Primo Levi
Primo Levi | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Born | 31 July 1919 Turin, Italy |
| Died | 11 April 1987 (aged 67) Turin, Italy |
| Resting place | Cimitero Monumentale di Torino, Turin, Italy |
| Pen name | Damiano Malabaila (used for some of his fictional works) |
| Occupation | Writer, chemist |
| Language | Italian |
| Nationality | Italian |
| Education | Degree in chemistry |
| Alma mater | University of Turin |
| Period | 1947–1986 |
| Genre | Autobiography, short story, essay |
| Notable works | |
| Spouse | Lucia Morpurgo (1947–1987, his death) |
| Children | 2 |
Primo Michele Levi[1][2] (Italian: [ˈpriːmo ˈlɛːvi]; 31 July 1919 – 11 April 1987) was a Jewish-Italian chemist, partisan, writer, and Holocaust survivor. He was the author of several books, collections of short stories, essays, poems and one novel. His best-known works include If This Is a Man (1947, published as Survival in Auschwitz in the United States), his account of the year he spent as a prisoner in the Auschwitz concentration camp in Nazi-occupied Poland; and The Periodic Table (1975), a collection of mostly autobiographical short stories each named after a chemical element as it played a role in each story, which the Royal Institution named the best science book ever written.[3]
Levi died in 1987 from injuries sustained in a fall from a third-story apartment landing. His death was officially ruled a suicide, although this has been disputed by some of his friends and associates and attributed to an accident.[4][5]
Biography
[edit]Early life
[edit]Levi was born in 1919 in Turin, Italy, at Corso Re Umberto 75, into a liberal Jewish family.[6] His father, Cesare, worked for the manufacturing firm Ganz and spent much of his time working abroad in Hungary, where Ganz was based. Cesare was an avid reader and autodidact. Levi's mother, Ester, known to everyone as Rina, was well educated, having attended the Istituto Maria Letizia. She too was an avid reader, played the piano, and spoke fluent French.[7][8] The marriage between Rina and Cesare had been arranged by Rina's father.[7] On their wedding day, Rina's father, Cesare Luzzati, gave Rina the apartment at Corso Re Umberto, where Primo Levi lived for almost his entire life.

In 1921 Anna Maria, Levi's sister, was born; he remained close to her all her life. In 1925 he entered the Felice Rignon primary school in Turin. A thin and delicate child, he was shy and considered himself ugly; he excelled academically. His school record includes long periods of absence during which he was tutored at home, at first by Emilia Glauda and then by Marisa Zini, daughter of philosopher Zino Zini.[9] The children spent summers with their mother in the Waldensian valleys southwest of Turin, where Rina rented a farmhouse. His father remained in the city, partly because of his dislike of the rural life, but also because of his infidelities.[10]
In September 1930 Levi entered the Massimo d'Azeglio Royal Gymnasium a year ahead of normal entrance requirements.[11] In class he was the youngest, the shortest and the cleverest, as well as being the only Jew. Only two boys there bullied him for being Jewish, but their animosity was traumatic.[12] In August 1932, following two years attendance also at the Talmud Torah school in Turin to pick up the elements of doctrine and culture, he sang in the local synagogue for his Bar Mitzvah.[13][6] In 1933, as was expected of all young Italian schoolboys, he joined the Avanguardisti movement for young Fascists. He avoided rifle drill by joining the ski division, and spent every Saturday during the season on the slopes above Turin.[14] As a young boy Levi was plagued by illness, particularly chest infections, but he was keen to participate in physical activity. In his teens, Levi and a few friends would sneak into a disused sports stadium and conduct athletic competitions.[8]
In July 1934 at the age of 14, he sat the exams for the Liceo Classico D'Azeglio, a Lyceum (sixth form or senior high school) specializing in the classics, and was admitted that year. The school was noted for its well-known anti-Fascist teachers, among them the philosopher Norberto Bobbio, and Cesare Pavese, who later became one of Italy's best-known novelists.[15] Levi continued to be bullied during his time at the Lyceum, although six other Jews were in his class.[16] Upon reading Concerning the Nature of Things by English scientist Sir William Bragg, Levi decided that he wanted to be a chemist.[17]
In 1937, he was summoned before the War Ministry and accused of ignoring a draft notice from the Italian Royal Navy—one day before he was to write a final examination on Italy's participation in the Spanish Civil War, based on a quote from Thucydides: "We have the singular merit of being brave to the utmost degree." Distracted and terrified by the draft accusation, he failed the exam—the first poor grade of his life—and was devastated. His father was able to keep him out of the Navy by enrolling him in the Fascist militia (Milizia Volontaria per la Sicurezza Nazionale). He remained a member through his first year of university, until the passage of the Italian Racial Laws of 1938 forced his expulsion. Levi later recounted this series of events in the short story "Fra Diavolo on the Po".[18]
He retook and passed his final examinations, and in October enrolled at the University of Turin to study chemistry. As one of 80 candidates, he spent three months taking lectures, and in February, after passing his colloquio (oral examination), he was selected as one of 20 to move on to the full-time chemistry curriculum.
In the liberal period as well as in the first decade of the Fascist regime, Jews held many public positions, and were prominent in literature, science and politics.[19] In 1929 Mussolini signed an agreement with the Catholic Church, the Lateran Treaty, which established Catholicism as the State religion, allowed the Church to influence many sectors of education and public life, and relegated other religions to the status of "tolerated cults". In 1936 Italy's conquest of Ethiopia and the expansion of what the regime regarded as the Italian "colonial empire" brought the question of "race" to the forefront. In the context set by these events, and the 1940 alliance with Hitler's Germany, the situation of the Jews of Italy changed radically.
