the Trent XWB-97 powerplant with 97,000 lbf (430 kN) thrust for the Airbus A350-1000.[17]
Operations
[edit]
On 26 July 2017, Airbus delivered the 100th A350, on track for 10 per month by 2018 end, and over the first 30 months most engine removals have been to stagger the on-wing life of a particular aircraft or to collect in-service data; nine in ten of the Trent XWBs have a long-term service agreements with Rolls, which has designated seven shops as MRO providers: its Derby facility, its joint ventures with HAECO, SIAEC, N3 Engine Overhaul Services and independents Delta TechOps, Mubadala and Air France Industries-KLM.[18] It passed 1 million flight hours in October 2017 without any in-flight disruptions and with a dispatch reliability of 99.4%.[19]
By February 2018, the Trent XWB has completed 1.3 million flight hours with a 99.9% dispatch reliability.[20] It took two years to reach one million flying hours and nine months for the second million by July 2018, as 500 were delivered; at that time, it had a 99.9% dispatch reliability and had had no in-flight shutdown.[21] As the fleet accumulated 2.2 million flight hours and the leading engine has operated 3,500 cycles, an Iberia A350-900 delivered at the end of July diverted to Boston after an inflight shutdown at 41,000 ft (12,000 m) on 11 September 2018 flight from New York to Madrid, apparently due to slight secondary damage on variable stator vanes.[7]
In 2019, the unit losses on the XWB-84 were reduced by over 20%, as Rolls-Royce expected break-even by the end of 2020, while fleet-leading engines had flown over 22,000h without a shop visit.[22] The higher-thrust XWB-97 for the A350-1000 remains a loss-maker, and could stay that way as extending time-on-wing is more profitable.[23]
At the 2023 Dubai Airshow, the president of the Emirates, Tim Clark, said the A350-1000's engine, Trent XWB-97, would offer only a quarter of the time between maintenance visits compared to their needs.[24][25] Citigroup analysts claim these comments form part of the airline's "commercial negotiation" tactics involving prices or guarantees. They claim the higher thrust 97-XWB would be expected to run at higher temperatures with faster wear, particularly in hot and sandy climates, noting Qatar Airways operates the Trent XWB-97 without major issues.[26] Rolls-Royce was later reported to be working with Emirates to improve durability in "hot and sandy conditions" [27]
On 2 September 2024, a Trent XWB powered Cathay Pacific A350-1000 suffered an in-flight engine fire. The aircraft was able to land safely, and the airline conducted an inspection of all 48 of its A350s, finding several with a defect similar to the incident aircraft, said to be a damaged flexible fuel line.[28] The European Union Aviation Safety Agency announced that it would require a one-time inspection of Trent XWB engines as a result of the incident.[29]
Design
[edit]
The Trent XWB is an axial flow, high bypass turbofan keeping the characteristic coaxial three-shaft architecture of the Rolls-Royce Trent. The 3 m (120 in) fan is driven by a 6-stage turbine, an 8-stage IP compressor is powered by a 2-stage turbine and a 6-stage HP compressor is turned by a single stage turbine, rotating in the opposite direction of the two others. The annular combustor has 20 fuel spray nozzles and the engine is controlled by a dual-channel FADEC.[8] It features a 2-stage IP turbine rather than a single stage from previous Trent engines designs.[30]
The 97,000 lbf (430 kN) engine version for the A350-1000 maintains the same 3m fan size and a 5% larger core. The additional thrust will require the fan to run 6% faster which will require strengthening to withstand the increased fan-blade forces produced.[30] It has thicker titanium fan blades and a stronger fan casing and takes advantage of technologies developed through the European Environmentally Friendly Engine (EFE) research programme. Its core operating temperature capability will be increased.[31]
Orders
[edit]On 18 June 2007, Rolls-Royce announced that it had signed a contract with Qatar Airways worth US$5.6 billion at list prices, to power 80 Airbus A350 XWBs: US$35 million each.[32]
