Army of the Socialist Republic of Romania
| Army of the Romanian People's Republic (1948–1965) Army of the Socialist Republic of Romania (1965–1989) | |
|---|---|
| Armata Republicii Populare Romîne (1948–1965) Armata Republicii Socialiste România (1965–1989) | |
 Ceremonial Flag (1966–1989) | |
| Motto | Pentru Patria Noastră ("For our Homeland") |
| Founded | 1948 |
| Disbanded | 1989 |
| Service branches | |
| Headquarters | Bucharest |
| Leadership | |
| Supreme Commander-in-chief | Nicolae Ceaușescu |
| Minister of Defence | Vasile Milea (last) |
| Chief of the General Staff | Ștefan Gușă (last) |
| Personnel | |
| Conscription | 16 months |
| Active personnel | 210,000 in 1989 270,000 at peak in 1984 |
| Deployed personnel | |
| Industry | |
| Foreign suppliers | |
| Annual exports | $1,000,000,000 (1982)[5] |
| Related articles | |
| History | |
| Ranks | Military ranks of the Socialist Republic of Romania |
The Army of the Socialist Republic of Romania (Romanian: Armata Republicii Socialiste România) was the army of the Socialist Republic of Romania (1965 to 1989), previously known as the Army of the Romanian People's Republic (Romanian: Armata Republicii Populare Romîne) during the Romanian People's Republic (1947 to 1965). Following the Romanian Revolution in 1989, it was renamed to the Romanian Armed Forces. It consisted of the Ground Forces, the Navy, and the Air Force.
History
[edit]In 1948-1960, they were ranked 3rd. In 1944, the Red Army invaded Romania in the Jassy-Kishinev Offensive, causing the overthrow of Ion Antonescu's regime via a Royal coup. In 1945, new military regulations were developed based on those of the Red Army[6] and in 1946, Romania came completely under the influence of the Soviet Union. It became part of the Eastern Bloc. The military regulations were finalized in 1949.[citation needed] Like all other socialist states, the Army was subjected to the rule of the Romanian Communist Party, whose general secretary was, since 1974, President of the Republic in addition to his role as commander-in-chief of the army.
During the tenure of General Emil Bodnăraș as defense minister, the Army went through a period of Sovietization, with Bodnăraș personally sending several Romanian Communists to Moscow to be trained in Soviet military institutions such as the Frunze Military Academy.[7][8] 30% of the experienced officers corps were purged from the military due to fears of opposition and monarchist loyalties.[9] Between 1949 and 1952, over 700 Romanian military personnel were being trained in the USSR, which would drop by over 200 in the next six years.[10] They also adopted a Soviet-style full dress and everyday uniform. In the Republic's early days, the Soviet Armed Forces had troops stationed there. The Soviet presence resulted from the Soviet occupation of Romania. Bodnăraș was seen to have influenced Nikita Khrushchev's decision to withdraw Soviet troops in 1958.[11][12][13]
From May 1955 to 1991, Romania was a member of the Warsaw Pact, which provided the Romanian Army with weapons, other Soviet-made equipment, and assistance in building up its own defense industry.[14] Under the presidency of Nicolae Ceaușescu, the RPA asserted functional independence in the defense industry and on equipment acquisitions while maintaining strong ties to the Warsaw Pact Command, with many of its armored vehicles, aircraft and artillery, as well as individual weaponry, being nationally produced. Also, a new set of enlisted and NCO ranks were adopted in the 1970s, alongside the reinstatement of the senior NCO ranks (maistru militar), which replaced the former Soviet rank model for such personnel. On 12 March 1958, the Sports Committee of Friendly Armies was created, with the Romanian Army becoming a founding member. In November 1986, a referendum was held by the government in which voters, when asked whether they approved of reducing the size of the army and cutting military spending by 5%, approved the proposals by 100%, with not a single vote counting against it.[15]
The Armed Forces would be renamed in 1989 following the Romanian Revolution, during which officers and personnel of the military defected to the side of the opposition after a public speech by Ceaușescu broadcast on state television[16] and a firing squad provided by paratroop regiment personnel Captain Ionel Boeru, Sergeant-Major Georghin Octavian and Dorin-Marian Cîrlan took part in the Trial and execution of Nicolae and Elena Ceaușescu on 26 December.[17] In the week after Ceaușescu's downfall, the defected Armed Forces fought bloody street battles, allegedly against Securitate forces who were still on Ceaușescu's side.[18]
Political and military leadership
[edit]Supreme Commander-in-Chief
[edit]The title of Supreme Commander-in-Chief was held by the de facto leader of the nation, General Secretary, even though the President of the State Council was the de jure head of state until 1974, when it was replaced by the President of Romania.