In July 1938 a group of prominent Italian scientists and intellectuals published the "Manifesto of Race," a mixture of racial and ideological antisemitic theories from ancient and modern sources. This treatise formed the basis for the Italian Racial Laws of October 1938. After its enactment Italian Jews lost their basic civil rights, positions in public offices, and their assets. Their books were prohibited: Jewish writers could no longer publish in magazines owned by Aryans. Jewish students who had begun their course of study were permitted to continue, but new Jewish students were barred from entering university. Levi had matriculated a year earlier than scheduled enabling him to take a degree.[8]
In 1939, Levi discovered a passion for mountain hiking.[20] A friend, Sandro Delmastro, taught him how to hike, and they spent many weekends in the mountains above Turin. Levi later wrote about this time in the chapter "Iron" in The Periodic Table: “To see Sandro in the mountains reconciled you with the world and made you forget the nightmare weighing on Europe [...] He stirred in me a new communion with earth and sky, in which my need for freedom, the fullness of my powers, and the hunger to understand things that had driven me to chemistry converged.”[21]
In June 1940, Italy declared war as an ally of Germany against Britain and France, and the first Allied air raids on Turin began two days later. Levi's studies continued during the bombardments. The family suffered additional strain as his father became bedridden with bowel cancer.
Chemistry
[edit]Because of the new racial laws and the increasing intensity of prevalent fascism, Levi had difficulty finding an advisor for his Ph.D dissertation, which was on the subject of Walden inversion, a study of the asymmetry of the carbon atom. Eventually taken on by Dr. Nicolò Dallaporta, he graduated in mid-1941 with full marks and merit, having submitted additional theses on x-rays and electrostatic energy. His degree certificate bore the remark, "of Jewish race". The racial laws prevented Levi from finding a suitable permanent job after graduation.[8]
In December 1941, Levi received an informal job offer from an Italian officer to work as a chemist at an asbestos mine in San Vittore. The project was to extract nickel from the mine spoil, a challenge he accepted with pleasure. Levi later understood that, if successful, he would be aiding the German war effort, which was suffering nickel shortages in the production of armaments.[22] The job required Levi to work under a false name with false papers. Three months later, in March 1942, his father died. Levi left the mine in June to work in Milan for the Swiss firm of A Wander Ltd on a project to extract an anti-diabetic from vegetable matter. Recruited through a fellow student at Turin University, he took the job in a Swiss company to escape the race laws. It soon became clear that the project had no chance of succeeding, but it was in no one's interest to say so.[23]
In July 1943, King Victor Emmanuel III deposed Mussolini and appointed a new government under Marshal Pietro Badoglio, which prepared to sign the Armistice of Cassibile with the Allies. When the armistice was made public on 8 September, the Germans occupied northern and central Italy, liberated Mussolini from imprisonment and appointed him as head of the Italian Social Republic, a puppet state in German-occupied northern Italy. Levi returned to Turin to find his mother and sister in refuge in their holiday home 'La Saccarello' in the hills outside the city. The three embarked to Saint-Vincent in the Aosta Valley, where they could be hidden. Being pursued as Jews, many of whom had already been interned by the authorities, they moved up the hillside to Amay in the Col de Joux, a rebellious area highly suitable for guerilla activities.[24]
Italian resistance movement
[edit]The Italian resistance movement became increasingly active in the German-occupied zone. Levi and some comrades took to the foothills of the Alps, and in October formed a partisan group in the hope of being affiliated to the liberal Giustizia e Libertà. Untrained for such a venture, he and his companions were arrested by the Fascist militia on 13 December 1943. Believing he would be shot as an Italian partisan, Levi confessed to being Jewish. He was sent to the internment camp at Fossoli near Modena.[25]
Levi later wrote the following about the conditions at Fossoli:
We were given, on a regular basis, a food ration destined for the soldiers and at the end of January 1944, we were taken to Fossoli on a passenger train. Our conditions in the camp were quite good. There was no talk of executions and the atmosphere was quite calm. We were allowed to keep the money we had brought with us and to receive money from the outside. We worked in the kitchen in turn and performed other services in the camp. We even prepared a dining room, a rather sparse one, I must admit.[26]
Auschwitz
[edit]This section needs additional citations for verification. (January 2024) |

50°02′10″N 19°16′32″E / 50.036094°N 19.275534°E
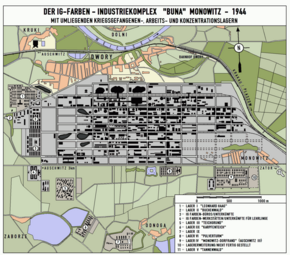
Fossoli was then taken over by the Germans, who started arranging the deportations of the Jews to eastern concentration and death camps. On the second of these transports, on 21 February 1944, Levi and other inmates were transported in twelve cramped cattle trucks to Monowitz, one of the three main camps in the Auschwitz concentration camp complex. Levi (record number 174517) spent eleven months there before the camp was liberated by the Red Army on 27 January 1945. Before their arrival, people were sorted according to whether they could work or not. An acquaintance said that it would make no difference, in the end, and declared he was unable to work and was killed immediately. Of the 650 Italian Jews in his transport, Levi was one of twenty who left the camps alive. The average life expectancy of a new entrant at the camp was three to four months.
Levi knew some German from reading German publications on chemistry; he worked to orient quickly to life in the camp without attracting the attention of the privileged inmates. He used bread to pay a more experienced Italian prisoner for German lessons and orientation in Auschwitz. He was given a smuggled soup ration each day by Lorenzo Perrone, an Italian civilian bricklayer working there as a forced labourer. Levi's professional qualifications were useful: in mid-November 1944, he secured a position as an assistant in IG Farben's Buna Werke laboratory that was intended to produce synthetic rubber. By avoiding hard labour in freezing outdoor temperatures he was able to survive; also, by stealing materials from the laboratory and trading them for extra food.[27] Shortly before the camp was liberated by the Red Army, he fell ill with scarlet fever and was placed in the camp's sanatorium (camp hospital). On 18 January 1945, the SS hurriedly evacuated the camp as the Red Army approached, forcing all but the gravely ill on a long death march to a site further from the front, which resulted in the deaths of the vast majority of the remaining prisoners on the march. Levi's illness spared him this fate.
