VR (nerve agent)
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
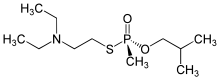
S-[2-(Diethylamino)ethyl] O-(2-methylpropyl) methylphosphonothioate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C11H26NO2PS | |
| Molar mass | 267.368 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
| Part of a series on | |||
| Chemical agents | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Lethal agents | |||
| Incapacitating agents | |||
|
|||
VR (Russian VX, VXr, Soviet V-gas, GOSNIIOKhT substance No. 33, Agent "November") is a "V-series" unitary nerve agent closely related (it is an isomer) to the better-known VX nerve agent.[1] It became a prototype for the series of Novichok agents. According to chemical weapons expert Jonathan Tucker, the first binary formulation developed under the Soviet Foliant program was used to make Substance 33, differing from VX only in the alkyl substituents on its nitrogen and oxygen atoms. "This weapon was given the code name Novichok."[2]
History
[edit]The development of VR started in 1957, after the Soviet Union obtained information about detection of high level of toxicity in phosphorylthiocholines[3] (the same year Lars-Erik Tammelin published his first articles on fluorophosphorylcholines and phosphorylthiocholines in Acta Chemica Scandinavica) by a team from the Soviet Union's Scientific Research Institute No. 42 (NII-42). Sergei Zotovich Ivin, Leonid Soborovsky, and Iya Danilovna Shilakova jointly developed this analogue of VX. They completed their work in 1963 and were later awarded the Lenin Prize for their achievement.[4] A binary weapon comprising two less toxic precursors which mixed during flight to form Substance 33 was later developed by a team led by Nikolai Kuznetsov.[5]
In 1972 the Soviets opened Cheboksary Khimprom, a manufacturing plant for VR in Novocheboksarsk.[6] All facilities in USSR produced 15,557 tons of VR according to their declaration to the Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW),[7] although most if not all of this has now been destroyed under disarmament treaties.[8]
Comparison to VX
[edit]VR has similar lethal dose levels to VX (between 10–50 mg), as well as being similar in appearance.[9] However, due to usage of diethylamino radicals instead of diisopropylamino it is more prone to decomposition. The former are worse at sterically protecting the nitrogen atom from attacking either phosphorus or the α-carbon atom adjacent to sulfur than the latter. According to UK Defence Science and Technology Laboratory Detection Department scientists Robin M. Black and John M. Harrison, chemical stability was an important factor why of all the similarly toxic phosphorylthiocholines, ethyl N-2-diisopropylaminoethyl methylphosphonothiolate in particular (now known as VX), was weaponized in the West.[10]
According to Russian CW developer Vil Mirzayanov, in the late 1980s a group of GosNIIOKhT chemists led by Georgiy Drozd prepared a scientific report that Substance 33 had much lower shelf life than VX. The report, writes Mirzayanov, caused 'panic' in the institute top management and the military representative office, and later was met with administrative resistance. This finding was independently verified by another chemist Igor Revelskiy but his report wasn't approved either.[11]
Following the poisoning of Sergei and Yulia Skripal, former head of the GosNIIOKhT security department Nikolay Volodin said in an interview to Novaya Gazeta that Substance 33 was decomposing too quickly in combat conditions, and implied that this fact may have influenced the decision to continue research on the Novichok program.[12]
Toxicity
[edit]Both agents have similar symptoms and method of action to other nerve agents that act on cholinesterase, and treatment remains the same. However, the window for effectively treating second generation V series seizures is shorter, as they rapidly denature the acetylcholinesterase protein in a similar manner to soman, making treatment with the standard nerve gas antidote pralidoxime ineffective unless it is given very soon after exposure.[citation needed] Pre-treatment with pyridostigmine prior to exposure, and treatment with other drugs such as atropine and diazepam after exposure, will reduce symptoms of nerve agent toxicity but may not be sufficient to prevent death if a large dose of nerve agent has been absorbed. In addition to the standard seizures, some of the second generation V series agents are known to cause comas.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Fedorov L. A. Undeclared Chemical War in Russia. Moscow, 1995 (Russian)
- ^ Peplow, Mark (19 March 2018). "Nerve agent attack on spy used 'Novichok' poison". Chemical & Engineering News. 96 (12). American Chemical Society: 3. Retrieved 28 March 2018.
- ^ Major General Antonov, Nikolai S. (1994). Khimicheskoe Oruzhiye na Rubezhe Dvukh Stoletii Химическое оружие на рубеже двух столетий [Chemical Weapons at the Turn of the Century] (PDF) (in Russian). Moscow: Progress. p. 22. ISBN 5-01-004462-5. LCCN 96160418.
- ^ Tucker, J. B.; War of Nerves; Anchor Books; New York; 2006; pp 181-182.
- ^ Vil S. Mirzayanov. State Secrets. An Insider's Chronicle of the Russian Chemical Weapons Program. (2009) pp166-168. ISBN 978-1-4327-2566-2
- ^ Tucker, J. B.; War of Nerves; Anchor Books; New York; 2006; pp 230–231.
- ^ "Factsheets on Chemical and Biological Warfare Agents".
- ^ "Chemical Weapons – Russian / Soviet Nuclear Forces".
- ^ "VR". American Chemical Society.
- ^ Black R.M., Harrison J.M. The chemistry of organophosphorus chemical warfare agents. Chapter 10 of The chemistry of organophosphorus compounds. Volume 4, Ter- and quinque-valent phosphorus acids and their derivatives. (1996) Black, R. M.; Harrison, J. M. (2009). "The Chemistry of Organophosphorus Chemical Warfare Agents". PATai's Chemistry of Functional Groups. doi:10.1002/9780470682531.pat0070. ISBN 978-0-471-95706-5.
- ^ Mirzayanov, Vil S. (December 2008). State Secrets: An Insider's Chronicle of the Russian Chemical Weapons Program. Outskirts Press, Incorporated. ISBN 978-1-4327-1923-4.
- ^ ""Новичок" — это слишком для одного Скрипаля"". Новая газета - Novayagazeta.ru. March 23, 2018.
