Surfactant

Surfactants are chemical compounds that decrease the surface tension or interfacial tension between two liquids, a liquid and a gas, or a liquid and a solid. The word "surfactant" is a blend of surface-active agent,[1] coined in 1950.[2] As they consist of a water-repellent and a water-attracting part, they enable water and oil to mix; they can form foam and facilitate the detachment of dirt.
Surfactants are among the most widespread and commercially important chemicals. Private households as well as many industries use them in large quantities as detergents and cleaning agents, but also for example as emulsifiers, wetting agents, foaming agents, antistatic additives, or dispersants.
Surfactants occur naturally in traditional plant-based detergents, e.g. horse chestnuts or soap nuts; they can also be found in the secretions of some caterpillars. Today one of the most commonly used anionic surfactants, linear alkylbenzene sulfates (LAS), are produced from petroleum products. However, surfactants are increasingly produced in whole or in part from renewable biomass, like sugar, fatty alcohol from vegetable oils, by-products of biofuel production, or other biogenic material.[3]
Classification
[edit]Most surfactants are organic compounds with hydrophilic "heads" and hydrophobic "tails." The "heads" of surfactants are polar and may or may not carry an electrical charge. The "tails" of most surfactants are fairly similar, consisting of a hydrocarbon chain, which can be branched, linear, or aromatic. Fluorosurfactants have fluorocarbon chains. Siloxane surfactants have siloxane chains.
Many important surfactants include a polyether chain terminating in a highly polar anionic group. The polyether groups often comprise ethoxylated (polyethylene oxide-like) sequences inserted to increase the hydrophilic character of a surfactant. Polypropylene oxides conversely, may be inserted to increase the lipophilic character of a surfactant.
Surfactant molecules have either one tail or two; those with two tails are said to be double-chained.[4]
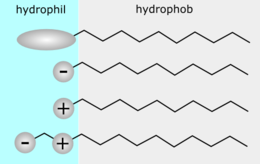
Most commonly, surfactants are classified according to polar head group. A non-ionic surfactant has no charged groups in its head. The head of an ionic surfactant carries a net positive, or negative, charge. If the charge is negative, the surfactant is more specifically called anionic; if the charge is positive, it is called cationic. If a surfactant contains a head with two oppositely charged groups, it is termed zwitterionic, or amphoteric. Commonly encountered surfactants of each type include:
Anionic: sulfate, sulfonate, and phosphate, carboxylate derivatives
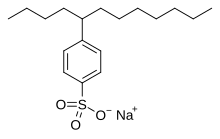
[edit]Anionic surfactants contain anionic functional groups at their head, such as sulfate, sulfonate, phosphate, and carboxylates. Prominent alkyl sulfates include ammonium lauryl sulfate, sodium lauryl sulfate (sodium dodecyl sulfate, SLS, or SDS), and the related alkyl-ether sulfates sodium laureth sulfate (sodium lauryl ether sulfate or SLES), and sodium myreth sulfate.
Others include:
- Alkylbenzene sulfonates
- Docusate (dioctyl sodium sulfosuccinate)
- Perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS)
- Perfluorobutanesulfonate
- Alkyl-aryl ether phosphates
- Alkyl ether phosphates
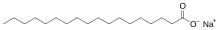
Carboxylates are the most common surfactants and comprise the carboxylate salts (soaps), such as sodium stearate. More specialized species include sodium lauroyl sarcosinate and carboxylate-based fluorosurfactants such as perfluorononanoate, perfluorooctanoate (PFOA or PFO).
Cationic head groups
[edit]pH-dependent primary, secondary, or tertiary amines; primary and secondary amines become positively charged at pH < 10:[5] octenidine dihydrochloride.
Permanently charged quaternary ammonium salts: cetrimonium bromide (CTAB), cetylpyridinium chloride (CPC), benzalkonium chloride (BAC), benzethonium chloride (BZT), dimethyldioctadecylammonium chloride, and dioctadecyldimethylammonium bromide (DODAB).
Zwitterionic surfactants
[edit]Zwitterionic (ampholytic) surfactants have both cationic and anionic centers attached to the same molecule. The cationic part is based on primary, secondary, or tertiary amines or quaternary ammonium cations. The anionic part can be more variable and include sulfonates, as in the sultaines CHAPS (3-[(3-cholamidopropyl)dimethylammonio]-1-propanesulfonate) and cocamidopropyl hydroxysultaine. Betaines such as cocamidopropyl betaine have a carboxylate with the ammonium. The most common biological zwitterionic surfactants have a phosphate anion with an amine or ammonium, such as the phospholipids phosphatidylserine, phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylcholine, and sphingomyelins.