| No. | Portrait | Supreme Commander-in-Chief | Took office | Left office | Time in office |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Lieutenant general Nicolae Ceaușescu (1918–1989) | 1969 | 22 December 1989 | 24 years, 275 days |
Minister of National Defence
[edit]The office of Minister of National Defence (Romanian: Ministrul Apărării Naționale) is the chief political leader of the military. Before that, it was the Minister of War (Romanian: Ministru de Război) who handled military affairs in the government. The country's defense policy was managed by the minister's agency, the Ministry of the National Defense, led by a professional officer with the rank of Colonel general or above. The minister was a permanent member of the Politburo of the PCR.
| No. | Portrait | Minister of National Defence | Took office | Left office | Time in office |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | General of the Army Emil Bodnăraș | 27 December 1947 | 3 October 1955 | 7 years, 280 days | |
| 2 | General of the Army Leontin Sălăjan | 3 October 1955 | 28 August 1966 | 10 years, 329 days | |
| 3 | General of the Army Ioan Ioniță | 29 October 1966 | 16 June 1976 | 9 years, 231 days | |
| 4 | Colonel General Ion Coman | 16 June 1976 | 29 March 1980 | 3 years, 287 days | |
| 5 | Colonel General Constantin Olteanu | 29 March 1980 | 16 December 1985 | 5 years, 262 days | |
| 6 | Colonel General Vasile Milea | 16 December 1985 | 22 December 1989[19] | 4 years, 6 days |
Chief of the General Staff
[edit]
| No. | Portrait | Chief of the General Staff | Took office | Left office | Time in office |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 33 | Colonel General Constantin Popescu (1893–?) | 30 January 1948 | 18 March 1950 | 2 years, 47 days | |
| 34 | General of the Army Leontin Sălăjan (1913–1966) | 18 March 1950 | 26 April 1954 | 4 years, 39 days | |
| 35 | General Ion Tutoveanu (1914–2014) | 26 April 1954 | 15 June 1965 | 11 years, 50 days | |
| 36 | General Ion Gheorghe (1923–2009) | 15 June 1965 | 29 November 1974 | 9 years, 167 days | |
| 37 | Lieutenant General Ion Coman (born 1926) | 29 November 1974 | 16 June 1976 | 1 year, 200 days | |
| 38 | Lieutenant General Ion Hortopan (1925–2000) | 1 July 1976 | 31 March 1980 | 3 years, 274 days | |
| 39 | Colonel General Vasile Milea (1927–1989) | 31 March 1980 | 16 February 1985 | 4 years, 322 days | |
| 40 | Colonel General Ștefan Gușă (1940–1994) | 25 September 1986 | 28 December 1989 | 3 years, 97 days |
Components
[edit]As of 1985, the Army was organized into the following service branches:[20]
- Ground Forces (Forțele Terestre)
- Air Forces (Forțele Aeriene)
- Navy (Marina)
Several other branches were not part of the Ministry of National Defense but were directly controlled by the Romanian Army or the PCR:[20]
- Patriotic Guards (Gărzile Patriotice)
- Security Troops (Trupele de securitate)
- Border Troops (Trupele de frontieră)
A distinctive feature of the system of manning the RAF armed forces was the continued possibility of conscription of women for military service (although the bulk of the female military personnel serving at that time were doctors, nurses, and radio communications operators).[20]
The Army active personnel amounted to the following numbers:[21]
| Branch | Size |
|---|---|
| Ground Forces | 125,000[22] |
| Navy | 5,000 |
| Air Force | 8,000 |
| Total | 138,000 officers and troops |
From 1947 to 1960, the military was organized into three military regions: Western (based in Cluj), Eastern (based in Bacău), and South (based in Bucharest).[9] Succeeded by army corps in the 60s, they were areas that in wartime would become an army corps with their headquarters acting as areas of responsibility.