Although liberated on 27 January 1945, Levi did not reach Turin until 19 October 1945. After spending some time in a Soviet camp for former concentration camp inmates, he embarked on an arduous journey home in the company of former Italian prisoners of war who had been part of the Italian Army in Russia. His long railway journey home to Turin took him on a circuitous route from Poland, through Belarus, Ukraine, Romania, Hungary, Austria, and Germany – an arduous journey described especially in his 1963 work The Truce – noting the millions of displaced people on the roads and trains throughout Europe in that period.
Writing career
[edit]1946–1960
[edit]Levi was almost unrecognisable on his return to Turin. Malnutrition edema had bloated his face. Sporting a scrawny beard and wearing an old Red Army uniform, he returned to Corso Re Umberto. The next few months gave him an opportunity to recover physically, re-establish contact with surviving friends and family, and start looking for work. Levi suffered from the psychological trauma of his experiences. Having been unable to find work in Turin, he started to look for work in Milan. On his train journeys, he began to tell people he met stories about his time at Auschwitz.
At a Jewish New Year party in 1946, he met Lucia Morpurgo, who offered to teach him to dance. Levi fell in love with Lucia. At about this time, he started writing poetry about his experiences in Auschwitz.
On 21 January 1946, he started work at DUCO, a Du Pont Company paint factory outside Turin. Because of the extremely limited train service, Levi stayed in the factory dormitory during the week. This gave him the opportunity to write undisturbed. He started to write the first draft of If This Is a Man.[28] Every day he scribbled notes on train tickets and scraps of paper as memories came to him. At the end of February, he had ten pages detailing the last ten days between the German evacuation and the arrival of the Red Army. For the next ten months, the book took shape in his dormitory as he typed up his recollections each night.
On 22 December 1946, the manuscript was complete. Lucia, who now reciprocated Levi's love, helped him to edit it, to make the narrative flow more naturally.[29] In January 1947, Levi was taking the finished manuscript around to publishers. It was rejected by Einaudi on the advice of Natalia Ginzburg, and in the United States was turned down by Little, Brown and Company on the advice of rabbi Joshua Liebman, an opinion which contributed to the neglect of his work in that country for four decades.[30][31] The social wounds of the war years were still too fresh, and he had no literary experience to give him a reputation as an author.
Eventually, Levi found a publisher, Franco Antonicelli, through a friend of his sister's.[32] Antonicelli was an amateur publisher, but as an active anti-Fascist, he supported the idea of the book.
At the end of June 1947, Levi suddenly left DUCO and teamed up with an old friend Alberto Salmoni to run a chemical consultancy from the top floor of Salmoni's parents' house. Many of Levi's experiences of this time found their way into his later writing. They made most of their money from making and supplying stannous chloride for mirror makers,[33] delivering the unstable chemical by bicycle across the city. The attempts to make lipsticks from reptile excreta and a coloured enamel to coat teeth were turned into short stories. Accidents in their laboratory filled the Salmoni house with unpleasant smells and corrosive gases.
In September 1947, Levi married Lucia and a month later, on 11 October, If This Is a Man was published with a print run of 2,000 copies. In April 1948, with Lucia pregnant with their first child, Levi decided that the life of an independent chemist was too precarious. He agreed to work for Accatti in the family paint business which traded under the name SIVA. In October 1948, his daughter Lisa was born.
During this period, his friend Lorenzo Perrone's physical and psychological health declined. Lorenzo had been a civilian forced worker in Auschwitz, who for six months had given part of his ration and a piece of bread to Levi without asking for anything in return.[34] The gesture saved Levi's life. In his memoir, Levi contrasted Lorenzo with everyone else in the camp, prisoners and guards alike, as someone who managed to preserve his humanity. After the war, Lorenzo could not cope with the memories of what he had seen and descended into alcoholism. Levi made several trips to rescue his old friend from the streets, but in 1952 Lorenzo died.[32] In gratitude for his kindness in Auschwitz, Levi named both of his children, Lisa Lorenza and Renzo, after him.
In 1950, having demonstrated his chemical talents to Accatti, Levi was promoted to Technical Director at SIVA.[35] As SIVA's principal chemist and troubleshooter, Levi travelled abroad. He made several trips to Germany and carefully engineered his contacts with senior German businessmen and scientists. Wearing short-sleeved shirts, he made sure they saw his prison camp number tattooed on his arm.
He became involved in organisations pledged to remembering and recording the horror of the camps. In 1954 he visited Buchenwald to mark the ninth anniversary of the camp's liberation from the Nazis. Levi dutifully attended many such anniversary events over the years and recounted his own experiences. In July 1957, his son Renzo was born.
Despite a positive review by Italo Calvino in L'Unità, only 1,500 copies of If This Is a Man were sold. In 1958 Einaudi, a major publisher, published it in a revised form and promoted it.
In 1958 Stuart Woolf, in close collaboration with Levi, translated If This Is a Man into English, and it was published in the UK in 1959 by Orion Press. Also in 1959 Heinz Riedt, also under close supervision by Levi,[36] translated it into German. As one of Levi's primary reasons for writing the book was to get the German people to realise what had been done in their name, and to accept at least partial responsibility, this translation was perhaps the most significant to him.[citation needed]
1961–1974
[edit]Levi began writing The Truce early in 1961; it was published in 1963, almost 16 years after his first book. That year it won the first annual Premio Campiello literary award. It is often published in one volume with If This Is a Man, as it covers his long return through eastern Europe from Auschwitz. Levi's reputation was growing. He regularly contributed articles to La Stampa, the Turin newspaper. He worked to gain a reputation as a writer about subjects other than surviving Auschwitz.
In 1963, he suffered his first major bout of depression. At the time he had two young children, and a responsible job at a factory where accidents could and did have terrible consequences. He travelled and became a public figure. But the memory of what happened less than twenty years earlier still burned in his mind. Today the link between such trauma and depression is better understood. Doctors prescribed several different drugs over the years, but these had variable efficacy and side effects.