A large contract with Emirates to power 70 aircraft with Trent XWBs was announced on 11 November 2007, but never filled. The announced contract concerned 50 A350-900 and 20 A350-1000 aircraft, with a further 50 option rights. Due to be delivered from 2014, the Emirates order was potentially worth up to $8.4 billion at list prices, including options.[33] However, on 11 June 2014, Airbus announced that Emirates Airline had decided to cancel its order of 70 A350 XWB aircraft.[34]
More than 1,500 engines had been sold by July 2015 to 40 customers. Rolls-Royce offered its maintenance programme to Vietnam Airlines for £340 million for 14 airplanes, or £12.1 million per engine.[35]
On 15 December 2023, Rolls-Royce announced that Turkish Airlines had ordered 100 XWB-84 and 40 XWB-97 engines. In addition to the airline's existing 66 Trent engines, resulting in a total of nearly 210, the airline has become the largest operator of Trent XWB engines.[36]
Variants
[edit]| Designation | Certified | Net Take-off Rating | Net Maximum Continuous |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trent XWB-75 | 7 February 2013 | 74,200 lbf (330 kN) | 66,600 lbf (296 kN) |
| Trent XWB-79 | 7 February 2013 | 78,900 lbf (351 kN) | 71,400 lbf (318 kN) |
| Trent XWB-79B | 7 February 2013 | 78,900 lbf (351 kN) | 71,400 lbf (318 kN) |
| Trent XWB-84 | 7 February 2013 | 84,200 lbf (375 kN) | 71,400 lbf (318 kN) |
| Trent XWB-97 | 31 August 2017 | 97,000 lbf (430 kN) | 83,100 lbf (370 kN) |
Specifications
[edit]
| Variant | -84 | -97 |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Three-shaft, high bypass ratio, axial flow, turbofan | |
| Fan | 1-stage, 3.00 m / 118" diameter, 22 blades[9][a] | |
| Compressor | 8-stage IP, 6-stage HP | |
| Combustor | annular, 20 fuel spray nozzles | |
| Turbine | single stage HP, 2-stage IP, 6-stage LP[b] | |
| Length | 5,812 mm / 228.8 in[c] | |
| Dry weight | 7,277 kg (16,043 lb) | 7,550 kg (16,640 lb) |
| Takeoff thrust | 84,200 lbf (375 kN) | 97,000 lbf (431 kN) |
| TSFC (cruise) | 0.478 lb/(lbf⋅h) (13.5 g/(kN⋅s)) | |
| Specific impulse | 7,530 s | |
| Rotor speed (RPM) | LP: 2700, IP: 8200, HP: 12600 | |
| Bypass ratio | 9.6:1[9] | |
| Pressure ratio | 50:1[9] | |
| Thrust-to-weight ratio | 5.25 | 5.82 |
| Air mass flow | 1,436 kg/s / 3,166 lb/s[30] | |
See also
[edit]Related development
Comparable engines
Related lists
Notes
[edit]- ^ swept fan,[30] low hub:tip ratio[verification needed]
- ^ one more IP stage than previous Trents, air-cooled HPT[30] and IPT, uncooled LPT[verification needed]
- ^ tip of spinner to rear of Cold Nozzle
References
[edit]- ^ "PICTURE: A350's Trent XWB engine runs for first time". Flightglobal.com. 18 June 2010. Archived from the original on 12 April 2019. Retrieved 9 May 2013.
- ^ a b Norris, Guy (25 July 2006). "Farnborough: Airbus A350 powerplant race ignites as Rolls-Royce reaches agreement to supply Trent, Alliance confirms interest". Flight International.
- ^ a b Kaminski-Morrow, David (18 June 2010). "A350's Trent XWB engine runs for first time". Flight Global. Archived from the original on 12 April 2019. Retrieved 9 May 2013.
- ^ a b Perry, Dominic (18 February 2012). "Trent XWB powerplant makes maiden sortie". Flight Global. Archived from the original on 14 December 2014. Retrieved 9 May 2013.
- ^ a b "Trent XWB achieves important milestone with award of EASA type certification" (Press release). Rolls-Royce. 7 February 2013. Archived from the original on 26 March 2023.
- ^ a b "World's most fuel efficient engine powers first flight" (Press release). Rolls-Royce. 14 June 2013.
- ^ a b Norris, Guy (17 September 2018). "Rolls Reaffirms A350 Diversion Unrelated To Trent 1000 Issues". Aviation Week Network. Archived from the original on 21 September 2018. Retrieved 19 September 2018.
- ^ a b c d "Type certificate data sheet E.111" (PDF). EASA. 1 April 2019.
- ^ a b c d "Trent-XWB infographic" (PDF). Rolls-Royce. May 2017. Archived (PDF) from the original on 14 March 2023. Retrieved 1 July 2017.
- ^ "Gas Turbine Engines" (PDF). Aviation Week. 28 January 2008. pp. 137–138. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 November 2018. Retrieved 9 January 2025.
- ^ Kaminski-Morrow, David (6 October 2005). "Rolls-Royce to develop Trent 1700 for A350". Flight International. Archived from the original on 23 July 2019. Retrieved 1 July 2017.
- ^ Kingsley-Jones, Max (13 May 2009). "Airbus revises A350 Trent XWB thrust values following weight increases". Flight International. Archived from the original on 14 May 2016. Retrieved 1 July 2017.