Ground Forces
[edit]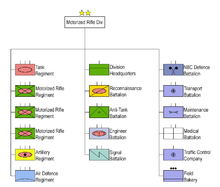
The senior units in the ground forces were the Tudor Vladimirescu Division and the Horia, Cloșca și Crișan Division, both of which were used as political tools by communist leaders. They were composed of former prisoners of war, Soviet trainees, and Communist activists such as Valter Roman.[23]
In 1980, the Romanian Ground Forces were reorganized in 4 Army Commands:[24]
- 1st Army Command (Bucharest)
- 2nd Army Command (Buzău)
- 3rd Army Command (Craiova)
- 4th Army Command (Cluj-Napoca)
All four Army Commands consisted of 8 Mechanized Infantry Divisions, 2 Armoured Divisions, 1 Armoured Brigade, 4 Mountain infantry Brigades as specialized motorized infantry units, and an administrative division of 4 parachute infantry regiments. Between 1960 and 1964, the rifle/mechanized divisions were converted to mechanized infantry (motorized rifle) divisions, which resulted in reductions in size due to the merger of both types of units. The newly established mechanized infantry divisions were structured similarly to the Soviet ones, organized into a division HQ, three mechanized infantry regiments, a tank regiment, and a field artillery regiment, as well as battalion-size subunits of other specialties, while the armoured divisions were structured in three tank regiments, a mechanized infantry regiment, a field artillery regiment and several other battalion-size subunits of different specialities.
The degree of mechanization of the infantry was not complete, unlike the other member states of the Warsaw Treaty, for in 1985 only two of the three infantry battalions from the composition of the mechanized regiments were equipped with wheeled armoured personnel carriers TAB-71 and TAB-77. Even though since 1985, the infantry regiments began receiving new amphibious tracked infantry fighting vehicles MLI-84, the mechanization of the whole infantry had not succeeded until 1989.
Disbanded by the Soviets in the early years of occupied and post-war Romania, the Vânători de munte (Mountain Huntsmen) was re-established in 1958. It was the equivalent of the Soviet 7th Guards Mountain Air Assault Division or the American 10th Mountain Division. Due to its equipment comprising MLVM APCs and 76mm mounted guns, it was considered the Ground Forces' best-trained unit. It was organized into four brigades stationed in mountainous areas.
Navy
[edit]
In the early postwar years, the Romanian Navy was deprived of its merchant fleet due to the rapid takeover of the Romanian vessels by the Soviet Navy. In September 1944, the Soviet Navy transferred all Romanian warships to ports in the Caucasus near Azerbaijan and Georgia, all of which were not returned until just over a year later, with the exception o the Regele Ferdinand-class that was kept by the Black Sea Fleet until the early 1950s.[25] Several warships such as Amiral Murgescu were never returned and stayed in Soviet service until they were decommissioned. Once possessing patrol ships, the Romanian Navy formed the Danube Squadron, which later changed its name to the River Brigade in 1959. As a result of the 1940s reform of the naval forces, a patrol squadron was converted into an independent unit, which operated under the Naval Headquarters until May 1951. Four years later, naval ships and Marine units were subordinated to the headquarters.