In 1964 Levi collaborated on a radio play based upon If This Is a Man with the state broadcaster RAI, and in 1966 with a theatre production.
He published two volumes of science fiction short stories under the pen name of Damiano Malabaila, which explored ethical and philosophical questions. These imagined the effects on society of inventions which many would consider beneficial, but which, he saw, would have serious implications. Many of the stories from the two books Storie naturali (Natural Histories, 1966) and Vizio di forma (Structural Defect, 1971) were later collected and published in English as The Sixth Day and Other Tales.
In 1974 Levi arranged to go into semi-retirement from SIVA in order to have more time to write. He also wanted to escape the burden of responsibility for managing the paint plant.[37]
1975–1987
[edit]In 1975, a collection of Levi's poetry was published under the title L'osteria di Brema (The Bremen Beer Hall). It was published in English as Shema: Collected Poems.
He wrote two other highly praised memoirs, Lilit e altri racconti (Moments of Reprieve, 1978) and Il sistema periodico (The Periodic Table, 1975). Moments of Reprieve deals with characters he observed during imprisonment. The Periodic Table is a collection of mostly autobiographical short stories and also includes two fictional stories that he wrote while being employed in 1941 at the asbestos mine in San Vittore. Each story is named after a chemical element and the story matter is related to that element. At London's Royal Institution on 19 October 2006, The Periodic Table was declared to be the best science book ever written.[3]
In 1977 at the age of 58, Levi retired as a part-time consultant at the SIVA paint factory to devote himself full-time to writing. Like all his books, La chiave a stella (1978), published in the US in 1986 as The Monkey Wrench and in the UK in 1987 as The Wrench, is difficult to categorize. Some reviews describe it as a collection of stories about work and workers told by a narrator who resembles Levi. Others have called it a novel, created by the linked stories and characters. Set in the Fiat-run Russian company town of Togliattigrad, it portrays the engineer as a hero on whom others depend. The Piedmontese engineer Faussone has travelled the world as an expert in erecting cranes and bridges. Most of the stories involve the solution of industrial problems by the use of troubleshooting skills; many stories come from the author's personal experience. The underlying philosophy is that pride in one's work is necessary for fulfilment. The Wrench won the Strega Prize in 1979 and brought Levi a wider audience in Italy, though left-wing critics regretted that he did not describe the harsh working conditions on the assembly lines at Fiat.[38]
In 1984, Levi published his only novel, If Not Now, When?—or his second novel, if The Monkey Wrench is counted. It traces the fortunes of a group of Jewish partisans behind German lines during World War II as they seek to survive and continue their fight against the occupier. With the ultimate goal of reaching Palestine to take part in the development of a Jewish national home, the partisan band reaches Poland and then German territory. There the surviving members are officially received as displaced persons in territory held by the Western allies. Finally, they succeed in reaching Italy, on their way to Palestine. The novel won both the Premio Campiello and the Premio Viareggio.
The book was inspired by events during Levi's train journey home after release from the camp, narrated in The Truce. At one point in the journey, a band of Zionists hitched their wagon to the refugee train. Levi was impressed by their strength, resolve, organisation, and sense of purpose.
Levi became a major literary figure in Italy, and his books were translated into many other languages. The Truce became a standard text in Italian schools. In 1985, he flew to the United States for a 20-day speaking tour. Although he was accompanied by Lucia, the trip was very draining for him.
In the Soviet Union his early works were not accepted by censors as he had portrayed Soviet soldiers as slovenly and disorderly rather than heroic. In Israel, a country formed partly by Jewish survivors who lived through horrors similar to those Levi described, many of his works were not translated and published until after his death.[6]

In March 1985, he wrote the introduction to the re-publication of the autobiography[39] of Rudolf Höss, who was commandant of Auschwitz concentration camp from 1940 to 1943. In it, he writes, "It's filled with evil ... and reading it is agony."
Also in 1985, a volume of his essays, previously published in La Stampa, was published under the title L'altrui mestiere (Other People's Trades). Levi used to write these stories and hoard them, releasing them to La Stampa at the rate of about one a week. The essays ranged from book reviews and ponderings about strange things in nature, to fictional short stories.[6]
In 1986, his book I sommersi e i salvati (The Drowned and the Saved) was published. In it he tried to analyse why people behaved the way they did at Auschwitz and why some survived whilst others perished. In his typical style, he makes no judgments but presents the evidence and asks the questions. For example, one essay examines what he calls "The grey zone", those Jews who did the Germans' dirty work for them and kept the rest of the prisoners in line.[40] He questioned, what made a concert violinist behave as a callous taskmaster?
Also in 1986, a collection of short stories, previously published in La Stampa, was assembled and published as Racconti e saggi (some of which were published in the English volume The Mirror Maker).
At the time of his death in April 1987, Levi was working on another selection of essays called The Double Bond, which took the form of letters to "La Signorina".[41] These essays are very personal in nature. Approximately five or six chapters of this manuscript exist. Carole Angier, in her biography of Levi, describes how she tracked some of these essays down. She wrote that others were being kept from public view by Levi's close friends, to whom he gave them, and they may have been destroyed.
Posthumous publications
[edit]In March 2007, Harper's Magazine published an English translation of Levi's story "Knall", about a fictitious weapon that is fatal at close range but harmless more than a meter away. It originally appeared in his 1971 book Vizio di forma but was published in English for the first time by Harper's.
A Tranquil Star, a collection of seventeen stories translated into English by Ann Goldstein and Alessandra Bastagli[42][43] was published in April 2007.
In 2015, Penguin published The Complete Works of Primo Levi, ed. Ann Goldstein. This is the first time that Levi's entire oeuvre has been translated into English.