Lauryldimethylamine oxide and myristamine oxide are two commonly used zwitterionic surfactants of the tertiary amine oxides structural type.
Non-ionic
[edit]Non-ionic surfactants have covalently bonded oxygen-containing hydrophilic groups, which are bonded to hydrophobic parent structures. The water-solubility of the oxygen groups is the result of hydrogen bonding. Hydrogen bonding decreases with increasing temperature, and the water solubility of non-ionic surfactants therefore decreases with increasing temperature.
Non-ionic surfactants are less sensitive to water hardness than anionic surfactants, and they foam less strongly. The differences between the individual types of non-ionic surfactants are slight, and the choice is primarily governed having regard to the costs of special properties (e.g., effectiveness and efficiency, toxicity, dermatological compatibility, biodegradability) or permission for use in food.[6]
Ethoxylates
[edit]Fatty alcohol ethoxylates
[edit]- Narrow-range ethoxylate
- Octaethylene glycol monododecyl ether
- Pentaethylene glycol monododecyl ether
Alkylphenol ethoxylates (APEs or APEOs)
[edit]Fatty acid ethoxylates
[edit]Fatty acid ethoxylates are a class of very versatile surfactants, which combine in a single molecule the characteristic of a weakly anionic, pH-responsive head group with the presence of stabilizing and temperature responsive ethyleneoxide units.[7]
Special ethoxylated fatty esters and oils
[edit]Ethoxylated amines and/or fatty acid amides
[edit]Terminally blocked ethoxylates
[edit]Fatty acid esters of polyhydroxy compounds
[edit]Fatty acid esters of glycerol
[edit]Fatty acid esters of sorbitol
[edit]Fatty acid esters of sucrose
[edit]Alkyl polyglucosides
[edit]Other classifications
[edit]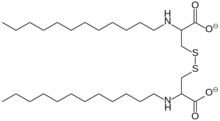
- Amino acid-based surfactants are surfactants derived from an amino acid. Their properties vary and can be either anionic, cationic, or zwitterionic, depending on the amino acid used and which part of the amino acid is condensed with the alkyl/aryl chain.[8]
- Gemini surfactants consist of two surfactant molecules linked together at or near their head groups. Compared to monomeric surfactants, they have much lower critical micelle concentrations.[8]
Composition and structure
[edit]
Surfactants are usually organic compounds that are akin to amphiphilic, which means that this molecule, being as double-agent, each contains a hydrophilic "water-seeking" group (the head), and a hydrophobic "water-avoiding" group (the tail).[9] As a result, a surfactant contains both a water-soluble component and a water-insoluble component. Surfactants diffuse in water and get adsorbed at interfaces between air and water, or at the interface between oil and water in the case where water is mixed with oil. The water-insoluble hydrophobic group may extend out of the bulk water phase into a non-water phase such as air or oil phase, while the water-soluble head group remains bound in the water phase.
The hydrophobic tail may be either lipophilic ("oil-seeking") or lipophobic ("oil-avoiding") depending on its chemistry. Hydrocarbon groups are usually lipophilic, for use in soaps and detergents, while fluorocarbon groups are lipophobic, for use in repelling stains or reducing surface tension.
World production of surfactants is estimated at 15 million tons per year, of which about half are soaps. Other surfactants produced on a particularly large scale are linear alkylbenzene sulfonates (1.7 million tons/y), lignin sulfonates (600,000 tons/y), fatty alcohol ethoxylates (700,000 tons/y), and alkylphenol ethoxylates (500,000 tons/y).[6]
Structure of surfactant phases in water
[edit]In the bulk aqueous phase, surfactants form aggregates, such as micelles, where the hydrophobic tails form the core of the aggregate and the hydrophilic heads are in contact with the surrounding liquid. Other types of aggregates can also be formed, such as spherical or cylindrical micelles or lipid bilayers. The shape of the aggregates depends on the chemical structure of the surfactants, namely the balance in size between the hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail. A measure of this is the hydrophilic-lipophilic balance (HLB). Surfactants reduce the surface tension of water by adsorbing at the liquid-air interface. The relation that links the surface tension and the surface excess is known as the Gibbs isotherm.