In 1962, the 42nd Maritime Division was founded, continuing the traditions of the Sea Division, a large unit that had ceased to carry out functions since the end of World War II. In the late 70s and early 80s, several naval ships were built in the Romanian shipyards, specifically the Midia and Constanța escort ships from the Brăila shipyard.[26] In the early 1980s, the Navy ramped up efforts to develop its domestic naval industry by building new patrol boats using Chinese and Soviet technology and designs. In 1989, the Romanian Navy had more than 7,500 sailors, all organized into the Black Sea Fleet, the Danube Squadron, and the Coastal Defense. Its major naval bases and shipyards were the ports of Mangalia and Constanța on the Black Sea. Based in Constanța, the 2,000-member Coastal Defense Regiment was the shore-based component of defense against attack from the Black Sea.[27][28]
Air Force
[edit]
In 1946, following a reorganization, the Air Force consisted of seven Air Flotillas, of which two were fighter flotillas and the rest were bombardment, assault, information, and transport. A total of 953 aircraft were in service; these included both pre-war and WW2 models like the Bf 109G, IAR 80, IAR 37, Ju 88, etc.[29]
Following a condition imposed during the Paris Peace Treaties of 1947, the strength of the military aviation of Romania was reduced to 150 aircraft, of which 100 were for combat and the rest for training.[29] On 15 February 1949, the Romanian Aviation Command was established following the Soviet model of aviation regiments instead of the British squadron model. This would later be renamed to the Romanian Air Force.
The first jet fighters arrived in 1951, with the first Jet Air Division (Divizia Aeriană Reactivă) being established on 1 April of the same year, at Ianca.[30] The unit was equipped with Soviet-made Yak-23 and Yak-17 fighters and had three Regiments (the 11th, 12th, and 13th).[29] The 97th Jet Fighter Aviation Division was declared combat ready on 15 September 1951. The first interception mission was carried out on the night of 28/29 October 1952, when a Soviet Il-28 bomber entered Romanian airspace unauthorized.[31] The first MiG-15s also entered service in 1952. These aircraft were first in use with the Soviet Regiments deployed at Craiova and Deveselu and were transferred to the Romanian Air Force in September 1952.[29] The first supersonic flight happened on 5 March 1958, with a MiG-19 at the Deveselu Air Base.[32]
In 1969, an air defence unit was created to protect against air attacks, while a paratrooper regiment was founded in 1980, both of which were assigned to the Câmpia Turzii Air Base (now the RoAF 71st Air Base). A Romanian-made IAR-93 attack aircraft flew its first flight on 31 October 1974 over Bacău,[33] marking the first jet fighter in the Eastern Bloc to be domestically manufactured. The Mikoyan MiG-29 aircraft entered the inventory of the Air Force just a few days before the Romanian Revolution of December 1989.
Patriotic Guards
[edit]
Formed in 1968 after Ceaușescu's speech of 21 August 1968, the Romanian Patriotic Guards was an organization dedicated to public security, with its functions including civil policing to an active reserve for the Army. During wartime, the President of the Republic could authorize the guards to become a large "Militia" that would provide military police-style security, as well as augment the ground forces, and operate as guerrillas forces. The force was not part of the Ministry of National Defence but was a direct reporting unit of the PCR and the Union of Communist Youth, of which it drafted members of both. Members of the guards were considered territorial troops (Forțele teritoriale), as they were organized into companies and/or platoons and were based in every județ, municipality, and industrial/agricultural area under the command of the first secretary of the local PCR.
Securitate Troops
[edit]On 23 January 1949, the communist government disbanded the Royal Romanian Gendarmerie only to purge its personnel and redistribute them to the newly created Directorate for Security Troops (DTO) of the Securitate (Department of State Security), modeled after the NKVD's Internal Troops and the KGB.[34] It acted as a 20,000-strong elite paramilitary force consisting of select people drawn from the Army's conscript pool. It was organized into infantry units equipped with small arms, artillery, and armored personnel carriers. The security troops were directly responsible to the Minister of the Interior and the Supreme Commander-in-Chief, allowing them to guard important installations, including PCR office buildings and state radio and television stations.[35]
The regime of Ceaușescu could have theoretically called in the security troops as a private army to prevent a military coup d'état and/or suppress antiregime riots. It operated under a more strict discipline and routine than the regular military, which resulted in their special treatment and enjoyment of better living conditions than their counterparts.[35] In late 1989, the directorate was disbanded and replaced first by the Guard and Order Troops (Trupele de Pază și Ordine) and later on by the reformed Gendarmerie.