Death
[edit]Levi died on 11 April 1987 after a fall from the interior landing of his third-story apartment in Turin to the ground floor below. The coroner ruled his death a suicide. Three of his biographers (Angier, Thomson and Anissimov) agreed, but other writers (including at least one who knew him personally) questioned that determination.[44][45]
In his later life, Levi indicated that he was suffering from depression; factors likely included responsibility for his elderly mother and mother-in-law, with whom he was living, and lingering traumatic memories of his experiences.[46] According to the chief rabbi of Rome Elio Toaff, Levi telephoned him for the first time ten minutes before the incident. Levi said he found it impossible to look at his mother, who was ill with cancer, without recalling the faces of people stretched out on benches in Auschwitz.[47] The Nobel laureate and fellow Holocaust survivor Elie Wiesel said, at the time, "Primo Levi died at Auschwitz forty years later."[48]
However, several of Levi's friends and associates have argued otherwise. The Oxford sociologist Diego Gambetta noted that Levi left no suicide note, nor any other indication that he was considering suicide. Documents and testimony suggested that he had plans for both the short- and longer-term at the time. In the days before his death, he had complained to his physician of dizziness due to an operation he had undergone some three weeks earlier. After visiting the apartment complex, Gambetta suggested that Levi lost his balance and fell accidentally.[49] The Nobel laureate Rita Levi-Montalcini, a close friend of Levi, agreed. "As a chemical engineer," she said, "he might have chosen a better way [of exiting the world] than jumping into a narrow stairwell with the risk of remaining paralyzed."[50]
Legacy and impact
[edit]Holocaust writing
[edit]Levi is frequently referred to as a "Holocaust writer",[51][52] a label he disliked.[53][54] He is considered to have composed some of the most important writing about the Holocaust[55][56] which has greatly contributed to the memory and understanding of the Holocaust.[53] Philip Roth eulogized him as someone who "set out systematically to remember the German hell on earth, steadfastly to think it through, and then to render it comprehensible in lucid, unpretentious prose".[51] Martin Amis has credited Levi's work with assisting him in writing The Zone of Interest, calling him "the visionary of the Holocaust, its presiding spirit and the most perceptive of all writers on this subject."[57]
Posthumous honors
[edit]- In 1995, five health and human rights organizations established the Primo Levi Center in Paris to provide services to torture survivors. The Center was named for Levi because his name is "synonymous with the refusal of inhuman, cruel and degrading treatment".[58][59]
- The Primo Levi Center, a non-profit organisation dedicated to studying the history and culture of Italian Jewry, was established in New York City in 2003.[60]
- In 2008, the City of Turin and other partners established the International Primo Levi Studies Center to preserve and promote Levi's legacy.[61]
- Beginning in 2017, the Primo Levi Prize has been awarded by the German Chemical Society and the Italian Chemical Society to honor chemists for their commitment to human rights.[62][63]
- In 2019, Levi's 100th birthday was commemorated throughout the world, including the United States,[64][65] Portugal,[66] and Italy.[67]
- The SIVA factory has been turned into the Museo della Chimica, a chemistry museum for children. Levi's former office now holds an exhibit about his life.[68][69][70]
In popular culture
[edit]- Till My Tale is Told: Women's Memoirs of the Gulag (1999), uses a part of the quatrain by Coleridge quoted by Levi in The Drowned and the Saved as its title.
- Christopher Hitchens' book The Portable Atheist, a collection of extracts of atheist texts, is dedicated to the memory of Levi, "who had the moral fortitude to refuse false consolation even while enduring the 'selection' process in Auschwitz". The dedication quotes Levi in The Drowned and the Saved, asserting, "I too entered the Lager as a nonbeliever, and as a nonbeliever I was liberated and have lived to this day."[71][72]
- A quotation from Levi appears on the sleeve of the second album by the Welsh rock band Manic Street Preachers, titled Gold Against the Soul. The quote is from Levi's poem "Song of Those Who Died in Vain".[73][74]
- David Blaine has Primo Levi's Auschwitz camp number, 174517, tattooed on his left forearm.[75]
- In Lavie Tidhar's novel, A Man Lies Dreaming, the protagonist encounters Levi and Ka-Tzetnik in Auschwitz and witnesses them discuss how they should write about the Holocaust. Levi says they should be "accurate and dispassionate" while Ka-Tzetnik advocates "the language of [...] pulp".[76][77]
- In the pilot episode of Black Earth Rising, Rwandan genocide survivor Kate Ashby has a therapy session addressing her survivors' guilt and suicide attempt. She tells her therapist that she has read the Primo Levi book he'd assigned her and that if she chooses to attempt suicide, she'll "take a leaf out of Mr Levi's book and jump straight out the window."