Dynamics of surfactants at interfaces
[edit]The dynamics of surfactant adsorption is of great importance for practical applications such as in foaming, emulsifying or coating processes, where bubbles or drops are rapidly generated and need to be stabilized. The dynamics of absorption depend on the diffusion coefficient of the surfactant. As the interface is created, the adsorption is limited by the diffusion of the surfactant to the interface. In some cases, there can exist an energetic barrier to adsorption or desorption of the surfactant. If such a barrier limits the adsorption rate, the dynamics are said to be ‘kinetically limited'. Such energy barriers can be due to steric or electrostatic repulsions. The surface rheology of surfactant layers, including the elasticity and viscosity of the layer, play an important role in the stability of foams and emulsions.
Characterization of interfaces and surfactant layers
[edit]Interfacial and surface tension can be characterized by classical methods such as the -pendant or spinning drop method. Dynamic surface tensions, i.e. surface tension as a function of time, can be obtained by the maximum bubble pressure apparatus
The structure of surfactant layers can be studied by ellipsometry or X-ray reflectivity.
Surface rheology can be characterized by the oscillating drop method or shear surface rheometers such as double-cone, double-ring or magnetic rod shear surface rheometer.
Applications
[edit]Surfactants play an important role as cleaning, wetting, dispersing, emulsifying, foaming and anti-foaming agents in many practical applications and products, including detergents, fabric softeners, motor oils, emulsions, soaps, paints, adhesives, inks, anti-fogs, ski waxes, snowboard wax, deinking of recycled papers, in flotation, washing and enzymatic processes, and laxatives. Also agrochemical formulations such as herbicides (some), insecticides, biocides (sanitizers), and spermicides (nonoxynol-9).[10] Personal care products such as cosmetics, shampoos, shower gel, hair conditioners, and toothpastes. Surfactants are used in firefighting (to make "wet water" that more quickly soaks into flammable materials[11][12]) and pipelines (liquid drag reducing agents). Alkali surfactant polymers are used to mobilize oil in oil wells.
Surfactants act to cause the displacement of air from the matrix of cotton pads and bandages so that medicinal solutions can be absorbed for application to various body areas. They also act to displace dirt and debris by the use of detergents in the washing of wounds[13] and via the application of medicinal lotions and sprays to surface of skin and mucous membranes.[14] Surfactants enhance remediation via soil washing, bioremediation, and phytoremediation.[15]
Detergents in biochemistry and biotechnology
[edit]In solution, detergents help solubilize a variety of chemical species by dissociating aggregates and unfolding proteins. Popular surfactants in the biochemistry laboratory are sodium lauryl sulfate (SDS) and cetyl trimethylammonium bromide (CTAB). Detergents are key reagents to extract protein by lysis of the cells and tissues: they disorganize the membrane's lipid bilayer (SDS, Triton X-100, X-114, CHAPS, DOC, and NP-40), and solubilize proteins. Milder detergents such as octyl thioglucoside, octyl glucoside or dodecyl maltoside are used to solubilize membrane proteins such as enzymes and receptors without denaturing them. Non-solubilized material is harvested by centrifugation or other means. For electrophoresis, for example, proteins are classically treated with SDS to denature the native tertiary and quaternary structures, allowing the separation of proteins according to their molecular weight.
Detergents have also been used to decellularise organs. This process maintains a matrix of proteins that preserves the structure of the organ and often the microvascular network. The process has been successfully used to prepare organs such as the liver and heart for transplant in rats.[16] Pulmonary surfactants are also naturally secreted by type II cells of the lung alveoli in mammals.
Quantum dot preparation
[edit]Surfactants are used with quantum dots in order to manipulate their growth,[17] assembly, and electrical properties, in addition to mediating reactions on their surfaces. Research is ongoing in how surfactants arrange themselves on the surface of the quantum dots.[18]
Surfactants in droplet-based microfluidics
[edit]Surfactants play an important role in droplet-based microfluidics in the stabilization of the droplets, and the prevention of the fusion of droplets during incubation.[19]
Heterogeneous catalysis
[edit]Janus-type material is used as a surfactant-like heterogeneous catalyst for the synthesis of adipic acid.[20]
Increased surface tension
[edit]Agents that increase surface tension are "surface active" in the literal sense but are not called surfactants as their effect is opposite to the common meaning. A common example of surface tension increase is salting out: adding an inorganic salt to an aqueous solution of a weakly polar substance will cause the substance to precipitate. The substance may itself be a surfactant, which is one of the reasons why many surfactants are ineffective in sea water.