- ^ Cohen, Aubrey (20 June 2011). "Airbus delays A350-1000, boosts thrust". Seattle Post-Intelligencer. Archived from the original on 29 June 2019.
- ^ Perry, Dominic (23 October 2012). "Airbus advances towards first flight of A350 twinjet". Flightglobal. Archived from the original on 6 October 2014. Retrieved 9 May 2013.
- ^ "Rolls-Royce dispatches first Trent XWB for entry into service" (Press release). Rolls-Royce. 15 May 2014. Archived from the original on 30 April 2017. Retrieved 1 July 2017.
- ^ "Rolls-Royce starts final assembly of Trent XWB production engine for entry into service" (Press release). Rolls-Royce. 10 February 2014. Archived from the original on 27 April 2017. Retrieved 1 July 2017.
- ^ "Higher-thrust Rolls-Royce Trent XWB engine runs for first time" (Press release). Rolls-Royce. 15 July 2014.
- ^ Broderick, Sean (31 August 2017). "Issues With Newest Engines Provide Early MRO-Proving Opportunities". Aviation Week Network. Archived from the original on 20 September 2017. Retrieved 20 September 2017.
- ^ Unnikrishnan, Madhu (12 November 2017). "Rolls-Royce Marks One Millionth Hour For Trent XWB". Aviation Week Network. Archived from the original on 15 November 2017. Retrieved 14 November 2017.
- ^ Kaminski-Morrow, David (21 February 2018). "Rolls-Royce 'confident' XWB will not suffer Trent 1000 issues". Flightglobal. Archived from the original on 21 February 2018. Retrieved 21 February 2018.
- ^ "Rolls-Royce Trent XWB celebrates new milestones" (Press release). Rolls-Royce. 15 July 2018. Archived from the original on 27 September 2007. Retrieved 17 July 2018.
- ^ Kaminski-Morrow, David (28 February 2020). "Rolls-Royce nears break-even delivery for A350-900 powerplant". Flightglobal. Archived from the original on 28 February 2020. Retrieved 28 February 2020.
- ^ Kaminski-Morrow, David (28 February 2020). "Rolls-Royce could choose not to break-even on A350-1000 engine". Flightglobal.
- ^ Hepher, Tim; Cornwell, Alexander; Magid, Pesha (14 November 2023). "Emirates holds off on Airbus A350 order in engine rift". Reuters. Archived from the original on 14 November 2023. Retrieved 14 November 2023.
- ^ "Rolls-Royce defends A350-1000 engine from Emirates criticism". Reuters. 14 November 2023. Retrieved 14 November 2023.
- ^ "Rolls-Royce 'defective' engine barb from Emirates all part of negotiations, says analyst". Proactiveinvestors UK. 15 November 2023. Retrieved 15 January 2024.
- ^ Kamel, Deena (16 November 2023). "Rolls-Royce to work with Emirates on jet engine performance issues, senior executive says". The National. Archived from the original on 15 January 2024. Retrieved 15 January 2024.
- ^ Hradecky, Simon (5 September 2024). "Incident: Cathay Pacific A35k at Hong Kong on Sep 2nd 2024, engine fire". The Aviation Herald. Archived from the original on 3 September 2024. Retrieved 5 September 2024.
- ^ Philip, Siddharth (5 September 2024). "Airbus A350 Checks Ordered by EASA After Cathay Engine Fire". BNN Bloomberg. Retrieved 5 September 2024.
- ^ a b c d e Kjelgaard, Chris (June 2016). "Trent XWB". Air International. pp. 48–51.
- ^ Doyle, Andrew (6 March 2009). "R-R details Trent XWB development strategy". Flight International. Archived from the original on 22 November 2018. Retrieved 1 July 2017.
- ^ "Rolls-Royce inks biggest-ever sale". Flight Global. 19 June 2007. Archived from the original on 15 December 2018. Retrieved 1 July 2017.
- ^ "Emirates places $8.4bn order for Rolls-Royce Trent XWB" (Press release). Rolls-Royce. 11 November 2007. Archived from the original on 27 April 2017. Retrieved 1 July 2017.
- ^ "Airbus and Emirates Airline agree to cancel A350 XWB order". Airbus. Archived from the original on 14 December 2018. Retrieved 17 March 2019.
- ^ Johnson, Robin (29 July 2015). "Derby's Rolls-Royce signs £340m engine support deal with Vietnam Airlines". Derby Telegraph. Archived from the original on 17 September 2015.
- ^ "Rolls-Royce announces Turkish Airlines will become largest operator of Trent XWB engines as Türkiye's national airline selects 70 Airbus A350 aircraft" (Press release). Rolls-Royce. 15 December 2023. Archived from the original on 1 January 2024. Retrieved 16 December 2023.