- The last track on The Noise by Peter Hammill is entitled "Primo on the Parapet".[78]
Views
[edit]Nazi death camps versus Soviet gulags
[edit]Levi vigorously repudiated historical revisionist attitudes in German historiography that emerged in the Historikerstreit led by the works of people like Andreas Hillgruber and Ernst Nolte, who drew parallels between Nazism and Stalinism.[79] Levi rejected the idea that the labor camp system depicted in Aleksandr Solzhenitsyn's The Gulag Archipelago and that of the Nazi Lager (German: Konzentrationslager; see Nazi concentration camps) were comparable. The death rate in Stalin's gulags was 30% at worst, he wrote; while in the extermination camps, he estimated it to be 90–98%.[80][81][82]
His view was that the Nazi death camps and the attempted annihilation of the Jews were a horror unique in history because the goal was the complete destruction of a race by one that saw itself as superior. He noted that it was highly organized and mechanized; it entailed the degradation of Jews to the point of using their ashes as materials for paths.[83]
The purpose of the Nazi extermination camps was not the same as the purpose of Stalin's gulags, Levi wrote in an appendix to If This Is a Man, though it is a "lugubrious comparison between two models of hell."[84] The goal of the Lager was the extermination of the Jewish race in Europe, and no one could renounce Judaism; the Nazis considered Jews a racial group rather than a religious group. Levi, along with most of Turin's Jewish intellectuals, had not been religiously observant before World War II, but the Italian racial laws and the Nazi camps impressed his identity as a Jew upon him. Of the many children who were deported to the camps, almost all of them were murdered.[85]
German people
[edit]According to biographer Ian Thomson, Levi intentionally excluded any experiences with Germans who helped him from If This Is a Man and included "collective condemnations, coloured by the author's rage, of the German people". However, Levi's opinion of Germans improved through his friendship with a German woman named Hety Schmitt-Maas. Her father had lost his job and she had been expelled from school due to their anti-Nazi beliefs. For 17 years, Levi and Schmitt-Maas discussed "their shared hatred of Nazism" together in their letters to each other until Schmitt-Maas died in 1983.[86]
Almost forty years after If This Is A Man was published, Levi stated that he did not hate German people because hating a whole ethnic group would be too much like Nazism. However, he also stated that he did not forgive "the culprits". According to Levi, the German people largely knew about the concentration camps but did not know the extent of the atrocities occurring there. However, "most Germans didn’t know because they didn’t want to know. Because, indeed, they wanted not to know".[87]
Works
[edit]| Title | Year | Type | English language translations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Se questo è un uomo | 1947 and 1958 | Memoir | If This Is a Man (US: Survival in Auschwitz) |
| La tregua | 1963 | Memoir | The Truce (US: The Reawakening) |
| Storie naturali (as Damiano Malabaila) | 1966 | Short stories | The Sixth Day and Other Tales |
| Vizio di forma | 1971 | Short stories | Mainly in The Sixth Day and Other Tales. Some stories are in A Tranquil Star |
| Il sistema periodico | 1975 | Short stories | The Periodic Table |
| L'osteria di Brema | 1975 | Poems | In Collected Poems |
| Lilìt e altri racconti | 1981 | Short stories | Part 1: Moments of Reprieve. Some stories from Parts 2 and 3 are in A Tranquil Star |
| La chiave a stella | 1978 | Novel | The Wrench (US: The Monkey's Wrench) |
| La ricerca delle radici | 1981 | Personal anthology | The Search for Roots: A Personal Anthology |
| Se non ora, quando? | 1982 | Novel | If Not Now, When? |
| Ad ora incerta | 1984 | Poems | In Collected Poems |
| L'altrui mestiere | 1985 | Essays | Other People's Trades |
| I sommersi e i salvati | 1986 | Essays | The Drowned and the Saved |
| Racconti e Saggi | 1986 | Essays | The Mirror Maker |
| Conversazioni e interviste 1963–1987 | 1997 | Various (posthumous) | Conversations with Primo Levi and The Voice of Memory: Interviews, 1961–1987 |
| 2005 | Essays (posthumous) | The Black Hole of Auschwitz | |
| 2006 | Factual (posthumous) | Auschwitz Report | |
| 2007 | Short stories (posthumous) | A Tranquil Star | |
| 2011 | Short stories | The Magic Paint (Selection from A Tranquil Star) |
Adaptations
[edit]- Five of Levi's poems (Shema, 25 Febbraio 1944, Il canto del corvo, Cantare and Congedo) have been set to music by Simon Sargon in the song cycle Shema: 5 Poems of Primo Levi in 1987.[88] In 2021 the work was performed by Megan Marie Hart during the opening event of the festival year 1700 Jahre jüdisches Leben in Deutschland commemorating the first documented mention of Jewish communities in the territory of present-day Germany.[89]
- The 1997 film La Tregua (The Truce), starring John Turturro, was adapted from his 1963 memoir of the same title and recounts Levi's long journey home with other displaced people after his liberation from Auschwitz.
- If This Is a Man was adapted by Antony Sher into a one-man stage production Primo in 2004. A version of this production was broadcast on BBC Four in the UK on 20 September 2007.[90]
References
[edit]Notes
- ^ Ian Thomson, Primo Levi (2019) pp. 17–18, 138
- ^ Carole Angier,The Double Bond: Primo Levi: A Biography, Penguin 2002 p.35:'Although Cesare never talked about his father he called his son after him, Primo Michele – I don’t know whether Primo thought of this as a fateful link but at the end of his life he thought more than once of his grandfather. Several times he spoke of a hereditary taint of suicide in his family. What he didn’t know about it was that it had come out not once but twice in his grandfather’s generation and he did not know that Michele himself had thrown himself to his death from a height, as he himself would do 99 years later. Michele had even leapt into a small inner courtyard, as he would leapt from a stairwell.'
- ^ a b Randerson, James (20 October 2006). "Levi's memoir beats Darwin to win science book title". The Guardian. Retrieved 30 March 2012.
- ^ Intern (9 July 2012). "Primo Levi's Last Moments". Boston Review. Retrieved 11 January 2021.
- ^ "Primo Levi's Work Outshines His Murky Death". Moment Magazine. 11 November 2019. Retrieved 11 January 2021.
- ^ a b c d "LEVI, Primo in "Dizionario Biografico"". Dizionario Biografico degli Italiani (in Italian). Retrieved 6 September 2021.
- ^ a b Angier p. 50.
- ^ a b c d Motola, Gabriel (1995). "Primo Levi, The Art of Fiction No. 140". The Paris Review. Vol. Spring 1995, no. 134. ISSN 0031-2037. Retrieved 6 September 2021.
- ^ Angier, p. 44.
- ^ Angier, p. 62.
- ^ Thomson p. 40.
- ^ Thomson, p. 42.
- ^ Thomson 2019 p. 44:'Half a century later, he could still remember 200 words, but had little idea what they meant. The sole aim of the Torah, it seemed to Levi was to teach boys how to read their prayer books so fluently that their grandparents could reap honours with them on Bar Mitzvah day.'
- ^ Thomson, p. 48.
- ^ It is often reported that Pavese was Levi's teacher of Italian. This is refuted strongly by Thomson (2002).
- ^ Thomson p. 55.
- ^ The Search for Roots, p. 31.
- ^ Sam Magavern, Primo Levi’s Universe: A Writer’s Journey, Macmillan 2009 p. 12.
- ^ The Jews in Mussolini's Italy: From Equality to Persecution, translation by John and Anne C. Tedeschi, Wisconsin University Press, Madison 2006, p. 419
- ^ Thomson p 93.