In biology
[edit]
The human body produces diverse surfactants. Pulmonary surfactant is produced in the lungs in order to facilitate breathing by increasing total lung capacity, and lung compliance. In respiratory distress syndrome or RDS, surfactant replacement therapy helps patients have normal respiration by using pharmaceutical forms of the surfactants. One example of a pharmaceutical pulmonary surfactant is Survanta (beractant) or its generic form Beraksurf, produced by Abbvie and Tekzima respectively. Bile salts, a surfactant produced in the liver, play an important role in digestion.[21]
Safety and environmental risks
[edit]Most anionic and non-ionic surfactants are non-toxic, having LD50 comparable to table salt. The toxicity of quaternary ammonium compounds, which are antibacterial and antifungal, varies. Dialkyldimethylammonium chlorides (DDAC, DSDMAC) used as fabric softeners have high LD50 (5 g/kg) and are essentially non-toxic, while the disinfectant alkylbenzyldimethylammonium chloride has an LD50 of 0.35 g/kg. Prolonged exposure to surfactants can irritate and damage the skin because surfactants disrupt the lipid membrane that protects skin and other cells. Skin irritancy generally increases in the series non-ionic, amphoteric, anionic, cationic surfactants.[6]
Surfactants are routinely deposited in numerous ways on land and into water systems, whether as part of an intended process or as industrial and household waste.[22][23][24]
Anionic surfactants can be found in soils as the result of sewage sludge application, wastewater irrigation, and remediation processes. Relatively high concentrations of surfactants together with multimetals can represent an environmental risk. At low concentrations, surfactant application is unlikely to have a significant effect on trace metal mobility.[25][26]
In the case of the Deepwater Horizon oil spill, unprecedented amounts of Corexit were sprayed directly into the ocean at the leak and on the sea-water's surface. The apparent theory was that the surfactants isolate droplets of oil, making it easier for petroleum-consuming microbes to digest the oil. The active ingredient in Corexit is dioctyl sodium sulfosuccinate (DOSS), sorbitan monooleate (Span 80), and polyoxyethylenated sorbitan monooleate (Tween-80).[27][28]
Biodegradation
[edit]Because of the volume of surfactants released into the environment, for example laundry detergents in waters, their biodegradation is of great interest. Attracting much attention is the non-biodegradability and extreme persistence of fluorosurfactant, e.g. perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA).[29] Strategies to enhance degradation include ozone treatment and biodegradation.[30][31] Two major surfactants, linear alkylbenzene sulfonates (LAS) and the alkyl phenol ethoxylates (APE) break down under aerobic conditions found in sewage treatment plants and in soil to nonylphenol, which is thought to be an endocrine disruptor.[32][33] Interest in biodegradable surfactants has led to much interest in "biosurfactants" such as those derived from amino acids.[34] Biobased surfactants can offer improved biodegradation. However, whether surfactants damage the cells of fish or cause foam mountains on bodies of water depends primarily on their chemical structure and not on whether the carbon originally used came from fossil sources, carbon dioxide or biomass.[3]
See also
[edit]- Anti-fog – Chemicals that prevent the condensation of water as small droplets on a surface
- Cleavable detergent – class of chemical compounds
- Disodium cocoamphodiacetate – mixture of chemicals used as a surfactant
- Emulsion – Mixture of two or more immiscible liquids
- Hydrotrope – chemical substance
- MBAS assay – Scientific testing method, an assay that indicates anionic surfactants in water with a bluing reaction.
- Niosome – Non-ionic surfactant-based vesicle
- Oil dispersants – Mixture of emulsifiers and solvents used to treat oil spills
- Surfactants in paint
- Surfactant leaching
References
[edit]- ^
Rosen MJ, Kunjappu JT (2012). Surfactants and Interfacial Phenomena (4th ed.). Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons. p. 1. ISBN 978-1-118-22902-6. Archived from the original on 8 January 2017.
A surfactant (a contraction of surface-active agent) is a substance that, when present at low concentration in a system, has the property of adsorbing onto the surfaces or interfaces of the system and of altering to a marked degree the surface or interfacial free energies of those surfaces (or interfaces).
- ^ "surfactant". Oxford English Dictionary (Online ed.). Oxford University Press. (Subscription or participating institution membership required.) – "A new word, Surfactants, has been coined by Antara Products, General Aniline & Film Corporation, and has been presented to the chemical industry to cover all materials that have surface activity, including wetting agents, dispersants, emulsifiers, detergents and foaming agents."
- ^ a b "Biobased Surfactants Market Report: Market Analysis". Ceresana Market Research. Retrieved 5 January 2024.