Equipment
[edit]
| Weapon | Origin | Type | Notes | Photo |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TTC | Semi-automatic pistol | TT-33 pistol produced in Roumania under TTC designation.[36] | 
| |
| Pistol Carpați Md. 1974 | Semi-automatic pistol | Standard issue pistol. | 
| |
| Orița M1941 | Submachine gun | Used by the Patriotic Guards until the 1970s.[37] | 
| |
| Pistol Mitralieră model 1963/1965 | Assault rifle | Standard issue until the 1980s when it was replaced by Pușcă Automată model 1986 | 
| |
| Pușcă Automată model 1986 | Assault rifle | Ment to replace Pistol Mitralieră model 1963/1965. | 
| |
| PM md. 64 | Light machine gun | 
| ||
| ZB vz. 30 | Light machine gun | Produced under license. Used by the Patriotic Guards. | 
| |
| Mitralieră md. 66 | General purpose machinegun | Copy of PK machine gun | 
| |
| PSL | Designated sniper rifle | Standard marksman rifle . | 
| |
| SKS M56 | Semi-automatic rifle | Produced under license. | 
| |
| RPG-2 | Light AT weapon | [38] | 
| |
| RPG-7 | Light AT weapon | 
| ||
| Mosin–Nagant | Bolt-action rifle | [39] | 
| |
| vz. 24 | Bolt-action rifle | Used by the Patriotic Guards.[40] | 
|
Armored fighting vehicles
[edit]| Tank | Origin | Type | In service | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-34 | 85 | 1,053 | [41] | |
| T-55 | AM, AM2 | 756 | [41] | |
| TR-85 | 617 | [41] | ||
| TR-850 | 413 | [41] | ||
| T-72 | M | 30 | [41] | |
| SU-76 | 326 | |||
| SU-100 | 66 | |||
| ISU-152 | 20 |
| IFV/APC | Origin | Type | In service | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MLI-84 | IFV | 154 | [42] | |
| BTR-40 | APC | 26 | [42] | |
| BTR-50 | APC | 35 | [42] | |
| BTR-60 | APC | 50 | [42] | |
| TAB-71 | APC | 1,870 | [42] | |
| TAB-77 | APC | 155 | [42] | |
| TABC-79 | APC | 441 | [42] | |
| MLVM | APC | 53 | [42] | |
| BRDM-2 | Reconnaissancel Vehicle | 139 | [42] | |
| TAB-80 | Reconnaissancel Vehicle | 8 | [42] |
Air Force
[edit]| Model | Origin | Type | In service | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MiG-21 | Fighter | 300[43] | ||
| MiG-23 | Fighter | 46[43] | ||
| IAR-93 | Ground attack | 86 | ||
| IAR 99 | Trainer | 90[43] | ||
| L-29 Delfín | Trainer | 52 | ||
| L-39 Albatros | Trainer | 32 | ||
| Ilyushin Il-28 | Bomber | 11 | Replaced by the Harbin H-5 in 1972 | |
| Harbin H-5 | Bomber | 16 | ||
| Antonov An-24 | Transport | 12[43] | ||
| Antonov An-26 | Transport | 16[43] | ||
| IAR 330 | Helicopter | 60 | [44] | |
| IAR 316 | Helicopter | 136 | [45] | |
| Mil Mi-8 | Helicopter | 39 | [46] | |
| S-75 Dvina | SAM | N/A | ||
| S-125 Neva/Pechora | SAM | N/A | ||
| 9K33 Osa | SAM | N/A | ||
| 9K31 Strela-1 | SAM | N/A |
Artillery
[edit]Total: 3,707[42]
Navy
[edit]Ships:[28]
 Poti-class corvette
Poti-class corvette Kronshtadt-class submarine chaser
Kronshtadt-class submarine chaser Osa-class missile boat
Osa-class missile boat Type 025 torpedo boat
Type 025 torpedo boat Epitrop class fast attack craft
Epitrop class fast attack craft Type 062 gunboat
Type 062 gunboat Cosar class minelayer
Cosar class minelayer Democrația-class minesweeper
Democrația-class minesweeper
In the early 1990s, the equipment for major units were scrapped due to age and the cost of maintenance.