- ^ Il sistema periodico in Primo Levi, Opere Einaudi vol. 1 1987 pp. 464–473 [470]. The vignette commemorates the memory of his friend, who was indifferent to Levi's Jewish origins, and who was the first resistance fighter of the anti-fascist Partito d'Azione's Piemont Military Command to fall in action when he was shot in the neck by a burst of a machine-gun wielded by a 'monstruous child-executor', a paid-up adolescent henchman of the diehard Republic of Salò in April 1944 while escaping from detention. (p. 473)
- ^ Angier p. 174.
- ^ Thomson p 119.
- ^ Peter Thomson, Primo Levi Random House, (2003) 2019 ISBN 978-1-448-18073-8 pp. 135–136
- ^ Levi, Primo (1958). Survival in Auschwitz. Translated by Woolf, Stuart. New York: Touchstone. pp. 13–14. ISBN 0-684-82680-1.
- ^ Rapoport, Meron (3 October 2007). "Scholar Unearths Previously Unknown Primo Levi Text at Yad Vashem". Haaretz. Archived from the original on 21 May 2024. Retrieved 20 May 2024.
- ^ See the chapter "Cerium" in Levi's book The Periodic Table
- ^ Thomson p. 229
- ^ Thomson p. 241.
- ^ Ian Thompson, Primo Levi, (2003) 2019 pp. 241–242
- ^ Ian Thomson, 'Talked into Life,' Times Literary Supplement 29 June 2012 pp. 13–15 [14–15]
- ^ a b Thomson p. 246.
- ^ Thomson p. 249.
- ^ If This Is Man Chapter – 'The Events of Summer'
- ^ Angier p. 487
- ^ Thomson p. 287.
- ^ Thomson p. 366.
- ^ Thomson p. 400.
- ^ Commandant of Auschwitz: Rudolf Höß. ISBN 1-84212-024-7
- ^ Lee, Sander H. (1 August 2016). "Primo Levi's Gray Zone: Implications for Post-Holocaust Ethics". Holocaust and Genocide Studies. 30 (2): 276–297. doi:10.1093/hgs/dcw037. ISSN 8756-6583. S2CID 151930376.
- ^ Angier p. 80.
- ^ "A Tranquil Star –Primo Levi – Penguin UK". Archived from the original on 27 September 2007.
- ^ "A Tranquil Star (Main Page)". Archived from the original on 20 April 2007.
- ^ Intern (9 July 2012). "Primo Levi's Last Moments". Boston Review. Retrieved 12 January 2021.
- ^ "Primo Levi's Work Outshines His Murky Death". Moment Magazine. 11 November 2019. Retrieved 12 January 2021.
- ^ George Jochnowitz, "Review of Primo Levi: A Life by Ian Thomson". New York: Metropolitan Books, Henry Holt and Company, 2003
- ^ Diego Gambetta, 'Primo Levi's Plunge: A Case Against Suicide,' The New York Times 7 August 1999
- ^ Elie Wiesel: "Con l'incubo che tutto sia accaduto invano." La Stampa, Turin, 14 April 1987, p. 3. [1]
- ^ Gambetta, Diego (9 July 2012). "Primo Levi's Last Moments". Retrieved 10 April 2020.
- ^ Nadkarni, VC. "Forgive, but don't forget". Economic Times. Retrieved 6 October 2014.
- ^ a b TAGLIABUE, JOHN (12 April 1987). "Primo Levi, Holocaust Writer is Dead at 67". The New York Times. Retrieved 10 June 2024.
- ^ Kirsch, Adam (15 September 2015). "Primo Levi's Unlikely Suicide Haunts His Lasting Work". Tablet. Retrieved 10 June 2024.
- ^ a b "Why Do We View Primo Levi's Work Through the Prism of His Death?". The New Republic. ISSN 0028-6583. Retrieved 10 June 2024.
- ^ "Primo Levi's First Draft Of History". The Forward. 13 January 2007. Retrieved 10 June 2024.
- ^ Rothberg, Michael; Druker, Jonathan (2009). "A Secular Alternative: Primo Levi's Place in American Holocaust Discourse". Shofar. 28 (1): 104–126. doi:10.5703/shofar.28.1.104. ISSN 0882-8539.
- ^ "New Primo Levi Stories Published". WUSF. 15 April 2007. Retrieved 11 June 2024.
- ^ "Martin Amis and Ian Thomson on the legacy of Primo Levi". CBC Radio. 13 December 2019. Retrieved 10 June 2024.
- ^ Gilles van Kote (3 September 2014). "L'indispensable Centre Primo-Levi". Le Monde.fr (in French). LeMonde.fr. ISSN 1950-6244. Retrieved 13 October 2015.
- ^ "Our history". Centre Primo Levi. Retrieved 20 June 2024.
- ^ "About Primo Levi". Retrieved 14 January 2020.
- ^ "Who we are". Centro Internazionale di Studi Primo Levi. 7 July 2021. Retrieved 9 June 2024.
- ^ "Primo Levi Prize". Gesellschaft Deutscher Chemiker e.V. Retrieved 9 June 2024.
- ^ Goedecke, Catharina (4 September 2023). "Primo Levi Prize for Henning Hopf". ChemistryViews. Retrieved 9 June 2024.
- ^ "Italy commemorates the 2019 International Holocaust Remembrance Day in the USA on the centenary of Primo Levi's birth". ambwashingtondc.esteri.it. 29 January 2019. Retrieved 7 June 2024.
- ^ "Primo Levi at 100". Primo Levi Center. 17 May 2019. Retrieved 7 June 2024.
- ^ "Lisbon: celebrations for the 100th anniversary of the birth of Primo Levi". Ministero degli Affari Esteri e della Cooperazione Internazionale. 4 July 2019. Retrieved 7 June 2024.
- ^ "Primo Levi's Centennial Program Presented in Turin". Pagine Ebraiche International. 22 April 2019. Retrieved 7 June 2024.
- ^ "Visita il museo". Museo della Chimica (in Italian). Retrieved 9 June 2024.