- ^ "Surfactant | Defination, Classification, Properties & Uses". www.esteem-india.com.
- ^ Reich, Hans J. (2012). "Bordwell pKa Table (Acidity in DMSO)". University of Wisconsin. Archived from the original on 27 December 2012. Retrieved 2 April 2013.
- ^ a b c Kurt Kosswig "Surfactants" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, 2005, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a25_747
- ^ Chiappisi, Leonardo (December 2017). "Polyoxyethylene alkyl ether carboxylic acids: An overview of a neglected class of surfactants with multiresponsive properties". Advances in Colloid and Interface Science. 250: 79–94. doi:10.1016/j.cis.2017.10.001. PMID 29056232.
- ^ a b Bordes, Romain; Holmberg, Krister (28 March 2015). "Amino acid-based surfactants – do they deserve more attention?". Advances in Colloid and Interface Science. 222: 79–91. doi:10.1016/j.cis.2014.10.013. PMID 25846628.
- ^ "Bubbles, Bubbles, Everywhere, But Not a Drop to Drink". The Lipid Chronicles. 11 November 2011. Archived from the original on 26 April 2012. Retrieved 1 August 2012.
- ^ Paria, Santanu (2008). "Surfactant-enhanced remediation of organic contaminated soil and water". Advances in Colloid and Interface Science. 138 (1): 24–58. doi:10.1016/j.cis.2007.11.001. PMID 18154747.
- ^ Better Than Water? How Wet Water Outperforms Regular Water in Firefighting
- ^ Firefighters Turn to "Wet Water" to Fight Larger, More Complex Fires
- ^ Percival, S.l.; Mayer, D.; Malone, M.; Swanson, T; Gibson, D.; Schultz, G. (2 November 2017). "Surfactants and their role in wound cleansing and biofilm management". Journal of Wound Care. 26 (11): 680–690. doi:10.12968/jowc.2017.26.11.680. ISSN 0969-0700. PMID 29131752.
- ^ Mc Callion, O. N. M.; Taylor, K. M. G.; Thomas, M.; Taylor, A. J. (8 March 1996). "The influence of surface tension on aerosols produced by medical nebulisers". International Journal of Pharmaceutics. 129 (1): 123–136. doi:10.1016/0378-5173(95)04279-2. ISSN 0378-5173.
- ^ Bolan, Shiv; Padhye, Lokesh P.; Mulligan, Catherine N.; Alonso, Emilio Ritore; Saint-Fort, Roger; Jasemizad, Tahereh; Wang, Chensi; Zhang, Tao; Rinklebe, Jörg; Wang, Hailong; Siddique, Kadambot H. M.; Kirkham, M. B.; Bolan, Nanthi (5 February 2023). "Surfactant-enhanced mobilization of persistent organic pollutants: Potential for soil and sediment remediation and unintended consequences". Journal of Hazardous Materials. 443: 130189. Bibcode:2023JHzM..44330189B. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.130189. ISSN 0304-3894. PMID 36265382.
- ^ Wein, Harrison (28 June 2010). "Progress Toward an Artificial Liver Transplant – NIH Research Matters". National Institutes of Health (NIH). Archived from the original on 5 August 2012.
- ^ Murray, C. B.; Kagan, C. R.; Bawendi, M. G. (2000). "Synthesis and Characterization of Monodisperse Nanocrystals and Close-Packed Nanocrystal Assemblies". Annual Review of Materials Research. 30 (1): 545–610. Bibcode:2000AnRMS..30..545M. doi:10.1146/annurev.matsci.30.1.545.
- ^ Zherebetskyy D, Scheele M, Zhang Y, Bronstein N, Thompson C, Britt D, Salmeron M, Alivisatos P, Wang LW (June 2014). "Hydroxylation of the surface of PbS nanocrystals passivated with oleic acid". Science. 344 (6190): 1380–4. Bibcode:2014Sci...344.1380Z. doi:10.1126/science.1252727. PMID 24876347. S2CID 206556385. Archived from the original on 26 March 2020. Retrieved 24 June 2019.
- ^ Baret, Jean-Christophe (10 January 2012). "Surfactants in droplet-based microfluidics". Lab on a Chip. 12 (3): 422–433. doi:10.1039/C1LC20582J. ISSN 1473-0189. PMID 22011791. Archived from the original on 14 February 2020. Retrieved 18 April 2020.