See also
[edit]- Korean People's Army
- Nationale Volksarmee
- Polish People's Army
- Czechoslovak People's Army
- Hungarian People's Army
- Bulgarian People's Army
- Albanian People's Army
- List of wars involving Romania
Videos
[edit]- 110. Armata României în Decembrie 1989
- Cenusa pasarii din vis (1989) (1)
- Revoluţia română: La TVR se anunță că Armata Română va apăra obiective importante din Bucureşti
- Armata Republicii Socialiste România
- Socialist Romania Military Oath – Jurământul Militar din Armata RSR
References
[edit]- ^ United States. Joint Publications Research Service, 1977, Translations on Sub-Saharan Africa, Issues 1742-1754, p. 13
- ^ Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars. International Security Studies Program, Ballinger Publishing Company, 1988, Superpower Competition and Security in the Third World, p. 100
- ^ American-African Affairs Association, 1983, Spotlight on Africa, Volumes 16-17
- ^ United States. Congress. Senate. Committee on Finance. Subcommittee on International Trade, U.S. Government Printing Office, 1985, Continuing Presidential Authority to Waive Freedom of Emigration Provisions, p. 372
- ^ Pinstripes and Reds: An American Ambassador Caught Between the State Department and the Romanian Communists, 1981–1985, p. 183, David B. Funderburk, Selous Foundation Press, 1987
- ^ Oroian, p. 37
- ^ Oroian; Vankovska, Wiberg, p. 115; Final Report, p. 125
- ^ Pacepa, p. 357-358
- ^ a b "Development of the Romanian Armed Forces after World War II" Archived 2007-07-11 at the Wayback Machine, from the Library of Congress Country Studies and the CIA World Factbook.
- ^ Oroian, p. 40-41
- ^ Arachelian
- ^ Final Report, p. 43 n. 32, p. 205
- ^ Nikita Sergeevich Khrushchev, Sergeĭ Khrushchev. Memoirs of Nikita Khrushchev: Statesman, 1953–1964, Pennsylvania State University Press, 2007, page 706, ISBN 0-271-02935-8
- ^ "The Warsaw Pact is formed". HISTORY. Retrieved 2019-08-31.
- ^ Rumänien, 23. November 1986 : Verkleinerung des Heeres, Senkung der Rüstungsausgaben um 5% Direct Democracy
- ^ Hirshman, Michael (2009-11-06). "Blood And Velvet In Eastern Europe's Season Of Change". Rferl.org. Retrieved 2019-08-31.
- ^ "120 bullets found in Ceausescus". The Day. 23 January 1990. Retrieved 31 August 2019.
- ^ Blaine Harden (December 30, 1989). "DOORS UNLOCKED ON ROMANIA'S SECRET POLICE". The Washington Post.
- ^ Flavius Cristian Marcau, "Revolution of 1989: Milea's Suicide", University of Târgu Jiu, Letter and Social Science Series, Issue 4, 2013, Retrieved February 27, 2016.
- ^ a b c Армия Социалистической Республики Румынии // На страже мира и социализма / сост. В. С. Шкаровский. М., "Планета", 1985. стр. 110-119
- ^ Assembly of Captive European Nations, First Session, pp. 65-67
- ^ Library of Congress Country Studies, Romanian Land Forces, DR 205. R613, 1990
- ^ Mihailov
- ^ 'Romanian Army during the Cold War' via "Sovietization of the Romanian Army". Archived from the original on 2012-10-18. Retrieved 2011-05-27.
- ^ Robert Gardiner, Conway's All the World Fighting Ships 1922–1946, p. 361
- ^ "Romania's Naval Forces at crossroads".
- ^ Șperlea, Florin (2009). From the royal armed forces to the popular armed forces: Sovietization of the Romanian military (1948–1955). East European monographs. Boulder: New York: East European Monographs; distributed by Columbia University Press. ISBN 9780880336628.
- ^ a b "Romania – Navy". GlobalSecurity.org. Archived from the original on 13 April 2013. Retrieved 23 March 2014.
- ^ a b c d Vasile Tudor. "Modernizarea aviatiei militare romane" Orizont Aviatic magazine no. 26, December 2004.