- ^ "Factory where Primo Levi worked becomes museum". The Times of Israel. 18 May 2014. Retrieved 9 June 2024.
- ^ "Do not NOT touch: the new MU-CH Chemistry Museum is open". ETT. 30 June 2022. Retrieved 9 June 2024.
- ^ Hitchens, The Portable Atheist.
- ^ Primo Levi (1986). "sommersi e i salvati" [The Drowned and the Saved]. Retrieved 14 January 2020.
- ^ "Manic Street Preachers interview, Raw Soup 1993 (higher quality)". YouTube. 8 September 2009. Archived from the original on 11 December 2021. Retrieved 19 May 2014.
- ^ Peters, Mathijs (2020). Popular Music, Critique and Manic Street Preachers. Palgrave Macmillan. p. 179.
- ^ Belkin, Douglas (15 August 2004). "Jews With Tattoos". The Boston Globe. Archived from the original on 18 August 2004.
- ^ Mahvesh Murad (28 October 2014). "Holocaust Noir: A Man Lies Dreaming by Lavie Tidhar". Retrieved 22 November 2016.
- ^ Tidhar, Lavie (2014). "Chapter 8". A Man Lies Dreaming. London: Hodder & Stoughton. ISBN 978 1 444 76296 9.
- ^ "The Noise - Peter Hammill". AllMusic. Retrieved 9 June 2024.
- ^ Ernesto Ferrero, 'Cronologia,' in Primo Levi, Opere, Einaudi vol. 1, 1987 p. lxi.
- ^ Appendix to an Italian schools edition of Se questo è un uomo, reprinted in Opere Einaudi, 1987 vol. 1, pp. 185–212 [199].
- ^ Thomson, Primo Levi, 2019 p. 523.
- ^ Primo Levi, Il buco nero di Auschwitz, La Stampa 22 January 1987.
- ^ The Drowned and the Saved (1986) Abacus ed. (1988) p. 100.
- ^ (Abacus 2001 ed., p. 391)
- ^ Appendix to an Italian schools edition of Se questo è un uomo, section 6, reprinted in: Se questo è un uomo – La tregua Einaudi, Torino (1989) p. 339 "... nei Lager tedeschi la strage era pressoché totale: non si fermava neppure davanti ai bambini, che furono uccisi nelle camere a gas a centinaia di migliaia, cosa unica fra tutte le atrocità della storia umana." "... in the German camps the massacre was almost total: it did not even stop in front of children, who were killed in the gas chambers by the hundreds of thousands, something unique among all of the atrocities of human history."
- ^ Thomson, Ian (7 April 2007). "The good German". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 21 June 2024.
- ^ Levi, Primo (17 February 1986). "Primo Levi's Heartbreaking, Heroic Answers to the Most Common Questions He Was Asked About 'Survival in Auschwitz'". The New Republic. Retrieved 17 January 2019.
- ^ "Shemà | Music of Remembrance". musicofremembrance.org. Archived from the original on 28 August 2022. Retrieved 28 August 2022.
- ^ "100 Tage 1700 Jahre – Jüdisches Leben in Darmstadt" (PDF). darmstadt.de (in German). p. 10. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 August 2021. Retrieved 28 August 2022.
- ^ "Press Office – Primo: a unique drama for BBC Four". www.bbc.co.uk.
Bibliography
- Angier, Carole (2002). The Double Bond: Primo Levi: A Biography. London: Penguin. ISBN 978-0-14-016587-6.
- Anissimov, Myriam (1999). Primo Levi: Tragedy of an Optimist. New York: Overlook. ISBN 978-0-87951-806-6.
- Gordon, Robert (2007). The Cambridge Companion to Primo Levi. Cambridge: Cambridge. ISBN 978-0-521-60461-1.
- Thomson, Ian (2002). Primo Levi. London: Hutchison. ISBN 978-0-09-178531-4.
- Vincenti, Fiora (1981). Primo Levi. Mursia.
Further reading
- Giffuni, Cathe. "An English Bibliography of the Writings of Primo Levi," Bulletin of Bibliography, Vol. 50 No. 3 September 1993, pp. 213–221.
External links
[edit]- Announcement of The Complete Works of Primo Levi
- Works by or about Primo Levi at the Internet Archive
- International Primo Levi Studies Center
- Centro Primo Levi New York
- "Primo Levi's journeys of peace": an article in the TLS by Clive Sinclair, 11 July 2007
- Scriptorium – Primo Levi Includes writing by Levi
- Primo Levi page by the Operatist who composed in honor of Levi
- Primo Levi's Last Moments by Diego Gambetta, Boston Review, Summer 1999 issue.
- Gabriel Motola (Spring 1995). "Primo Levi, The Art of Fiction No. 140". The Paris Review. Spring 1995 (134).
- Poliakoff, Martyn (2010). "Primo Levi". The Periodic Table of Videos. University of Nottingham.
- Primo Levi's house
- BBC Interview with Primo Levi
- Thames Television interview from 1972
- 1919 births
- 1987 deaths
- 1987 suicides
- 20th-century Italian Jews
- 20th-century Italian novelists
- 20th-century Italian poets
- 20th-century Italian politicians
- 20th-century male writers
- 20th-century memoirists
- Action Party (Italy) politicians
- Auschwitz concentration camp survivors
- Fossoli camp survivors
- Italian anti-fascists
- Italian atheists
- 20th-century Italian chemists
- Italian male novelists
- Italian male poets
- Italian male short story writers
- Italian science fiction writers
- Writers about the Holocaust
- Italian memoirists
- Jewish memoirists
- Jewish atheists
- Jewish anti-fascists
- Jewish chemists
- Jewish Italian writers
- Jewish partisans
- Jews in the Italian resistance
- Levites
- Members of Giustizia e Libertà
- Modernist writers
- Scientists from Turin
- Premio Campiello winners
- Strega Prize winners
- Suicides by jumping in Italy
- University of Turin alumni
- Unsolved deaths
- Viareggio Prize winners