- ^ Vafaeezadeh, Majid; Wilhelm, Christian; Breuninger, Paul; Ernst, Stefan; Antonyuk, Sergiy; Thiel, Werner R. (20 May 2020). "A Janus-type Heterogeneous Surfactant for Adipic Acid Synthesis". ChemCatChem. 12 (10): 2695–2701. doi:10.1002/cctc.202000140. ISSN 1867-3880.
- ^ Maldonado-Valderrama, Julia; Wilde, Pete; MacIerzanka, Adam; MacKie, Alan (2011). "The role of bile salts in digestion". Advances in Colloid and Interface Science. 165 (1): 36–46. doi:10.1016/j.cis.2010.12.002. PMID 21236400.
- ^ Metcalfe TL, Dillon PJ, Metcalfe CD (April 2008). "Detecting the transport of toxic pesticides from golf courses into watersheds in the Precambrian Shield region of Ontario, Canada". Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 27 (4): 811–8. Bibcode:2008EnvTC..27..811M. doi:10.1897/07-216.1. PMID 18333674. S2CID 39914076.
- ^ "Simultaneous analysis of cationic, anionic and neutral surfactants from different matrices using LC/MS/MS | SHIMADZU (Shimadzu Corporation)". www.shimadzu.com. Archived from the original on 14 November 2021. Retrieved 14 November 2021.
- ^ Murphy MG, Al-Khalidi M, Crocker JF, Lee SH, O'Regan P, Acott PD (April 2005). "Two formulations of the industrial surfactant, Toximul, differentially reduce mouse weight gain and hepatic glycogen in vivo during early development: effects of exposure to Influenza B Virus". Chemosphere. 59 (2): 235–46. Bibcode:2005Chmsp..59..235M. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.11.084. PMID 15722095.
- ^ Hernández-Soriano Mdel C, Degryse F, Smolders E (March 2011). "Mechanisms of enhanced mobilisation of trace metals by anionic surfactants in soil". Environ. Pollut. 159 (3): 809–16. Bibcode:2011EPoll.159..809H. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2010.11.009. PMID 21163562.
- ^ Hernández-Soriano Mdel C, Peña A, Dolores Mingorance M (2010). "Release of metals from metal-amended soil treated with a sulfosuccinamate surfactant: effects of surfactant concentration, soil/solution ratio, and pH". J. Environ. Qual. 39 (4): 1298–305. Bibcode:2010JEnvQ..39.1298H. doi:10.2134/jeq2009.0242. PMID 20830918.
- ^ "European Maritime Safety Agency. Manual on the Applicability of Oil Dispersants; Version 2; 2009". Archived from the original on 5 July 2011. Retrieved 19 May 2017.
- ^ Committee on Effectiveness of Oil Spill Dispersants (National Research Council Marine Board) (1989). Using Oil Spill Dispersants on the Sea. National Academies Press. doi:10.17226/736. ISBN 978-0-309-03889-8. Archived from the original on 3 January 2019. Retrieved 31 October 2015.
- ^ USEPA: "2010/15 PFOA Stewardship Program" Archived 27 October 2008 at the Wayback Machine Accessed October 26, 2008.
- ^ Rebello, Sharrel; Asok, Aju K.; Mundayoor, Sathish; Jisha, M. S. (2014). "Surfactants: Toxicity, remediation and green surfactants". Environmental Chemistry Letters. 12 (2): 275–287. Bibcode:2014EnvCL..12..275R. doi:10.1007/s10311-014-0466-2. S2CID 96787489.
- ^ Ying, Guang-Guo (2006). "Fate, behavior and effects of surfactants and their degradation products in the environment". Environment International. 32 (3): 417–431. Bibcode:2006EnInt..32..417Y. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2005.07.004. PMID 16125241.
- ^ Mergel, Maria. "Nonylphenol and Nonylphenol Ethoxylates." Toxipedia.org. N.p., 1 Nov. 2011. Web. 27 Apr. 2014.
- ^ Scott MJ, Jones MN (November 2000). "The biodegradation of surfactants in the environment". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1508 (1–2): 235–51. doi:10.1016/S0304-4157(00)00013-7. PMID 11090828.
- ^ Reznik GO, Vishwanath P, Pynn MA, Sitnik JM, Todd JJ, Wu J, et al. (May 2010). "Use of sustainable chemistry to produce an acyl amino acid surfactant". Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 86 (5): 1387–97. doi:10.1007/s00253-009-2431-8. PMID 20094712. S2CID 3017826.
External links
[edit] Media related to Surfactants at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Surfactants at Wikimedia Commons