- ^ "FARGO 1". rumaniamilitary.ro (in Romanian). 20 November 2020.
- ^ "70 de ani de la integrarea aeronavei de luptă cu motor reactiv în Serviciul de Luptă Permanent". Aviatia Magazin (in Romanian). 20 September 2021.
- ^ "Primul zbor cu un avion de lupta supersonic in Romania". Aviatia Magazin (in Romanian). 5 March 2015.
- ^ "IAR-93 History". Archived from the original on 2012-02-27. Retrieved 2019-09-15.
- ^ (in Romanian) Repere istorice Archived 2007-04-12 at the Wayback Machine, Romanian Gendarmerie website, accessed on 14 April 2007
- ^ a b "Romania: Ministry of Interior and Security Forces". loc.gov. Archived from the original on 2004-10-30.
- ^ Jones, Richard D. Jane's Infantry Weapons 2009/2010. Jane's Information Group; 35 edition (January 27, 2009). ISBN 978-0-7106-2869-5.
- ^ Plăvcan, Liviu; Plăvcan, Dora. "Romanian Firepower: 9mm Orita Model 1941 Submachine Gun".
- ^ Suciu, Peter (2022-07-26). "RPG-2 — The Original ComBloc Anti-Tank Weapon". The Armory Life. Retrieved 2022-10-18.
- ^ "Mosin Nagant Master Model Reference". 2017-07-16. Archived from the original on 2017-07-16. Retrieved 2024-07-07.
- ^ "Prezentare Pusca ZB, model 1924". armevechi.com (in Romanian). 2022-03-21.
- ^ a b c d e Bogdan Szajkowski, James Gow, Longman Group, 1993, Encyclopaedia of Conflicts, Disputes, and Flashpoints in Eastern Europe, Russia, and the Successor States, p. 274
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k Bogdan Szajkowski, James Gow, Longman Group, 1993, Encyclopaedia of Conflicts, Disputes, and Flashpoints in Eastern Europe, Russia, and the Successor States, p. 274
- ^ a b c d e admin (2018-01-19). "Romanian Air Force". Aeroflight. Retrieved 2024-07-07.
- ^ Romania 2009, pp. 78-79.
- ^ "World Air Forces 2013" (PDF). Flightglobal Insight. 2013. Retrieved 28 February 2013.
- ^ Svetozar Jokanović. "Ми-8/14/17/171 В НЕБЕ БАЛКАН" (in Russian). Retrieved 24 November 2023.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w Stroea, Adrian (2010). Artileria Română în date și imagini (PDF) (in Romanian). Bucharest: Editura Centrului Tehnic-Editorial al Armatei. pp. 140–146. ISBN 9786065240803. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 March 2023.
- ^ 1976, Military Review, Volume 56, Issue 3, p. 101
- Socialist Republic of Romania
- Military history of Romania
- 1947 establishments in Romania
- 1989 disestablishments in Romania
- Military units and formations established in 1947
- Military units and formations disestablished in 1989
- 1950s in Romania
- 1960s in Romania
- 1970s in Romania
- 1980s in Romania
- Warsaw Pact
- Disbanded armies
- Disbanded armed forces
- Military units and formations of the Cold War
- Military wings of communist parties








![Constantin Olteanu [ro]](http://up.wiki.x.io/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/46/ConstantinOlteanu.jpg/100px-ConstantinOlteanu.jpg)

![Constantin Popescu [ro]](http://up.wiki.x.io/wikipedia/commons/thumb/7/7c/ConstantinGhPopescu.jpg/100px-ConstantinGhPopescu.jpg)
![Ion Tutoveanu [ro]](http://up.wiki.x.io/wikipedia/commons/thumb/0/0e/IonTutoveanu.jpg/100px-IonTutoveanu.jpg)
![Ion Gheorghe [ro]](http://up.wiki.x.io/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/8c/IonGheorghe.jpg/100px-IonGheorghe.jpg)
![Ion Hortopan [ro]](http://up.wiki.x.io/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/da/IonHortopan.jpg/100px-IonHortopan.jpg)

